IB Chemistry Quiz 1.
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Chemical Element
Pure substance composed of identical atoms.
Atoms of the same element are identical.
Atom
Smallest particle of an element, exhibiting its characteristic properties.
Distinct Nature of Atoms . . .
Imparts unique properties to each element.
Elements in Nature
Some exist naturally in pure, uncombined forms.
Compound.
Combination of different elements with fixed ratios.
Held together by chemical bonds, altering properties.
Mixture.
Blend of substances with distinct properties.
Variable composition.
Homogeneous Mixtures.
Uniform throughout, consistent properties.
Heterogeneous Mixtures.
Non-uniform, varying properties.
Methods of Separating Components.
Filtration: Solids separated from liquids.
Recrystallization: Substance crystallized from a solution.
Distillation: Separation by boiling and condensation.
Paper Chromatography: Separation based on adsorption.
Filtration.
Solids removed from liquids using a filter.
Recrystallization.
Substance isolated from a solution via a solvent and crystallization.
Distillation.
Separation through selective boiling and condensation.
Paper Chromatography.
Components separated based on adsorption to a solid phase.
Kinetic Theory.
Matter exists in different states due to temperature and pressure.
States depend on particle energy.
Temperature relates to average kinetic energy.
State determined by inter-particle forces.
Temperature.
Measures average particle kinetic energy.
Ek
Solid.
Dense, fixed shape and volume, no atom compression.
Liquid.
Less dense, takes container shape, fixed volume.
Gas.
Spreads to fill space, no fixed shape or volume, compressible.
Fluids.
Liquids and gases due to flow ability.
Diffusion.
Particles evenly disperse via random movement.
Kinetic Energy (Ek).
Energy linked to motion.
Inverse mass-velocity relationship.
Increases with temperature.
Changes of State.
State changes occur at fixed temperature and pressure.
Include sublimation, deposition, vaporization, condensation, melting, freezing.
Vaporization.
Liquid to gas via evaporation or boiling.
Deposition.
Gas to solid (e.g., frosting).
Sublimation.
Solid to gas without liquid phase (e.g., dry ice).
Evaporation.
Surface liquid to gas below boiling point.
Boiling.
Liquid becomes gas throughout.
Boiling Point.
All molecules become gas.
Vapour Pressure.
Liquid's pressure on container walls.
Boiling when equals atmospheric pressure.
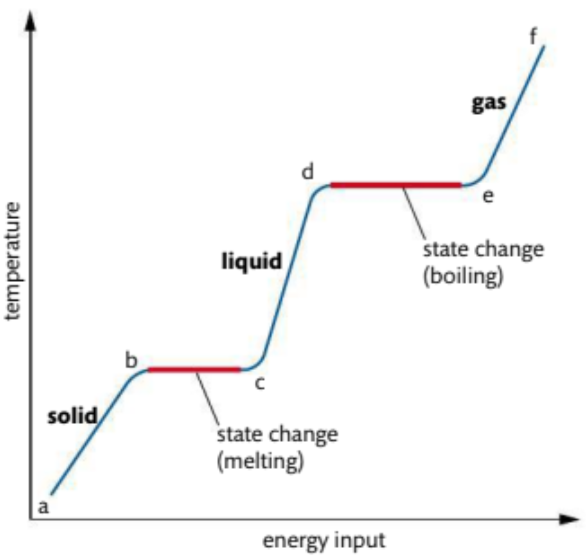
Temperature Change During Heating a Solid at Constant Pressure.
Energy shifts inter-particle forces, not temperature.
Temperature Change Stages.
a-b: Solid heats, temperature rises.
b-c: Melting point, temperature constant.
c-d: Liquid heats, temperature rises.
d-e: Boiling point, temperature constant.
e-f: Gas heats, temperature rises.
Temperature in Kelvin.
Absolute temperature scale.
Absolute zero at 0 K (-273.15°C).
Kelvin and Celsius Conversion.
Temperature (K) = Temperature (°C) + 273.15.
Atom Contents.
Nucleus with protons and neutrons.
Electrons orbit outside nucleus.
Atomic Number & Mass Number.
Mass Number (A) = Protons + Neutrons.
Atomic Number (Z) = Protons.
