OTH 5430–Exam 3: Cardiopulmonary
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What is ischemic heart disease?
-part of heart is temporarily deprived of sufficient O2 to meet demand
-poor blood supply to the heart muscle via the coronary arteries
-common cause: atherosclerosis (coronary artery disease)
What is coronary artery disease (CAD)?
-a disease caused by the buildup of plaque resulting in the arteries to become hardened and narrowed (atherosclorosis)
-platelets gather on arterial wall, clogging arteries and increasing risk of blood clots
-develops over time without symptoms ("silent killer")
What happens if a patient experiences a partial blockage of coronary artery?
patient may be free of symptoms at rest but have angina with
-eating
-exercise
-exertion
-exposure to cold
What is angina?
Chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart
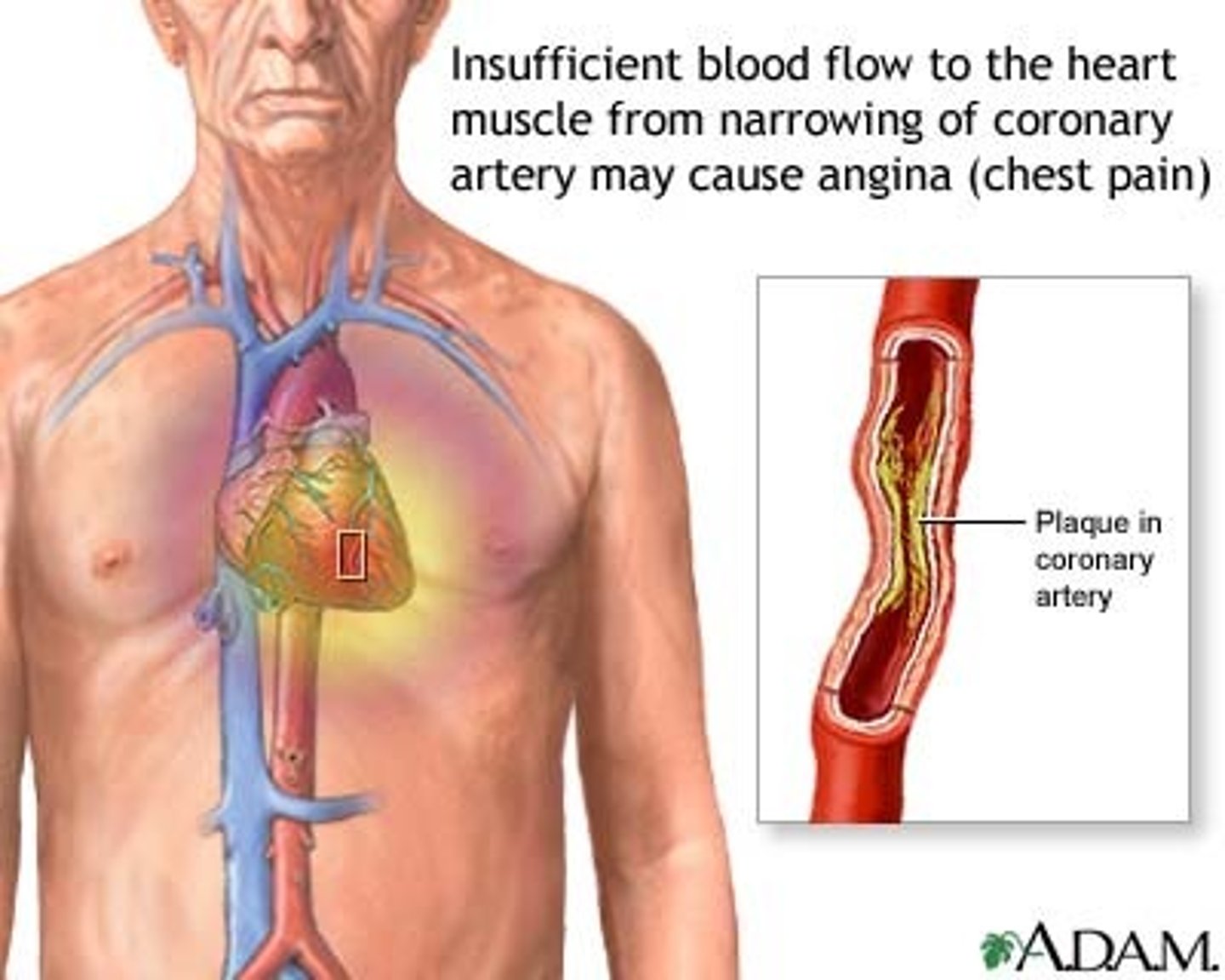
Angina varies from person to person, but the most common symptoms include ___________. How are the symptoms relieved?
squeezing
tightness
fullness
pressure
sharp pain in chest
pain that may radiate back to arm, neck, jaw
can be confused with indigestion
relieved by rest and/or medications (nitroglycerin)
Chest pain (angina) that is not relieved by rest or nitroglycerin likely indicates a ___________.
myocardial infarction (heart attack)
a medical emergency! although some patients likely to delay seeking care bc they attribute the symptoms to anxiety
What is a myocardial infarction (MI)?
-blockage of one or more coronary arteries
-heart muscles deprived of blood begin to die
if a substantial section of the heart is damaged, it will stop pumping AKA cardiac arrest
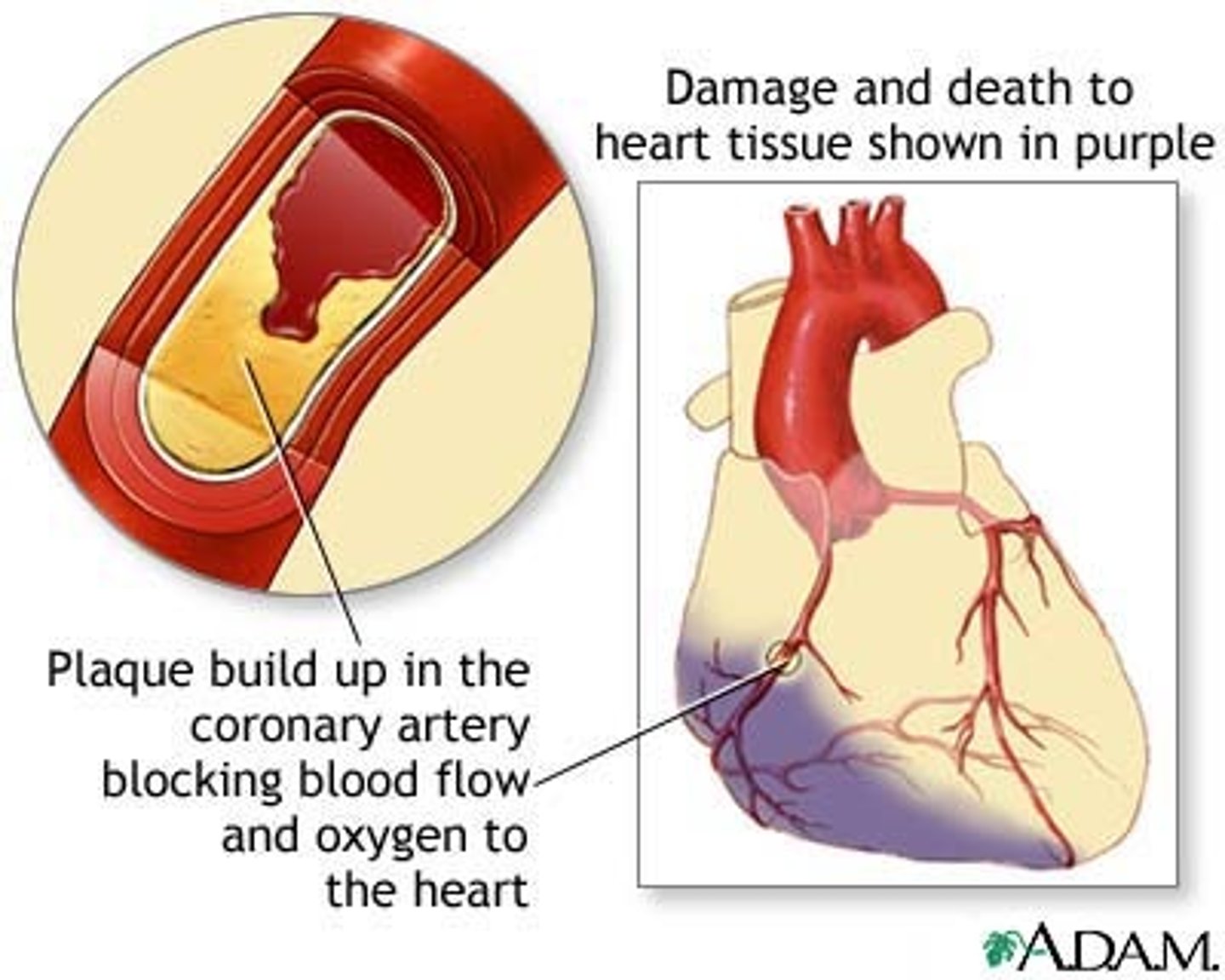
What is prescribed for the first 6 weeks post MI? Why?
