PGY Exam 5 Review
1/293
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
294 Terms
alimentary canal
30 ft long tube (mouth to anus)
five specialized sub-sections of the GI tract:
pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine
GI accessory glands
parotid salivary glands, sublingual salivary gland, submandibular salivary gland, liver, gallbladder, (exocrine) pancreas
primary function of the digestive system
transfer ingested nutrients, electrolytes, and water from the external environment into the body’s internal environment
digestion
chemical and mechanical breakdown of foods into small units to facilitate absorption
absorption
passive or active transfer of substances from the lumen of the GI tract to the circulatory system
secretion
release of substances (hydrochloric acid, bile, digestive enzymes) into the lumen of the GI tract to facilitate digestion
motility
mixing of luminal contents and movement of material along the GI tract by muscle contraction
structure of the GI tract wall
Mucosa: layer of luminal epithelial cells → connective tissue (lamina propria) → muscularis mucosa
Submucosa: connective tissue containing blood/lymphatic vessels and the submucosal plexus
Muscularis Externa: circular and longitudinal smooth muscle and the myenteric plexus
Serosa: connective tissue
total area of the luminal surface of the small intestine is increased by….
circular folds of the mucosa and submucosa
villi: projections of the mucosa into the lumen
microvilli: projections of the luminal membrane of the epithelial cells covering the villi (“brush-border”)
outer epithelial cell layer of each villus includes….
goblet cells that secrete
enteroendocrine cells that secrete hormones involved in the regulation of GI function
the interior of the villus contains
a capillary system…. takes up most of the materials absorbed from the lumen of the GI tract
a single blind-ended lymphatic vessel (lacteal) which is essential for fat absorption
immune cells…Peyers patches
venous drainage from the GI tract initially passes through the liver via the
hepatic portal vein
allows absorbed material to potentially be processed by the liver prior to release into the general circulation
digestive actions of the stomach reduce ingested material to a solution called….
chyme
function of the salivary glands
secretes a hypotonic, alkaline fluid containing:
mucus, which lubricates the ingested material and facilitates swallowing
enzymes including alpha-amylase (ptyalin) and lingual lipase to initiate carbohydrate and lipid digestion
lysozyme, lactoferrin, and binding globulin for IgA….antibacterial action
function of the exocrine pancreas
secretes enzymes into the small intestine that digest fats, proteins, and nucleic acids
secretes bicarbonate into the small intestine to neutralize the acidic chyme coming from the stomach
function of the liver
secretes bile consisting of bicarbonate, cholesterol, phospholipids, and bile salts (required for fat digestion)
bile is stored in the gallbladder, concentrated between meals and injected into the duodenum via the common bile duct
input vs output in the GI tract (solids)
On average, we ingest up to 800 grams of solid material per day, but…
of this approximately 50 grams is excreted, thus 90-95% is absorbed (primarily by the small intestine)
input versus output in the GI tract (liquids)
on average, we ingest approximately 1200 mL of fluid per day but
an additional 7000 mL of fluid is added to the GI tract via salivary, gastric, liver, pancreatic, and intestinal secretions
of this 8.2 L total. 99% is absorbed
almost all salts in the secreted fluids are absorbed
GI tract epithelial cells consist of
a luminal membrane
basolateral membrane
transcellular: through the cell across two membranes (luminal and basolateral)
paracellular: between cells (across tight junctions by simple diffusion)
the (primary) transcellular route requires transport proteins on both membranes
carbohydratess are ingested primarily as…..
polysaccharides (starch) and disaccharides (sucrose and maltose)
only monosaccharides can be absorbed across the….
