Biostatistics, Chapters I & II
Sampling
- Population: complete collection of all measurements or data that are being considered.
- Sample: sub-collecion of members selected from a population
- Simple Random Sample: each member of the population has the same change of being included, and samples are chosen independently
- Cluster Sampling: dividing the population into groups by a category. All of the individuals within the single group are the sample.
- Stratified Random Sampling: divide the population into groups (strata) based on one+ classification criteria. Then perform a simple random sample within each strata
- Sampling Bias: some members of the population have a higher chance to be selected than others.
Variables
- Categorical Variables: two+ categories, but no intrinsic ordering (ex: blood type)
- Ordinal Variable: categorical variables but with a clear ordering (small/medium/large)
- Numeric Variables
- Discrete Variables: a numeric variable for which we can list the possible values (think: integers)
- Continuous Variable: a numeric variable that is measured on a continuous scale (temperature, height)
- Bar Charts: frequency distribution for categorical variables
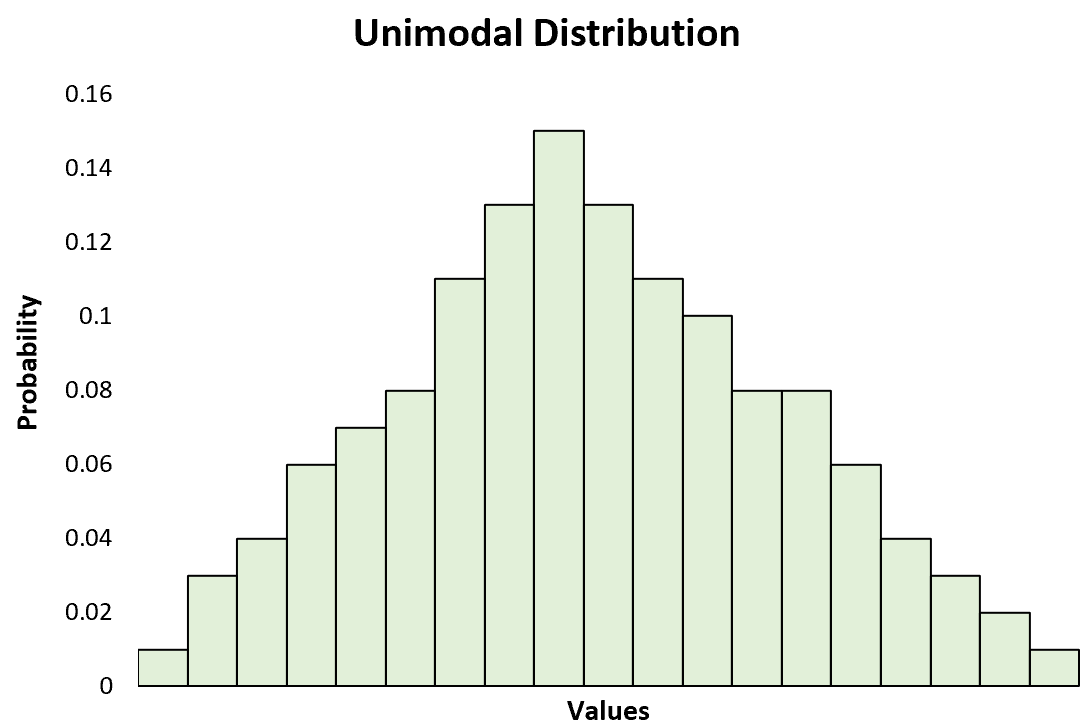
- Histograms: frequency distribution but no spaces
Frequency Variables
- Mean, denoted by ȳ
- Mean: The average of the observations
- Only for discrete or continuous data
- ȳ = (Σ yi)/(n)
- Sensitive to outliers
- Median, denoted by ỹ
- N is odd: (n + 1)th largest value
- N is even: average of (n/2)th largest value and (n/(2) + 1)th
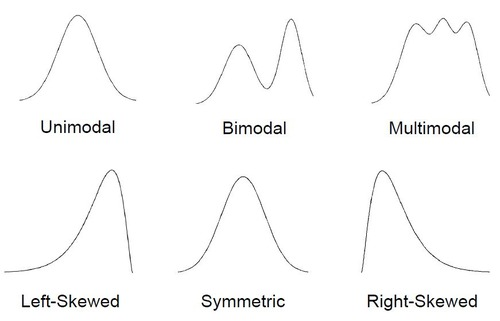
- Symmetric and Unimodal Curve
- Symmetric and Multimodal Curve
Box Plots
- Quartiles
- Q1 = 25th Percentile
- Q2 = 50th Percentile (Median)
- Q3 = 75th Percentile
- Fences
- LF = Q1 - h
- UF = Q3 + h
- h = 1.5(Q3 - Q1)
- Outliers are any points that lie outside of the LF and UF
- Drawing a Box Plot
- Central box from Q1 to Q3
- Line in the middle is Q2
- Whiskers extend to the point CLOSEST to the LF & UF (not the actual values of the fences)
- Outliers are marked by small circles
Label y axis
Variance
- Sample variance
- s^2 = Σ(yi - ȳ)^2 / n - 1
- Remember to subtract one from n
- Simple Standard deviation
- Sqrt(s^2)
- Same unit as the original data value
- \