Lacrimal System Disorders III- lacrimal duct
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What are causes of watery eyes?
> Hypersecretion → excessive secretion of tears
Inadequate drainage
What are the causes of hypersecretion?
primary (rare)
central hyper lacrimation (crying)
secondary to anterior segment conditions
- Allergic/infective/irritative conjunctivitis
- Trichiasis , distichiasis
- Corneal disease
what are the causes of inadequate drainage?
Malposition of lids
Lacrimal pump failure
Nasolacrimal duct obstruction:
—> congenital + acquired
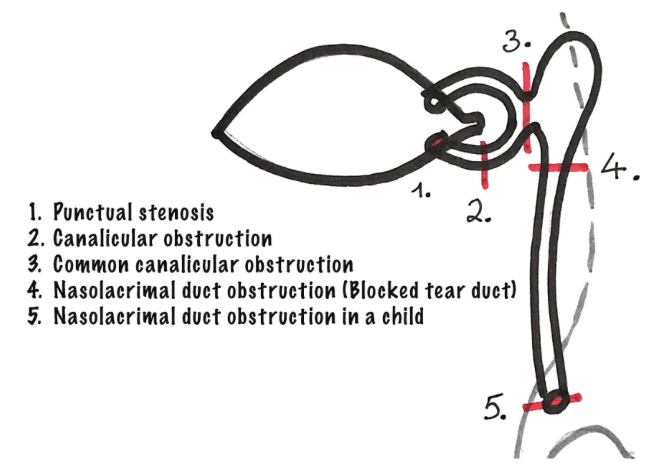
What are the 5 Drainage obstructions?
1) Punctual Stenosis
2) Canalicular obstruction → inferior or superior
3) Common canalicular obstruction
4) Nasolacrimal duct obstruction
5) Congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction
What is punctual stenosis + what are the symptoms?
narrowing of puncta → can be age-related
Symptoms:
Epiphora
Irritation
Blurred vision → downgaze
What is the Management of punctual stenosis?
saline syringing
do probing at same time to remove blockage
What is the secondary Care of Punctual stenosis?
Lacrimal syringing +probing
canalicular curettage → incision
Punctual dilation (stenosis) → same time as syringing + probing
surgery (DCR, Lester-Jones tube)
What is Canaliculitis (caused by canalicular obstruction)?
infection/inflammtion of canaliculi
What are the symptoms of Canalicular obstruction?
epiphora
chronic + refractory mucopurulent conjucntivitis
peri canalicular redness + oedema
mucopurulent discharge on pressure over canaliculus
‘pouting’ punctum
no lacrimal sac involvement → dacryocystitis
What is the treatment of Canaliculitis?
topical antibiotic
canaliculotomy usually required → incision to remove blockages
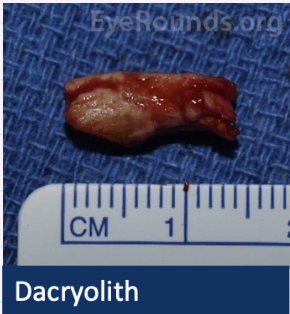
What are Dacryoliths?
Lacrimal stones → solid material
concretion of material in any part of lacrimal system
unclear pathogenesis
present in late adulthood
epiphora
recurrent attacks of acute dacryocystitis + lacrimal sac distension
what is the treatment for dacryoliths?
surgery
What is the Aetiology for Nasolacrimal duct obstruction?
idiopathic → no known cause
Age-related stenosis
secondary causes:
- Injury/trauma
- systemic inflammatory conditions
- Eye drops
- Cancer treatment
Infection:
> dacryocystitis
> Canaliculitis
Tumour of lacrimal sac or canaliculi → rare
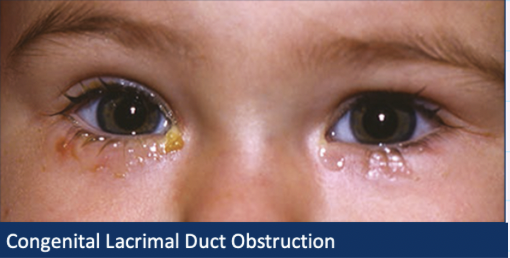
What is the Aetiology for congenital obstruction?
persistent membrane at opening of nasolacrimal duct (uni or bilateral)
common ~20% of babies
What are the signs of congenital obstruction?
Epiphora + mucous dsicharge
Mucopurulent discharge if infected
Pressure over lacrimal sac may cause mucous reflex
What are the differential diagnosis of congenital obstruction?
Congenital glaucoma
Punctual atresia (congenital)→ absence or narrowing of puncta
What is the management of congenital obstruction ?
Reassure → 95% resolve by 1yr
parent massage 2x day
clean lids
Treat infections
Probe > 12months
What is Dacryocystitis?
infection/ inflammation of lacrimal sac
usually secondary to nasolacrimal duct obstruction
acute or chronic
What are the signs of Chronic Dacryocystitis?
Lacrimal sac mucocele (fluid filled)
± chronic /recurrent unilateral conjunctivitis
Mucocele usually evident → painless swelling at inner canthus
mucopurulent canalicular reflex → when you press pus comes out of puncta
What is the treatment for Chronic Dacryocystitis?
> optometric management:
warm compress
refer routinely if symptoms persist or recur
What is acute Dacryocystitis + when is it most common?
infection of lacrimal sac
commonest in infants + post menopausal women
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Acute Dacryocystitis?
sudden onset
epiphora
painful, red, tender swelling over lacrimal sac
may discharge to skin surface
fever
What is the treatment for Acute Dacryocystitis?
emergency or urgent referral
antibiotics
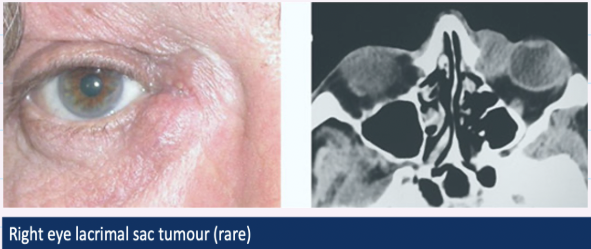
Lacrimal sac tumours
rare
Painless swelling
Punctual reflex of pus + blood
image: swelling at inner corner of eye biopsy, revealing a rare tumour of lacrimal sac → vast majority of swelling in this area due to being expansions of lacrimal sac