fundamentals exam 2 study guide (copy)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
1
New cards
what’re the 3 layers of the skin
1. epidermis
2. dermis
3. subcutaneous
2
New cards
what factors can affect skin integrity
* wounds
* vascular wounds
* vascular disease
* diabetes
* malnutrition
* cholesterol and fatty acids
* vitamins and minerals
* medications
* excessive moisture
* external forces (pressure, shear, friction)
* aging (skin elastic decreases)
* vascular wounds
* vascular disease
* diabetes
* malnutrition
* cholesterol and fatty acids
* vitamins and minerals
* medications
* excessive moisture
* external forces (pressure, shear, friction)
* aging (skin elastic decreases)
3
New cards
what is an open wound
actual break in the skins surface
4
New cards
what is a closed wound
the skin is still intact
5
New cards
what are 3 terms used to describe wound depth
* superficial: involves only the dermis
* partial thickness: involves the epidermis and dermis but doesn’t extend through eh dermis to the subQ
* full thickness wound: extends through the dermis to the subQ layer and could extend farther to muscle or bone
* partial thickness: involves the epidermis and dermis but doesn’t extend through eh dermis to the subQ
* full thickness wound: extends through the dermis to the subQ layer and could extend farther to muscle or bone
6
New cards
what is the definition of a clean wound
no infection and the risk o one is low
7
New cards
what is the definition of a contaminated wound
results from a break in sterile technique during surgery
8
New cards
what is the definition of a clean contaminated wound
it is like a clean wound but because the surgery involves organ systems that are likely to contain bacteria the risk of infection is greater
9
New cards
what is the definition of an infected wound
shows clinical signs of infection (redness, warmth, increased drainage that may or may not be purulent (pus containing), and has bacterial counts in the tissue when sampled)
10
New cards
what is the definition of a colonized wound
1 or more organisms are present of the surface of the wound when a culture is obtained but theres no overt sign of an infection in the tissue below the surface
11
New cards
what is an acute wound (healing process term)
a wound that progresses through the phases of wound healing in rapid uncomplicated manner (healed by primary intention) → surgical incisions or traumatic wounds which the edges can be approximated (brought together) to heal
12
New cards
what is a chronic wound (healing process term)
commonly heals by secondary intention → when a wound heals this way new tissue must fill in from the bottom and sides of the wound nail the wound bed is filled with entirely new tissue (these wounds are associated with disease processes → diabetes/vascular disease or wounds that have inhibited proper wound healing)
13
New cards
what are the 3 phases of wound healing
1. inflammatory
2. proliferative
3. maturation
14
New cards
what’re the 3 types of healing intentions
* primary intention: wounds that tend to heal quickly and result in minor scar formation because the edges of the skin can be brought together
* secondary intention: new tissue fills in from the bottom and sides of the wound until the wound bed is filled
* tertiary intention: a delay in wound healing between injury and closure
* secondary intention: new tissue fills in from the bottom and sides of the wound until the wound bed is filled
* tertiary intention: a delay in wound healing between injury and closure
15
New cards
what is an approximated wound
a wound that can be brought together by the edges
16
New cards
what is the inflammatory healing process
* the body initial inflame response happens and lasts about 3 days
* when the injury fort happens bleeding occurs triggering the coagulation cascade which forms a clot to prevent the bleeding
* there is an increased pain, warmth, and swelling in the injured area since the blood vessels are dilated and leak fluid into the tissue surrounding the injury
* when the injury fort happens bleeding occurs triggering the coagulation cascade which forms a clot to prevent the bleeding
* there is an increased pain, warmth, and swelling in the injured area since the blood vessels are dilated and leak fluid into the tissue surrounding the injury
17
New cards
what is the proliferative phase
* when the wound is filled with new granulated tissue (theres development of new blood vessels that are needed to support the new tissue, wound contraction, and epithelialization)
* this lasts usually several weeks (can be shorter if its a surgical closed wound or longer if the wound is larger or left to heal via secondary intention)
