Inherited Metabolic Disorders: PKU, Hypothyroidism, Galactosemia & More
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Deficiency of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, necessary for converting phenylalanine into tyrosine.
PKU Treatment
Dietary restriction of protein; patients avoid high-protein foods and artificial sweeteners like aspartame.
PKU in Pregnant Women
If a mother has PKU, she must restrict her protein intake to avoid mental delays in her unborn fetus.
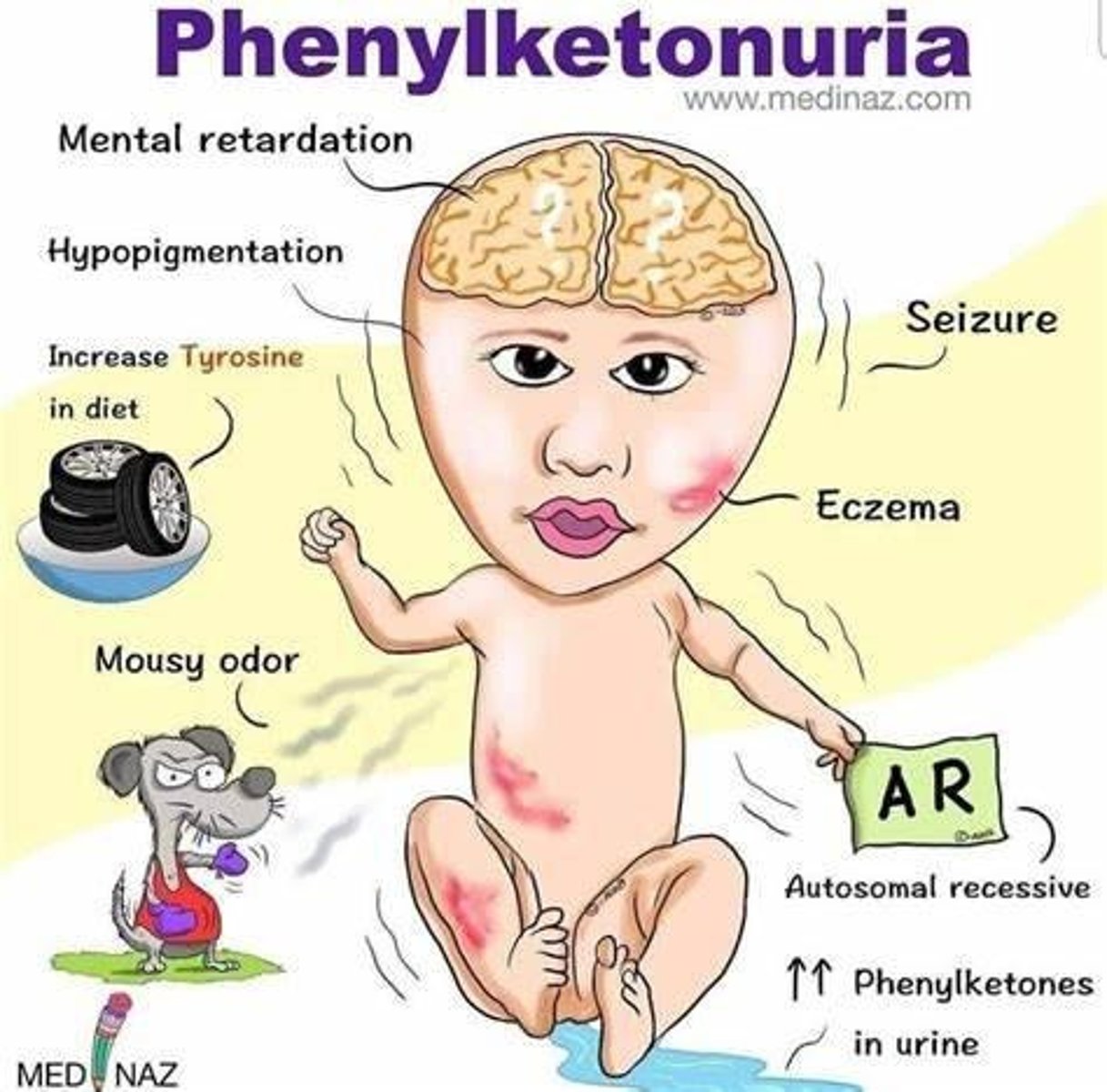
Untreated PKU Symptoms
Developmental delays, seizures, mousy odor, hypopigmentation, and autistic-like behavior.
