Tests 1-3 Descriptive Astronomy
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
About how much does one teaspoon of a white dwarf weigh?
A bus
Which element, when undergoing thermos-nuclear fusion, absorbs energy rather tahn producing it thus leading to a Super nova?
Iron
Which type of star is the smallest in physical size?
White Dwarfs
True or false: there are enough wandering black holes in the galaxy that our solar system could one day be swallowed up by a collision with one?
False
What are globular clusters?
Spherical clusters of old stars that live in the halo of the Milky Way
What class of black hole resides at the center of our milky way?
a supermassive blackhole
True or false: if you replaced the Sun with a black hole, it would NOT gravitationally impact the planets?
True
About where does the Sun reside within our Milky way?
in the disk of the galaxy, about 2/3 of the way from the galactic center
About how wide is the Milky way?
100 light years across
What type of galaxy is the Milky Way? (based on most recent results?)
a barred spiral galaxy
What object would be closest to representing the overall shape of the Milky way?
A frisbee
Where are the youngest stars found in the Milky way?
in the spiral arms of the disk in the galaxy
How big (in radius) was the white dwarf discussed in the video quiz?
About the size of Earth
About how big is a neutron star?
the size of a city
Which type of star is the largest in physical size?
Red Supergiants
About how many stars do we think compose our milky way?
over 300 billion
Nebula are clouds of what?
gas and dust
What is a pulsar?
A neutron star with a strong magnetic field that is rotating rapidly and giving off radio pulses
What astrophysical phenomenon is responsible for producing some of the heaviest elements in the Universe? Such as gold and silver?
Supernova
The eventual final fate of the Sun is a?
white dwarf
One day, the Sun will be at the center of a?
planetary nebulae
How many red dwarf (M) stars are visible to the naked eye?
None
If we are observing a group of stars in a stellar cluster, what two properties can we assume are the same among them all?
Their age and distance
How do stars produce energy in their cores?
thermo-nuclear fusion reactions
Which element is not produced in a supernova explosion?
hydrogen
About how long is the total lifetime of our sun?
10 billion years
What would you see if you hover just outside of the event horizon of a black hole?
the back of your head
black holes are?
an object that can form from a massive star with such strong gravity that even light cannot escape
Which of these is not a method of heat flow?
magnetic flow
What are the two most common elements found in stars?
hydrogen and helium
What type of nebula is the location in which stars are born?
an emission nebula
What are the basic anatomical components of a neutron star?
an atmosphere, crust and core
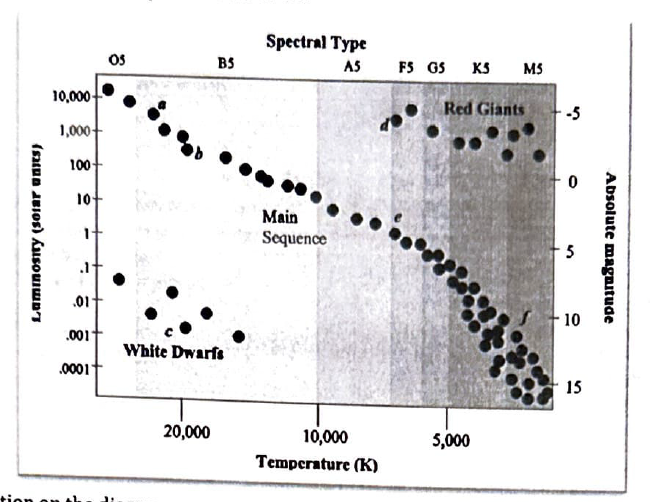
Which location on the diagram represents stars with the largest radius?
D
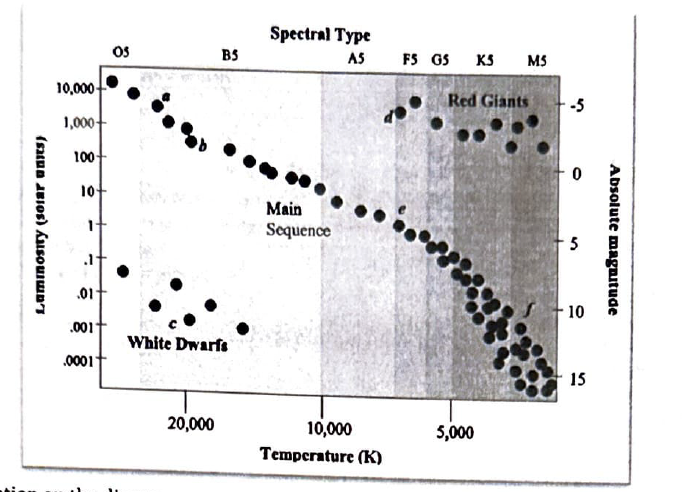
Which location on the diagram represents blue giants (O) stars?
