Ultimate AP Human Geography Vocabulary cards
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All vocab from all 7 units
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Physical Geography
the study of natural processes and the distribution of features in the environment
Human Geography
the study of the events and processes that have shaped how humans understand, use, and alter Earth (the why of where)
Spatial Perspective
where something occurs and why it is located there
Ecological Perspective
the relationship between living beings and their environments
Location
the position that a point or object occupies on Earth. It can be expressed in absolute or relative terms
Place
a location on Earth that is distinguished by its physical and human characteristics
Site
a place’s absolute location as well as its physical characteristics
Situation
a place’s location in relation to other places or its surrounding features
Space
the area between two or more things on Earth’s surface
Distributed
how things are arranged in a given space
Density
the number of things in a specific area
Pattern
how things are arranged in a particular space
Environmental Determinism
a theory that argues that human behavior is largely controlled by the physical environment
Possibilism
a theory that humans have more agency, or ability, to produce a result that is able to conflict with or make the best of environmental factors
Distance Decay
a principle that states that the farther away one thing is from another, the less interaction the two things will have
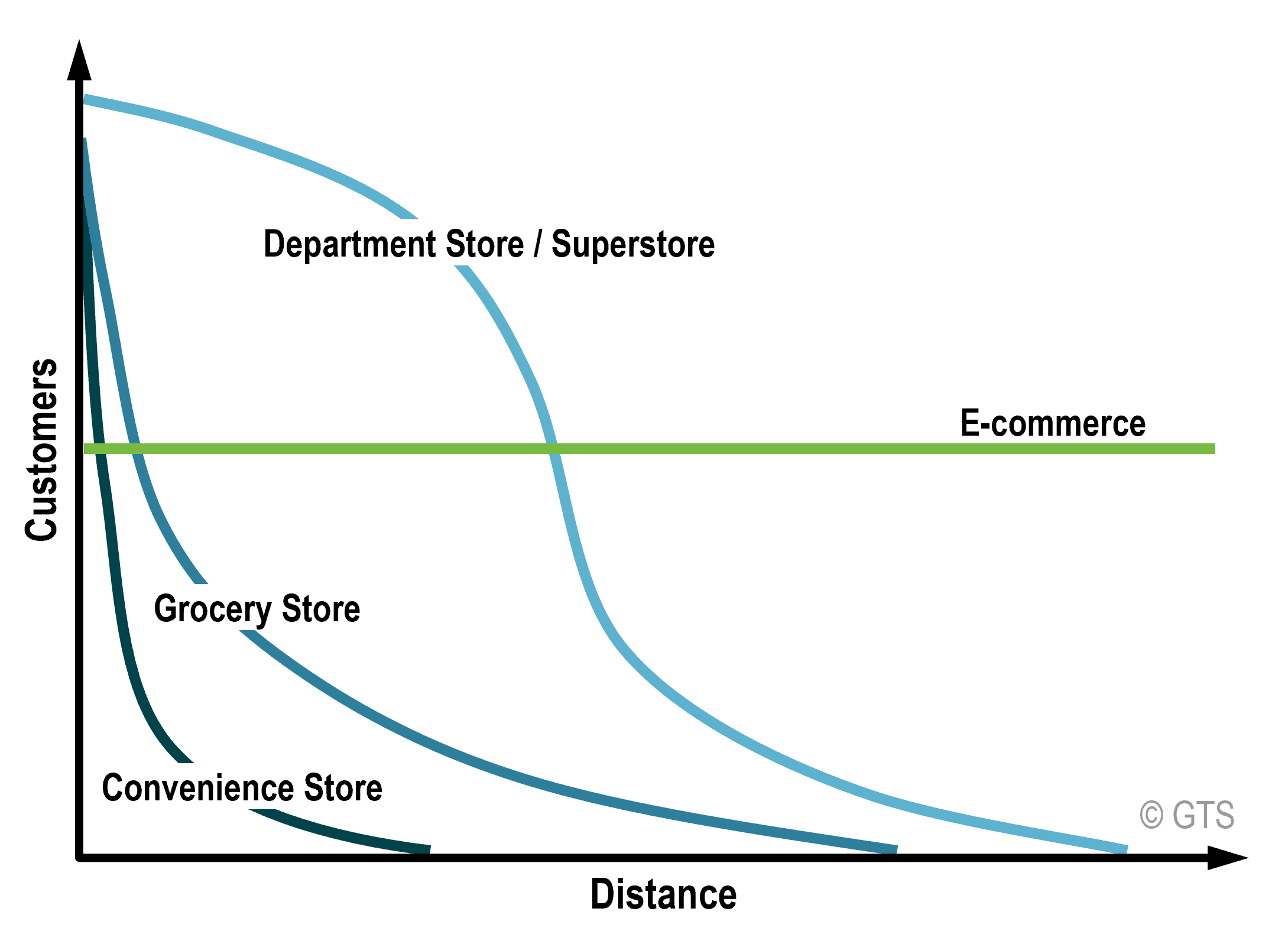
Time-Space Compression
a principle that says that, as technology, travel, and communication improves, the relative distance between places shrink
Sustainability
the use of Earth’s land and natural resources in ways that ensure they will continue to be available in the future
Scale
the area of the world being studied
Region
an area of Earth’s surface with certain characteristics that make it distinct from other areas
Formal Region
an area with distinct boundaries that has one or more shared traits
Functional Region
an area organized by its function around a focal point or the center of an interest or activity
Node
The focal point or center activity of a functional region
Suburbs
residential areas surrounding a city
Vernacular (Perceptual) Region
a type of region that is subjective and reflects people’s feelings and attitudes about a place
Globalization
the expansion of economic, cultural, and political processes on a worldwide scale
Theory
a system of ideas intended to explain certain phenomena
World System Theory
a theory invented by Immanuel Wallerstein to describe the spatial and functional relationships between countries in the world economy. Wallerstein divided countries into 3 categories; core, semi-periphery, and periphery

Periphery
countries that have less wealth, lower education levels, and less sophisticated technology
Semi-Periphery
countries where both core and periphery processes occur
Core
countries that are wealthy, have high education levels, more sophisticated technology, and are a global influence
