Introduction to Genetics in Biology 305
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
Photic Sneeze Reflex
Genetic trait causing sneezing in bright light.
Epigenetics
heritable changes in gene expression that occur without changes to DNA; is reversible; can be influenced by the environment; DNA Methly
Meiosis I: Prophase I
Chromosomes condense, homologous chromosomes pair up, the membrane breaks down, and spindles form. Cross over occurs
Genetics
Study of heredity and inherited characteristics.
Genetic Material
Molecules encoding, replicating, and expressing heredity.
Transmission of Inheritance
Patterns through which traits are passed to offspring.
Molecular Biology
Study of biological processes at the molecular level.
Gene Expression
Process by which information from genes is used.
Genetic Variation
Differences in DNA sequences among individuals.
Model Organisms
Species used for genetic analysis due to specific traits.
Bioinformatics
Use of software tools to analyze biological data.
GWAS
Genome-wide association studies linking genes to traits.
Sickle Cell Anemia
Disease caused by a single genetic mutation.
CRISPR-Cas
Gene editing technology for precise DNA modifications.
Recombinant DNA
DNA formed by combining genetic material from different sources.
Alleles
Different versions of a gene at a locus.
Phenotypes
Observable traits resulting from gene expression.
Germplasm Theory
Concept that heredity is transmitted through germ cells.
PCR
Technique to amplify specific DNA sequences.
Gene Therapy
Treatment aiming to correct defective genes.
Synthetic Organisms
Organisms created with engineered genetic material.
Evolutionary Theory
Framework explaining the diversity of life through genetics.
DNA Sequencing
Determining the precise order of nucleotides in DNA.
RNA-based Vaccines
Vaccines designed using RNA to provoke immune response.
Human Genome Project
International effort to map all human genes.
Genetic Association Studies
Research linking genetic variations to specific traits.
Genetics in Society
Modern medicine, understanding genetic disorders, personalized treatment, GMO agriculture, selective animal breeding, Forensic science, conservation
Aristotle Genetics Theory
"Form" from the father and "matter" from the mother. He believed that environmental factors could affect the ultimate result.
Preformationism
inside egg or sperm is a tiny version of an adult (homunculus)