activity restrictions are prescribed to decrease the risk of re-injury
-this includes a delicate balance between rest and activity with no excessive exertion/fatigue
(newly damaged heart muscle is easily re-injured)
What happens 6 weeks after an MI? What can be prescribed?
-scar tissue forms and the risk of re-injury decreases
-scarred heart tissue does NOT contract with each heartbeat (no longer elastic)
-heart efficiency is compromised
graded exercise program can be prescribed (cardiac rehab)
CAD can lead to ____________.
congestive heart failure (CHF)
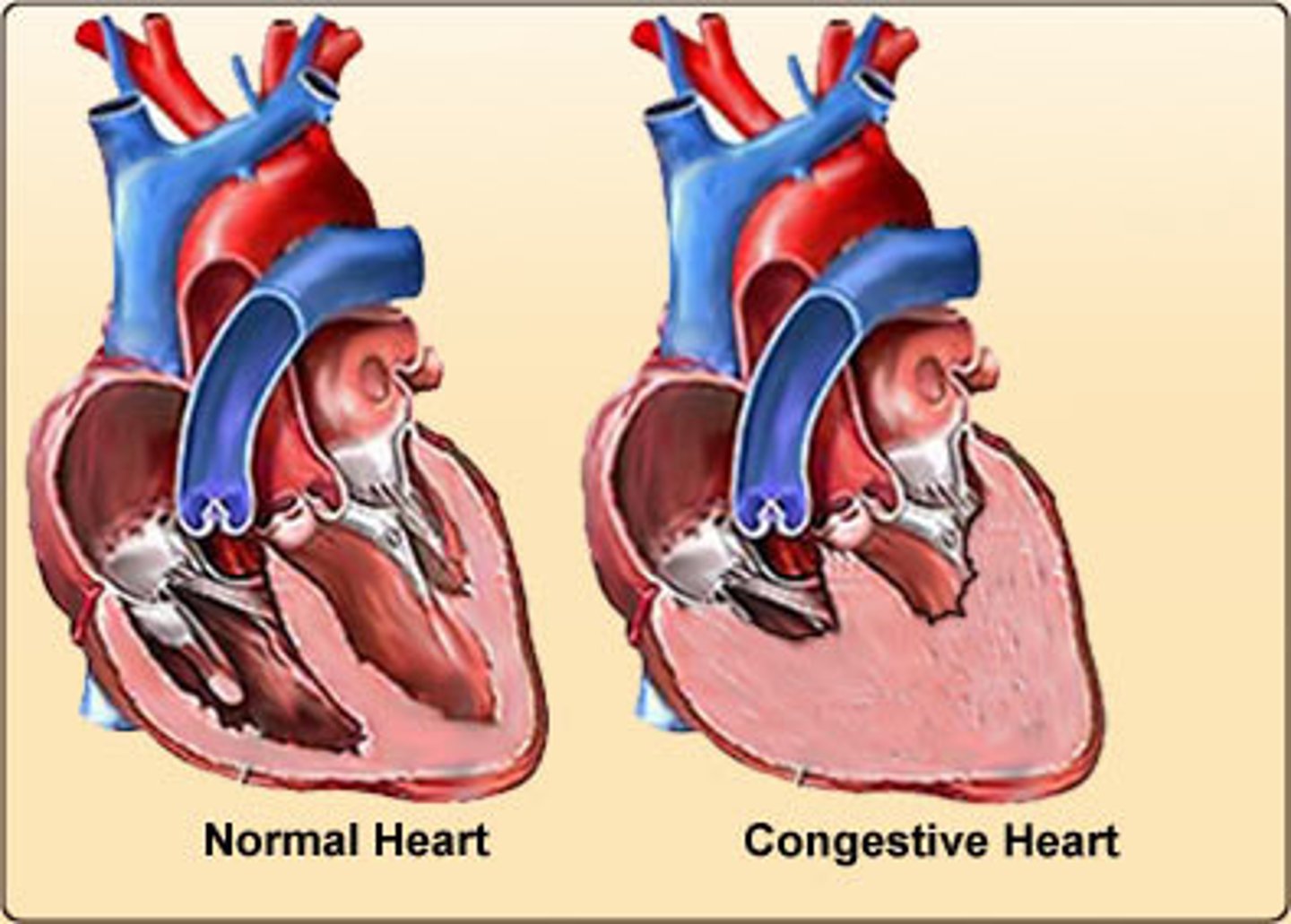
What is congestive heart failure?
-when the heart muscle is overworked due to stress, high blood pressure, arteriosclerosis, and fluids begin to collect in the body tissues, esp. the lungs
-heart is unable to pump effectively enough and becomes progressively weaker
-the fluid buildup causes SOB
no cure
There are 4 functional classifications of heart disease. At what stages can an OT be most beneficial in providing treatment and interventions?
stages 3 and 4

There are 4 functional classifications of heart disease. At what stages can an OT provide preventative programs?