A

Which location on the diagram shows the stars which are the most common in our galaxy?
F
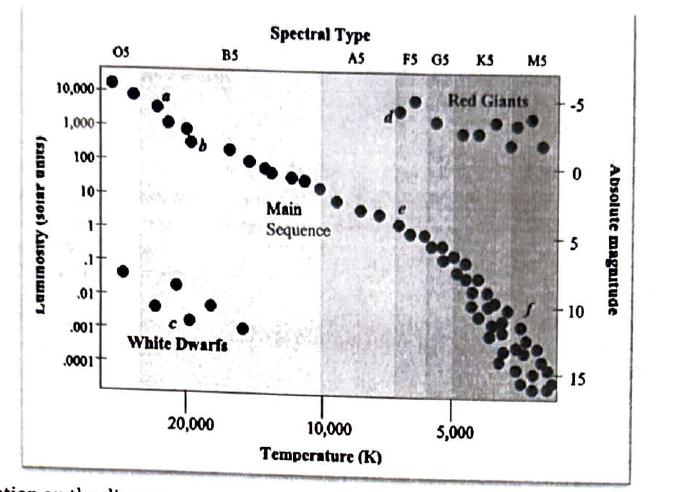
Which letter on the main sequence represents those stars which will spend the longest amount of time there?
F
Which of these is not one of the steps of star/planet formation?
these are all the steps of star/planet formation
If there are two stars, A and B, which are at the same distance and star A is twice as big as star B. Which star is more luminous?
Star A
Which of the following sequence of letters represents the order of stellar spectral types from most populous star to least populous star?
MKGFABO
Which of the following sequence of letters represents the order of stellar spectral types from hottest stars to the coolest star?
OBAFGKM
What is the most common shape of a star?
sphere
What are the different types of binary systems?
visual, spectroscopic and eclipsing
About how old is the disk of the milky way?
9 billion years old
What is the name of the mysterious material that exists in the outer parts of galaxies and in large galaxy clusters but cannot be seen?
dark matter
What property of a star most determines how long it will live and how it will die?
its mass
What is the primary source of evidence did we use to confirm the supermassive balck hold at the center of the Milky Way?
The orbits of a collection of stars and Kepler’s laws to estimate the mass
the scenario in which a star is experiencing a balance between the energy being produced in the core wanting to make the star expand and gravity wanting to make the star collapse is called____
hydrostatic equilibrium
What are the three physical properties of black hole?
mass, spin, and charge
If you place a pizza under a heat lamp, what form of energy/heat transport is the dominate mechanism involved in keeping the pizzas warm?
Radiation
What is an astronomical unit?
The average distance from Earth to the Sun
What is a planet?
A spherical object sometimes solid which is usually found orbiting a star
What is a star?
A ball of hot plasma undergoing thermonuclear fusion
What is a galaxy?
An island or collection of stars sometimes in the shape of a spiral
What is a nebula?
a cloud og gas and dust where stars sometimes form
What do Kepler’s laws desribe?
how planets move around the galaxy
Which of these is the primary function of a telescope?
to improve details and to make faint objects more visible
What is a light year?
How far light travels in a year
How big is the current biggest optical telescopes in the world?
10 yards in diameter
What physical property of a telescope determines its resolution?
the diameter of the primary lense and the wavelength of the light being collected
Which planet in our solar system is the most similar in size to earth?
Venus
If we flew at the speed of light, how long would it take to reach Proxima Centauri?
