CSD 329 Fluency Disorders
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
fluency disorder
an interruption in the flow of speaking characterized by atypical rate, rhythm, and disfluencies which may also be accompanied by excessive tension, speaking avoidance, struggle behaviors, and secondary mannerisms
developmental stuttering, neurogenic stuttering, psychogenic stuttering, and cluttering
what are the different types of fluency disorders
psychological, emotional, social, and functional
people with fluency disorders also frequently experience __________, __________, ________, and __________ impacts as a result of their communication disorder
developmental stuttering
we don't know much about neurogenic stuttering, psychogenic stuttering, and cluttering. stuttering not a heavily researched area. what type of stuttering do we know the most about?
rate
appropriate speech timing
continuity
smooth connections
tension/effort
appropriate force
rate, continuity, and tension/effort
what three dimensions are going to be affected in a fluency disorder
voice
inappropriate tension/effort will raise the pitch until the point there will be no ________
disfluency
observable interruptions in on-going speech
all, not
disfluency refers to ____ speech interruptions. occurs in everyone's speech, PWS (people who stutter) and those who do ____ stutter
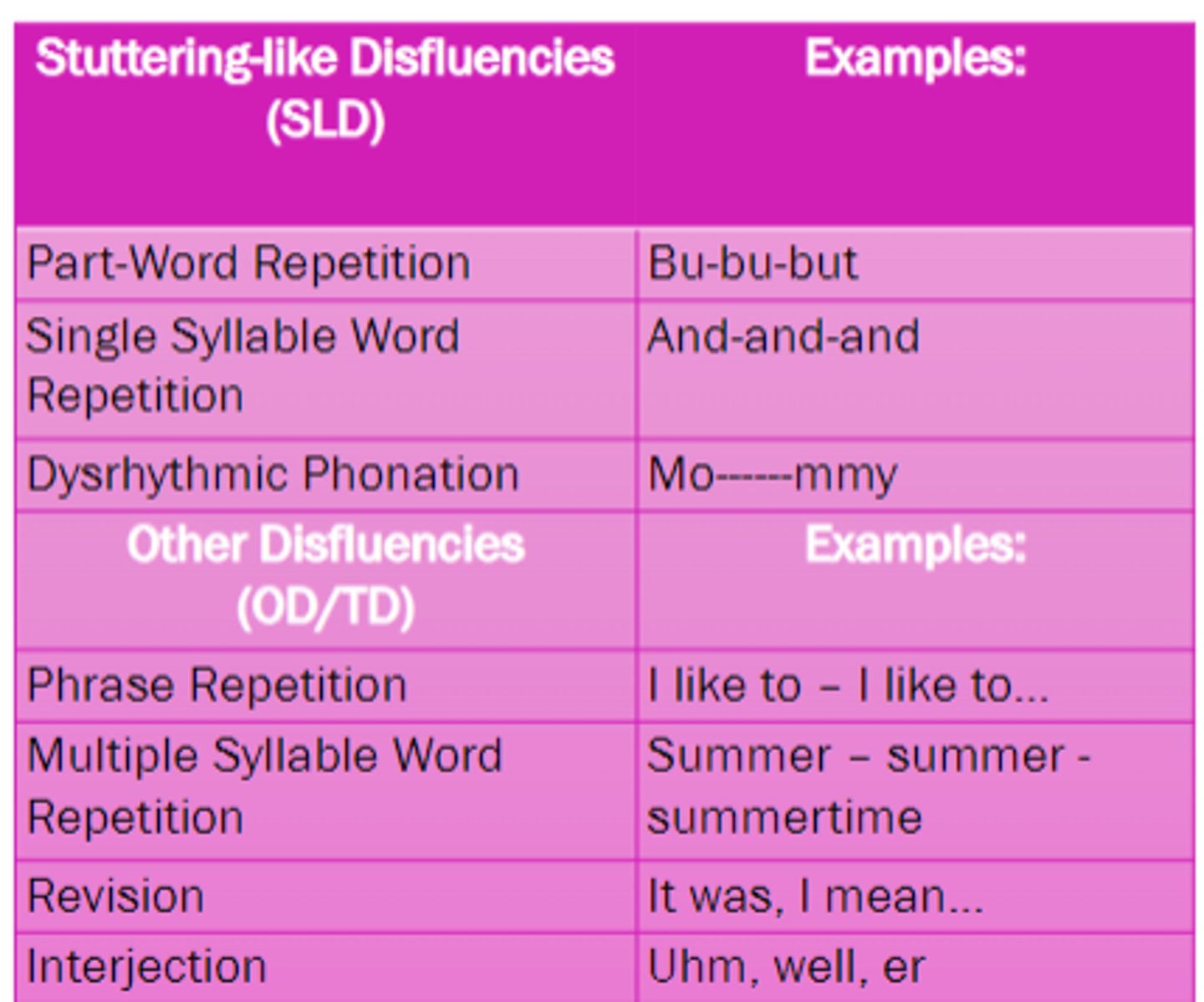
part-word repetitions, prolonged sounds, interjections, and revisions
what are some types of disfluent speech?