stages 1 and 2

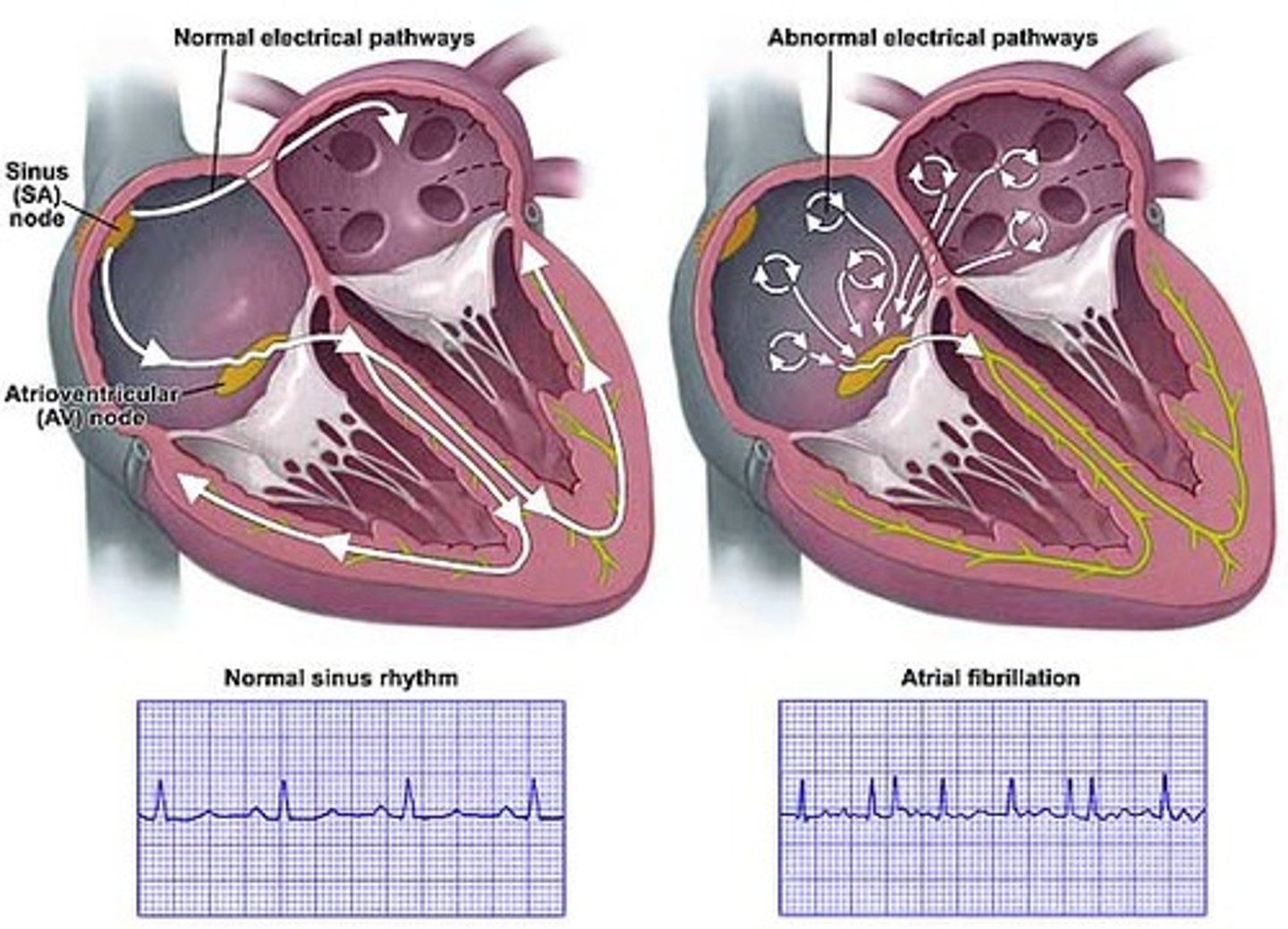
What is atrial fibrillation?
-valvular disease that results in irregular, ineffective heartbeat/contractions in both atria due to damage by disease or infection
-increases the risk of stroke
volume overload results when fluid accumulates in lungs causing SOB and this overload increases the risk for AFib
What are non-modifiable cardiac risk factors?
hereditary
male gender
age
What are modifiable cardiac risk factors?
high BP
cigarette smoking
cholesterol levels
inactive lifestyle
What are contributing cardiac risk factors?
diabetes
stress
obesity
T or F: There is a bidirectional link between depression and CAD.
true
ppl with CAD more likely to develop depression and ppl with depression are more likely to develop CAD
What surgical procedures can correct CAD?
percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA)
coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
cardiac ablation
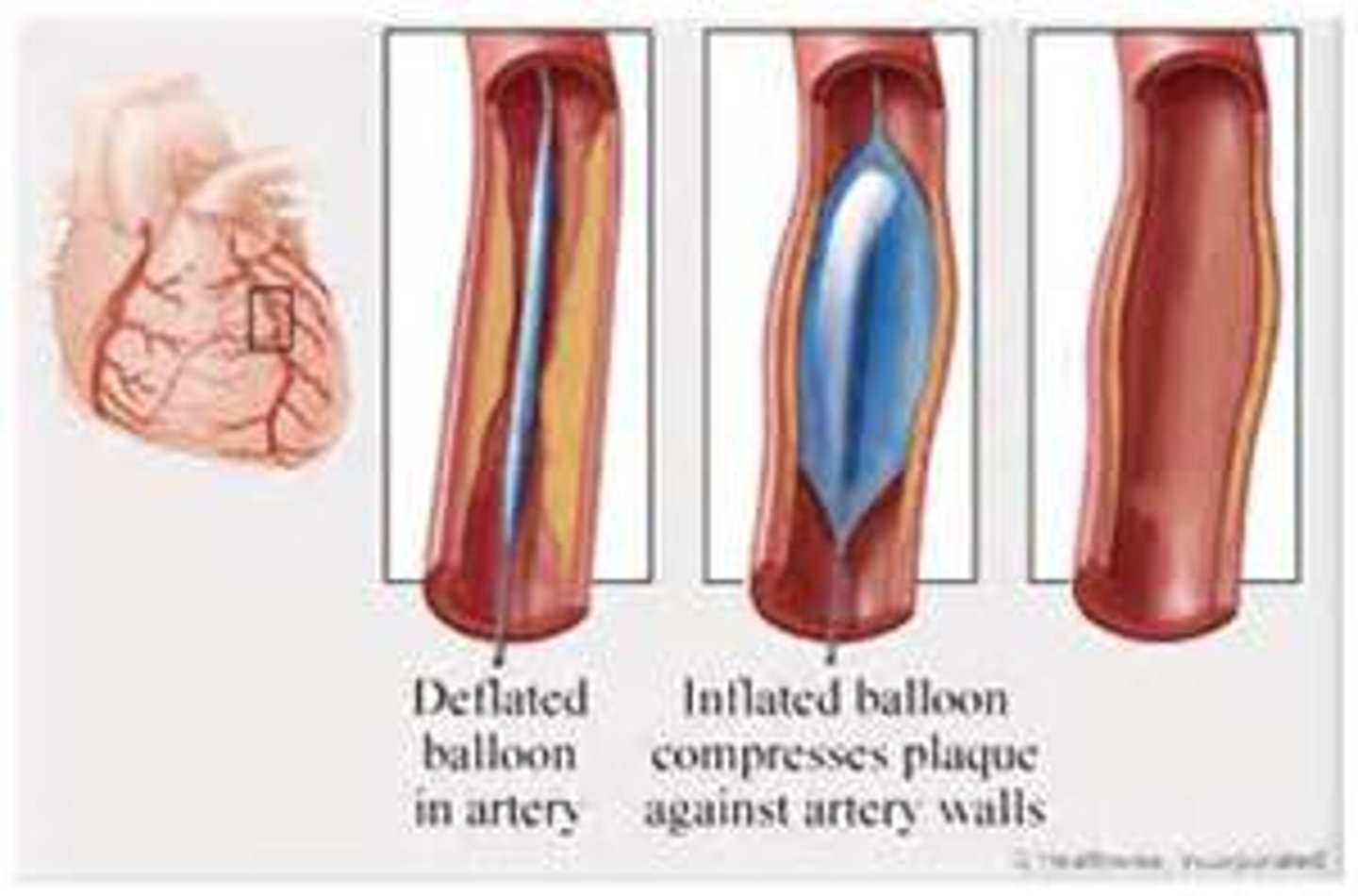
What is a percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA)?