* epithelial cells move laterally form the edges of the wound across the granulated moist tissue until the wound has been resurfaced with epithelial cells and normal skin layers are reestablished (THIS IS WHY WE USE MOIST WOUND DRESSINGS TO PROMOTE AND SUPPORT WOUND HEALING IN THIS WAY)
* this lasts usually several weeks (can be shorter if its a surgical closed wound or longer if the wound is larger or left to heal via secondary intention)
* epithelial cells move laterally form the edges of the wound across the granulated moist tissue until the wound has been resurfaced with epithelial cells and normal skin layers are reestablished (THIS IS WHY WE USE MOIST WOUND DRESSINGS TO PROMOTE AND SUPPORT WOUND HEALING IN THIS WAY)
18
New cards
what is the maturation phase
* this is remodeling that can last up to a year
* collagen is deposited more cuasing scar tissue formation thats strengthened due to the collagen
* the strength of scar tissue only can reach 80% of its previous strength
* collagen is deposited more cuasing scar tissue formation thats strengthened due to the collagen
* the strength of scar tissue only can reach 80% of its previous strength
19
New cards
what factors affect wound healing
* oxygenation and tissue perfusion
* diabetes
* nutrition
* age
* infection
* diabetes
* nutrition
* age
* infection
20
New cards
what is dehiscence
a PARTIALof separation of the tissue layers during the healing process (usually deals with connection with surgical incisions) → if sutures break open because of something you possibly did
21
New cards
what is evisceration
TOTAL separation of the tissue layer allowing the protrusion of visceral organs through the incision
22
New cards
what is the best form of action for an eviscerate wound
splinting (if its not splinted it will create a FISTULA/hole)
23
New cards
what is a stage 1 pressure ulcer description
* an intact, non-blistered skin with non-blanchable erythema (persistent redness) → NO SKIN BREAK DOWN YET
24
New cards
what is a stage 2 pressure ulcer description
a PARTIAL THICKNESS skin loss that involves the EPIDERMIS and exposes some of the DERMIS → blistering skin
25
New cards
what is a stage 3 pressure ulcer description
a FULL THICKNESS tissue loss the extends to the SUBQ layer but doesn’t go to the muscles or bones → can have tunneling that must be measured and recorded
26
New cards
what is a stage 4 pressure ulcer description
a FULL THICKNESS tissue loss with exposed MUSCLE AND BONE → osteomyelitis is a risk for this stage since exposed bone is possible (this stage MAY need to have slough cleaned out to determine the true depth and levels of tunneling thats occurred)
27
New cards
what is an unstageable pressure ulcer description
an OBSCURED FULL THICKNESS tissue/skin loss where the amount of necrotic tissue and eschar (black/brown) /slough (white/cream/yellow) in the wound makes it impossible to determine the true depth of wound and tunneling → just can tell how bad it is
28
New cards
what increases the risk for pressure ulcers
* patients inability to feel pain
* unable to respond to pain appropriately
* limited to their ability to move/maintain position
* unable to respond to pain appropriately
* limited to their ability to move/maintain position
29
New cards
what tools are used to assess pressure ulcers
braden scale → ranks the risk factor, sensory perception, moisture, activity, mobility, nutrition, and friction
Norton scale → ranks the physical condition, mental state, activity, mobility, continence of patient (low risk = 16-30 / moderate risk = 11-15 or below / high risk = 10 or below)
Norton scale → ranks the physical condition, mental state, activity, mobility, continence of patient (low risk = 16-30 / moderate risk = 11-15 or below / high risk = 10 or below)
30
New cards
what are the score description for Braden scale
* 23 means theres NO RISK for developing ulcer
* high risk = 10-12
* VERY high risk = 9 or less
* the lowest possible score of SIX means there at the highest risk for an ulcer
* high risk = 10-12
* VERY high risk = 9 or less
* the lowest possible score of SIX means there at the highest risk for an ulcer
31
New cards
what assessments need to be done if a patient has a wound
* location
* size
* presence of undermining or tunneling
* drainage (COCA)
* conditions of wound edges and surrounding tissue (white ring around wounds and fresh tissue growing right next to the wounds barrier → this is maceration (due to being exposed to excess moisture))
* size
* presence of undermining or tunneling
* drainage (COCA)
* conditions of wound edges and surrounding tissue (white ring around wounds and fresh tissue growing right next to the wounds barrier → this is maceration (due to being exposed to excess moisture))
32
New cards
what is the difference between serous, serosanguineous, and sanguineous
* serous: clear watery fluid from plasma
* serosanguineous: pink to pale red and contain a MIX of serous fluid and red bloody fluid