speech events, disorder
two meanings of "stuttering": overt, momentary disrupted ________ _______, such as repetitions (disordered speech phenomena). a complex ___________ including speech, physiological, emotional, and cognitive factors, lasting over time (not just speech, everything).
affective (emotional), behavioral (speech and physical), and cognitive (thoughts and beliefs)
abcs of stuttering. this model breaks down into three interconnected components:
abcs of stuttering
a framework used in stuttering therapy to address the multi-dimensional nature of stuttering
address
understanding these components helps clinicians and clients comprehensively _________ stuttering, considering not only the speech disruptions but also the underlying emotions and thoughts that contribute to the overall experience of stuttering.
overt speech characteristics, physical concomitants, physiological activity, social dynamics
Behavioral aspects of stuttering
cognitive processes, social dynamics
Cognitive aspects of stuttering
affective features, social dynamics
Affective aspects of stuttering
icf model
what does the six multidimensional aspects of stuttering and abc's align with?
speech dysfluency and related physical behaviors (squeezing hands and eyes, moving hands and feet)
what can we not hear and see related to stuttering? top of iceberg
emotional factors: surprise, anger, sadness, guilt, shame, self-worth, confidence, acceptance, courage, frustration, worry, despair, and concern
what can we not hear and see related to stuttering? bottom of iceberg
core stuttering behaviors (also referred to as stuttering like disfluency, SLD)
these are the primary speech disruptions that define stuttering
repetitions, prolongations, and blocks
what are some examples of core stuttering behaviors
repetition
repeating sounds, syllables, or words
prolongation
stretching out a sound
block
complete stoppages of speech, where the person is unable to produce a sound
secondary stuttering behaviors
these are learned behaviors that develop in response to stuttering
physical tension, avoidance behaviors, escape behaviors
what are some examples of secondary stuttering behaviors
physical tension
tensing muscles in the face, neck, or body during speech
avoidance behaviors
avoiding certain words, sounds, or speaking situations to prevent stuttering
escape behaviors
actions like blinking, head nodding, or using filler words to escape or minimize stuttering moments
strategy
a ________ can turn into a secondary stuttering behavior
cognitive
there is a __________ component to core and secondary stuttering behaviors.
SLD are much more typical and much more frequent in the speech of PWS and listeners show a strong inclination to perceive these disfluencies as "stuttering"
what are the two reasons for stuttering like disfluencies?
stuttering like disfluencies
people who stutter will have more stuttering like disfluencies (SLD) or typical disfluencies (TD)?
moments (not all the time. if they tap their foot all the time, it is not a secondary behavior)
secondary behaviors occur only during _________ of stuttering
miss
if we have a small definition, we are going to _____ a lot of things.
not
definition is ____ a diagnosis
essential
instead of strictly speaking, realistically we strive for an expression of the __________ rather than the exact nature or meaning. this helps us to distinguish it from other similar or related concepts
differential diagnosis
identify what you suspect by ruling everything else out
study this and make a better one for extra credit (turn in a paper copy 11/5/24)
fear, dread, anxiety, panic
emotions that happen prior to stuttering
blankness, being trapped, panic, frustration
emotions that happen during stuttering
shame, humiliation, anger, resentment
emotions that happen after stuttering
prior, during, and after stuttering
the a and c in the abc of stuttering happens when?
distorted
three utterances before and after stuttering, the speech signal was ________
ameliorating and inducing
conditions that affect b in the abc's of stuttering
time pressure, meaningfulness of the message (what is your name?), language complexity, authority (police), gender/attraction of communication partners, size of the audience/communication partners, specific physical environments, and communicative pressures
inducing conditions:
manner (singing, in rhythm, in a monotone, imitating a dialect, whispering, speaking slowly) and context (to an animal, to an infant, in unison, with DAF aka delayed auditory feedback, with masking noise, and with response contingent stimuli)
ameliorating conditions:
inducing
what is a condition that increases stuttering?
ameliorating
what is a condition that decreases stuttering?