-also known as balloon angioplasty (sx procedure)
-a catheter is inserted through femoral artery and guided to the coronary arteries
-balloon is inflated at lesion site to push plaque against arterial wall
-circulation improves after balloon deflates and catheter is removed
stent may be implanted to keep artery open
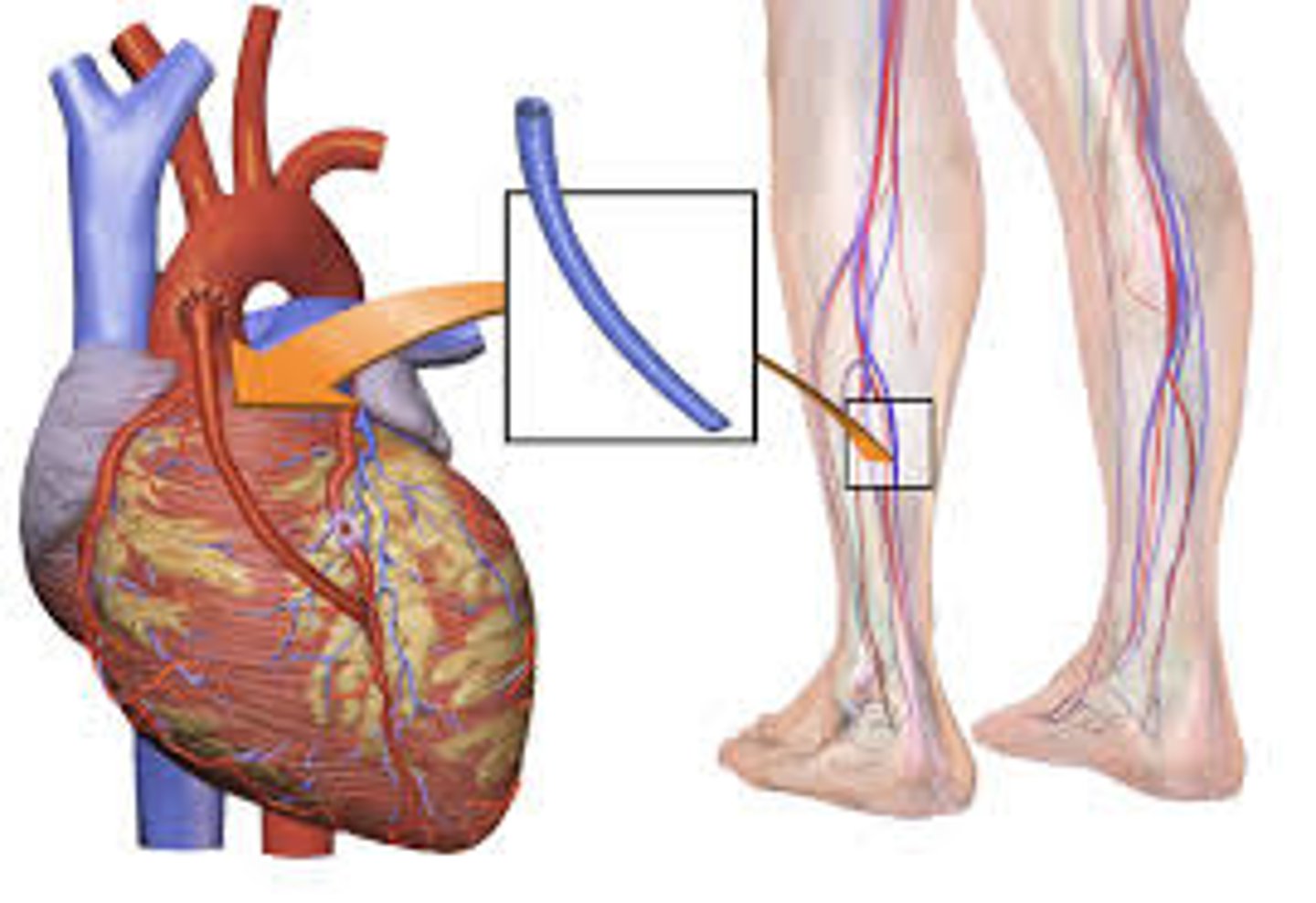
What is a coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)?
-diseased section of coronary arteries is bypassed with healthy blood vessels to improve coronary circulation (sx procedure)
-performed when lesion is too loose or if an artery reoccludes after PTCA
a sternotomy is performed to access the heart for a CABG (leads to sternal precautions post-sx)
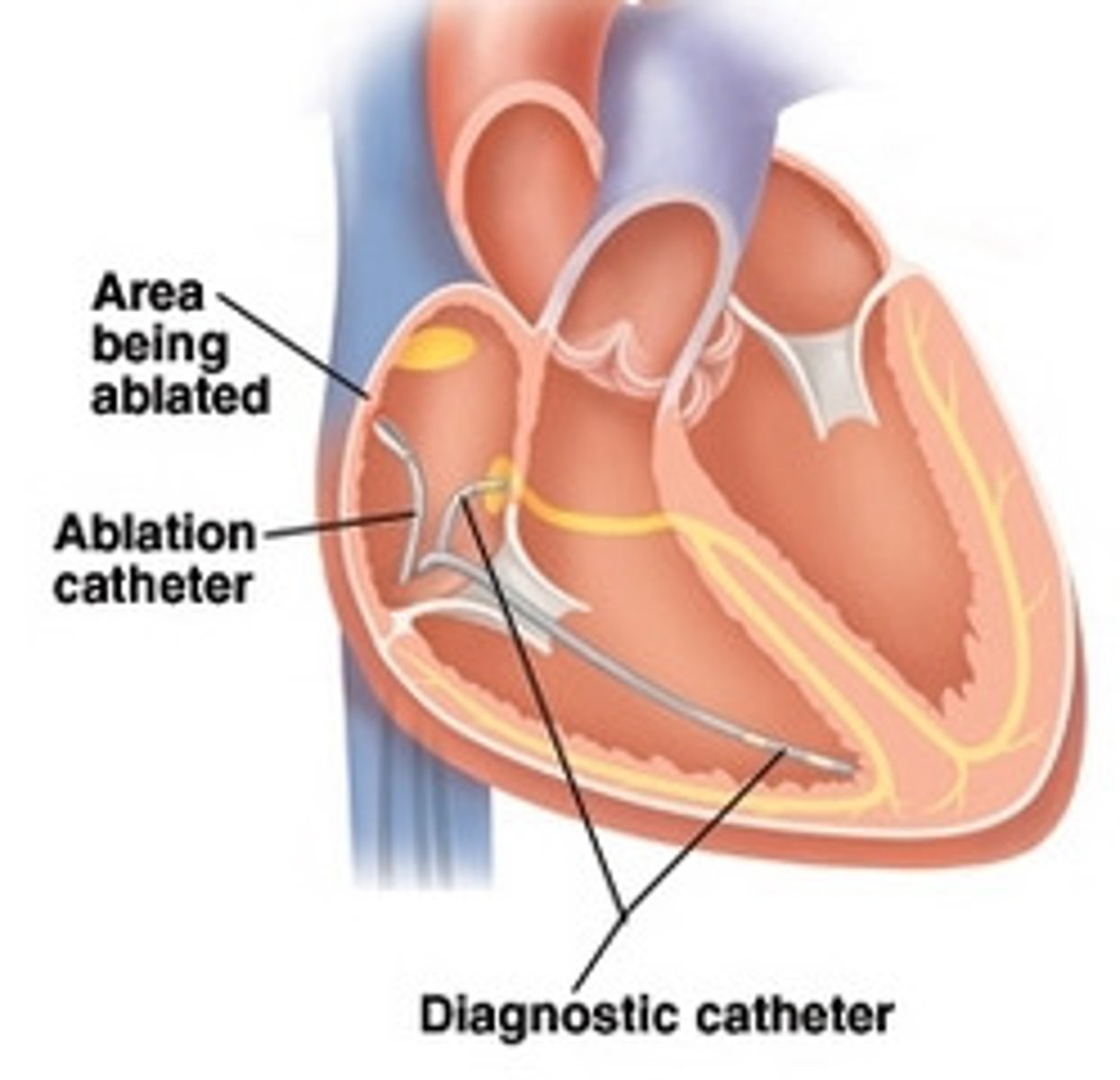
What is cardiac ablation?