Congenital Hypothyroidism
Most common and preventable cause of mental delays.
Congenital Hypothyroidism Symptoms
Neonatal jaundice, poor growth, constipation, myxedema, neurological defects, and cretinism.
Congenital Hypothyroidism Screening
Screened with T4 and TSH levels; low T4 and high TSH indicate the condition.
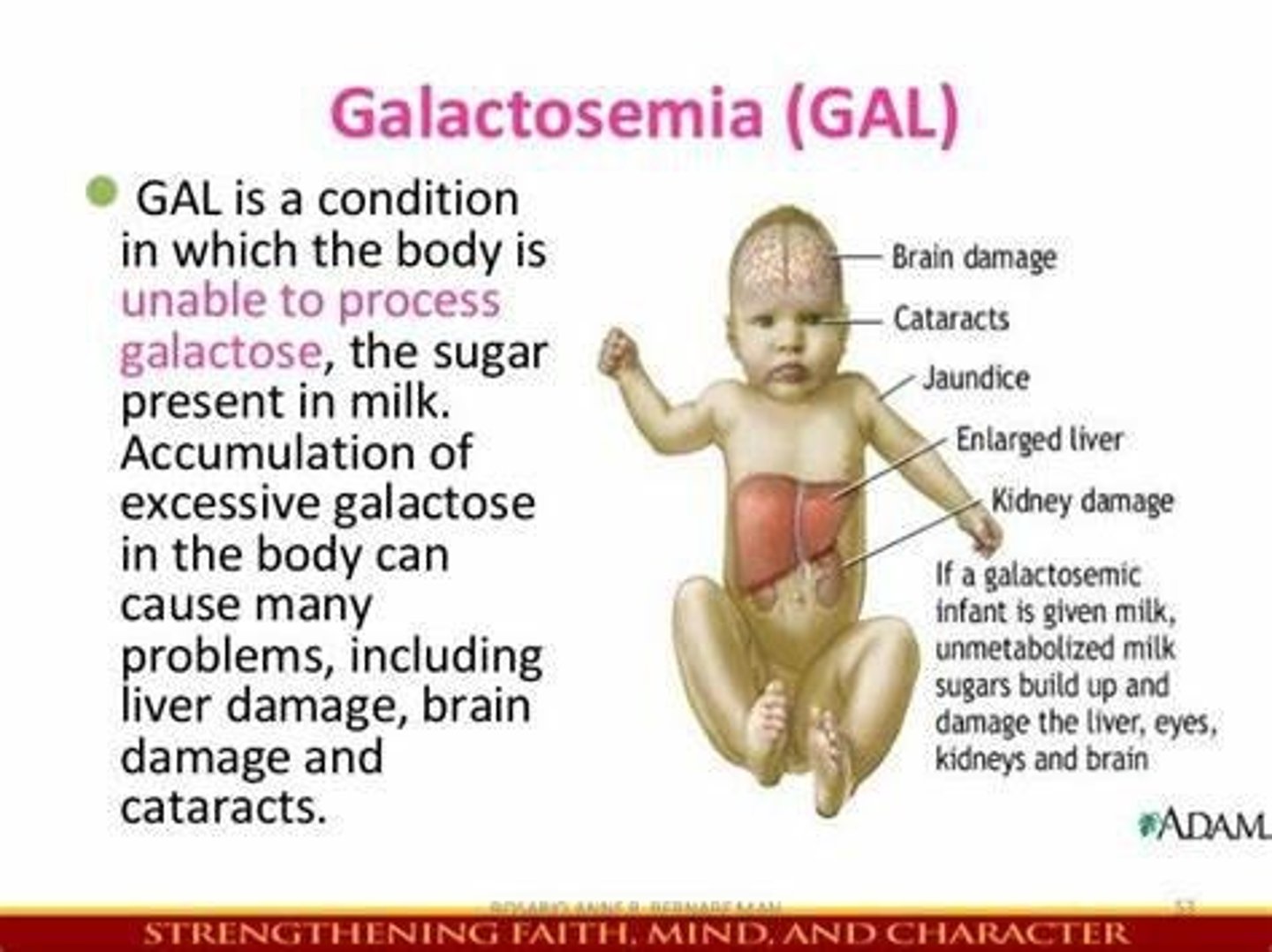
Galactosemia
Deficiency of galactose 1 phosphate uridyl transferase (GALT), leading to the inability to convert galactose to glucose.
