Chapter 14- Metals
- They are ductile and malleable because layers of cations can slide over eachother.
- They are hard except Group I metals.
- They have shiny appearances.
- They are good electrical and heat conductors because of a ‘sea’ of mobile electrons.
- They are sonorous.
- They have high melting and boiling points except Group I metals.
- They have high densities except Group I metals.
ALLOYS: MIXTURE OF METALM WITH ANOTHER ELEMENT
- Alloys are harder and stronger because layers cannot slide over each other due to varying sizes.
- Pure metals corrode far more easily than alloys.
- Alloys are often more beautiful and lustrous than pure metals.
- They lower the melting points of metals.
REACTIVITY SERIES
The reactivity series lists the metals in order of decreasing reactivity.
Potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, aluminium, CARBON, zinc, iron, tin, lead, HYDROGEN, copper, mercury, silver, gold, platinum.
Metals until aluminium are extracted by electrolysis only while after carbon they can be extracted by reduction with carbon while after hydrogen, they can be extracted by reduction with hydrogen.

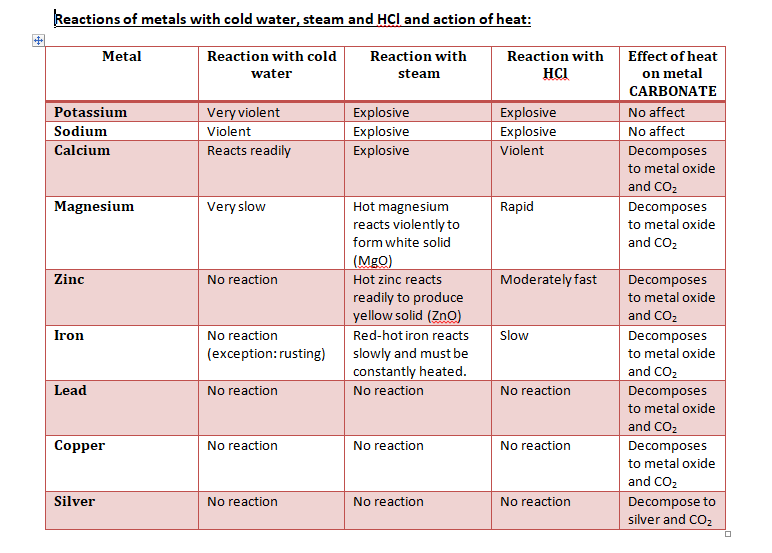
- More reactive metal has a greater tendency to form ions (loses electrons more easily)
- The more reactive a metal, the more difficult it is to reduce its oxide to the metal by carbon or hydrogen.
- The more reactive a metal, the more difficult it is to decompose its carbonate by heat.
EXTRACTION OF METALS
Extraction of metals is done in three main steps:
Concentrating the ore by removing dust and rock.
Extracting metal ores by reduction with carbon/hydrogen or electrolysis.
Purifying the metal.

EXTRACTION OF IRON FROM HAEMATITE 
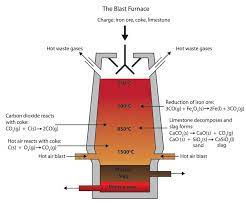
Rusting is the corrosion of the metal iron in presence of water and air. Salts may speed up the process.
It can be prevented by painting, sacrificial protection, galvanising or coating etc.
Sacrificial protection is the attaching of a more reactive metal with iron so it corrodes instead of iron, preventing rusting.
Recycling of metals is an essential process which conserves energy and resources, but is expensive and time-consuming.