small intestine
what breaks down starch into maltose and glucose
salivary and pancreatic amylase
maltose are subsequently broken down to monosaccharides by ____ located on the luminal membrane of small intestine epithelial cells
enzymes
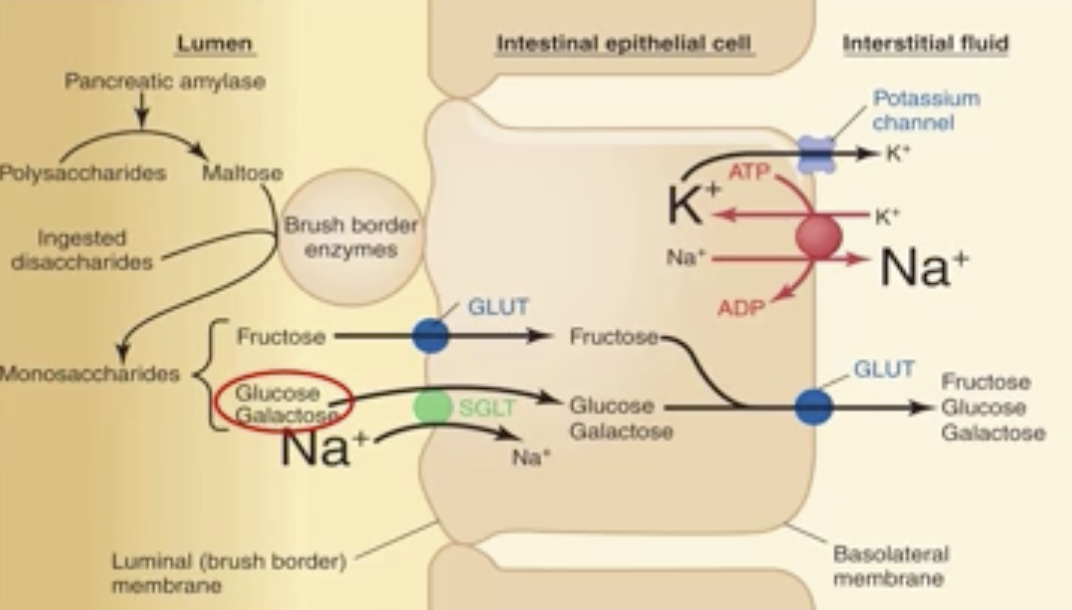
digestion and absorption of carbohydrates
Fructose: enters the cell across the luminal membrane by facilitated diffusion via a GLUT transporter
Glucose/Galactose: enter the cell via a Na+-glucose co-transporter
Most ingested carbohydrates are digested and absorbed within the first 20% of the small intestine
digestion and absorption of proteins
typical US diet contains 60-90 grams of protein per day
Only di- and tripeptides and amino acids can be absorbed by the small intestine
stomach pepsin
initially breaks down proteins to peptide fragments
pancreatic proteases (trypsin and chymotrypsin)
further break down fragments to tri- and dipeptides in the small intestine
peptide fragments can be absorbed directly or can be….
digested to free amino-acids by pancreatic carboxypeptidases or one of twenty aminopeptidases located on the luminal membrane of small intestine epithelial cells
how to tri-dipeptides enter the cell?
across the luminal membrane via a H+-peptide co-transporter
metabolized to amino acids within the cell
how do amino acids enter the cell?
via a Na+-amino acid specific co-transporter
how do tri-dipeptides exit the cell?
across the basolateral membrane via amino acid transporter
how do amino acids exit the cell?
across the basolateral membrane via an amino-acid transporter
how do proteins enter the cell?
small amounts of protein can be absorbed via luminal endocytosis and basolateral exocytosis
triglycerides must be digested to promote absorption, this occurs primarily….
in the small intestine via pancreatic lipase
emulsification
large lipid droplets are divided into smaller droplets, thus increasing digestion rate
emulsification is due to:
mechanical disruption of droplets caused by motility of the lower stomach and small intestine
amphipathic emulsifying agents including ingested phospholipids and liver bile salts
problem: emulsifying agent coating could impair lipase accessibility to the lipid
solution: the pancreas secretes colipase which attaches to the droplet and binds lipase
how do monoglycerides and fatty acids cross the intestinal cell luminal membrane
diffusion
bile salts promote the formation of….