Galactosemia Treatment
Lactose/galactose-free diet.
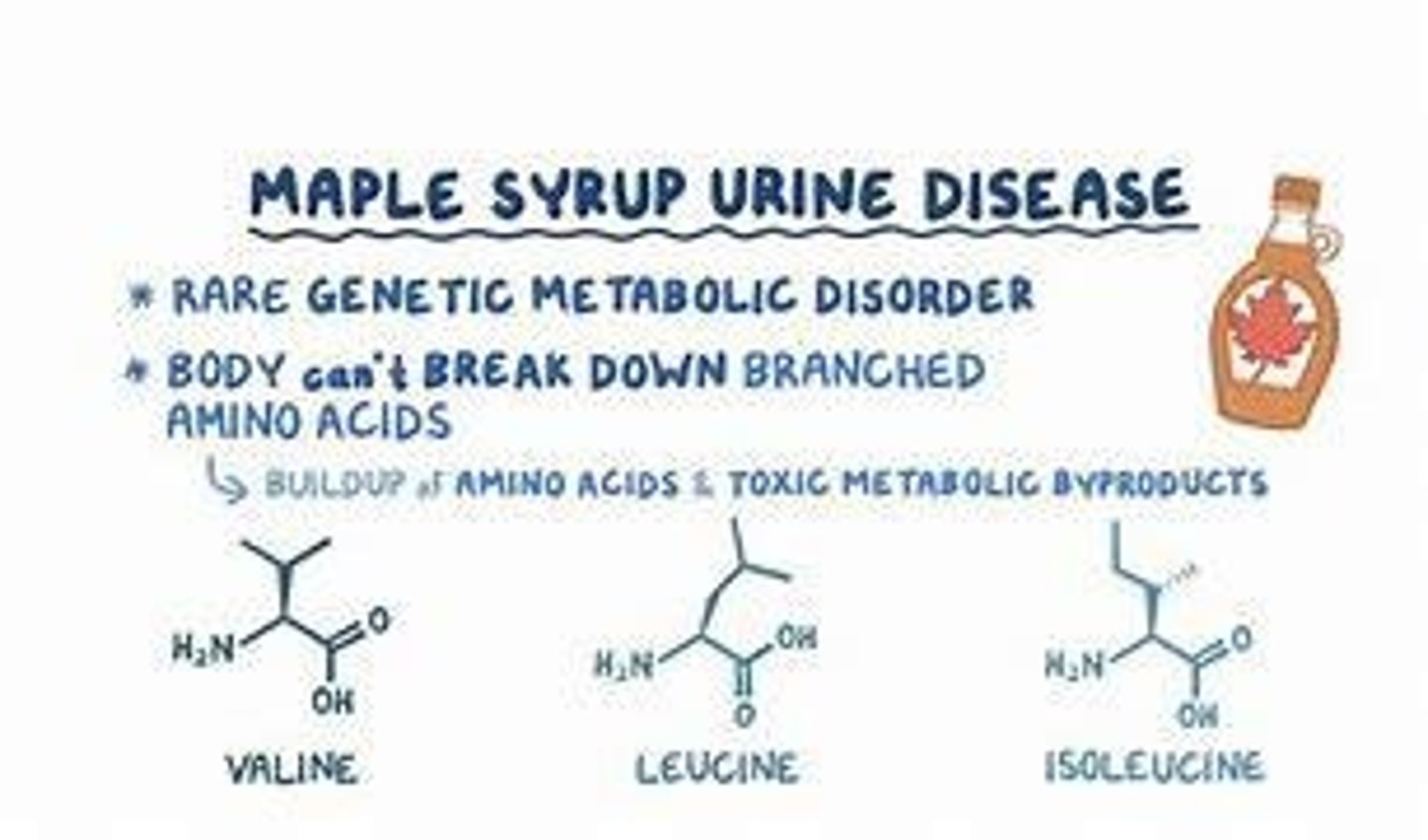
Maple Syrup Urine Disease
Inability to metabolize leucine, isoleucine, and valine due to branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase deficiency.
Maple Syrup Urine Disease Symptoms
Urine has a sweet smell, lethargy, irritability, and can lead to death within three to seven days after birth.
Homocystinuria
Increased homocysteine due to inability to break down methionine.
