3.1-3.7 sexual/asexual reproduction, reproduction of plants
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Advantages of sexual reproduction
produces variation - if the environment changes it is likely that an organism in the species will have a characteristic that allows them to survive (survival advantage), prevents extinction
Allows selective breeding- can breed organisms desirable characteristics to breed offspring with more desirable characteristics, speeds up natural selection
Advantages of asexual reproduction
only one parent is needed
Faster than sexual reproduction
Lots of identical offspring can be produced
Disadvantages of sexual reproduction
high energy and time
Slower process
Requires two parents
Disadvantages of asexual reproduction
Lack of genetic variation - entire population susceptible to a single disease/environmental shift
Limited adaptability - hindered evolution
Differences between sexual and asexual reproduction
S- two parents, A- one parent
S- involves gametes (sperm, egg), A- no gametes involved
S- requires fertilisation, A- none
S- offspring are genetically varied, A- offspring are genetically identical
S- involves meiosis and mitosis, A- primarily involves mitosis
S- slower and more energy, A- faster and less energy
What does fertilisation involve
The fusion of a male and female gamete to produce a zygote that undergoes cell division and develops into an embryo
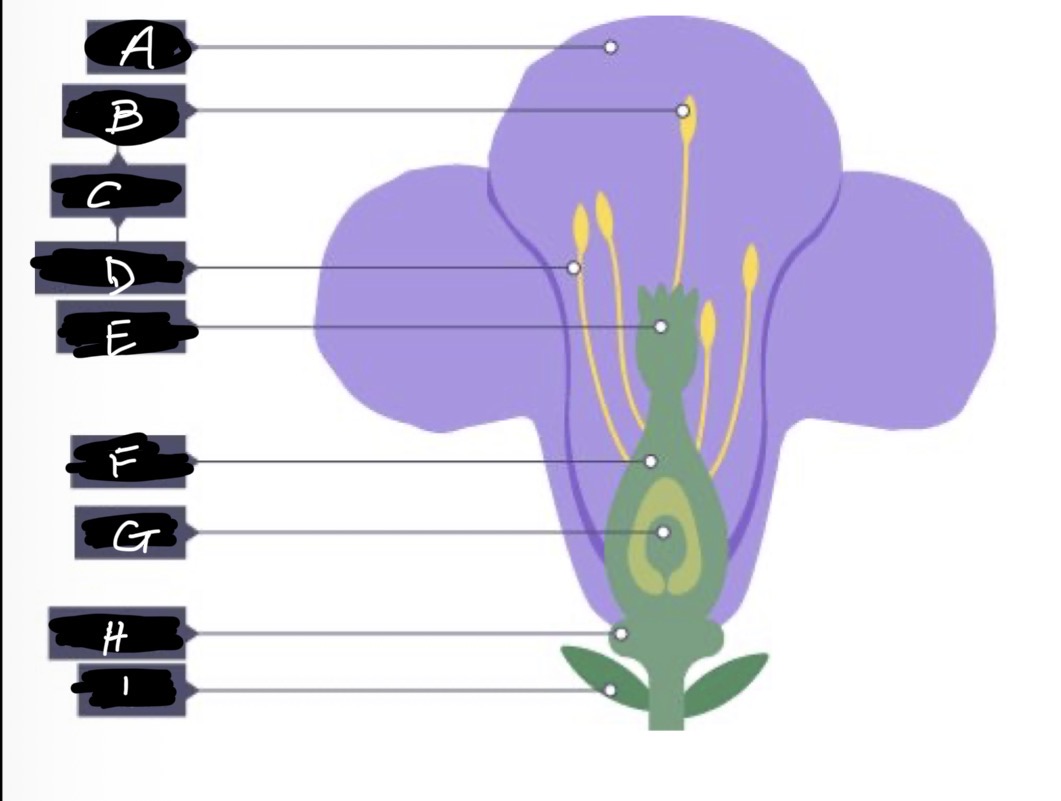
A name and adaptation
