Marketing mix and strategy
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Marketing mix
The collective term for the four major marketing decisions that a firm faces when trying to build a plan, or strategy for how its product will be marketed.
Factors of the design mix
Aesthetics
Function
Economic manufacture
Aesthetics
The word used to describe the look, taste, texture or feel of an item
Function
Relates to whether the product does what it is intended to do and the extent to which it surpasses expectations of quality and performance
Economic manufacture
Considers the ease and the economy with which the item can actually be made on the scale required
Benefits of a good design
Can add value
Provides a point of differentiation
Can reduce manufacturing costs, boosting profit margins
Improves brand image, therefore brand loyalty
Changes in the design mix to reflect social trends
Environmental concerns
Design for waste minimisation or reuse, designers are trying to minimise parts of a product that can’t be reused
Recycling
Even those parts of a product that cant be reused may be able to be recycled for another use
Ethical sourcing
Media coverage has began to examine the sources of products, which encourages designers to ensure their products are ethically sourced
Promotion
Methods by the business to communicate information and persuade consumers to buy a product
Types of promotion
Long term methods
Short term methods
Long term methods
Persuasive advertising
Public relations
Short term methods
Buy one get one free (BOGOF)
Seasonal price cutting promotions
Public relations
Attempts by the business to create publicity that’s reported as news, such as a party for the intro of a new product
Types of branding
Individual brand
Brand family
Corporate brand
Individual brand
These are single product brands, such as Marmite or Penguin. The manufacturer of these products make no attempt to push their company name, instead focusing on the singular brand
Brand family
A brand name used a range of related products, with Cadbury being a prime example.
Corporate brand
Using the company name as the brand, in the way that Nestle does, convinces consumers that all products across the range share similar benefits or drawbacks
Ways to build a brand
Advertising
USP
Sponsorship
Digital media
Advertising
This works best as a way of reinforcing the messages the company wants to send about its brand.
USP
This works best as a way of reinforcing the messages the company wants to send about its brand.
Sponsorship
This is a way of brand building by association. Sponsoring an event, a sports team or even a TV programme can help to create attachments in consumers minds that build the brands personality, e.g Redbull and extreme sports
Types of pricing strategy for new products
Price skimming
Penetration
Price skimming
Involves launching a brand new product at a high price while the product is unique
Advantages:
High prices help create a desirable image for the product
Early adopters will pay high for the exclusivity for the product
High prices generate rapid profits- helping recover the costs of innovation quickly
Disadvantages:
Will deter some customers as the price is seen as a rip off
Early buyers may be frustrated when the price starts to fall
Image may suffer when price begins to fall
Price penetration
Involves launching a product at a very low price to entice customers to try it
Advantages:
Low prices encourage lower-risk product sampling
Low prices boost sales volumes, lowering production costs
High volumes persuade retailers to buy the product, boosting distribution
Encourages customers to develop the habit of buying the product
Disadvantages:
Product’s image may be cast as cheap
Upmarket retailers may be unwilling to stock the product
Likely to create price sensitivity among customers, higher elasticity
Early adopters
People who use/buy a product as soon as it comes out
Pricing strategies for existing products
Cost plus
Predatory
Competitive
Physcological
Cost plus
Deciding price by adding a desired percentage onto total costs per unit
Benefits:
Should guarentee a profit is made on each unit sold
Drawback:
Ignoring a market may mean an unrealistic price is generated
It is appropriate when the firm is a market leader with no competition
Predatory
A strategy that sets price low enough to force a competitor out of business.
Often only on a local basis when competitors are smaller, local firms
Benefit:
Once a rival has been pushed out, prices can be pushed up, increasing margins
Drawback:
If it can be proven to specificially drive competitors out of business, predatory pricing is illegal
Competitive
Charging a price at the market average, or at a discount to the average price in the market.
Benefit:
This should ensure customers are not put off buying the product.
Drawback:
Firms that use a competitive pricing strategy have little control over the price they charge, thus the revenue they generate.
Psychological
Less of a strategy, and more of a tactic used to make fine tuned decisions on the price to charge, prices are set just below major psychological levels, such as £9.99 instead of £10
Advantage:
Helps nudge customers into making a purchase by making them believe they are not spending £10 or £100
Disadvantage
May have little effect on many planned services, and maybe even mildly annoy customers
Factors determining the most appropriate pricing strategy
The level of differentiation
The more different, the more control over prices
PED
Inelastic means more control, elastic likely means competitive pricing
Level of competition
The more competition, the lower chance for a firm moving away from competitive pricing
Strength of brand
Strong brands differentiate products, reducing price elasticity, this adds up the ability to take control over their own pricing, possibly cost plus
Stage of product life cycle
If intro, then use intro methods
Costs and the need of making a profit
Pricing below unit costs will lead to a loss making, which is unsustainable in the long term
Changes in pricing to reflect social trends
Online sales
Pricing online may be more sensitive than on the high street, because online consumers will find it easier to compare prices.
