Work, energy, power
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms

A
Can work be done on a system if there is no motion?
Yes, since motion is only relative.
No, since a system which is not moving has no energy.
Yes, if an outside force is provided.
No, because of the way work is defined.
D
If you push twice as hard against a stationary brick wall, the amount of work you do
is cut in half.
remains constant at zero.
remains constant but non-zero.
doubles.
B
A 50-N object was lifted 2.0 m vertically and is being held there. How much work is being done in holding the box in this position?
less than 100 J, but more than 0 J
more than 100 J
100 J
0 J
D
If you walk 5.0 m horizontally forward at a constant velocity carrying a 10-N object, the amount of work you do is
equal to 50 J.
less than 50 J, but more than 0 J.
more than 50 J.
zero.
D
Does the centripetal force acting on an object do work on the object?
Yes, since a force acts and the object moves, and work is force times distance.
No, because the force and the displacement of the object are perpendicular.
Yes, since it takes energy to turn an object.
No, because the object has constant speed
B
You throw a ball straight up. Compare the sign of the work done by gravity while the ball goes up with the sign of the work done by gravity while it goes down.
Work is + on the way up and - on the way down.
Work is + on the way up and + on the way down.
Work is - on the way up and + on the way down.
Work is - on the way up and - on the way down.
C
The area under the curve, on a Force versus position (F vs. x) graph, represents
work.
power.
kinetic energy.
potential energy.
A
If the net work done on an object is positive, then the object's kinetic energy
is zero.
decreases.
remains the same.
increases.
D
A truck weighs twice as much as a car, and is moving at twice the speed of the car. Which statement is true about the truck's kinetic energy compared to that of the car?
The truck has twice the kinetic energy of the car.
All that can be said is that the truck has more kinetic energy.
The truck has 8 times the kinetic energy of the car.
The truck has 4 times the kinetic energy of the car
C
A brick is moving at a speed of 3 m/s and a pebble is moving at a speed of 5 m/s. If both objects have the same kinetic energy, what is the ratio of the brick's mass to the rock's mass?
5 to 3
3 to 5
25 to 9
12.5 to 4.5
C
The quantity 1/2 kx2 is
the work done on the object by the force.
the kinetic energy of the object.
the elastic potential energy of the object.
the power supplied to the object by the force
C
An object is lifted vertically 2.0 m and held there. If the object weighs 90 N, how much work was done in lifting it?
360 J
0 J
90 J
180 J
D
A 500-kg elevator is pulled upward with a constant force of 5500 N for a distance of 50.0 m. What is the work done by the 5500 N force?
-2.45 × 105 J
2.75 × 105 J
3.00 × 104 J
-5.20 × 105 J
B
A 30-N box is pulled 6.0 m up along a 37° inclined plane. What is the work done by the weight (gravitational force) of the box?
- 11 J
- 1.8 × 102 J
- 1.4 × 102 J
- 1.1 × 102J
D
Matthew pulls his little sister Sarah in a sled on an icy surface (assume no friction), with a force of 60.0 N at an angle of 37.0° upward from the horizontal. If he pulls her a distance of 12.0 m, what is the work done by Matthew?
720 J
185 J
575 J
433 J
C
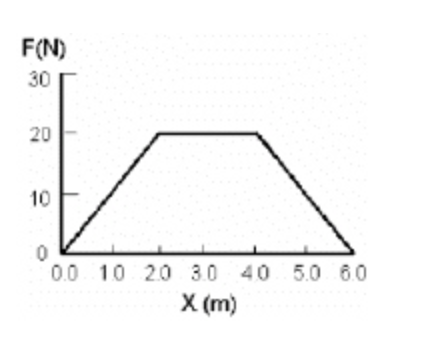
A force moves an object in the direction of the force. The graph in Fig. 6-1 shows the force versus the object's position. Find the work done when the object moves from 0 to 2.0 m.
60 J
20 J
80 J
40 J
B
A horizontal force of 200 N is applied to move a 55-kg cart (initially at rest) across a 10 m level surface. What is the final kinetic energy of the cart?
2.7 × 103 J
1.0 × 103 J
2.0 × 103 J
4.0 × 103 J
C
If it takes 50 m to stop a car initially moving at 25 m/s, what distance is required to stop a car moving at 50 m/s under the same condition?
100 m
400 m
50 m
200 m
D
A 10-kg mass is moving with a speed of 5.0 m/s. How much work is required to stop the mass?
100 J
50 J
75 J
125 J
D
What work is required to stretch a spring of spring constant 40 N/m from x = 0.20 m to 0.25 m? (Assume the unstretched position is at x = 0.)
0.050 J
0.80 J
1.3 J
0.45 J
D
Can work be done on a system if there is no motion?
Yes, since motion is only relative.
Yes, if an outside force is provided.
No, since a system which is not moving has no energy.
No, because of the way work is defined.
D
The quantity 1/2 mv2 is
the kinetic energy of the object.
the potential energy of the object.
the power supplied to the object by the force.
the work done on the object by the force
A
If the net work done on an object is positive, then the object's kinetic energy
remains the same.
decreases.
is zero
increases.
D
If the net work done on an object is zero, then the object's kinetic energy
increases.
is zero.
remains the same.
decreases
C
Car J moves twice as fast as car K, and car J has half the mass of car K. The kinetic energy of car J, compared to car K is
2 to 1.
1 to 2.
the same.
4 to 1.
A
An object hits a wall and bounces back with half of its original speed. What is the ratio of the final kinetic energy to the initial kinetic energy?