-medical procedure that destroys all small areas of the heart that are emitting dangerous signals causing abnormal contractions
-small catheters are threaded through a vein to the heart
-the dysfunctional cardiac tissue is reached and an electrical impulse is sent to the site, destroying the abnormal tissue
When the heart's pumping ability has become too compromised by CHF or cardiomyopathy, a _____________ may be considered.
heart transplant or heart-lung transplant
Cardiac medications produce various side effects. Why is this important for an OT to know?
because different side effects can have an impact on rehab and performing occupations
ex: blood thinners – increased risk of bleeding (opt for electric razor rather than blade)
ex: diuretics – increased urination
Common psychosocial considerations in cardiac rehab include _________. How can OT help?
depression
anger
anxiety disorders
social isolation
OT can help by educating on importance of coping mechanisms, returning to activities, finding social support (groups, family)
How many days after an MI is the patient's medical condition usually stabilized?
1-3 days (the acute phase)
acute phase is followed by period of early mobilization
How many phases are there in cardiac rehab? What are they?
3 phases
phase 1 - inpatient cardiac rehab
phase 2 - outpatient cardiac rehab
phase 3 - community-based exercise programs
Phase 1 - inpatient cardiac rehab
-monitored low-level physical activity
-participation in self-care
-reinforcement of cardiac and post-sx precautions
-instruction in energy conservation and graded activity
-establishment of guidelines for appropriate activity levels at DC
-education on S&S of cardiac distress
What are the signs and symptoms of cardiac distress?
angina
dyspnea
orthopnea
nausea/emesis
diaphoresis
fatigue
orthostatic hypotension

What is dyspnea?
shortness of breath with activity or at rest
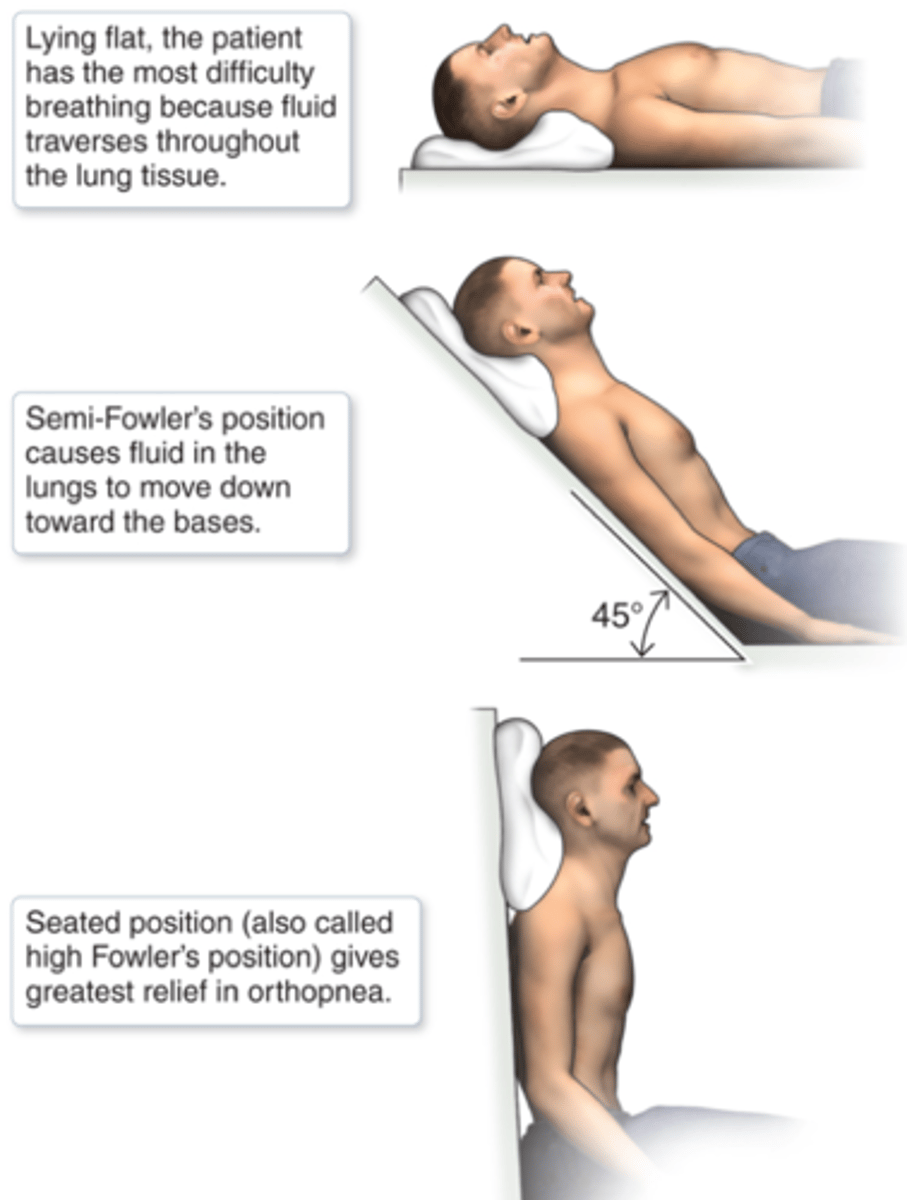
What is orthopnea?
difficulty breathing when supine
What is emesis?
vomiting
What is diaphoresis?
excessive sweating (cold, clammy)
Phase 2 - outpatient cardiac rehab
-usually begins at DC from inpatient cardiac rehab
-exercise intensity is advanced (and closely monitored)
-may be delivered in person's home initially to build tolerance for intervention in the clinic
-instruction in a sustainable program for optimal physical conditioning
Phase 3 - community-based exercise programs
-individualized recommendations for maintenance
-group fitness classes
What are sternal precautions?
precautions to prevent trauma to new graft sites, incisions, and sternum; generally last 8 weeks (vary amongst dr.'s and hospitals - controversial)
do not push or pull with arms when getting in/out of bed/chair
do not bring elbows above shoulders (keep shldr height)
avoid twisting and deep bending
hug a pillow when coughing or sneezing
no driving until cleared
report clicking or popping noises to surgeon
What vital signs do we monitor throughout activity?
HR
BP
O2Sat
arterial blood gas (ABG)
arterial pressure line
T or F: Heart rate should increase with physical activity.
true
OT's and patients should note whether HR is regular or irregular
A heart rate can be described as regular or irregular. How can an irregular heart rate be described?
