25: Plant transport systems (xylem)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
how do animal cells prevent rupturing by over-influx of ions?
possess a semi-permeable membrane and continually excrete solute ions
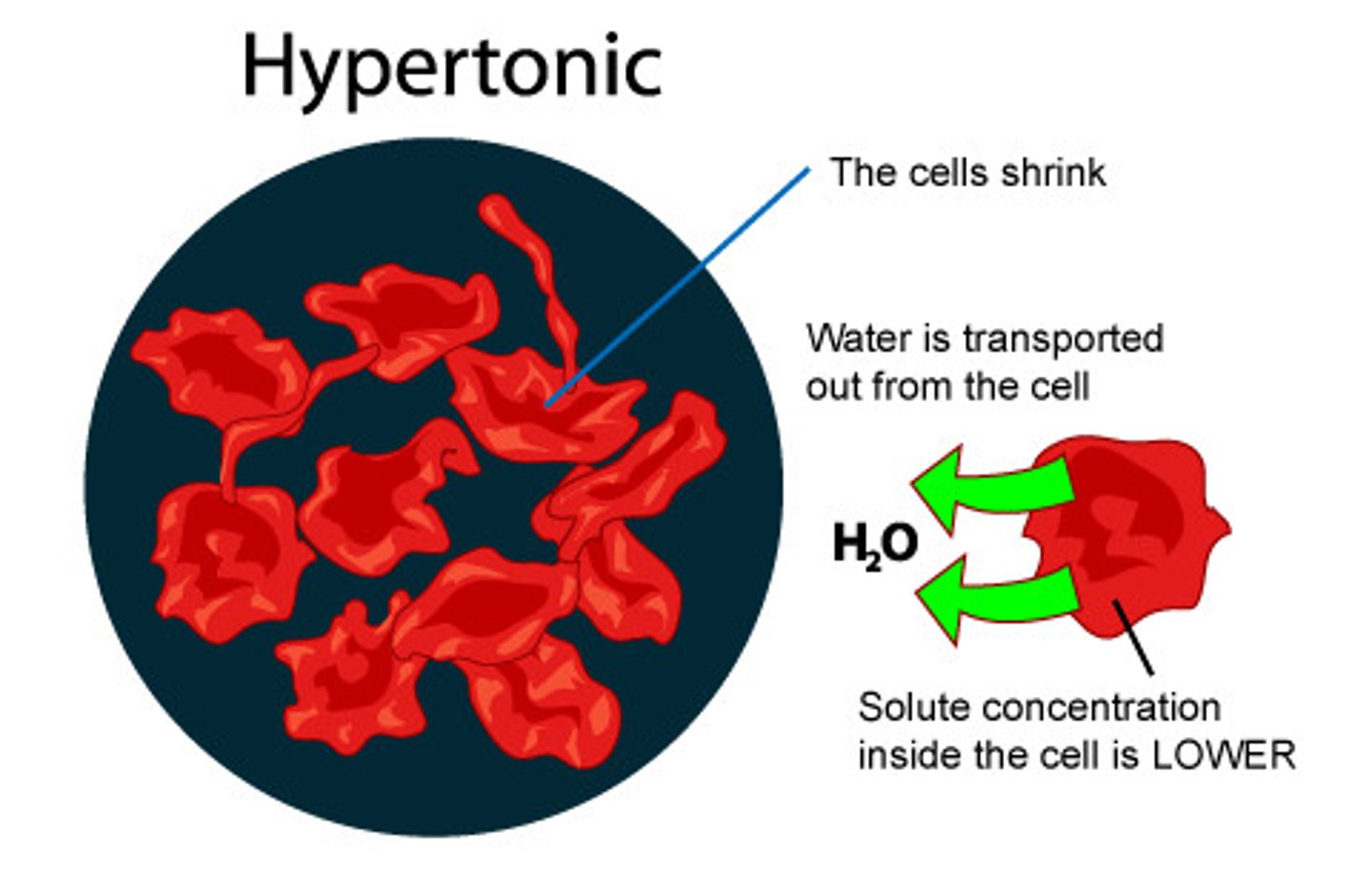
hypertonic solution
solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell, cell loses water and shrink
isotonic solution
solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell, water moves in and out

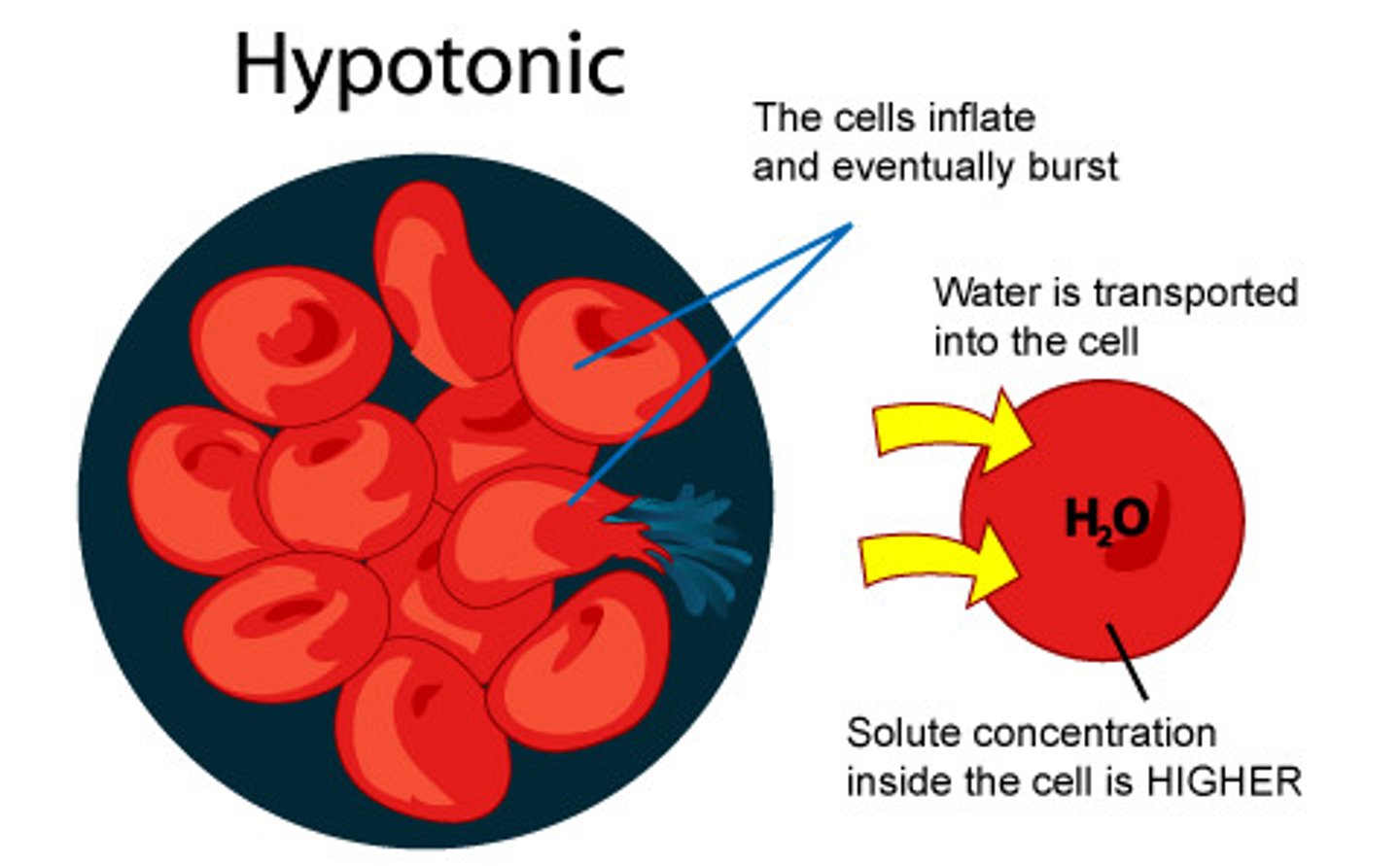
hypotonic solution
solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water and burst
turgor pressure
hydrostatic pressure that develops within the plant
average pressure inside a plant cell
1-2 MPa
Public Enemy No.1 (plant)
Japanese Knotweed
Japanese knotweed can extend up to ___m deep and __m in all directions, at a rate of __cm per day
Japanese knotweed can extend up to _3m deep and 7m in all directions, at a rate of 10cm per day
3 multiple choice options
leaves can be ___% air by volume
80-90%
symplast
interconnecting cytoplasm via plasmodesmata
apoplast
interconnecting cell walls
plant transport pathways
- symplast
- apoplast
- gas-filled intercellular spaces
apoplast is a ______ resistance pathway
low
symplast is a _____ resistance pathway
high
chemical potential of water
movement of water molecules in response to a gradient in free energy