Lecture #5: Chapter 4a (Tissue Level of Organization - Epithelial Cells
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What are the 5 main types of cell junctions?
Tight junctions
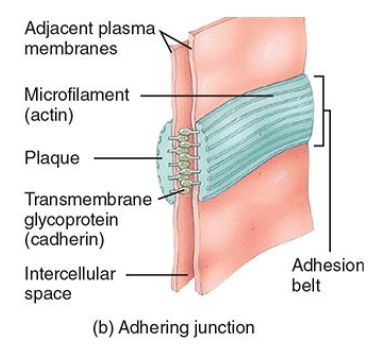
Adhering junctions
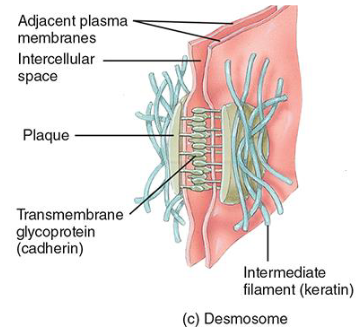
Desmosomes
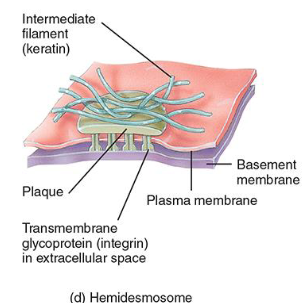
Hemidesmosomes
Gap junctions
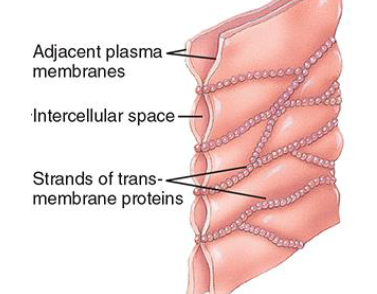
Give examples of where tight junctions are found.
Connect adjacent cells like adhering junctions but using intermediate filaments, providing stronger connections than adhering junctions to prevent separation.
½ a desmosome; Anchor cells to the basement membrane and resist abrasion.
Permit the flow of signals between cells through protein channels called connexons, allowing passage of ions and small molecules.
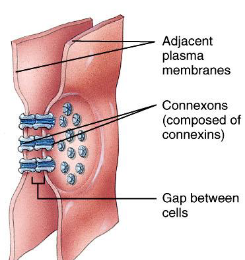
Compare and contrast epithelial and connective tissues.
epithelial
many cells tightly packed
avascular; NO blood vessels
function: covers surfaces & controls substance exchange
connective
fewer cells in extracellular matrix
well-vascularized; blood vessels
function: provide structural support & transport substances
What are the 3 functional classifications of exocrine glands?
Describe merocrine glands
discharge secretory products by EXOCYTOSIS
most of body’s glands = merocrine
Describe Apocrine glands.
accumulate secretory products at the apical surface
protrusion → DECAPITATION by exocytosis
e.g. mammary glands secreting breastmilk
Describe holocrine glands.
accumulate secretory products in the cytosol
mature cells RUPTURE & leaked contents are released
e.g. sebaceoous glands
What is the scientific study of tissues?
Histology
Describe the 2 structural components and functions of basement membrane.
2 layers of protein:
Basal Lamina (epithelial cells)
Reticular Lamina (connective tissue)
functions:
separates overlying epithelial tissue from underlying connective tissue
provides surface for epithia to anchor, migrate, and grow
List function & location of simple squamous epithelium.