Pricing may be lower because there are lower fixed costs than a physical business
Price comparison sites appear to encourage firms to price competitively so their products and services show up as the best value
Distribution channel
The route a product takes from producer to consumer
Intermediaries
Businesses between the producer and consumer in a distribution channel, such as retailers
Traditional physical channel
Many producers sell their products to wholesalers who act as suppliers to smaller retailers. This channel pushes selling prices up as wholesalers and retailers will both add a markup, however allows smaller firms to achieve a wide distribution across many outlets
Direct to retailer
Larger producers can ignore wholesalers and sell their products in bulk to major retail chains, avoiding wholesaler markup but exposing them to tough negotiations with retail chains on price and credit terms.
Be your own retailer
Producers that want to exert complete control over how their products are sold can set up their own retail outlets. For example, Apple stores are designed to showcase their phones in the best way, but this retailing method is more costly because of this
Direct online
Producers can set up their own websites - Often at a significant cost - to allow producers to buy products directly from them, meaning the producer keeps the full price paid, but can lose customers due to being uncomfortable buying online
Online retail
For smaller producers unable to afford the expense of building slick e-commerce, existing sites like eBay allow you to reach a wide audience, without the same investment, but the disadvantage is the ebay fee.
Changes in distribution to reflect social trends
Online:
Direct online distribution changed it in the way that you can see a wide range of products, which can be updated daily on online websites
From product to service
Some services will never be distributed online, or in any other way than face to face, such as haircuts, clubbing, or staying in a hotel will always involve personal interaction.
Product life cycle
A pattern of sales overtime that products tend to follow.
Phases of the product life cycle.
Introduction
Growth
Maturity
Decline
Sometimes, an additional phase, development is identified as happening before launch.
Introduction
Sales are slow and rise slowly
Growth
Sales begin to rise much quicker
Maturity
Growth in sales now slows, sales stabilise at their highest level.
Decline
During this phase, sales of the product begin to fall, until the product is phased out, or an extension strategy is placed.
Extension strategy
A medium to long term plan for extending the life cycle of a product.
The two adjustments leading to a successful extension strategy
Changes to the product
Changes to promotion
Changes to the product
Adding extra functions or features
Changing ingredients/ materials
Launching slightly different variations of the product, e.g size, shapes etc.
Change in promotion
Targeting a different market segment
Finding new uses for the product
Increasing use of product among existing customers
Product portfolio
The variety/range of products a business has.
The Boston Matrix
Used to assess each product within a firms product portfolio.
The key variables considered are market share and market growth
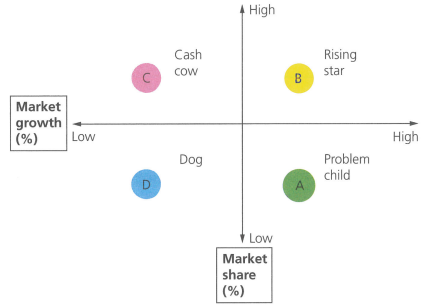
Quadrants of the Boston matrix diagram
Cash cow
Rising star
Dog
Problem Child
Cash cow
Products in stable markets that hold high market share.
Generate high sales with low market expenditure, as a result generating high profits which can be used to develop other products in the portfolio,
Rising star
These are products in exciting and rapidly growing markets that hold a high share, and are the future money makers for the firm.
Although these products will need alot of money spent on them, to fight off competitors.
If high share is maintained, future profitability is likely.
Dogs
These products have a low share of a low growth market, therefore unattractive members of the portfolio, They are most likely candidates to be killed off.
Problem child
These products may be successful in the future, but have low market share, their potential is based on the fact that they are being sold in rapidly growing markets offering the chance of rapid sales growth.
Marketing strategy
The general approach to marketing used by a business
Mass market strategy
Selling a standard product to almost all consumers in a market
Niche market strategy
Selling specialised product to smaller subsections of the market
Benefits of a successful mass market strategy
High distribution levels
Greater control over advertising and promotion
A degree of influence over pricing within the market.
Benefits of a successful niche marketing strategy
Able to meet customer needs more precisely
Able to charge a higher price than mass market products
Less direct competition
Niche market strategies
The key to successful niche marketing:
Depth of understanding of the product
Depth of understanding of consumer tastes that take years to build up
As a result, entering a niche market can’t be rushed, a patient approach is needed to ensure customers needs are met properly.
Business to consumer strategies.
Getting and keeping the right image for the product/service is vital.
The goal of any business to consumer marketing strategy must be developing customer loyalty among an ever growing base of customers.
Business to business strategies
Same principles as to consumer, but price and reliability are more important as factors.
Types of marketing strategies
Mass marketing
Niche marketing
B2B (Business to business)
B2C (Business to consumer)