IB Physics SL formula booklet
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
If: y = ± a b then: ∆y = + ∆a ∆b
unc. for a+ - b is uncertainty of end result y
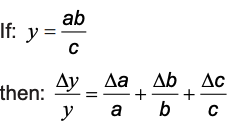
if y = ab/c
unc. for a / or x b, uncertainty is uncertainty over actual value
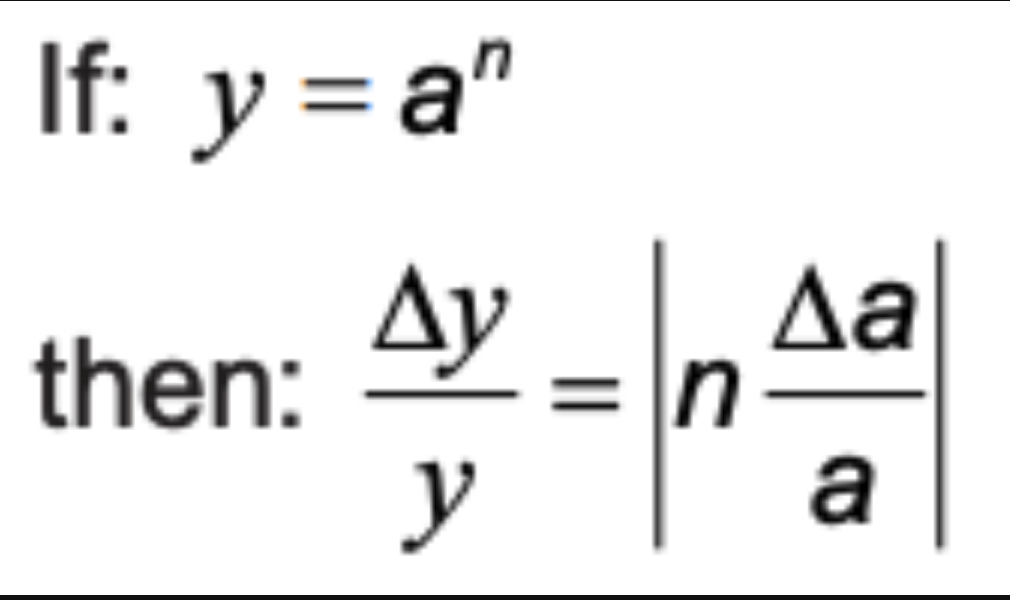
if y= a^n…
unc. for powers
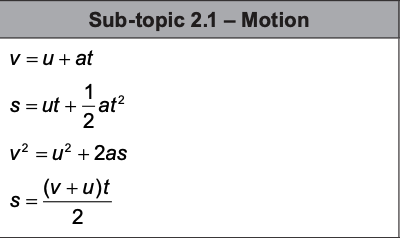
suvat
disp, initial velo, final velo, acc, time
F = ma
force is equal to mass times acceleration
Ff ≤ µsR
max fric force on static object is coefficient of stat fric times normal reaction force
Ff = µdR
max fric force on static object is coefficient of dynam fric times normal reaction force
W = F s cosθ
Work done along force direc = force times disp. times cos(θ)
Ek = ½ mv²
kinetic E = half mass velocity squared
Ep = ½ k del x²
potential E (elastic, in spring) = half spring constant times change in extension squared
∆Ep = m g ∆h
chnage in grav pot E = mass times gravity times change in height
power = Fv
power = force times velocity
efficiency = useful / total
efficiency = useful out or in / total out or in
p = m v
power = mass times velocity
F = ∆p / ∆t
force = del momentum over del time
KE = p² / 2m
kinetic E = momentum squared / 2 times mass
impulse = F ∆t = ∆p
impulse = avg force times del t = del momentum
Q = m c ∆T
heat = mass times spec heat capacity times del temp
Q = mL
heat = mass times latent heat
p = F / A
pressure = force / area
n = N / Na
num. moles = particle number / avogadro
pV = nRT
pressure Volume = num. particles times gas constant times temp
Ek = 3/2 kb T = 3/2 R/Na T
avg kinetic E = 3/2 boltzman const times temp = 3/2 gas constant / avogadro , times temp
T = 1/f
period = 1/freq
c = fλ
wave speed = frequency times wavelength
I prop A²
intensity proportional to amp squared
I prop x^-2
intensity proportional to dist. from source to the -2
I = Io cos² θ
intensity = initial intensity times cos²(θ)
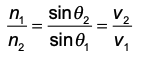
n1/n2 = sin thet / sin thet = v/v
snell’s law of refraction
s = λD/d
dist between spots on screen = wavelength times dist between splits on screen over distance between slits
Constructive interference: path difference = nλ
construc interf: path diff = num times wavelength
destructive interference: path difference = (n+ ½)λ
destruc interf: path diff = (num + 1/2) wavelength
I = del q / del t
current = del charge / del time
F = k (q1 q2 / r²)
elec force between points = coulomb const. (charge 1 times charge 2 over distance squared)
k = 1 / 4 pi ε0
coulomb const. = 1 over 4 pi permit. of free space
ΣV = 0 (loop)
sum pot. diff. = 0
ΣI = 0 (junction)
sum current = 0
V = I R
pot. diff. = current times resistance
P = V I
power = pot diff times current
R total = R1 +R2
total resistance = all resistors in series added together
ρ = R A / L
elec resistivity = resistance times cross section area / length
ε = I(R+r)
emf = current(resistance times internal resistance which is of battery of cell)
F = q v B sinθ
F = B I L sinθ
v = w r
lin speed = ang. speed times radius
a = v²/r = 4 pi² r / T² = w² r
centrip acc = lin speed² / radius = 4 pi² rad. / period² = ang.² times rad.
F = mv² / r = mw²r
centrip. force = mass times lin.velo² / rad. = mass times ang.velo² times rad.
F = G (Mm/r²)
grav force = newton’s const. times (mass of grav source times mass of experience / radius or dist)
g = F / m
grav force per unit mass experienced = force / mass
g = G (M / r²)
grav strength = newton’s const. (source mass / radius²)
E = h f
energy = planck times freq
λ = hc / E
wavelength = planck times light.speed / energy
del E = del mc²
del energy = del mass times light.speed²
power = energy / time
power = energy / time
power = ½ A ρ v³
power = half area swept by wind turbine times air or fuel density times air velocity³
P = e σ AT4
power = black body emmissivity times stefan boltzman times surface area times temp4
λmax (metres) = 2.9 × 10-3 / T(kelvin)
max wavelength = number / temp in kelvin
I = power / A
intensity = power / surface area
E = kq/r² = F/q
Elec field = tmap