cell movement
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
cell motility
move cell or organism thru environment
movement of environment past or thru cell
move components in cell
contractility
describe shortening of muscle cells, is a specialized form of motility
_______involved in ATP-dependent transport toward the plus ends (away from the centrosome).
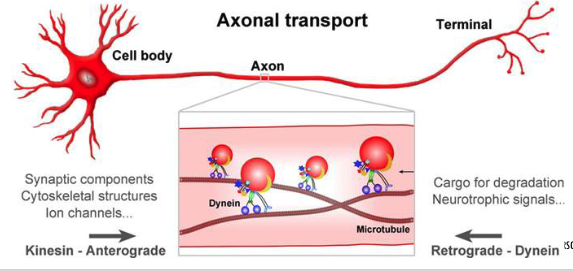
anterograde axonal transport
_________ associate with a protein complex called dynactin, which helps link dynein to cargo2.
cytoplasmic dynein
________ activate microtubule sliding in cilia/flagella2.
Dyneins
basal body looks like a centriole, with ________________ structure around the circumference
nine sets of triplets (three MTs)
Each outer doublet of the axoneme consists of one complete MT (the A tubule) and one _____ MT (the B tubule)
incomplete
At regular intervals, _______ project inward toward the central pair
radial spokes
•
In intraflagellar transport (IFT), ________ motor proteins move material to the tips of the flagella
plus-end-directed
In intraflagellar transport (IFT), ______ brings material back toward the base
dynein
Cell motility and intracellular movements are driven by motor
proteins, which couple _____ hydrolysis to movements.
ATP
_________ are important for shaping and transport of endomembrane system, and for intraflagellar transport
Microtubule (MT) motors
Kinesins move toward the ________ of MTs. There are many families of kinesins, which can travel great distances along MTs
plus ends
Dyneins move toward the___________. There are relatively few
dyneins, which can be (1) cytoplasmic or (2) axonemal.
minus ends
Cytoplasmic dyneins carry their cargo through the adapter called
the ____________
dynactin complex.
_______ ________ mediate the bending of cilia and eukaryotic
flagella.
Axonemal dyneins
Cilia and flagella consist of an axoneme connected to a basal body. ___________within the axoneme leads to bending of cilia and
flagella
Doublet sliding
Microfilament-based motility
Example: muscle contraction
Microtubules (MTs) and microfilaments (MFs)
provide a scaffold for motor proteins that
produce motion at the molecular level
MOLECULAR MOTORS
couple ATP hydrolysis to changes in
shape and attachment of the motor protein
They undergo cycles of ATP hydrolysis, ADP
release, and acquisition of new ATP
They have common structural features
They can move along a cytoskeletal filament
for significant distances
1. Microtubule-based motility – dyneins and
kinesins
2. Microfilament-based motility – myosins
ICROTUBULE-BASED
MOVEMENT INSIDE CELLS:
KINESINS AND DYNEINS
MTs provide a rigid set of tracks for
transport of a variety of organelles
and vesicles
Traffic toward minus ends of MTs