4.2 years
The local neighborhood of closest galaxies to us is called the
the local group
which of these objects is the largest?
a galaxy
What is closest to the Earth?
the Sun
Which of these represents light waves in order of increasing energy (from least to greatest?)
radio waves, microwaves, infrared light, optical light, UV, X-rays, Gamma
Which of the following has the shortest wavelength
an x-ray
True or False: Radio waves travel at the same speed as light waves
True
If a star is moving away from you, in what direction will its absorption lines move?
to redder wavelengths
What does an electron do to produce an absorption line spectrum?
absorb a photon and go from a lower energy state to a higher energy state
What happens to the lines in the spectrum of a star that is moving towards us?
they shift towards the blue part
In general, what kind of telescope is needed to observe the Universe at radio wavelengths?
a larger telescope than what we would use at optical wavelengths
Which of these orbiting objects are dictated by gravity?
an astroid orbiting another astroid, a star orbiting a black hole, a planet orbiting a star, and a galaxy orbiting a galaxy
What is another property of a star which can be used to determine its surface temperature besides the spectrum?
the color
WHat is the closest star to earth after the sun?
Proxima Centauri
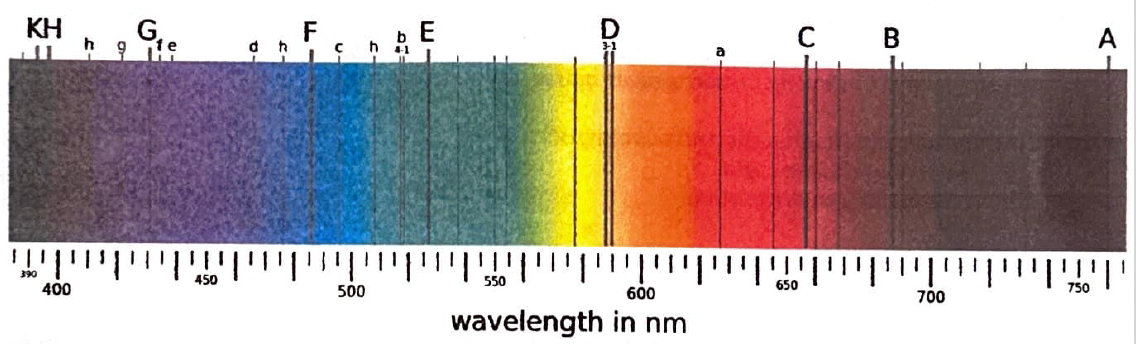
What type of spectrum is shown above?
absorption lines
What part of the atom is most responsible for hte pattern of absorption lines seen in stellar spectra?
electrons
What type of spectra do humans produce?
Emission
True or false: you have the same weight on the Moon as you do on Earth?
False!
Which is not a reason to send a telescope into orbit around the earth?
its cheaper
Which of these represents light waves in order of shortest to longest?
gamma, x-rays, uv, optical, infrared, microwaves, radio
Which of these lists the two main types of ground-based telescopes?
reflective and refractive
What is the main reason that radio telescopes need to have a larger diameter than optical telescopes?
they need to filter out optical light
What is an astronomer’s definition of the term “seeing”?
It is the blurriness of an object seen in a telescope due to turbulence in the Earth’s atmosphere
True or false: the fastest that anything can travel is the speed of light?
True!
Why are most ground based telescopes at the tops of mountains?
to get away from light pollutions

What is the object?
gravitational lensing
At which wavelength of light must a telescope be placed in space to collect images because their photons do not reach earth’s surface?
x-rays
True or false: All of the planets in the solar system could, if lined up, fit between the Earth and the Moon?
True
Why do galaxies collide but stars do not?
Because the distance between galaxies is smaller compared to their sizes (compared to the same factors in stars)
In the scale of the solar system video, what did Mark Rober use to represent the Sun?
a soccer ball
If you observe the emission line spectrum of a comet, and the lines are shifted to the blue wavelengths, waht can you determine form that observation?
The comet is moving towards earth
What type of spectrum does neon produce?
continuous spectrum
Which astronomical object produces the same type of emission as neon?
a hot cloud of gas like a nebula
What is an interferometer?
a collection of multiple telescopes which mimics one large telescope

Which constellation is this?
Orion

Which of these stars in this image have the coolest surface temp?
A
What causes the star/sun/planets/moon to rise and set everyday?
the rotation of Earth
If you are standing at the geographical north pole, what is the motion of the stars on any given night?
Some stars circle the south pole while other rise and set
The change in position the Sun makes across the sky ober the course oa=f a year is cause by
earth’s revolution
why do we have seasons on earth?
As the Earth goes around the sun, its axis remains pointed towards polarius (23.5 degrees)