1) regularly irregular - consistent irregular pattern
2) irregularly irregular - no pattern to the premature or skipped heart beat
T or F: When giving exercises to a client, the OT should always take a baseline of the client's heart rate to compare to throughout the exercise.
true
always check for irregularities or a drop in HR (HR should increase with exercise, not drop, but should also not exceed past 20 bpm of RHR)
Normal adult HR at rest
60-100 bpm
T or F: Physicians usually indicate treatment parameters for the HR and BP of patients in medical facilities. HR and BP will fluctuate in response to activity, and cardiac output is affected by both HR and BP.
true
What is rate pressure product?
-serves as an estimate of myocardial oxygen demand
-product of HR and systolic BP (RPP = HR × SBP)
-5 digit # but drop last 2 to report as 3 digit #
-during any activity, the RPP should rise at peak and return to baseline in recovery (after 5 to 10 minutes of rest)
ex: HR 100 × SBP 120 = 12,000 = RPP 120
Normal adult BP
≤ 120/80
Normal O2Sat range
92-100%
What do we do when O2Sat is less than 88% (<88%)?
What do we do when O2Sat is less than 84% (<84%) with COPD?
modify treatment
What is chronic lung disease?
umbrella term for chronic lung conditions such as
-sarcoidosis
-asthma
-COPD
-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
-cystic fibrosis
persons w/ these conditions may benefit from learning better ways to breathe and conserve their energy
What is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
chronic, progressive lung disease that includes two primary medical conditions: emphysema and bronchitis
-air sacs become damaged, lose their elasticity, and become clogged with mucus
-breathing takes more effort and therefore participation in ADL and IADL decreases
-damage is irreversible – NO CURE (modify approach)
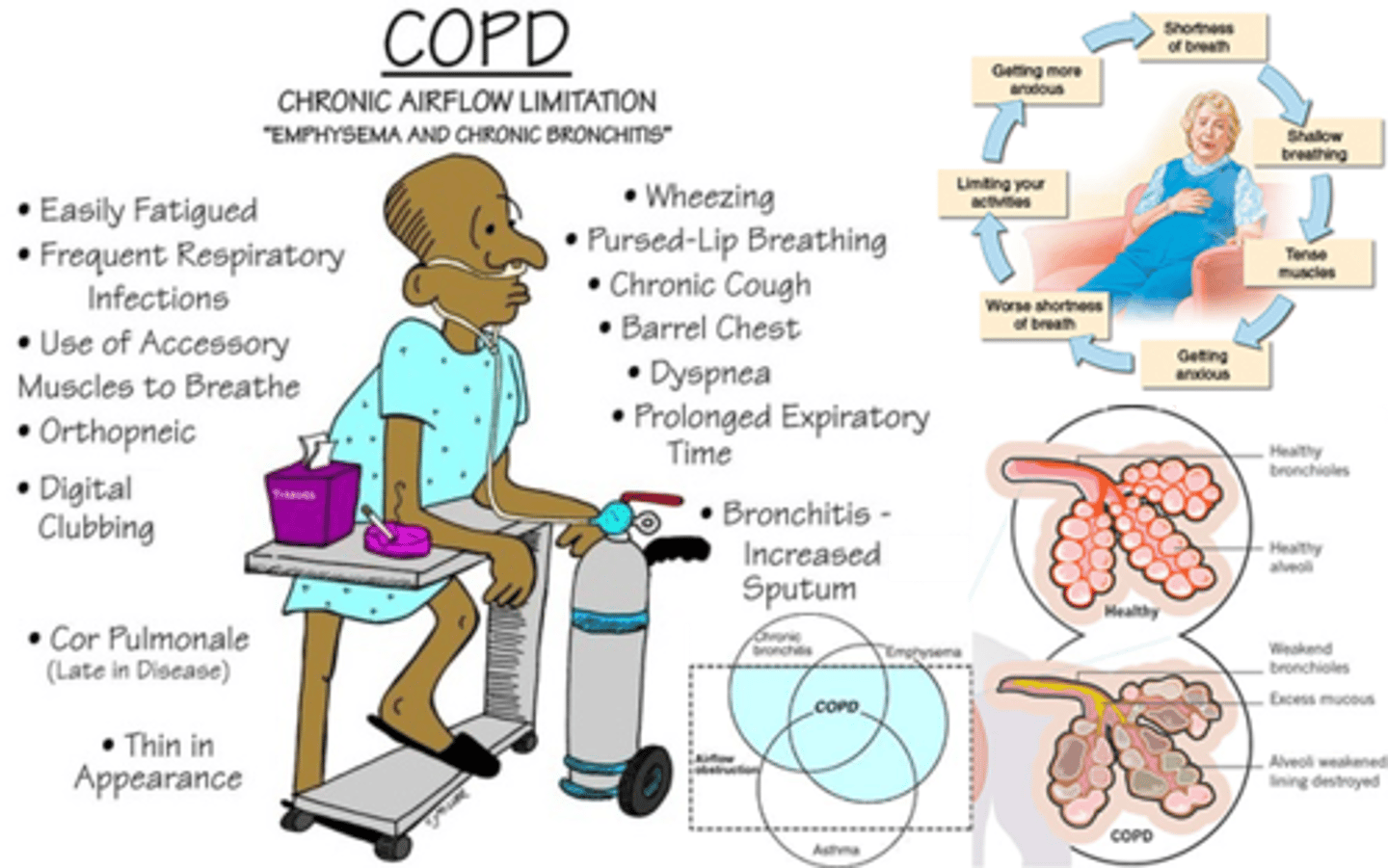
What is emphysema?
destruction of alveoli; a condition in which the air sacs of the lungs are damaged and enlarged, causing breathlessness
risk factors
-smoking, air pollutants, weed smoke, manufacture particles
What is bronchitis?
-inflammation of the bronchi leading to increased mucus production, cough, and airway obstruction
-experience SOB (dyspnea) on exertion and as disease progresses, dyspnea occurs at rest
-more prone to developing URI which worsens the disease
risk factors
-smoking
Pulmonary risk factors
cigarette smoking is the leading cause of COPD
air pollution
chemical exposure
dust
stress
overly vigorous work
How is COPD medically managed?
medications:
-anti-inflammatory agents (steroids)
-bronchodilators (albuterol - opens airways)
-expectorants (loosen and clear mucus)
-O2 therapy prescribed at specific flow rate
-mechanical ventilators (prescribed for acute exacerbation caused by flu, pneumonia, CHF)
-pulmonary rehab (dr, nurse, OT, PT, resp. therapist, psych)
Signs and symptoms of respiratory distress include ___________
difficulty breathing
extreme fatigue
non-productive cough
confusion
impaired judgement
cyanosis
The most severe form of shortness of breath (dyspnea) is __________
most severe form is shortness of breath even at rest
ex: unable to utter short phrases w/o gasping for air
ex: "SOB when washing face while standing at sink"
Respiratory rate
process by which O2 and CO2 are interchanged
breaths/1 min
described as normal, rapid, slow
What is the goal of pulmonary rehab?
stabilize or reverse the disease process and return the patient's function and participation in activity/occupation to the highest capacity
What are pulmonary rehab guidelines?