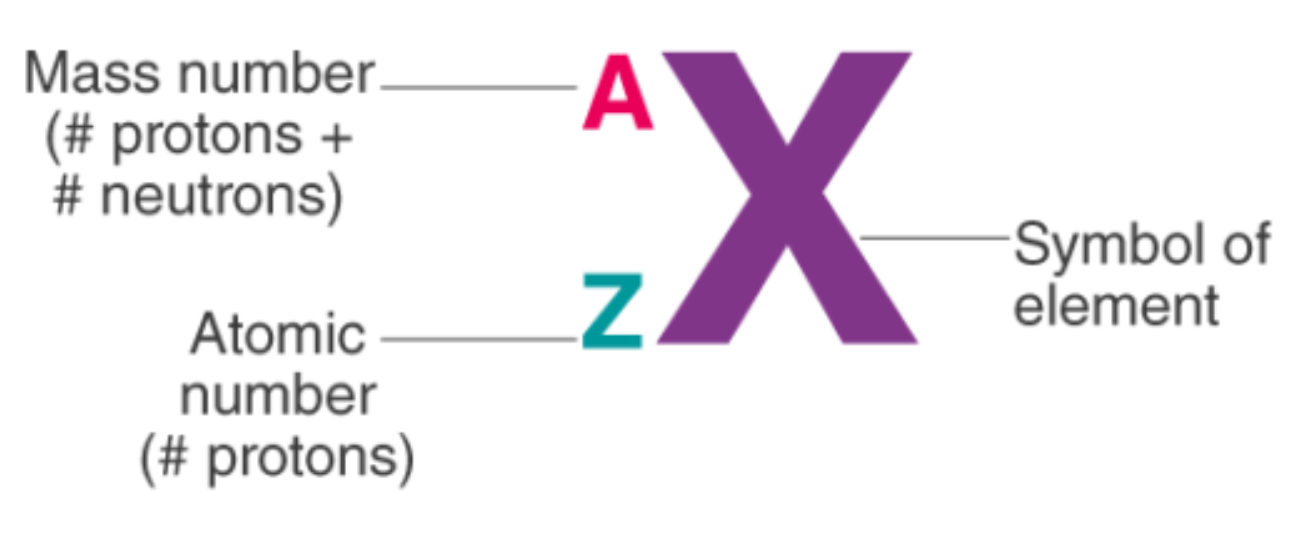
Ions.
Formed by gaining or losing electrons.
Cations: Lose electrons, positive charge.
Anions: Gain electrons, negative charge.
Isotopes.
Same protons, different neutrons.
Similar chemistry, distinct physical properties.
Relative Average Mass.
Calculated from isotope abundance and mass.
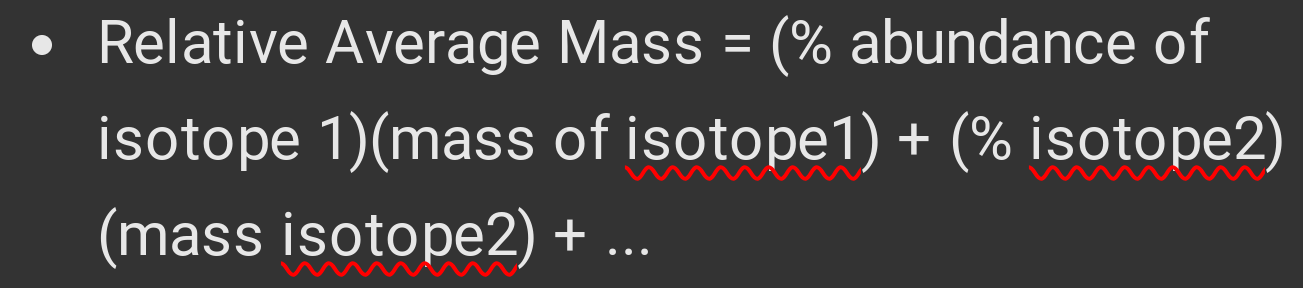
Mass Spectra.
Measures individual atom mass.
Presents percent abundance vs. mass/charge ratio.