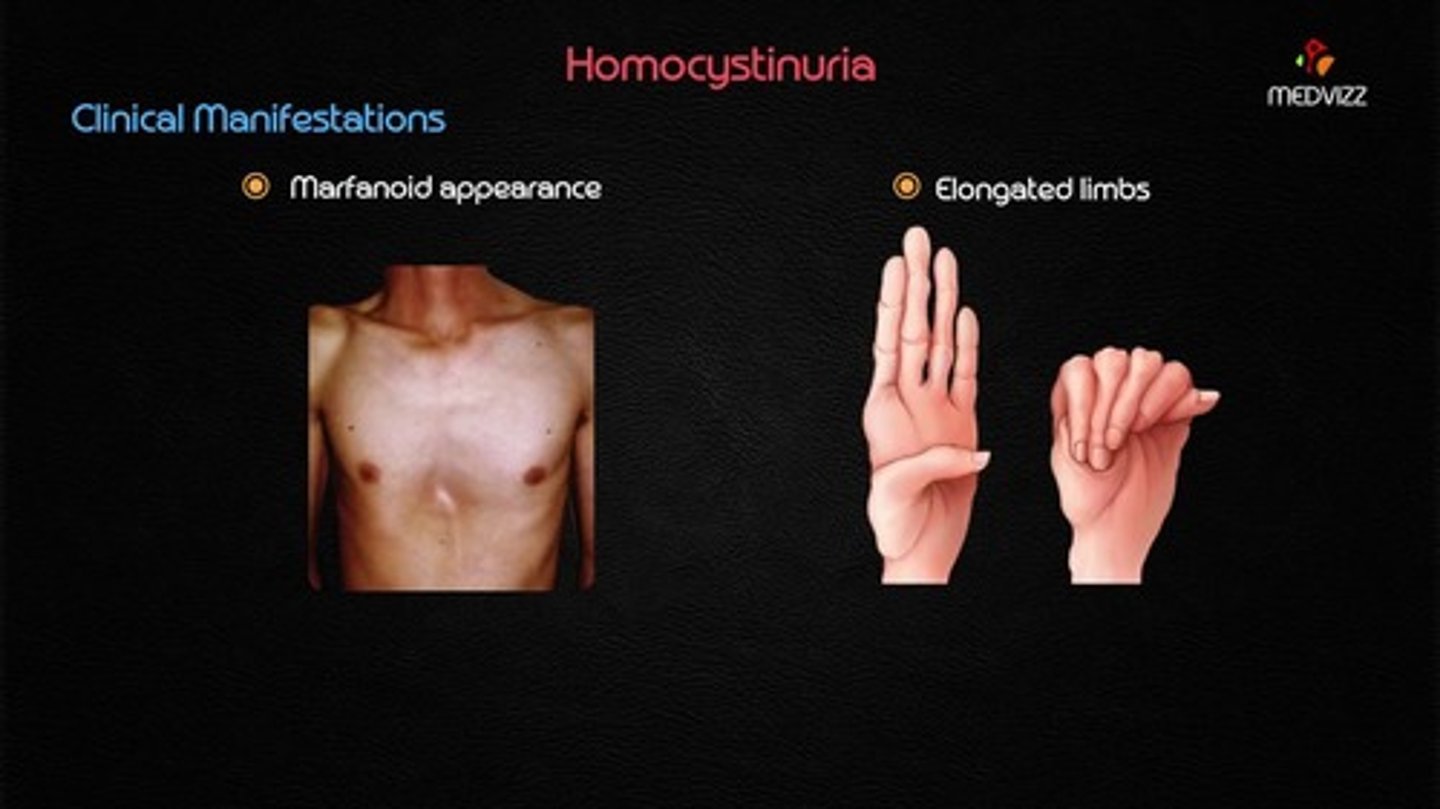
Homocystinuria Symptoms
Long limbs and fingers, thromboembolism, scoliosis, ocular lens dislocation, and mental delays.
Cystinuria
Genetic disorder causing recurrent kidney stones, most common in pediatric patients.
Cystinuria Treatment
Lithotripsy, dietary restriction, and maintaining urine pH above 7.5.
Biotinidase Deficiency
Inability to use biotin effectively due to enzyme deficiency, leading to various health issues.
Biotinidase Deficiency Symptoms
Hearing loss, optic nerve atrophy, metabolic acidosis, mental delays, and death within three months.