micelles (which contain released monoglyceride and fatty acid)
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
location within the cell where MG and FA are resynthesized into TG
vesicles containing the TG exit the cell across the basolateral membrane via…
exocytosis
chylomicrons
extracellular fat droplets (pass into the lacteals and ultimately the circulation)
what vitamins are fat-soluble
A, D, E, K
absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
essentially identical to that of fat
absorption of water-soluble vitamins
diffusion or mediated transport
vitamin B12
due to size/charge B12 must bind to intrinsic factor (secreted by stomach parietal cells)
vitamin b12/intrinsic factor complex
binds to receptors in the lower ileum (absorbed by endocytosis)
pernicious anemia
loss of intrinsic factor
heme
(derived from meat) important source of dietary iron
how is heme absorbed
across the luminal membrane of the small intestine by endocytosis → digested by lysosomal enzymes → released iron complexes with apoferritin to form ferritin within the epithelial cells
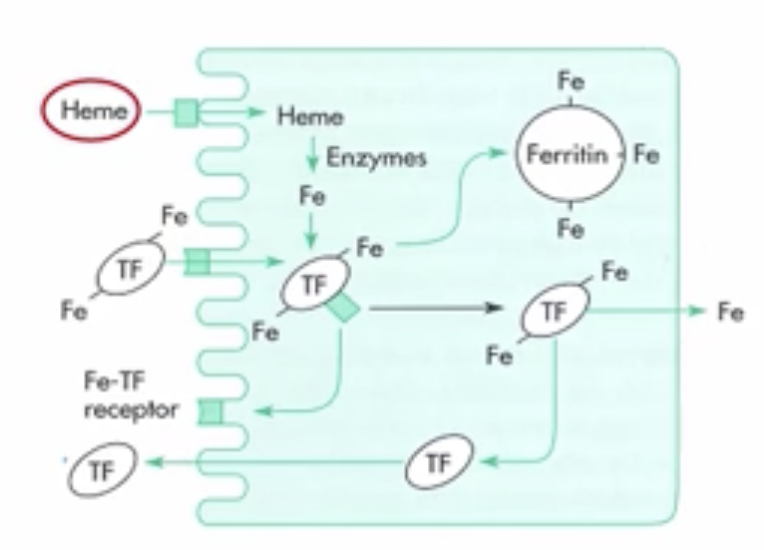
free lumen iron…
complexes with transferrin (secreted by the enterocytes) → binds to luminal receptors and is endocytosed → some iron is released across basolateral membrane; some binds to apoferritin to increase plasma iron concentration
decreased transferrin receptor expression
decreased iron uptake
increased ferritin transcription
decreased iron release, decreased plasma iron concentration
hematochromatosis
excess plasma iron
calcium absorption is dependent on….
Ca2+-binding protein (CaBP)
digestion and absorption of calcium
luminal content Ca2+ binds to a membrane CaBP and is transported intracellularly
intracellular CaBP's sequester released Ca2+ to prevent a rise in cytosolic Ca2+
Ca2+ transported across the basolateral membrane by Ca2+-ATPase and by Na+-Ca2+ exchanger
1,25 (OH2) vitamin D stimulates absorption (likely by an increase CaBP expression)
Where is most of the ingested (and secreted) water absorped
small intestine
why are membranes of epithelial cells very water permeable
aquaporins (H2O channels)
digestion and absorption of water
primary → basolateral transporter os solute (Na+) creates osmotic gradient for
water movement both transcellulary and paracellularly
enteric nervous system
located within the GI tract and consists of:
myenteric plexus (smooth muscle activity)
submucosal plexus (exocrine gland secretory activity)
two types of neural reflex arc exist…
short reflex: change in luminal status is detected by receptors, triggers afferent signal, carried exclusively by enteric nervous system to either muscle or exocrine gland
long reflex: afferent signal is transmitted via enteric nervous system to central nervous system where it is processed and an efferent signal then returns to an effector in the GI tract
four primary GI hormones (all peptides)
secretin
cholecystokinin (CCK)
gastrin
glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP)
cephalic phase of GI control
sight, smell, taste, chewing of food triggers primarily vagal parasympathetic efferents which, via the GI nerve plexus, affect secretory/contractile activity
gastric phase of GI control
reflexes triggered by stomach distension, acidity, amino acid and peptide content; mediated by short and long neural reflex responses and hormonally by gastrin
intestinal phase of GI control
reflexes triggered by small intestine distension, acidity, osmolarity, and solute content; mediated by short and long neural reflex responses and hormonally via secretin, CCK, and GIP
two primary regions of the stomach:
body
antrum
lower esophageal sphincter
controls input from the esophagus
pyloric phincter
controls transfer of chyme to the small intestine
the epithelial layer of the stomach invaginates into the mucosa to form tubular glands; secretions include….