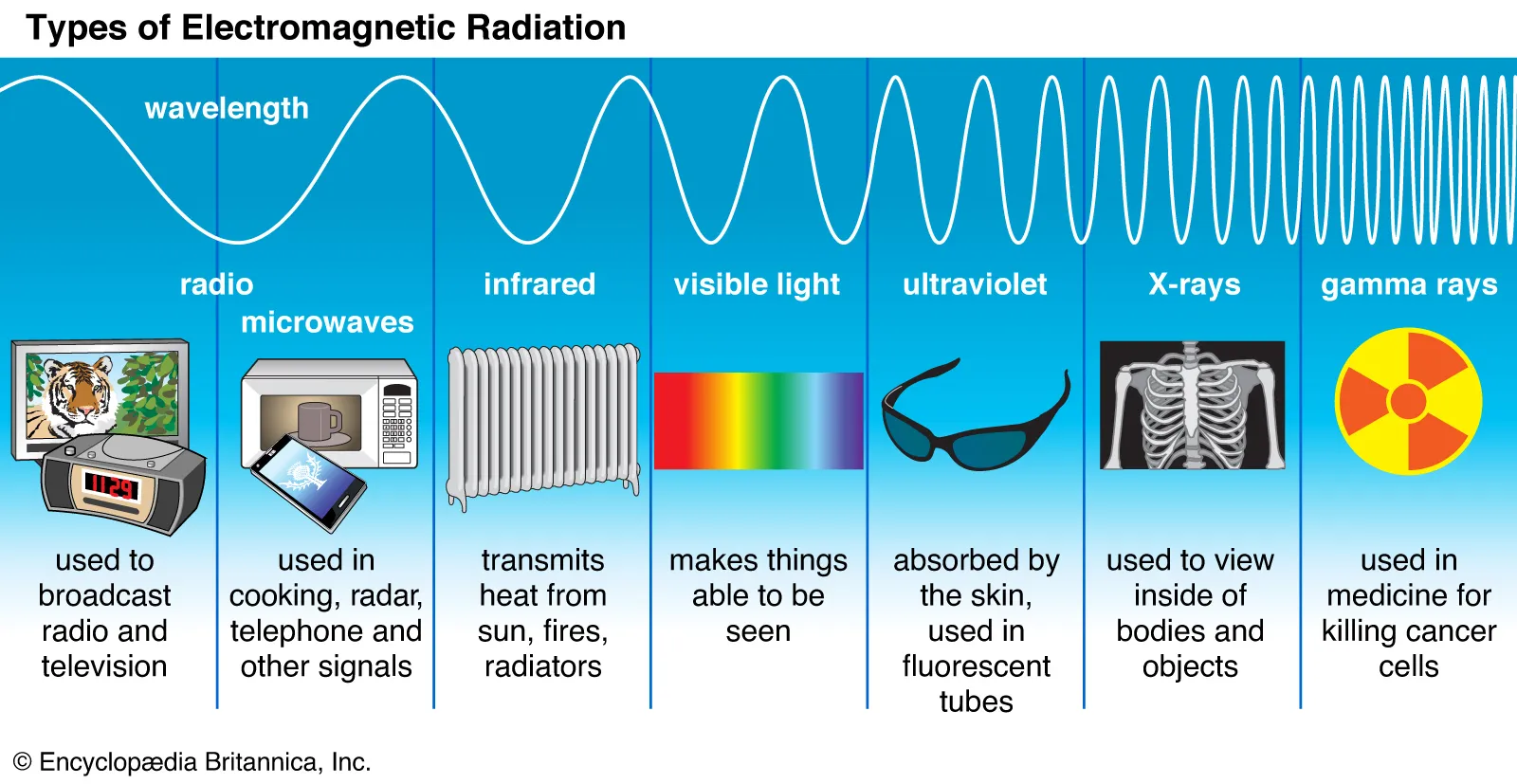
Electromagnetic Radiation.
Varies in energy forms.
Electromagnetic Waves.
Travel at constant speed, different wavelengths.
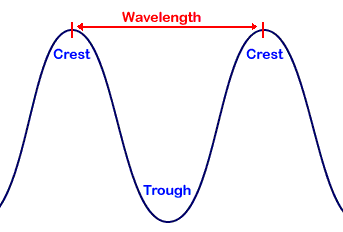
Frequency.
Waves passing a point per second.
Frequency-Wavelength Relation.
c = λv (c: speed of light, λ: wavelength, v: frequency)
Electromagnetic Spectrum.
Energy increases with frequency.
Atomic Absorption & Emission Line Spectra.
Absorption: Radiation absorbed by atoms.
Emission: Atoms emit light when electrons return to lower energy levels.
Line Spectra in Elements.
Unique line spectra for different elements.
Used for element identification.