blending inheritance
An outdated, disreputed theory that the phenotype of an offspring was a uniform blend of the parent's phenotypes.
Pangenisis Theory
A genetics theory that Darwin Believed
Germplasm
Weisman's Genetic Theory
Gregor Mendel
Peaplant research laid the foundations for modern genetics. Disproved blending inheritance theory, and highlighted the presence of dominant and recessive alleles. Helped develop Cell Theory.
Gregor Mendel Time Line
Conducted research in the late 1800s. Died in obscurity, and then his research was rediscovered by Tschermak in the early 1900s.
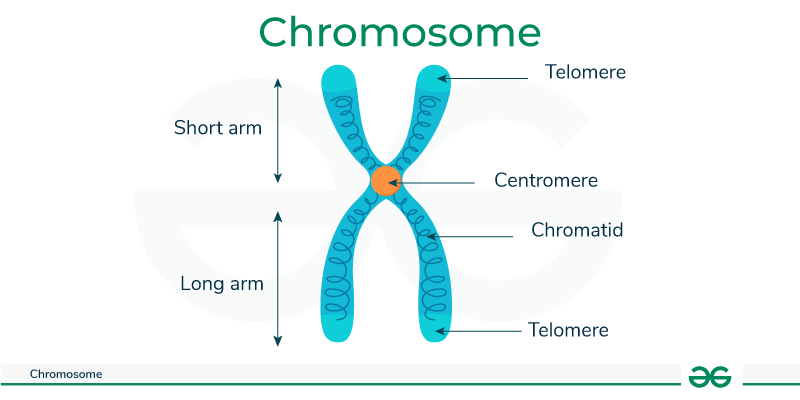
Chromosome Structure
Picture
cell theory
idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
kineticore
a disc shaped protein found in the centromoere region of a chromosome and attaches the chromosome to the mitotic spindle
Spindle Microtuble
microtubules organized in a spindle shape that separate chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
sister chromatids
joined copies of the original chromosome
Telomere
repetitive DNA at the end of a eukaryotic chromosome used for protection (end of a shoelace)
Eukaryotes
organisms made up of one or more cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles; linear DNA; Plants and Animals
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles; DNA is free flowing or circular; bacteria and archea
Transcription
(genetics) the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
Chromosome
a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
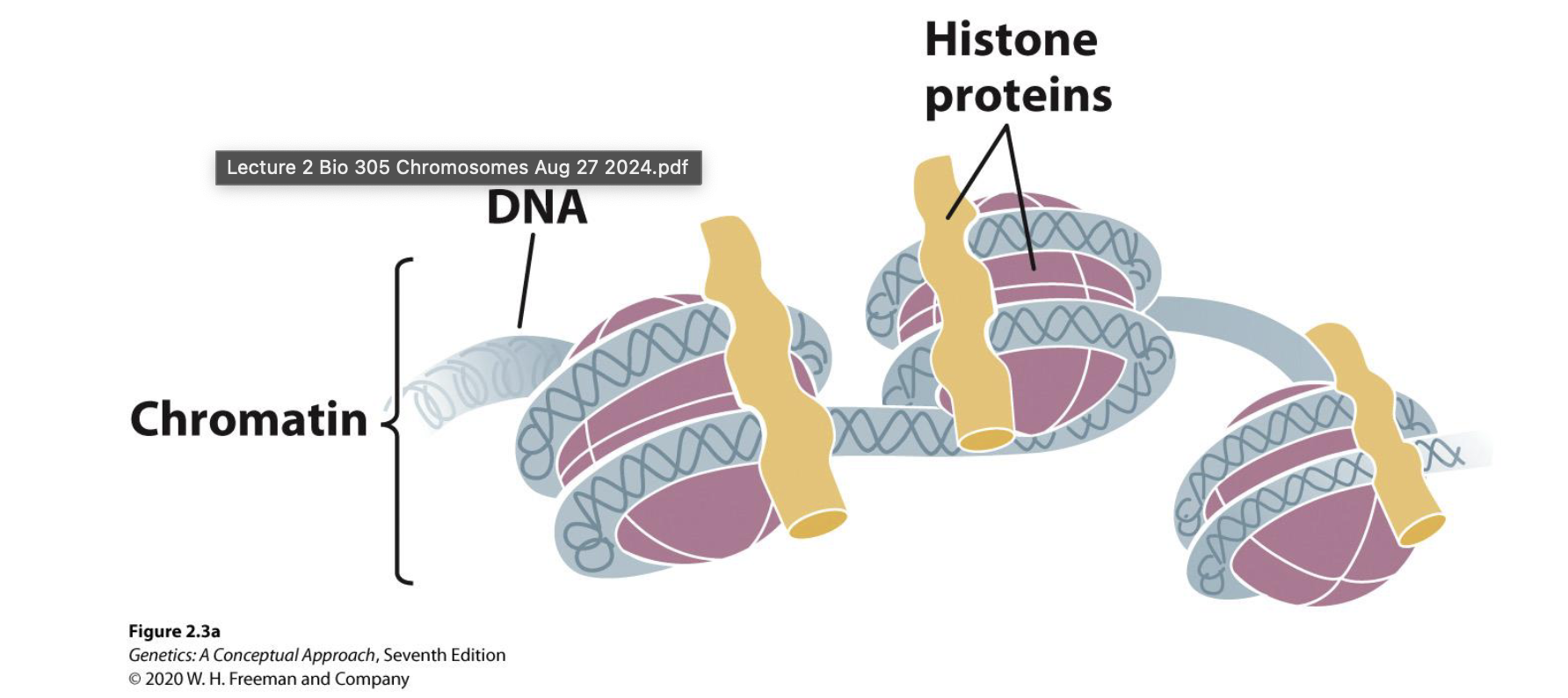
Chromatin structure
DNA + Histone proteins (look up image); (chromosomes are made of chromatin in a much more condensed form)
Phenotypes
Are affected by genes, gene interactions, development, and the eviorment
Mutations
Passed on during cell replication
Insertion
A mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene.
Deletion
A change to a chromosome in which a fragment of the chromosome is removed.
inversion mutation
Reversing of Gene order; recombination is reduced; if it does occur the gametes are often nonviable
Translocation
piece of a chromosome moves to another chromosome (fragile (repeated areas) are more likely to experience translocation)
Evolution
Change in frequency of alleles in a population over time
Bacteria Chromosome Replication
Binary fission
Homologous Pairs
A pair of chromosomes of the same type, one from each parent.
