DC CIRCUITS - RESISTANCE/OHM'S LAW/NETWORK THEOREM
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
The property of the material that opposes the flow of an electric current.
Resistance
Formula of Resistance (Constant Temperature only)

Specific resistance or resistivity of Hard drawn copper (HDC) at 20oc
1.77 × 10-8 ohm-meter or 10.66 (ohm-cm)/ft
Specific resistance or resistivity of annealed copper at 20oc
1.72 × 10-8 ohm-meter or 10.50 (ohm-cm)/ft
Specific resistance or resistivity of aluminum at 20oc
12.83 × 10-8 ohm-meter or 17.0 (ohm-cm)/ft
area of circle?
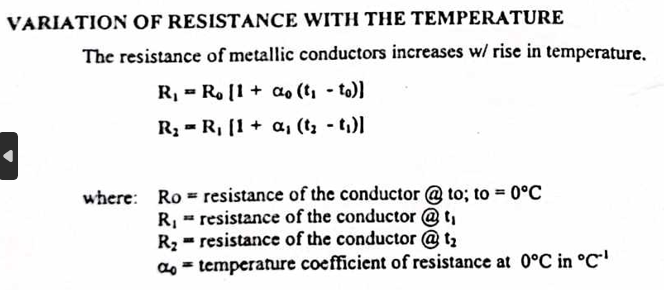
Variation of resistance with the temperature
Temperature coefficient of resistance at 0oc
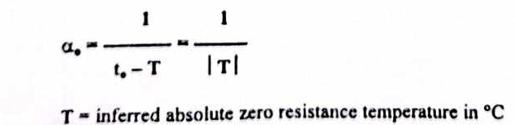
Inferred absolute temperature of copper
T = -234.5 oc
Temperature coefficient of resistance at t1
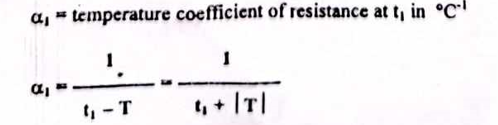
1 inch = ______ mils
1000 mils
Temperature coefficient of resistance at t2
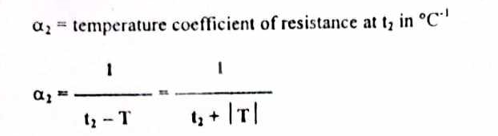
Change in temperature
T = t2 - t1
it states that the ratio of potential difference (V) between any two point on a conductor to the current (I) flowing through them is constant provided the physical conditions of the conductor does not change
ohms law
Enumerate the formula of series circuit characteristics
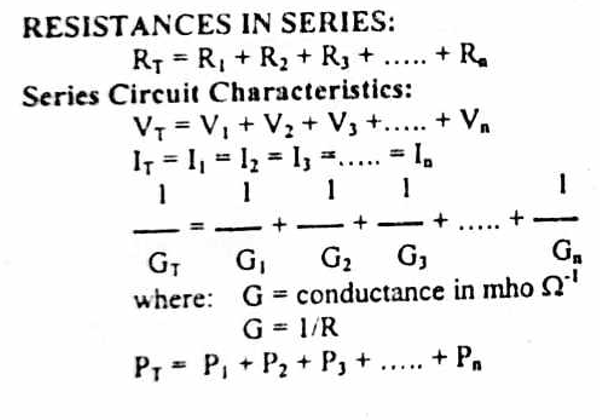
Enumerate the formula of parallel circuit characteristics
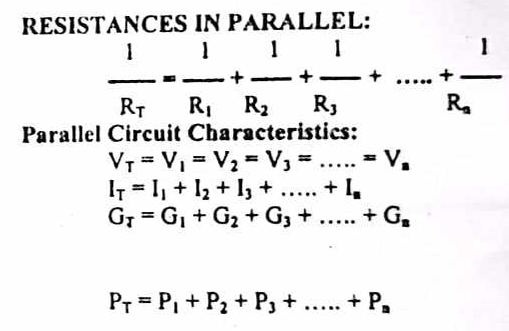
Current dividers
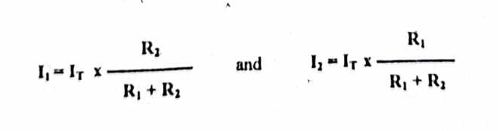
Voltage dividers
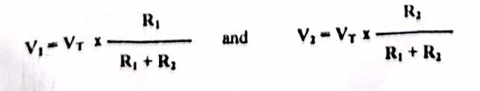
the amount of work required to maintain a current through a resistance for second is given by
Joule’s law of electric heating and
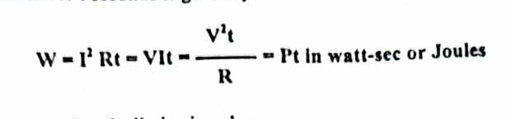
Formula of heat produce by electrical
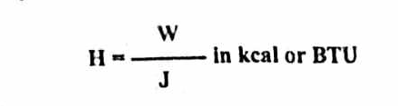
Joule = ______ KJ/ kcal = ________ ft-lb/BTU
1Joule = ___ ergs = ____ gm-calories
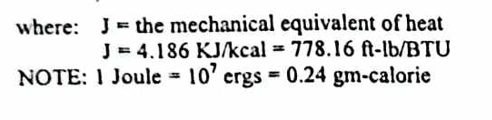
it is the ratio of the heat actually utilized to the total heat produced electrically
Thermal efficiency
Formula of thermal efficiency