is considered “inbound”; toward the
plus end is “outbound”
Microtubule-associated motor
proteins—kinesins and dyneins—
walk along the MTs and provide the
force needed for movement
MOTOR PROTEINS MOVE CARGOES ALONG MTS DURING AXONAL TRANSPORT. ______ is involved in ATP-dependent transport toward the plus ends (away from the centrosome), called anterograde axonal transport. While ______ moves particles (cargo) toward the minus ends, called retrograde axonal transport
Kinesin
Cytoplasmic dynein
Kinesins consist of 2 dimerized heavy chains and 2 light chains
The _______ chains contain globular domains that attach to
microtubules, a coiled-coil stalk, a lever-like neck that connects the two, and a tail
The ______ are associated with the tail
heavy; light chains
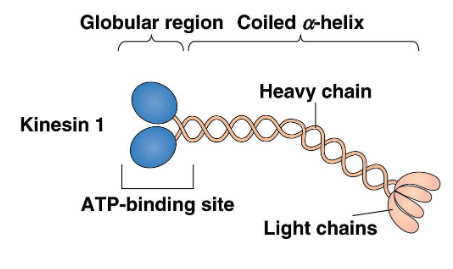
Kinesin movement looks like “_______,” with the two
globular head domains taking turns as the front foot
Each kinesin molecule exhibits ______
walking; processivity
processivity
it can move long distances along an MT before detaching
from it by releasing bound ADP and acquiring a new
ATP, so that the cycle repeats
Each kinesin molecule exhibits processivity
________ dyneins – associate with a protein complex called
dynactin, which helps link dynein to cargo. ______ dyneins – activate microtubule sliding in cilia/flagella
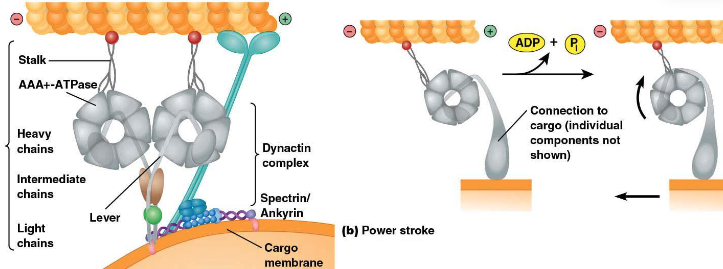
cytoplasmic; axonemal

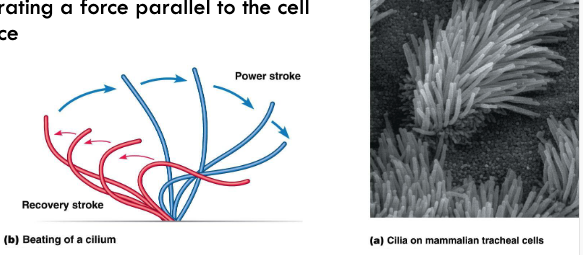
cilia
microtubule-based motility
About 2–10 μm long and occur in large
numbers on the surface of ciliated cells
Occur in both unicellular and multicellular
eukaryotes
Display an oarlike pattern of beating,
generating a force parallel to the cell
surface
flage
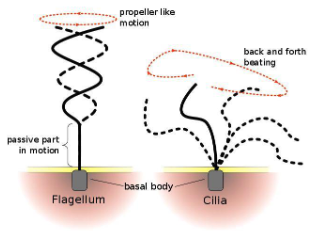
Move cells through a fluid environment
Same diameter as cilia, but usually much
longer (up to 200 μm)
Limited to one or a few per cell and
move with a propagated bending motion,
which generates a force parallel to the
flagellum

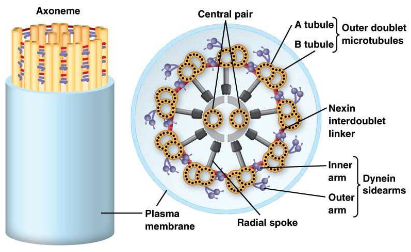
cilia and flagella
share a common
structure, the axoneme
It is connected to a basal body and
surrounded by an extension of the
cell membrane
basal body looks like a centriole, with nine sets of triplets (three
MTs) structure around the circumference
Between the axoneme and basal
body is a transition zone in which the
MTs take on the pattern
characteristic of the axoneme
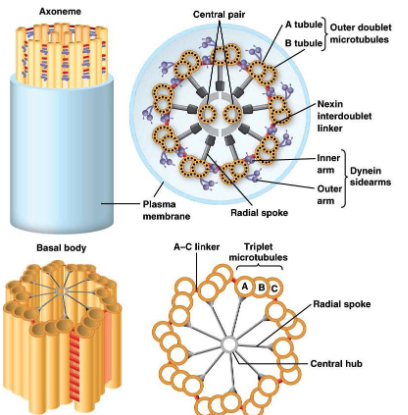
axonemes (cilia and flagella)
“9 + 2” pattern, with 9 outer doublets
and 2 MTs in the center, the central pair
Each outer doublet of the axoneme consists of one complete MT (the A
tubule) and one incomplete MT (the B tubule)
The A tubule has 13 protofilaments, whereas the B tubule has 10 or 11
The tubules of the central pair are both complete