Petals- large and bright to attract insects
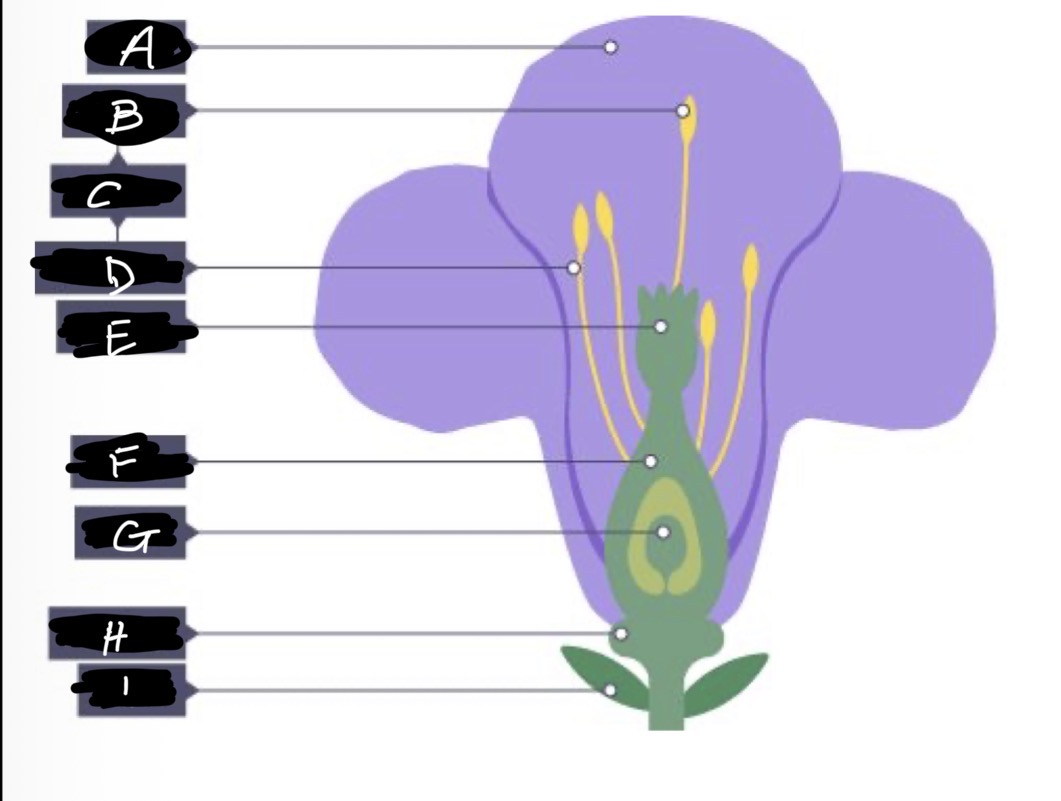
B name and adaptation
Anther- produces and holds pollen, stiff and attached inside the flower so that insects can brush past
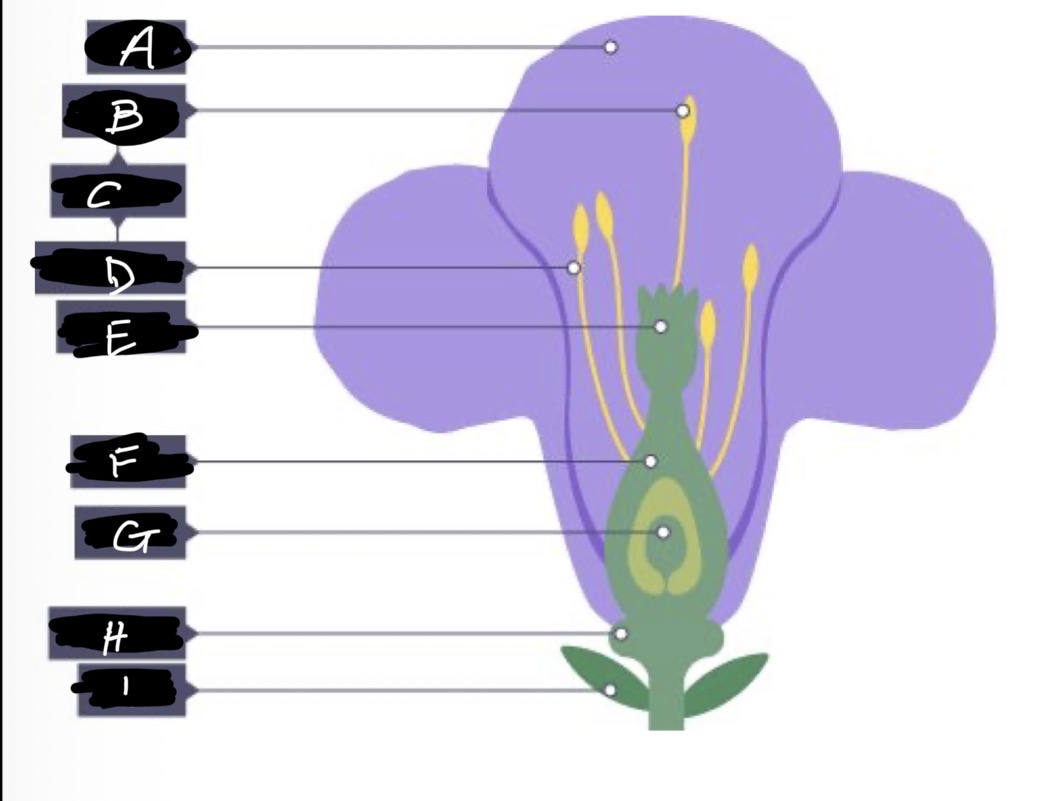
What are B and D (C) and function?
Stamen - male reproductive organ
D name and function
Filament- elevates and supports the anther
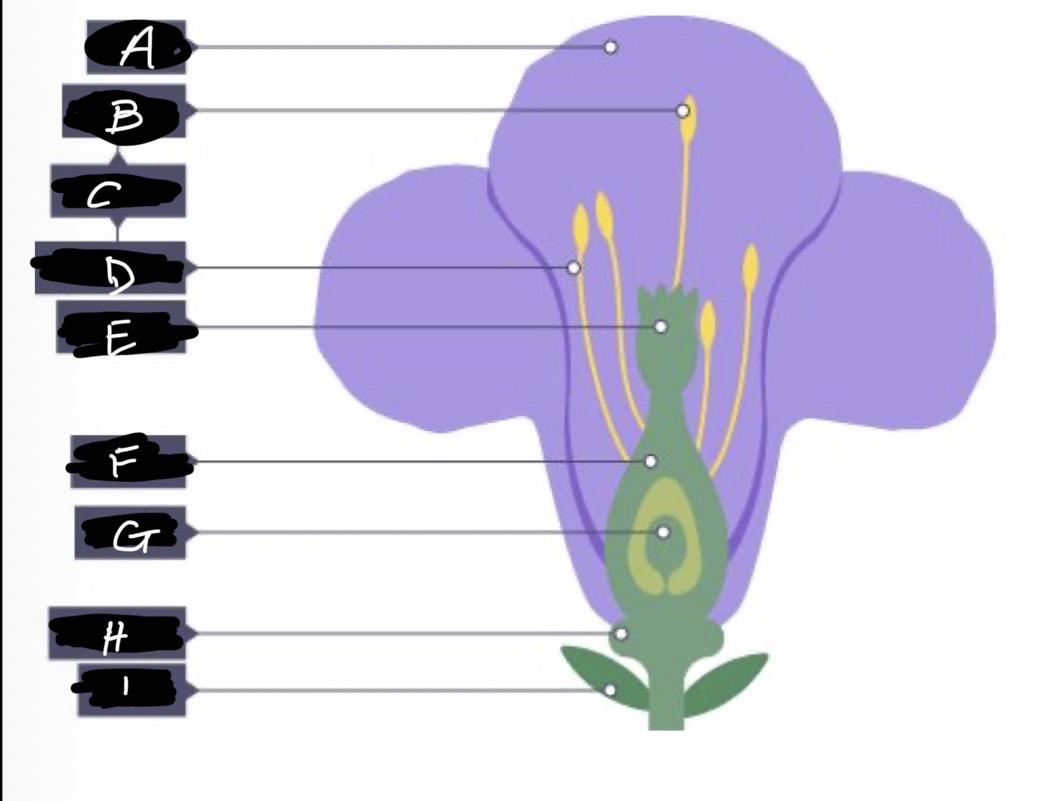
E name and adaptation
Stigma- inside flower, sticky so pollen grains stick to it when insects brush past
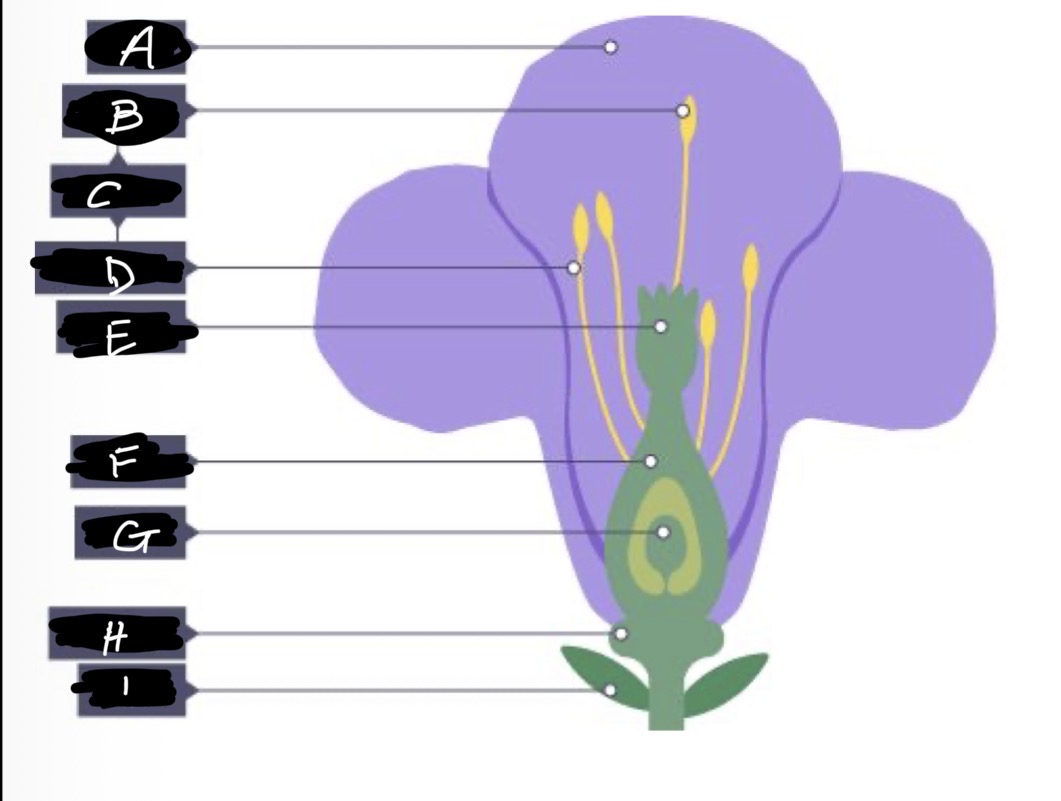
F name
Ovary
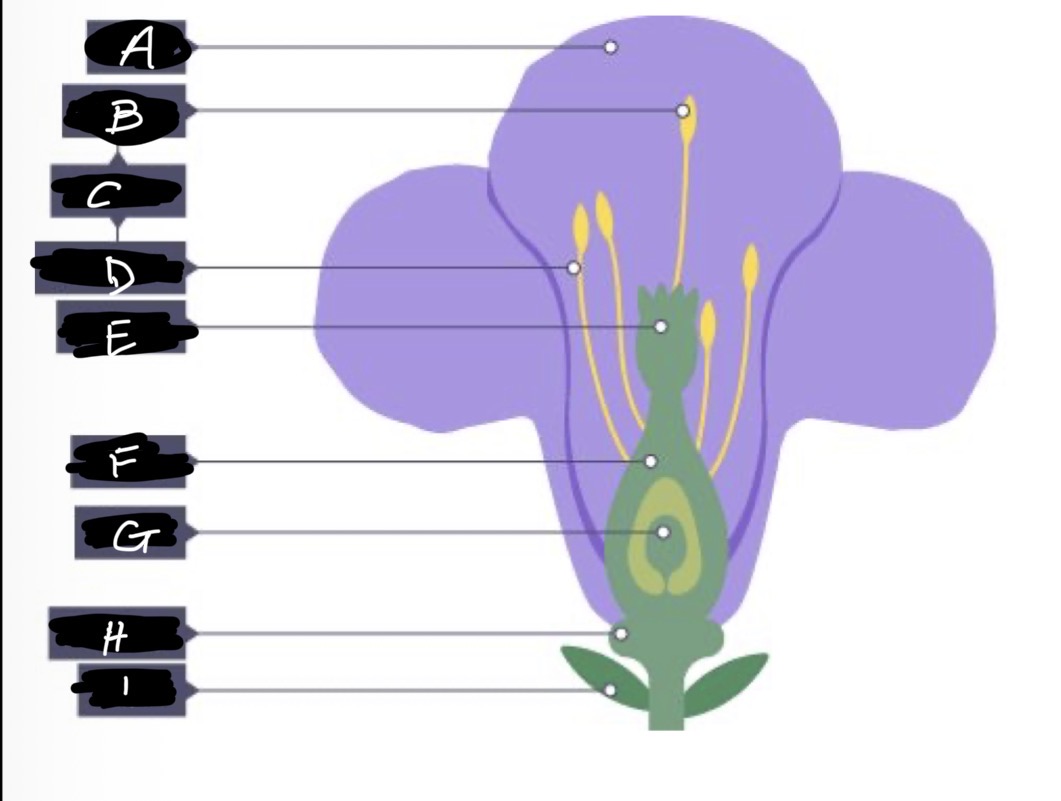
G name
Ovule
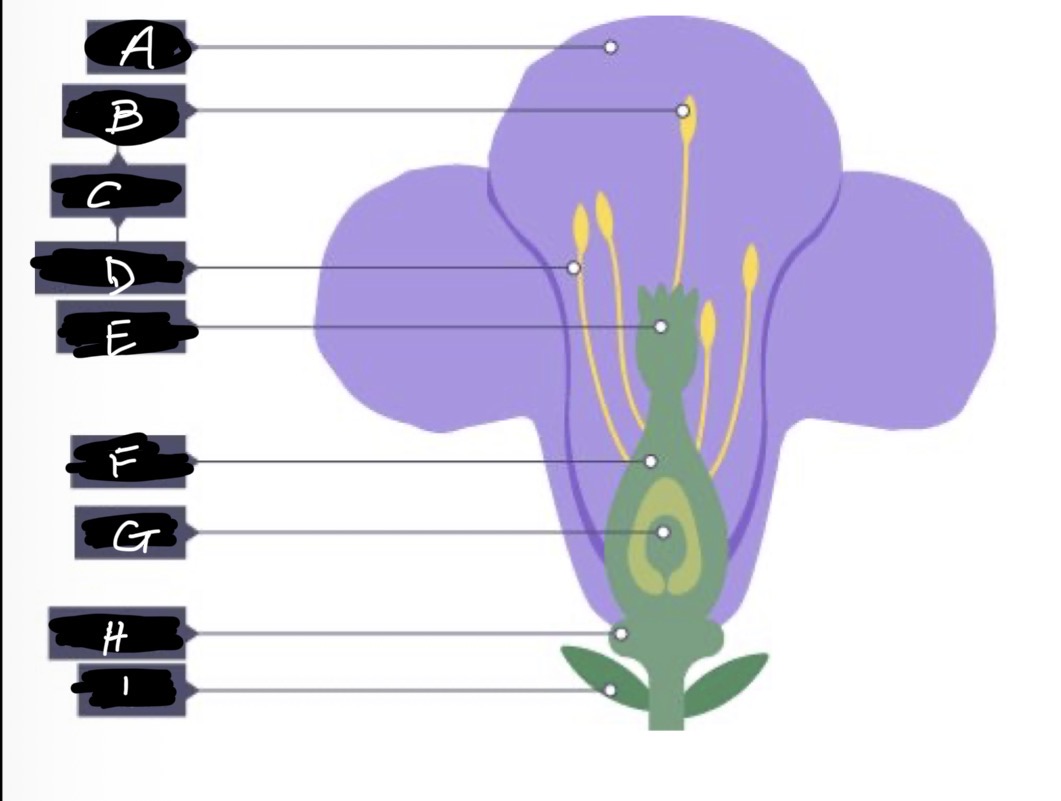
H name and adaptation
Nectary- secretes nectar which is scented to attract insects