Sustainable Development
development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Quantitative Data
information measured using mathematical terms like numbers or graphs
Qualitative Data
interpretations of data sources such as field observations, media reports, travel narratives, policy documents, personal interviews, landscape analysis, and visuals such as art or photographs
Census
an official count of the number of people in a defined area
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
information systems that capture, store, organize, and display geographic data that can then be used to configure maps
Topography
the shape and features of land surfaces
Remote Sensing
geospatial technologies that gather data remotely or without physical contact
Global Positioning System (GPS)
a network of satellites that transmit location data to handheld receivers
Cartographers
people who make maps
Absolute Distance
a distance that can be measured using a standard unit of length
Relative Distance
distance that can be measured in terms of criteria other than absolute such as time or money
Absolute Direction
an established sense of direction based on the cardinal compass directions (north, east, south, and west)
Relative Direction
a sense of direction based on people’s perceptions (left, right, up, down, front, back)
Map Scale
the mathematical relationship between the size of a map and the part of the real world it shows
Map Projections
ways to flatten the 3D Earth into a 2D map or plane
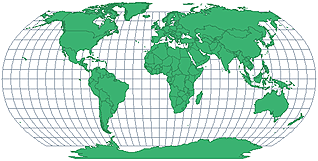
Robinson Projection
a projection that has curved lines of longitude and straight lines of latitude. The shapes of the continents and direction becomes more distorted farther away from the equator
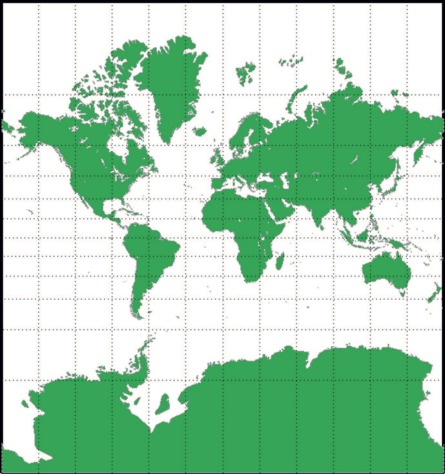
Mercator Projection
a projection where the continents’ shapes are maintained and direction is displayed accurately, but the sizes of the continents are very distorted. Often used for navigation
Gall-Peters Projection
a projection where the direction and the relative size of the continents are not distorted, but the shapes of them are
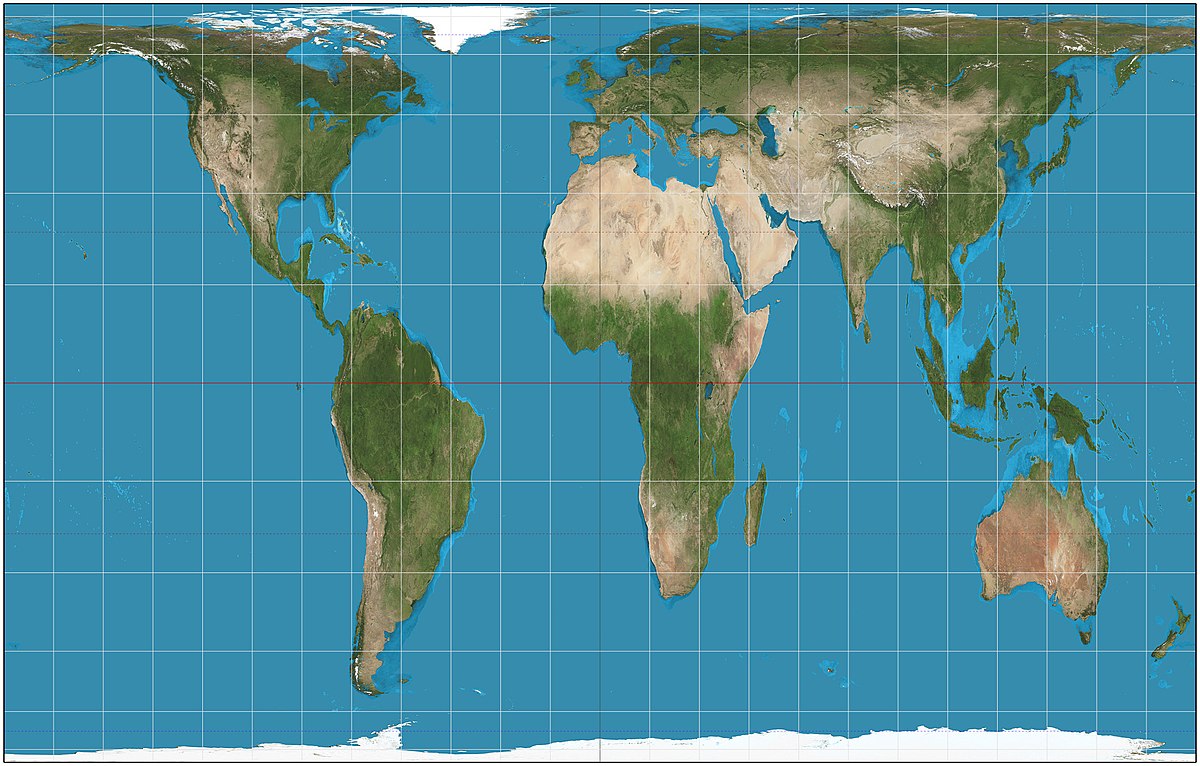
Azimuthal Projection
a projection that is a flattened, disk-shaped portion of Earth shown from a specific point
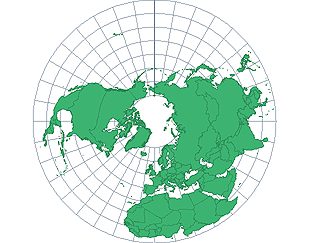
Reference Maps
generalized sources of geographic data and focus on location
Thematic Maps
maps that have a theme or specific purpose and focus on the relationship among geographic data
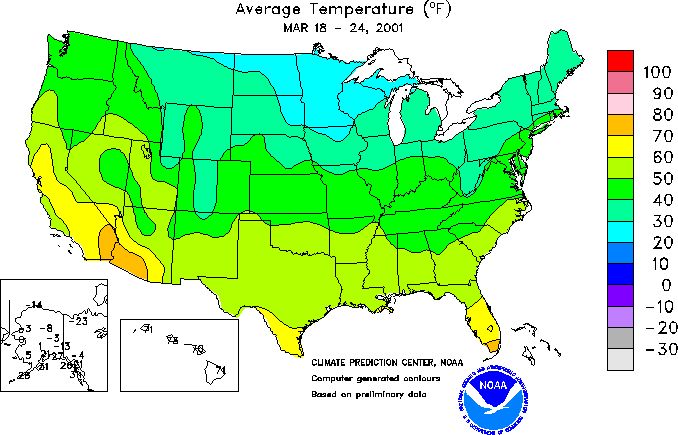
Isoline Map
maps where lines connect data points of the same value
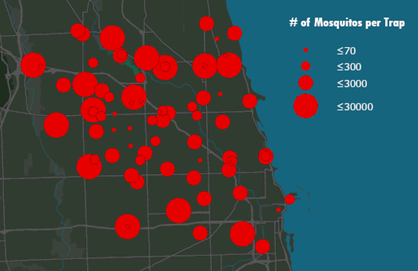
Graduated Symbols Map
a type of map where differently sized symbols are used to indicate quantitative data
Cartogram
a type of map that combines statistical data and geographic location to communicate information
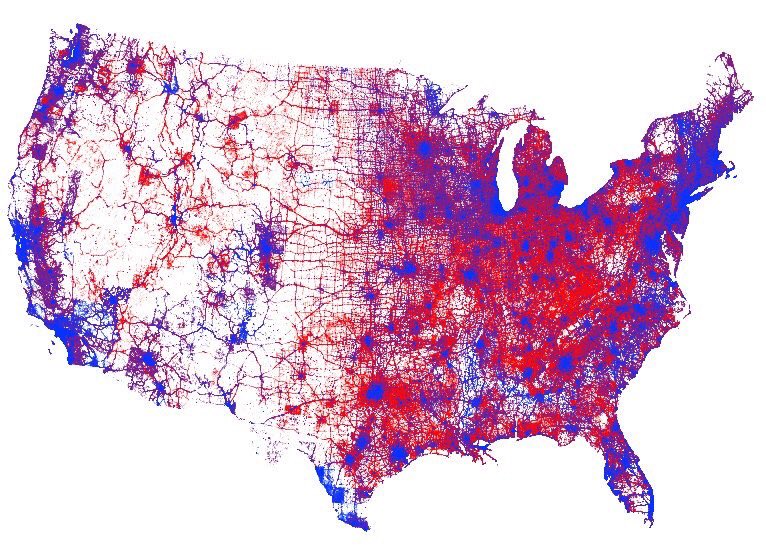
Dot Map
a type of map where dots are used to show locations of specific observations or events
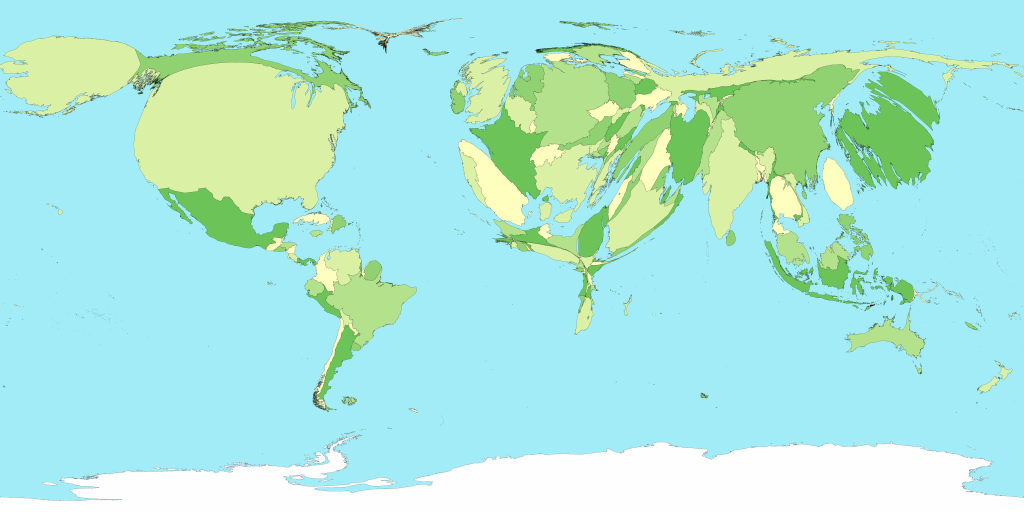
Chloropleth Map
a type of thematic map that uses colors or shading to represent categories of data