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Inborn error of steroid biosynthesis causing lack of cortisol and possibly aldosterone production.
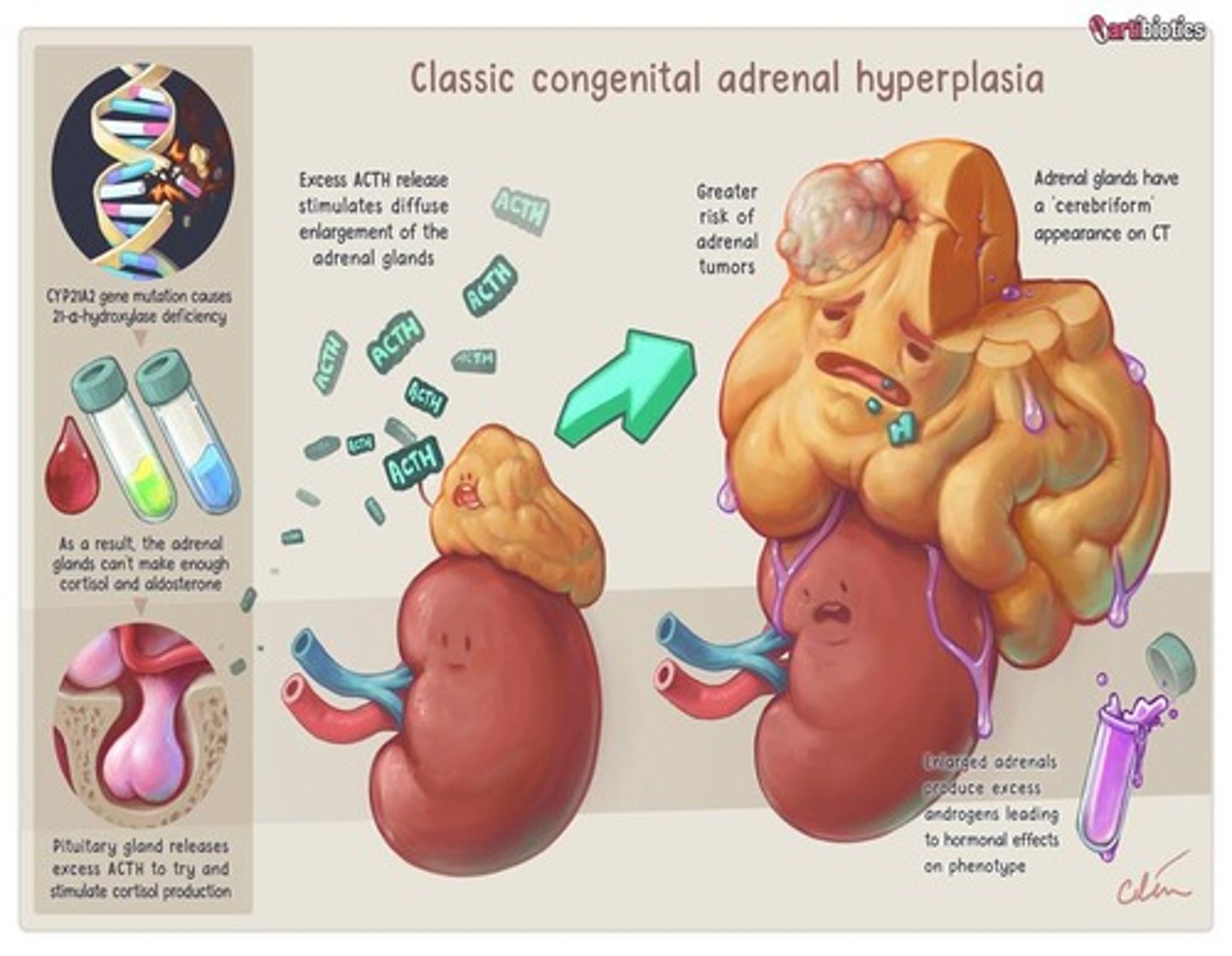
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Screening
Measured by 17 hydroxyprogesterone levels.
Hemoglobinopathies
Screen for HbS for sickle cell and other Hgb variants.