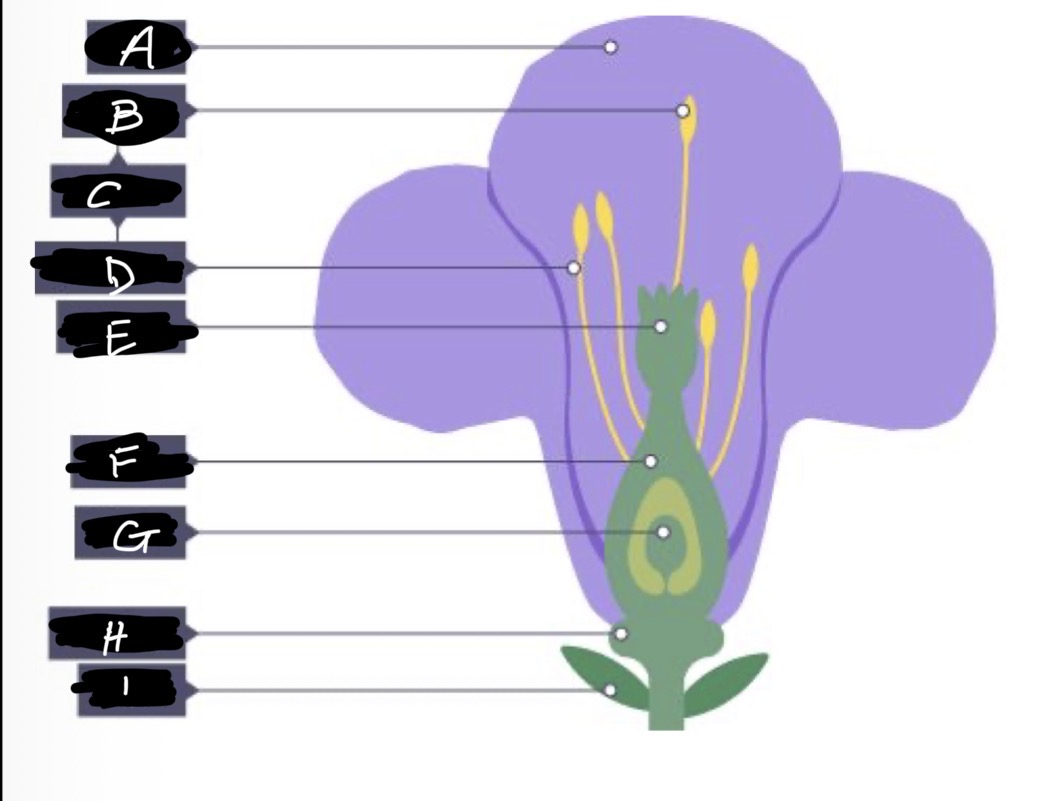
I name
Sepal
Different types of plants
Insect pollinated and wind pollinated
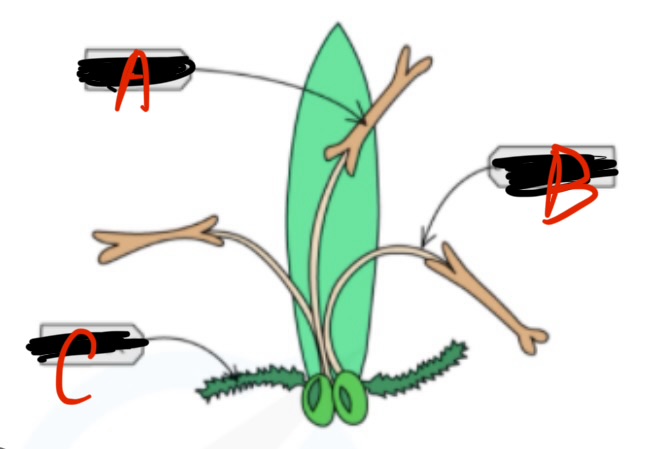
A name
Anther
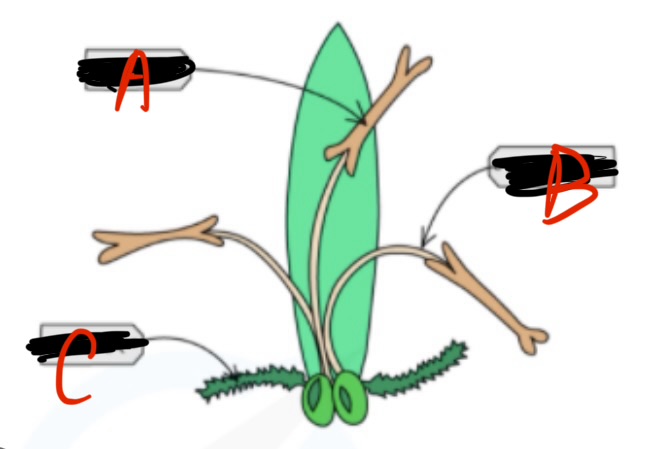
B name
Filament
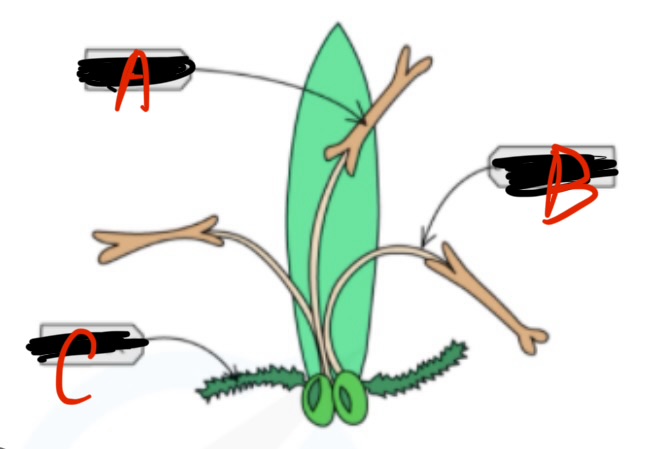
C name
Stigma
How are wind pollinated petals adapted
Small and dull, do not need to attract
How are wind pollinated plants’ nectar adapted?
There is no nectar or scent, do not need to attract
How are wind pollinated plants’ pollen grains adapted
Smooth and light so they can be easily carried in the wind and in large amounts to make sure some reach other flowers
How are wind pollinated plants’ anthers and filaments adapted
They are outside the flower, loose on long ligaments so that pollen can be easily released
