cambridge computer science as semester 1 finals
1/695
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cambridge computer science as, mrs. preston
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
696 Terms
What does ASCII stand for?
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
The number of character that can be represented in ASCII-7 are
128
The number of character that can be represented in ASCII-8 are
256
What is the aim of Unicode?
Representing all characters with 1 system
Why does the correction factor of 0110 work in Binary Coded Decimals?
The correction factor 6 is used because a nibble can represent up to 15, yet a BCD can only express up to 9. The 6 carries it to the next nibble.
What are integers?
non-decimal numbers
What are signed integers?
integers with signs (e.g. -1)
What are unsigned integers?
integers without signs (e.g. 1)
Given the following decimal prefix, state its abbreviation and value: kilo
k, 10³
Given the following decimal prefix, state its abbreviation and value: mega
M, 10^6
Given the following decimal prefix, state its abbreviation and value: giga
G, 10^9
Given the following decimal prefix, state its abbreviation and value: tera
T, 10^12
Given the following binary prefix, state its abbreviation and value: kibi
Ki, 2^10
Given the following binary prefix, state its abbreviation and value: mebi
Mi, 2^20
Given the following binary prefix, state its abbreviation and value: gibi
Gi, 2^30
Given the following binary prefix, state its abbreviation and value: tebi
Ti, 2^40
What is One’s Complement?
a binary obtained by subtracting each binary digit from 1
What is Two’s Complement?
a binary obtained by adding 1 to One’s Complement
What is overflow?
a condition when the result is larger than capacity
What is BCD?
Binary Coded Decimal
What is a vector graphic?
a graphic consisting of drawing objects defined in a drawing list
What are examples of attributes for objects’ properties?
center and radius (of a circle), thickness, line style, line color, color that fills shape
What is a drawing object?
a component defined by geometric formulae and associated properties
What is a drawing list?
contains 1 set of values for each drawing object
What is a property?
defines 1 aspect of appearance of drawing object
What is an important property?
dimensions of objects are not defined explicitly, but are defined relative to images canvas
What are bitmaps?
2D array of pixels
What is a pixel?
smallest identifiable component of bitmap, has position in matrix and color
What is color depth?
number bits per pixel
What is bit depth?
number of bits used to store red, green, and blue in RGB scheme
What is resolution?
product of number of pixels per row and column
What is image resolution?
defined in bitmap file
What is screen resolution?
ability of device showing image
What is a file header?
contains information on how graphic was constructed
Vector graphic versus Bitmap:
a. _____ is chosen if a diagram is needed to be constructed for part of an architectural, engineering, manufacturing design.
Vector graphic
Vector graphic versus Bitmap:
b. Printing the image on laser or inkjet printer a _____ should be used.
bitmap
Vector graphic versus Bitmap:
c. Digital camera produce _____ images.
bitmap
Vector graphic versus Bitmap:
d. _____ is first choice for insertion of an image into document, publication, or web page.
Bitmap
Vector graphic versus Bitmap:
e. Generally images are stored as _____.
bitmaps
Vector graphic versus Bitmap:
f. _____ is scalable.
Vector graphic
Vector graphic versus Bitmap:
g. A _____ files contains a drawing list with commands for each object included in the image.
vector graphic
Sound consists of a large number of _____, each with a defined _____.
waves, frequency
Storing sound requires converting the _____ sound signal to _____.
analog, digital
Two factors that determine the quality of the sound recording are _____ and _____.
sampling rate, sampling resolution
Define sampling resolution
number of bits used to store each value
Define sampling rate
number of samples taken per second
Define analog data
data obtained physically with values within continuous range
Define digital data
data stored as binary values from discrete range
Define sampling
taking measurements at regular intervals and storing them
List two types of compression
lossy and lossless
Since all data is binary, which type of compression can be used for all files?
lossless
Which compression has specialized applications developed for particular file types?
lossy
Text files require which type of compression?
lossless
Give one example where lossy compression will be useful.