Diploid
2 sets of chromosomes; have the same genes but potentially different alleles on those genes
Halploid
contains one set of chromosomes
Polyploid
condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes
submetacentric chromosome
Chromosome in which the centromere is displaced toward one end, producing a short arm and a long arm (LOOK UP IMAGE)
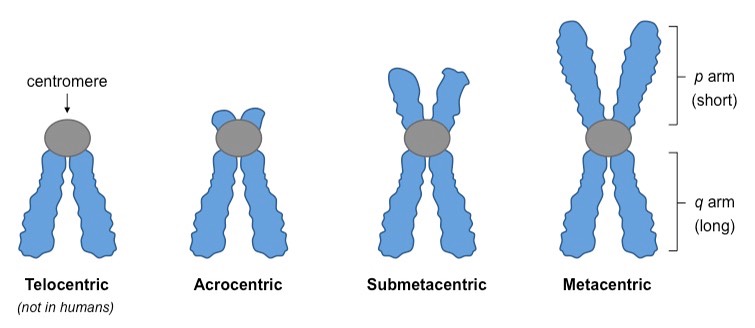
metacentric chromosome
centromere is in the middle (LOOK UP IMAGE)
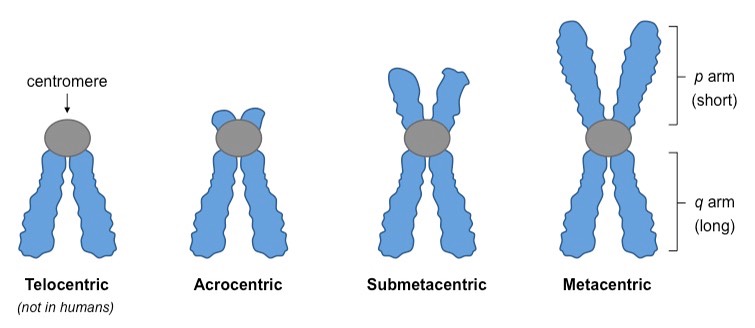
telocentric chromosome
Chromosome in which the centromere is at or very near one end.(LOOK UP IMAGE)
Arocentric chromosome
centromere close to end (LOOK UP IMAGE)
Cell Cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
Interphase
the cell grows and devlops
G1 phase
cell gets larger, proteins are synthesized
G0 phase
Cell is stable, soon renters G1
Check points
Places in the cell cycle that control whether the cell will divide
S phase
DNA is copied in each chromosome (2 sister chromatids)
Chohesin
A ring-shaped protein that keeps sister chromatids together.
G2 phase
cell prepares for mitosis
Interphase time line
23 hours ; difficult to see chromosomes
M phase (mitosis)
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Prophase
Condensin proteins bind DNA and condense into chromosomes (easy to see under microscope); Miotic spindle forms from microtubles
Condensin
proteins that help sister chromatids coil during prophase
mitotic spindle
An assemblage of microtubules and associated proteins that is involved in the movements of chromosomes during mitosis.
microtubles
long strands such a spindle fibers that move chromosomes (made of Tubulin)
Prometaphase
disintegration of the nuclear envelope; spindles enter the nuclear region, and chromosomes become anchored by a centrosome from 1 pole attacking to the kinetochore of a chromatid.
Metaphase
chromsomes align down the middle. Tension grows from spindle fibers pulling each side.
Anaphase
connection between chromatids disolves; microtubes cause splitting of chromatids, Cohesin protein breaks down
Telophase
chromosomes arrive at poles, 2 nuclear envelopes form, cytokinesis, chromosomes no longer visible.
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm (cytoplasm does not split equally)
Crossing Over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis, and produces recombination
Metaphase/Anaphase
Homologous pairs are pulled apart but chromatids stay together due to Shugoshin protein. Random splitting creates variation
Shugoshin
A protein implicated in the protection of cohesiveness of sister chromatids to the centromeres during the process of meiosis and in kinetochore regulation during mitosis and meiosis.
Telophase I (Meiosis)
chromosomes arrive at poles
Meiosis II
Very similar to mitosis, however, you finish with 4 haploids
Anaphase II (Meiosis only)
Shugoshin no longer protects chromatids, and the seperation of chromatids occurs
Meiosis differences from Mitosis
4 cells; half the chromosomes; different cells; crossing over; random distriubtion; over all more variation
Physical entities of genes
Specific segments of DNA that determine traits
Wild Type
the phenotype for a character most commonly observed in natural populations
dihybrid cross
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene (A common ratio is 9:3:3:1)
9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio
Ratio representing possible set of alleles of a dihybrid cross
Male Sex Chromosomes
XY
Female Sex Chromosomes
XX
Biological Sex determination
determined by sex chromosomes; many different types within the animal kingdom
hermaphrodite
an organism that has both male and female sexes (many flowering plants)
monoecious
reproductive structures from both sexes present