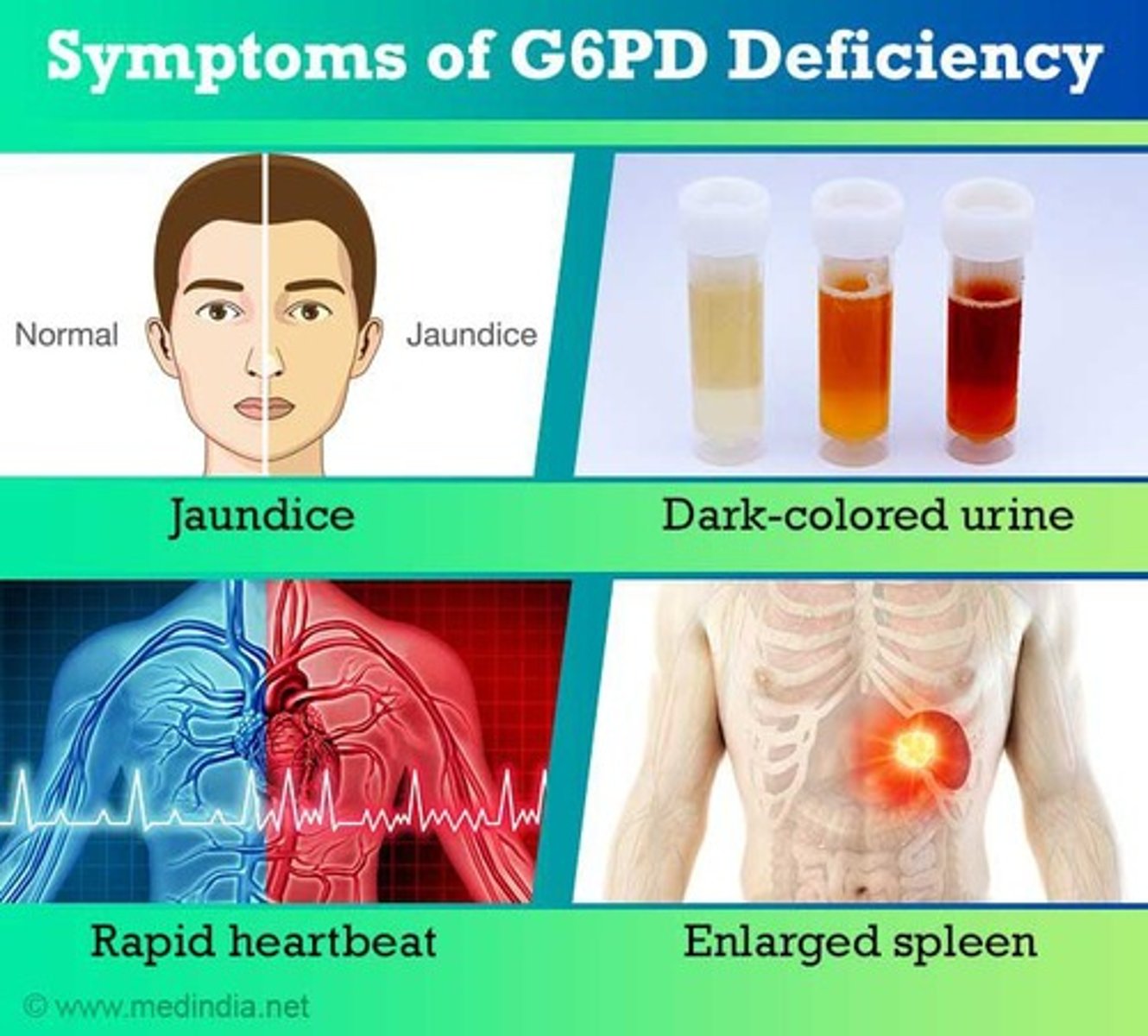
Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
Causes neonatal hyperbilirubinemia and chronic hemolytic anemia.
Tyrosinemia Type I
Failure to thrive, renal tubular dysfunction, and developmental delays with a cabbage-like odor.
Cystic Fibrosis
Symptoms include poor growth, respiratory infections, and malabsorption due to abnormal chloride channels.

Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis
Sweat chloride results over 60 mmol/L are diagnostic.
Albinism
Inherited autosomal recessive condition due to absence of tyrosinase.
Smith-Lemli Opitz Syndrome
Inborn error of cholesterol synthesis causing various developmental issues.
Alkaptonuria
Inborn error of protein metabolism due to deficiency of homogentisate 1,2 dioxygenase.
Alkaptonuria Symptoms
Accumulation of homogentisic acid leading to ochronosis and darkening of urine.