-both low and high intensity exercises are beneficial (higher intensity is better if tolerable)
-arm exercises should be unsupported (active motion with no outside assistance), against gravity and without resistance
-leg exercises should be included
-supplemental O2 is helpful during rehab exercises
apply these guidelines during ADL training
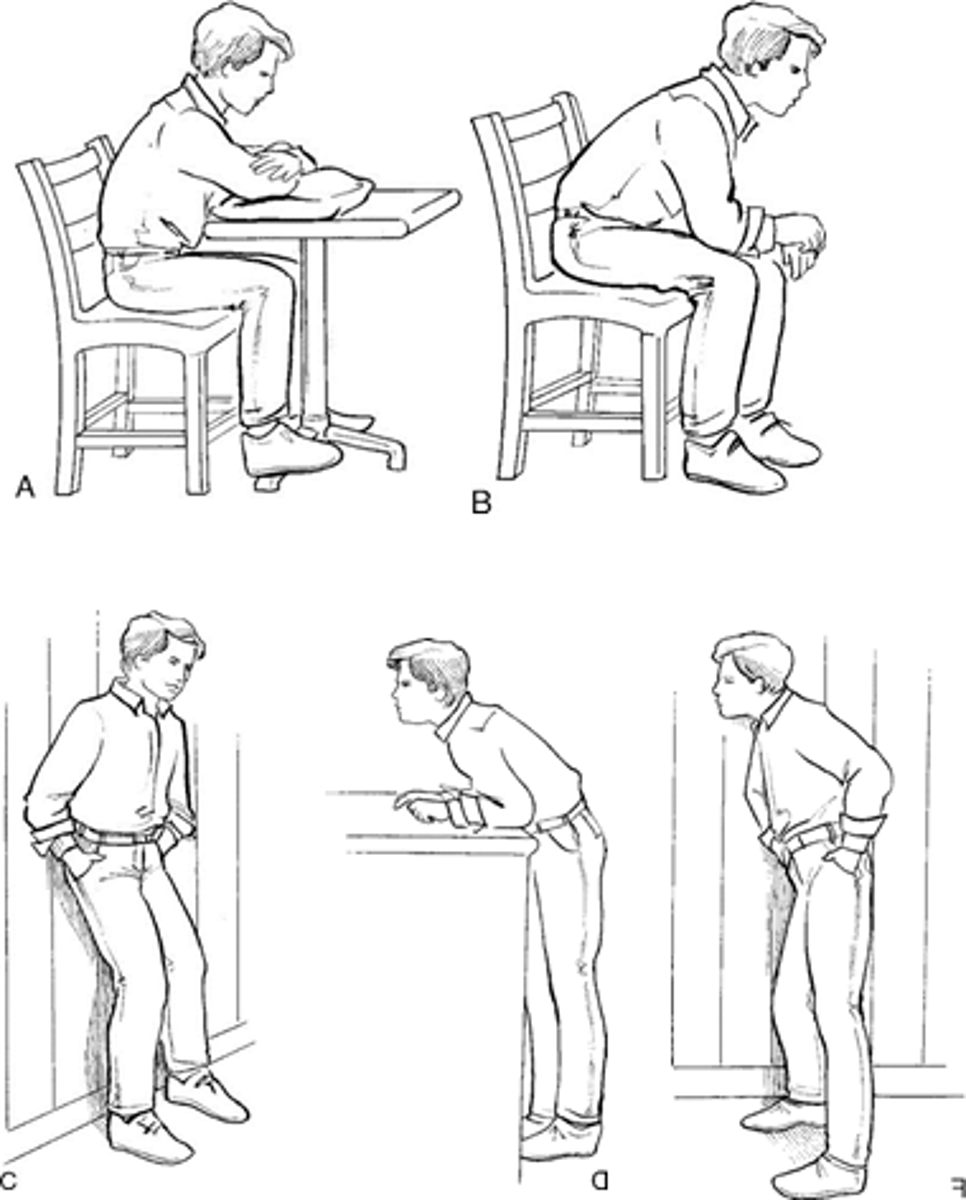
Dyspnea control postures
When sitting – the patient bends forward slightly at the waist while supporting the upper body by leaning the forearms on the table or thighs
When standing – leaning forward and propping the body on a counter or shopping cart may relieve the problem
Pursed-lip breathing (PLB)
-a technique of exhaling against pursed lips to prolong exhalation, preventing bronchiolar collapse and air trapping
-done to increase expiratory airway pressure, improve oxygenation of the blood, and help prevent early airway closure
some ppl with COPD instinctively adopt this technique, others are taught
1) relax neck and shoulders
2) inhale slowly through nose for count of 2
3) purse lips as if to whistle
4) exhale slowly through lips for a count of 4

When should pursed-lip breathing be used?
should be used when bending, lifting, and stair climbing
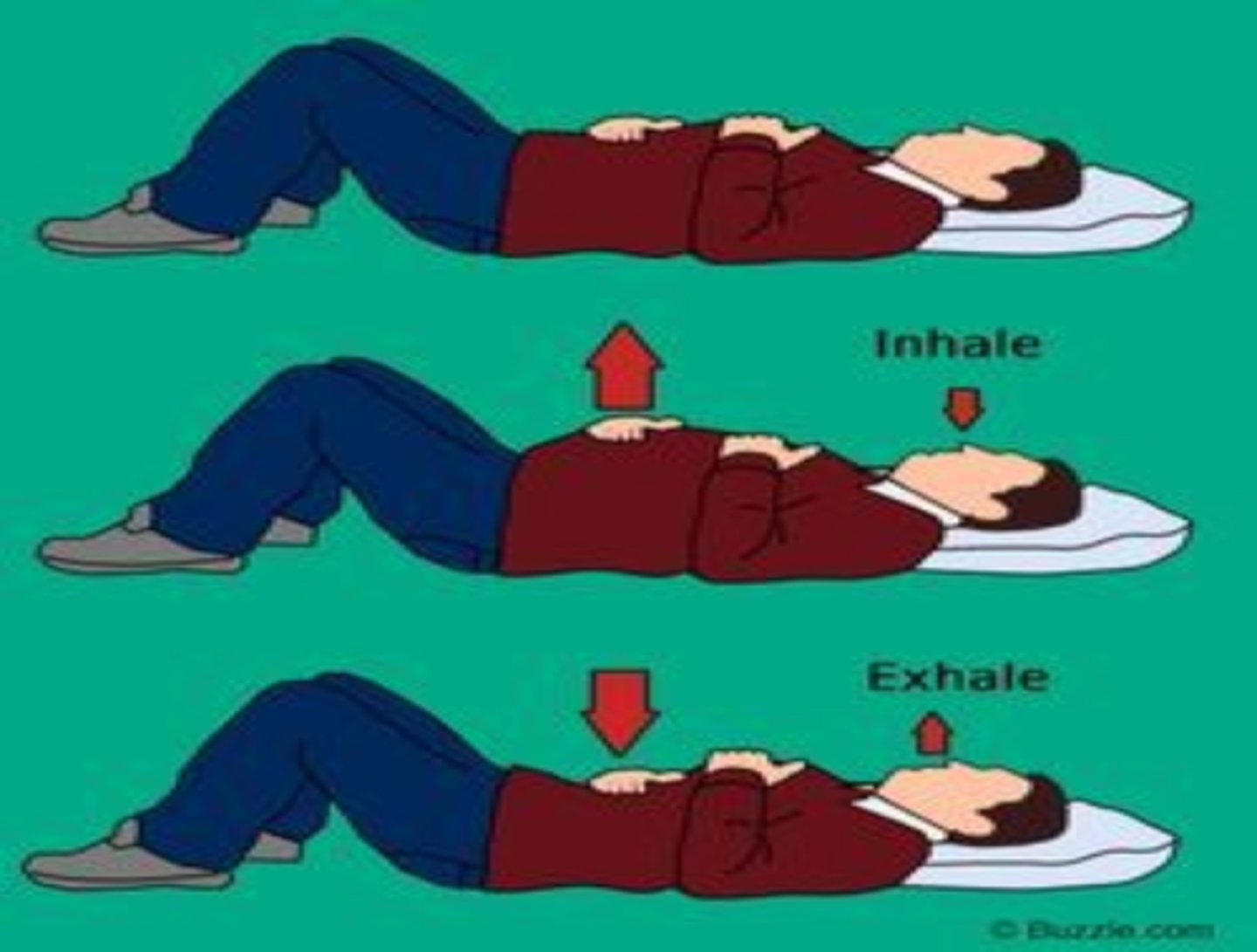
Diaphragmatic breathing
-breathing pattern which calls for increased use of diaphragm to improve chest volume
-breathing with the use of the diaphragm to achieve maximum inhalation and slow respiratory rate
1) have pt lie in supine
2) place a small book on base of sternum
3) instruct to inhale slowly and make the book rise
4) instruct to exhale through pursed lips and make the book come down again
Relaxation techniques
promotes relaxation using breathing techniques while thinking peaceful thoughts (passive relaxation) or while tensing and relaxing specific muscle groups (progressive relaxation)
helpful in decreasing anxiety and controlling SOB
1) When performing a clinical evaluation, clients with impairments in cardiovascular system will require monitoring of _______. 2) When should monitoring of these occur?