* sanguineous: indicates bleeding and is BRIGHT red
* serosanguineous: pink to pale red and contain a MIX of serous fluid and red bloody fluid
* sanguineous: indicates bleeding and is BRIGHT red
33
New cards
what does COCA stand for
color
odor
consistency
amount
odor
consistency
amount
34
New cards
what does maceration mean
condition where excessive moisture causes a softening of the skin (white ring forms around a wound)
35
New cards
what’re ways to prevent a pressure ulcer
* frequent position changes: every 2 hours, elevate egad NO MORE than 30 degrees to reduce shear effects, when side lying position patient at 30 degrees rather than 90 to prevent pressure on bony prominences
* use cushions (waffle padded boots)
* skin hygiene
* spread out body weight over a greater surface area
* use cushions (waffle padded boots)
* skin hygiene
* spread out body weight over a greater surface area
36
New cards
what is a Jackson Pratt (JP) drain
a closed drainage system (usually sutured in place) where a soft drain is attached to a springlike suction device → these deal with orthopedic and abdominal surgery patients
* this promotes healing and reduces number of microorganism entering because its closed (no open ends)
* this promotes healing and reduces number of microorganism entering because its closed (no open ends)
37
New cards
what is a hemovac drain
a closed drainage system (usually sutured in place) where a soft drain is attached to a springlike suction device → these deal with orthopedic and abdominal surgery patients
* this promotes healing and reduces number of microorganism entering because its closed (no open ends)
* this promotes healing and reduces number of microorganism entering because its closed (no open ends)
38
New cards
what is a Penrose drain
an open drainage system thats a flexible piece of tubing not surgically sutured inplace
* \*abdominal surgery\* particularly after incision and drainage procedures, gallbladder surgery, or other operative procedures involving the common bile duct
* The system drains excess fluid to the outside of the body (the pressure inside the wound is greater than the pressure outside the body; therefore the drainage flows out of the tube onto the dressing)
* the drains typically are inserted through stab wounds a few centimeters away from the surgical incision line, to prevent any interference with healing of the main surgical site
* \*abdominal surgery\* particularly after incision and drainage procedures, gallbladder surgery, or other operative procedures involving the common bile duct
* The system drains excess fluid to the outside of the body (the pressure inside the wound is greater than the pressure outside the body; therefore the drainage flows out of the tube onto the dressing)
* the drains typically are inserted through stab wounds a few centimeters away from the surgical incision line, to prevent any interference with healing of the main surgical site
39
New cards
what is a wound va drain
uses negative pressure to remove excess wound fluid, stabilize wound edges, and stimulate granulated tissues
40
New cards
what is an infection
a disease state caused by an infectious agent that occurs when a pathogen multiplies in a susceptible host
41
New cards
what is asepsis
freedom from and prevention of disease causing contamination
42
New cards
what is sepsis
a serious condition resulting from the presence of harmful __microorganisms__ in the blood or other tissues and the body’s response to their presence, potentially leading to the __malfunctioning__ of various organs, shock, and death
43
New cards
what is a sterile body area vs a non sterile body area
sterile: any place a microorganism can’t reach (blood, urine, CSF)
unsterile: any place where microorganisms can reach (skin, mouth, organs)
unsterile: any place where microorganisms can reach (skin, mouth, organs)
44
New cards
what’re the lines fo defense of the body
1. normal flora
2. inflammatory
3. immune response (innate (immediate defense)/adaptive (long term immunity))
45
New cards
what normal flora may cause problems
* S. aureus
* C. Diff
* C. Diff
46
New cards
signs and symptoms of inflammation
* fever
* chills
* malaise
* altered mental status
* redness
* heat
* pain and swelling at the site
* chills
* malaise
* altered mental status
* redness
* heat
* pain and swelling at the site
47
New cards
what is an ANTIGEN
substance that provokes adaptive immune response (nonliving things: toxins chemicals, drugs, foreign particles)
48
New cards
what is an ANTIBODY
immunoglobulin molecules that recognizes foreign invaders
49
New cards
what is innate immunity
(nonspecific) provides immediate defense against foreign antigens, produces chemical mediators that fight infection, remove foreign substance (activate the adaptive immune system)
50