mucus (and bicarbonate) from cells at the opening of the glands
HCl (and intrinsic factor) from parietal cells
pepsinogen from chief cells
histamine (paracrine) from enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells
gastrin from antral enteroendocrine G-cells
somatostatin (endocrine) from D cells
parietal cells
possess luminal invaginations (canaliculi) which increases total surface area
HCl is primarily generated in the ____ of the stomach
body
how is HCl generated
intracellularly from CO2-H2O interaction
reaction catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase
carbonic anhydrase catalyzed reaction
hydrogen generated is actively secreted into the lumen by H+-K+-ATPase
bicarbonate generated is transported across the basolateral membrane into the bloodstream via bicarbonate/chloride exchanger
chloride that enters the cell on this exchanger is secreted into the lumen via a chloride selective channel
regulation of HCl secretion by the parietal cells
acid secretion is increased by insertion of more H-K-ATPase units into the luminal membrane. vesicles containing ATPase units translocated from the cytosol and fuse with the luminal membrane
four factors regulate this insertion (and thus H+ secretory capacity)
three stimulate: acetylcholine, gastrin, histamine
one inhibits: somatostatin
histamine potentiates the response to acetylcholine and to gastrin
cephalic parasympathetic activity leads to:
acetylcholine release from the enteric nervous system
gastrin and histamine secretion
gastric phase stimuli (distension, peptides)…
vagovagal reflex: sensory nerve endings in the stomach wall detect stretch/distension
long/short neural reflexes increase vagal efferent activity → acetylcholine, gastrin, histamine → increase HCl
luminal contents can directly stimulate gastrin release (G cells)
neural, endocrine, and paracrine factors that regulate HCl secretion
neural: direct stimulation of the parietal cell
hormonal: gastrin release from G cells
parasympathetic efferent fibers (note: release unique neurotransmitter gastrin releasing peptide (GRP))
stomach contents
paracrine: histamine release from ECL cells
parasympathetic efferent nerve activity
gastrin
luminal HCl also regulates HCl secretion…
increase HCl secretion=inhibits gastrin secretion
increase HCl secretion=stimulates somatostatin
directly inhibits HCl secretion by parietal cells
inhibits the release of gastrin and histamine
intestinal phase regulation of acid secretion
digestive activity of enzymes and bile salts in the small intestine is reduced by acidic solutions
high acidity in the duodenum reflexly inhibits gastric acid secretion
via short and long neural reflexes
via the intestinal hormones secretin and CCK…enterogastrones
regulation of pepsin secretion
pepsin secreted by chief cells as an inactive precursor, pepsinogen (zymogen)
acidity of the stomach lumen initiates autocatalysis (pepsinogen → pepsin) & then released pepsin can then cleave additional pepsinogen as well as cleave ingested proteins
pepsin is optimally active at low pH, passage through to the small intestine results in inactivation since secreted bicarbonate neutralizes the chyme pH
most of the factors that regulate HCl secretion elicit parallel effects on pepsin secretion
what is the functional unit of the salivary duct system?
salivon
four primary elements of the salivon
terminal (blind-ended) acinus: epithelial cells secrete the initial saliva
myoepithelial cells: surround the acinar cells, contractile
intercalated duct: channels saliva to striated duct
striated duct: bidirectional ion transport that modifies the composition of the saliva
chloride exchanged for bicarbonate, sodium exchanged for potassium
saliva composition is _______ dependent
flow-rate
at essentially all flow rates, when compared to plasma composition…
salivary bicarbonate and potassium levels are higher
salivary sodium and calcium are lower
both parasympathetic and sympathetic fibers innervate the salivary glands….
unique in that both stimulate salivary secretion (parasympathetic to a much greater extent)
xerostomia: absence of saliva
the exocrine portion of the pancreas seretes:
bicarbonate: to neutralize the acidic chyme coming from the stomach
digestive enzymes: to breakdown proteins, fats, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids
secreted into the pancreatic duct, joins the common bile, enters the duodenum
bicarbonate synthesis and secretion:
generated intracellularly from CO2 and H2O, catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase
crosses the lumenal membrane via a chloride-bicarbonate exchanger
chloride ions recycle to the lumen via cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR)
hydrogen ions are transported across the basolateral membrane via Na-H exchanger, interacts with bicarbonate produced by stomach parietal cells
sodium transported into the lumen paracellularly, driven by lumen-negative potential due to CFTR-dependents chloride transport across the basolateral membrane
accumulation of sodium and chloride in the lumen creates osmotic gradient for paracellular flux of water
what substrate does trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase work on
proteins
what is the action of trypsin, chymotrypsin, or elastase on proteins
break peptide bonds in proteins to form peptide fragments
what substrate does carboxypeptidase work on
proteins
what does carboxypeptidase do to proteins
splits off terminal amino acid from carboxyl end of proteins
what substrate does lipase act on
fats
what does lipase do to fats
splits off two fatty acids from triglycerides, forming free fatty acids and monoglycerides
what substrate does amylase act on
polysaccharides
what does amylase do to polysaccharides
splits polysaccharides into glucose and maltose
all proteolytic enzymes are secreted as:
inactive zymogens (prevents autolysis of producing cells)
what cleaves trypsinogen to trypsin
enterokinase