a group of cells that generate electric energy from their internal chemical reaction
battery

battery
1 ampere = _____ abampere
0.1 abampere
1ft² = _____cmil
183.35 ×10^6 cmil
Formula of Maximum Power Transfer
Pmax = V² /(4)(Rth)
1 liter = _____ m³
10^-3 m³
Cp of water = specific heat of water = _____j/kg°c
4200 j/kg°c
Density of water= ?
1000 kg
What is the other formula of R =pL²/V
R2/R1 = (L2/L1)²
What is the other formula of R =pV/A²
R2/R1 = (d1/d2)^4
What is the other formula of R =pL/A
R2/R1 = (d1/d2)²
Specific Resistance or resistivity of Silver
9.9 ohm-CM/ft
Specific Resistance or resistivity of Copper
10.37 ohm-CM/ft
Specific Resistance or resistivity of aluminum
17 ohm-CM/ft
Specific Resistance or resistivity of tungsten
33 ohm-CM/ft
Specific Resistance or resistivity of zinc
36 ohm-CM/ft
inferred absolute temperature of silver
243oc
inferred absolute temperature of copper
234.5oc
inferred absolute temperature of aluminum
236oc
inferred absolute temperature of tungsten
202oc
inferred absolute temperature of zinc
250oc
temperature coefficient of silver at 20oc
3.8×10-3
temperature coefficient of copper at 20oc
3.93×10-3
temperature coefficient of aluminum at 20oc
3.9×10-3
temperature coefficient of tungsten at 20oc
4.5×10-3
temperature coefficient of zinc at 20oc
3.7×10-3
Insulation resistance of cables

Formula of conductance

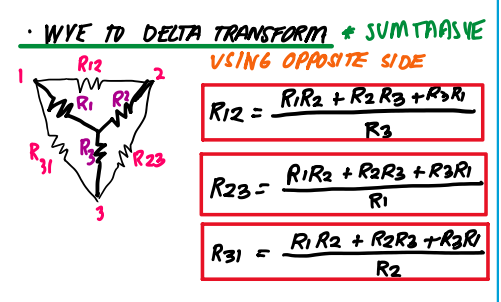
Delta to wye transform
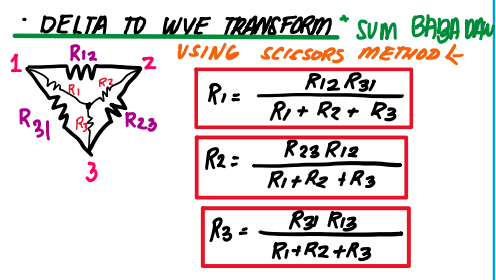
wye to delta tranform
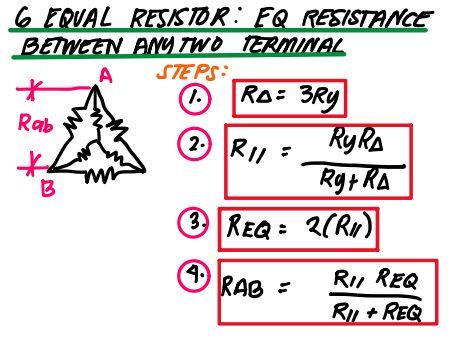
6 Equal resistor : EQ resistance between any two terminal
Cubical -Connected 12 identical resistor - two terminals
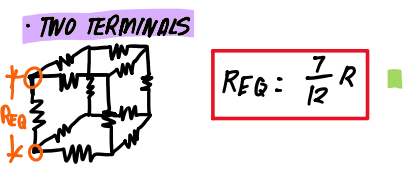
Cubical -Connected 12 identical resistor - two terminals in diagonal
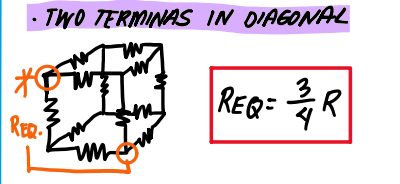
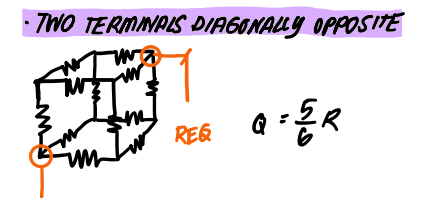
Cubical -Connected 12 identical resistor - two terminals in diagonally opposite
named after the German physicist, Gustav Robert Kirchhoff
Kirchhoff’s law
the algebraic sum of the currents at any junction or node of an electric circuit is zero
Current law (KCL)
the algebraic sum of the emf and the resistance voltage drop in any closed loop of an electric circuit is zero
Voltage law (KVL)
involves a set of independent loop currents assigned to “as many meshes” as it exist in the circuit
Maxwell mesh method
the current in any resist is equal to the algebraic sum of the current delivered by each independent sources assuming that each source is acting “acting alone or independently”
a circuit with “n” nodes, has a solution with only “n-1” number of equations needed.
Nodal node method