function:
filter body fluids
diffusion of nutrients & gases
where:
endothelium → lines blood vessels
mesothelium → makes SEROUS MEMBRANES
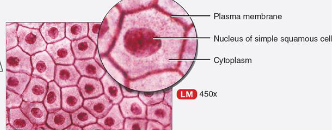
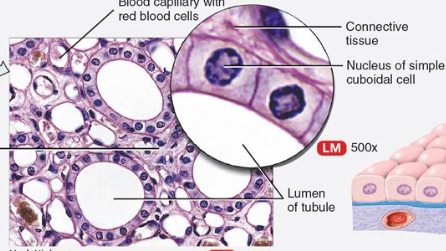
List function & location of simple cuboidal epithelium
function:
secretion of hormones & other substances
absorption of water/solutes
where:
lining kidney tubules
bronchioles
thyroid, pancreas
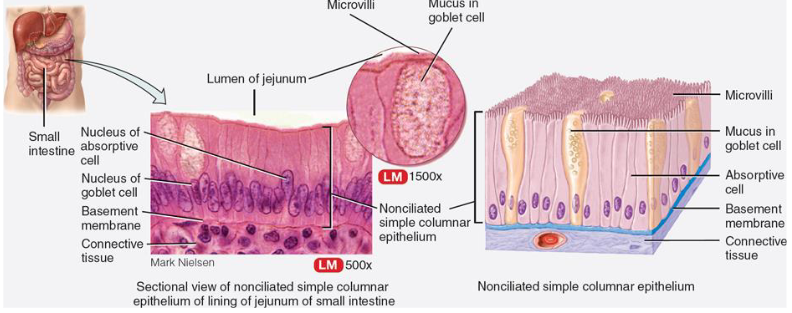
List function & location of simple non-ciliated columnar epithelium
function:
secretion of mucus; contain goblet cells
absorption of nutrients
microvilli at apical surface inc. surface area
where:
stomach
mucus protects the lining from hydrochloric acid
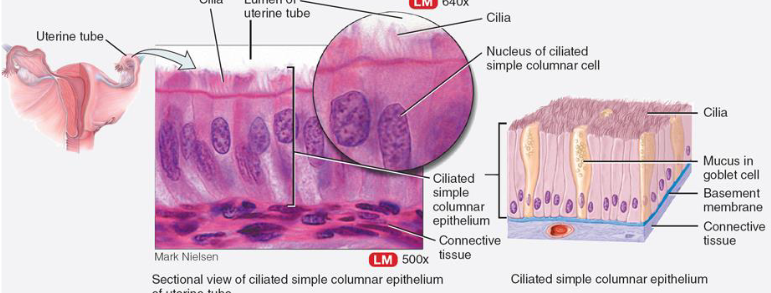
List function & location of simple ciliated columnar epithelium
function:
cilia move mucus from goblet cells
protection from invasion (e.g. air pollutants)
where:
bronchioles; pollutants stuck in mucus and cilia “sweeps” it out
uterine tubes: cilia sweeps egg cells to destination
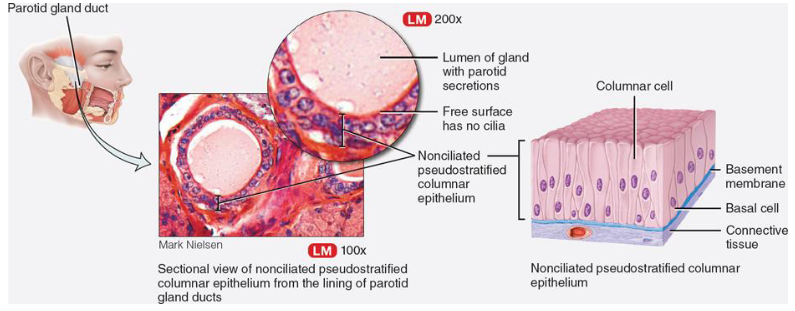
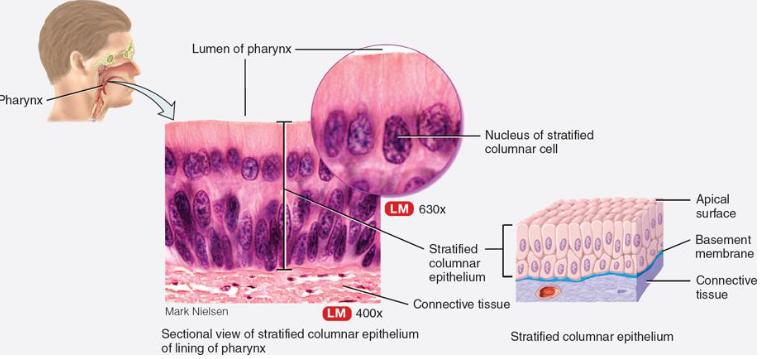
List function & location of pseudostratified non-ciliated columnar epithelium
function:
no cilia or goblet cells
absorption & secretion of mucus
where:
epididymis
ducts for larger glands
male urethra
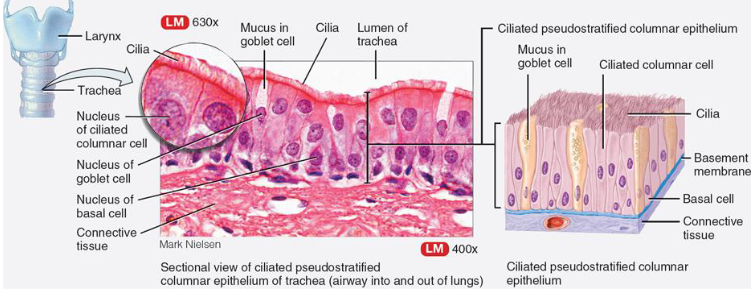
List function & location of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