1/2
1/4
2
4
B
You slam on the brakes of your car in a panic, and skid a certain distance on a straight, level road. If you had been traveling twice as fast, what distance would the car have skidded, under the same conditions?
It would have skidded 1.4 times farther.
It would have skidded 4 times farther.
It would have skidded twice as far.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
B
A planet of constant mass orbits the Sun in an elliptical orbit. Neglecting any friction effects, what happens to the planet's kinetic energy?
It increases when the planet approaches the Sun, and decreases when it moves farther away.
It decreases continually.
It remains constant.
It increases continually
A
The quantity mgy is
the gravitational potential energy of the object.
the work done on the object by the force.
the kinetic energy of the object.
the power supplied to the object by the force
A
The quantity 1/2 kx2 is
the kinetic energy of the object.
the elastic potential energy of the object.
the work done on the object by the force.
the power supplied to the object by the force
B
An object is released from rest a height h above the ground. A second object with four times the mass of the first if released from the same height. The potential energy of the second object compared to the first is
one-fourth as much.
twice as much.
four times as much.
one-half as much.
C
A 0.200-kg mass attached to the end of a spring causes it to stretch 5.0 cm. If another 0.200-kg mass is added to the spring, the potential energy of the spring will be
3 times as much.
twice as much.
the same.
4 times as much.
D
Describe the energy of a car driving up a hill.
entirely potential
entirely kinetic
both kinetic and potential
gravitational
C
A lightweight object and a very heavy object are sliding with equal speeds along a level frictionless surface. They both slide up the same frictionless hill. Which rises to a greater height?
cannot be determined from the information given
The heavy object, because it has greater kinetic energy.
The lightweight object, because it weighs less.
They both slide to the same height
D
The quantity Fd/t is
the work done on the object by the force.
the power supplied to the object by the force.
the potential energy of the object.
the kinetic energy of the object.
B
What is the correct unit of power expressed in SI units?
kg m2 s-2
kg m s-2
kg m2 s-3
kg2 m s-2
C
Of the following, which is not a unit of power?
watt
joule/second
watt/second
newton-meter/second
C
Compared to yesterday, you did 3 times the work in one-third the time. To do so, your power output must have been
one-third of yesterday's power output.
the same as yesterday's power output
3 times yesterday's power output.
9 times yesterday's power output.
D
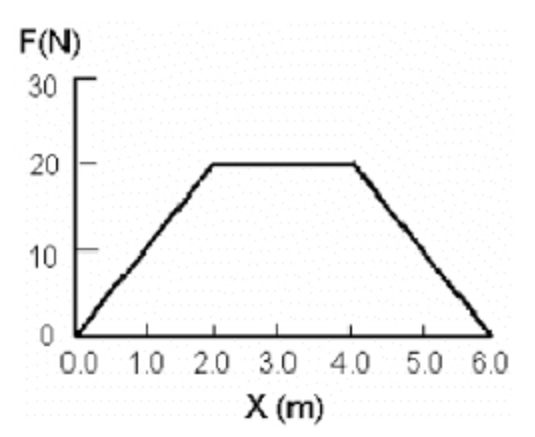
A force moves an object in the direction of the force. The graph in Fig. 6-1 shows the force versus the object's position. Find the work done when the object moves from 0 to 6.0 m.
60 J
80 J
20 J
40 J
B
A horizontal force of 200 N is applied to move a 55-kg cart (initially at rest) across a 10 m level surface. What is the final speed of the cart?
6.0 m/s
73 m/s
36 m/s
8.5 m/s
D
A 10-kg mass is moving with a speed of 5.0 m/s. How much work is required to stop the mass?
75 J
100 J
125 J
50 J
C
A 100-N force has a horizontal component of 80 N and a vertical component of 60 N. The force is applied to a box which rests on a level frictionless floor. The cart starts from rest, and moves 2.0 m horizontally along the floor. What is the cart's final kinetic energy?
120 J
160 J
200 J
zero
B
A 15.0-kg object is moved from a height of 7.00 m above a floor to a height of 13.0 m above the floor. What is the change in gravitational potential energy?
1910 J
zero
882 J
1030 J
C
A spring is characterized by a spring constant of 60 N/m. How much potential energy does it store, when stretched by 1.0 cm?
60 J
600 J
0.30 J
3.0 × 10-3 J
D
Calculate the work required to compress an initially uncompressed spring with a spring constant of 25 N/m by 10 cm.
0.25 J
0.13 J
0.10 J
0.17 J
B
A 60-kg skier starts from rest from the top of a 50-m high slope. What is the speed of the slier on reaching the bottom of the slope? (Neglect friction.)
22 m/s
41 m/s
9.8 m/s
31 m/s
D
A 1.0-kg ball falls to the floor. When it is 0.70 m above the floor, its potential energy exactly equals its kinetic energy. How fast is it moving?
45 m/s
14 m/s
3.7 m/s
6.9 m/s
C
A pendulum of length 50 cm is pulled 30 cm away from the vertical axis and released from rest. What will be its speed at the bottom of its swing?
2.8 m/s
1.4 m/s
0.50 m/s
0.79 m/s
B
A 1500-kg car moving at 25 m/s hits an initially uncompressed horizontal spring with spring constant of 2.0 × 106 N/m. What is the maximum compression of the spring? (Neglect the mass of the spring.)
0.68 m
0.34 m
0.17 m
1.2 m
A
The kinetic friction force between a 60.0-kg object and a horizontal surface is 50.0 N. If the initial speed of the object is 25.0 m/s, what distance will it slide before coming to a stop?
30.0 m
750 m
375 m
15.0 m
C