How are wind pollinated plants’ stigma adapted
They are outside the flower, feathery so it is easier to catch pollen grains drifting in the wind
What are the sex cells in plants that reproduce sexually?
Pollen grains are the male gametes, ovule is the female gamete
Describe the process of seed and fruit formation
1. Pollen grains land on stigma (via insect or wind pollination)
2. Pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain and down the style
3. The male nucleus travels down the pollen tube from the pollen grain to fuse with the female egg nucleus in the ovule, forming a zygote
4. The zygote undergoes mitosis to form a seed
5. The ovule will become the seed and the ovule wall will become the seed coat
6. The ovary will become the fruit of the plant
What is germination
The process in which seeds begin to develop into a new young plant
What conditions are needed for seed germination and why?
Water- needed to activate enzymes to break down the starch food reserves in the seeds
Oxygen- needed fr aerobic respiration to release energy for growth
Warmth- optimum temperature for enzymes will increase growth
What practical can you do to investigate the conditions needed for seed germination?
1. Set up 4 boiling tubes with 10 cress seeds in each, sitting on cotton wool
2. Tube A should have dry cotton wool and kept at 20°C
3. Tube B should have moist cotton wool and kept at 20°C
4. Tube C should have boiled water that has been cooled, covered with a layer of oil and kept at 20°C
5. Tube D should have moist cotton wool but kept at lower temp eg 4°C
Results: only Tube B seeds will germinate because it has water, temp, oxygen.
What is an embryo (in a plant)
Young root and shoot that becomes the adult plant
What is a food store
Starch for the plant to use until it is able to carry out photosynthesis
What is a seed coat
A protective covering
What is an example of natural asexual reproduction of plants?
Runners - grow horizontally over soil surface and put down roots to form new plants
Eg. Strawberry plants
What is an example of artificial asexual reproduction of plants
Cuttings- a piece of a parent plant that’s cut off and placed in a growth medium to grow into a new identical plant