function:
contains goblet cells & cilia
protection from invasion
filtering of air
where:
upper resp. tract
trachea, bronchi
List function & location of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
function:
superficial layer can be shed & replaced
keratin = insoluble
mechanical srength
protects skin from abrasion, fluid loss, UV radiation, invasion
where:
skin
mouth
esophagus
rectum

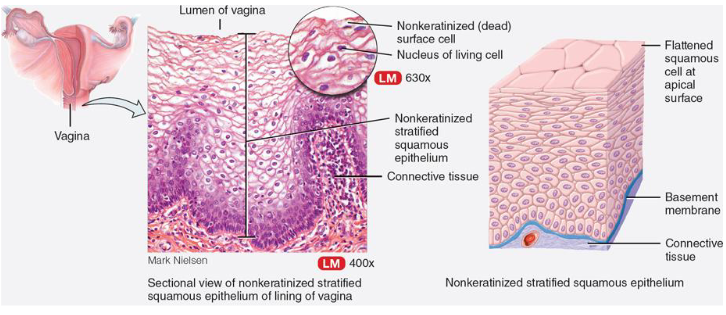
List function & location of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
function:
no large amounts of keratin
provides protection from abrasion & invasion
where:
most surfaces
mouth, esophagus, vagina, tongue
e.g. allows mouth to not bleed after eating chips; lots of layers of cells to shed/protect
List function & location of stratified cuboidal epithelium
function:
protects ducts and tubes from abrasion
where:
lining sweat/sudoriferous glands
parts of male urethra
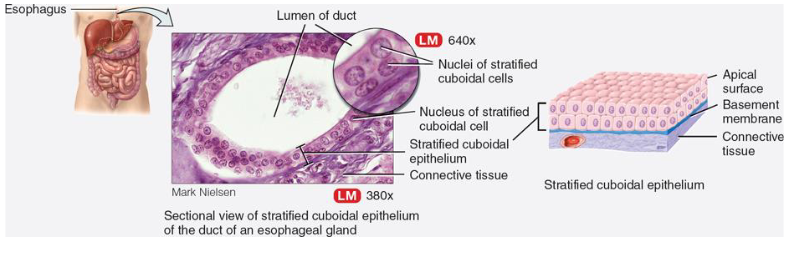
List function & location of stratified columnar epithelium
function:
protection from invasion
secretion of mucus for lubrication
where:
urethra
esophageal & salivary gland ducts
conjunctiva of eye (secrete mucus on surface of eye)
List function & location of transition epithelium (urothelium)
function:
lines hollow organs that expand to store fluids
where:
urinary bladder, ureters, portions of urethra