1) HR, RR, and S&S of respiratory distress (anxiety, SOB, confusion, difficulty comprehending, fatigue, dec. endurance, abnormal posture, reduced ability to move, etc.)
2) should occur during an assessment of tolerance to postural changes and during functional tasks
Heart rate - appropriate response to activity
increases with activity to no more than 20 bpm above resting HR
ex: RHR = 100 bpm ; anything surpassing 120 = bad!

Heart rate - inappropriate response to activity
HR more than 20 bpm above resting HR with activity
RHR ≥ 120
HR drops or does not rise with activity

Blood pressure - appropriate response to activity
SBP rises with activity

Blood pressure - inappropriate response to activity
SBP ≥ 220 mmHg
postural hypotension ( ≥ 10-20 drop in SBP)
decrease in SBP with activity

Signs and symptoms - appropriate response to activity
absence of adverse symptoms

Signs and symptoms - inappropriate response to activity
excessive SOB
angina
nausea
vomiting
excessive sweating
extreme fatigue (rate of perceived exertion ≥ 15)
cerebral/cognitive symptoms (confusion, etc.)

T or F: The energy costs of an activity or occupation and the factors that influence energy costs can further guide the clinician in the safe progression of activity or participation in occupation
true
Oxygen consumption suggests how hard the heart and lungs are working and is indicative of the amount of energy needed to complete a task. This is also known as ____________.
metabolic equivalent (MET)
as the activity level increases, the more O2 is needed to complete task
Resting quietly in bed requires the 1) _________ amount of O2 per kg of body weight and equates to 2) ______ basal MET.
1) lowest amount of O2
2) 1 basal MET
Why is the MET-level activity table beneficial to OTs?
helps guide OT in identifying effective progression of activity tolerance (based on the patient's response to activity or occupation, the prognosis, and goals)
progression of intensity increases as the MET level increases; duration of sustained physical activity must also be taken into consideration
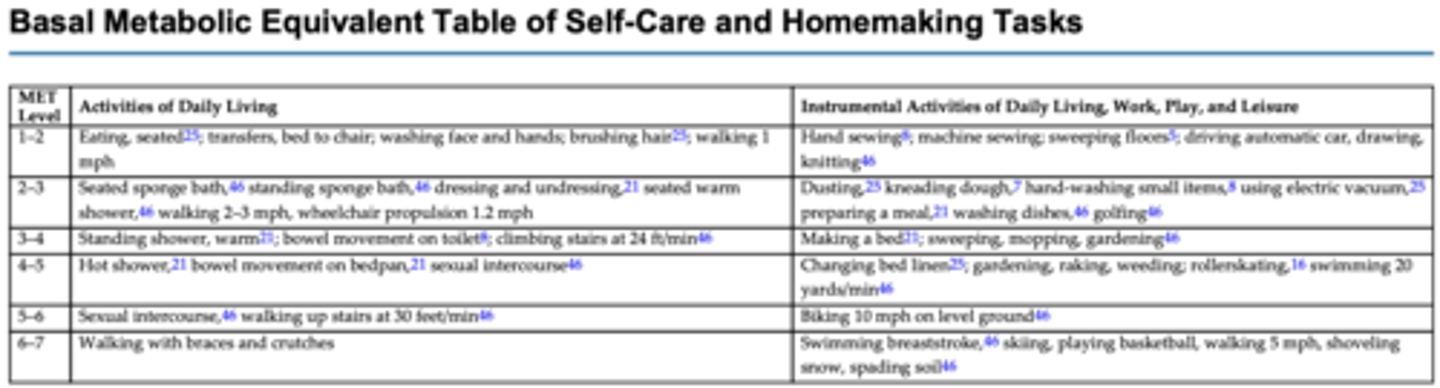
What would be the next intervention up from seated sponge bath? What is the MET level?
a standing sponge bath
2-3 METs
Dressing requires ______ METs, or roughly twice the amount of energy that lying in bed requires.
dressing requires 2.5 METs
At ______ METs, sexual activity is a grave concern for patients. However, patients are frequently able to return to sexual intercourse once they can climb up and down two flights of steps in 1 minute with appropriate cardiovascular responses
sexual activity = 5 METs
Which of the following activities fall within the MET Levels 1-2 for Activities of Daily Living (ADL)?
A) Running at 5 mph
B) Gardening and light housework
C) Transferring from bed to chair
D) Swimming and jogging
C) Transferring from bed to chair
Which of the following activities fall within the MET Levels 3-4 for Activities of Daily Living (ADL)?
A) Light housework, such as dusting or folding laundry
B) Running at 5 mph
C) Bowel movement on the toilet
D) Bowel movement on a bedpan
C) Bowel movement on the toilet
Which of the following activities fall within the MET Levels 3-4 for Instrumental Activities of Daily Living, Work, Play, and Leisure?
A) Sweeping, mopping
B) Using an electric vacuum
C) Washing dishes
D) Changing bed linen
A) Sweeping, mopping
What would be the next intervention up from a seated warm shower? What is the MET level?
next would be a standing warm shower (4-5 METs)
(seated warm shower = 2-3 METs)
Energy conservation principles
-decrease rate
-decrease resistance
-decrease use of large muscles
-decrease use of trunk musculature
-lowering one's arms
-decrease isometric work (straining) – contraindication
-UE activity is more demanding of than LE activity
-standing requires more energy than seated activity
-extremes of temp, high humidity, and pollution increase demand upon cardiopulmonary system
Energy conservation: time management
-high energy demanding tasks should be interspersed with lighter tasks
-rest breaks should be scheduled throughout the day (especially after meals)
ex: laying out next days clothes the night before to make mornings easier
Lifestyle modifications include
-guided programs of increased activity and participation in occupation
-stretching, strengthening, aerobic activity
-monitoring vitals and perceived exertion
-cool down
-safety issues related to clothing and environmental factors, and warning signs
-plan for resuming exercise (if skipped)
-emergency guidelines
meal prep activities focusing on nutrition
smoking cessation programs (altering habits to support cessation)
Patient and family education include focusing on _______
disease process
symptom management
risk factors
diet
exercise
energy conservation