Lossy compression is useful to use less storage for a file
Give one example where lossless compression will be useful.
Lossless compression is needed for text files because no information can be lost.
What is a WAN?
Wide Area Network, a system of networks across a large area.
List three benefits of having a WAN
A “job” could be run on a remote computer that had the required application software.
A data archive that was stored on a remote computer could be accessed.
A message could be transmitted electronically to a user on a remote computer.
List five characteristics of a WAN
It will be used by organization or company to connect sites or branches.
It will not be owned by the organization or company.
It will be leased from a PSTN.
A dedicated link will be provided by the PTSN.
Transmission within the WAN will be switch to switch.
Define end systems
either a user workstation or server
Define server
a system providing a service to end systems
What is a LAN?
Local Area Network, a system of networks in a small area
List five benefits of having a LAN
save expenses of installing application software by attaching to LAN
file server attach to LAN to store larger files and allow file sharing
1 or more printers attached to print server connected to LAN
use electronic mail to communicate
“paper-less office”
List five characteristics of a LAN
used by organization or site within site or branch
owned by organization or computer
one of many LANs
transmission medium is twisted pair cable or WiFi
contain device allowing connection to other networks
Describe the two options for client-server model are
thin-client: client only provides input
thick-client: client involved in some processing
Describe three approaches when it is appropriate to use client-server architecture
server stores databases
server stores web applications for information
server stores web applications for e-commerce and financial transaction
Describe peer-to-peer network file sharing
peers act as clients to seek files
Describe peer-to-peer file network file sharing advantages over client-server downloading
avoids network congestion
parts of file downloaded separately
parts available from multiple hosts
Describe client-server file network file sharing advantages
organizations control download and usage of files
better protected from malware
Five requirements for a data communication systems
a. sender
b. receiver
c. transmission medium
d. message
e. protocol
Define simplex mode
one-way data flow
Define half duplex mode
data flow in either direction, but not simultaneous
Define full duplex
data flow in both ways
Define broadcast message
one-to-all communication
Define multicast message
one-to-many communication
Define unicast message
one-to-one communication
A bus topology has _____ link but it is shared by a number of _____.
1, end systems
Therefore, a bus topology is described as a _____-point connection.
multi
In a bus topology, _____ messages are _____ even if intended for one end-system.
all, broadcast
A bus topology is _____ because a fault in one end-system or in the link to it _____ effect the use of the network.
resilient, does not
A mesh topology each _____ has a point-to-point connection to each of the other end systems.
end system
In a mesh topology, transmission is _____.
duplex
In a mesh topology, messages can be sent in 3 ways: _____, _____, and _____.
unicast, multicast, broadcast
A mesh topology may be unrealistic due to?
amount of cabling needed
A mesh topology can be used when individual _____ switches are _____in a network.
LAN, connected
A mesh topology is essential for the _____ of _____ within the infrastructure of the internet.
connect, routers
What is a router?
device that acts as a node
In a star topology each end system has a _____-to-_____ connection to a _____ device.
point, point, central
In a star topology, transmission is _____.
duplex
In a star topology, messages can be sent in 3 ways: _____, _____, and _____.
unicast, multicast, broadcast
In a star topology, failure of an end system or its link leaves other end systems _____.
unaffected
In a star topology, the _____ device must not fail.
central
In a bus topology most end systems might be user _____ and other are _____.
workstations, servers
In a star topology, the end systems might be workstations or servers, but the central device is _____.
different
In a star topology, the central device is a specialized device with the purpose of _____ other devices in the network.
connecting
Currently, a star topology is the _____ way to configure a network.
usual
Main reason for star topology is the central device can be used to connect to other _____ such as the _____.
networks, Internet
Define hybrid networks.
a collection of connected LANs where some have different topologies and technologies
Define cable
transmission using copper wire or fiber optic
Define bandwidth
measure of amount of data transmitted per system
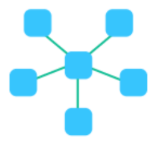
Which topology does the image represent?
star topology