New cards
what is adaptive immunity
(specific/aquired) provides long-term immunity when the body is exposed to an antigen
* Humoral (antibody-mediated → WBC involvement, and happens within lamp and and blood)
* Cellular (cell-mediated → WBC involvement when body doesn’t know whats attacking it)
^^both are types of adaptive immunity^^
* Humoral (antibody-mediated → WBC involvement, and happens within lamp and and blood)
* Cellular (cell-mediated → WBC involvement when body doesn’t know whats attacking it)
^^both are types of adaptive immunity^^
51
New cards
what is active immunity
immunity to a pathogen that occurs following exposure to said pathogen (vaccines)
52
New cards
what is passive immunity
immunity given from one person to another (breastfeeding or placenta)
53
New cards
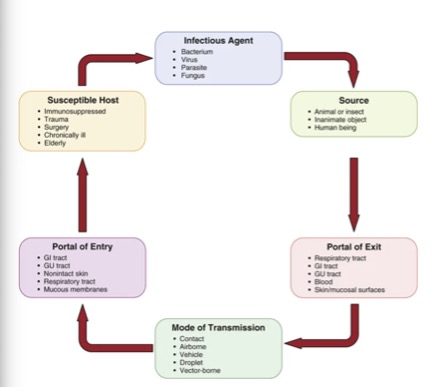
what are the steps in chain of infection (with examples)
54
New cards
what is HAI
healthcare associated infections → formerly referred to as NOSOCOMIAL infections
* infections acquired while the patient is receiving treatment in a facility (hospital, long term care, nursing home)
* HAIs are associated with the use of medical devices such as catheters and ventilators, complications after a surgical procedure, contagious transmission between patients and health care workers, and the overuse of antibiotics
* infections acquired while the patient is receiving treatment in a facility (hospital, long term care, nursing home)
* HAIs are associated with the use of medical devices such as catheters and ventilators, complications after a surgical procedure, contagious transmission between patients and health care workers, and the overuse of antibiotics
55
New cards
what is the most effective method to fighting infections
* hand washing/ alcohol based sanitizer
* precautions and isolation (airborne, droplet, contact precautions)
* precautions and isolation (airborne, droplet, contact precautions)
56
New cards
what is an acute infection
develop and run their coarse rapidly (coughs, colds, ear infections) → last 10-14 days
57
New cards
what is a chronic infection
may persist for months/years (wounds, bone infections, hepatitis, AIDS)
58
New cards
what’re are signs and symptoms of systemic infections
infections that infiltrate the bloodstream → can cause fever, increases in heart and respiratory rates, lethargy, anorexia, and tenderness or enlargement of lymph nodes
59
New cards
what patients are risk for infection
people with chronic diseases, alterations in the immune system, medications such as chemotherapeutic drugs, alterations in skin integrity, malnutrition, indwelling medical devices such as urinary catheters, lack of proper immunizations
60
New cards
what is the complete blood count (CBC) lab
* identifies and counts the 7 types of cells found in the blood, red blood cell, neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, and platelet
* it can detect: Anemia, Autoimmune disorders, Bone marrow disorders, Dehydration, Infections, Inflammation, Hemoglobin abnormalities, Leukemia.
* it can detect: Anemia, Autoimmune disorders, Bone marrow disorders, Dehydration, Infections, Inflammation, Hemoglobin abnormalities, Leukemia.
61
New cards
what is a differential white blood cell count (WBC) lab
* It helps determine whether the body is mounting an immune response to an infection
* a normal level is 4500-10500 → anything higher than this can indicate infection
* a normal level is 4500-10500 → anything higher than this can indicate infection
62
New cards
what is an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) lab
* it measures the degree of inflammation in the body
* An ESR that remains elevated indicates a poor response to current therapy, whereas an ESR that decreases indicates a good response
* An ESR that remains elevated indicates a poor response to current therapy, whereas an ESR that decreases indicates a good response
63
New cards
what is a culture and sensitivity test (C&S)
* this is used to determine what kind of bacteria is in a possible infection → the presence of bacteria has a positive result
* there is a blood, urine, stool, or wound drainage
* the culture parts determine the pathogen and the sensitivity determines the nit biotic needed
* there is a blood, urine, stool, or wound drainage
* the culture parts determine the pathogen and the sensitivity determines the nit biotic needed
64
New cards
who should we use standard precaution on and what is standard precaution
* everyone
* hand washing/sanitizing and gloving
* hand washing/sanitizing and gloving
65
New cards
what is contact isolation
* transmission of contagious disease may occur through several routes: direct and indirect
* disease requiring contact precaution: multi drug resistant organisms, scabies and herpes simplex virus, and draining wounds where they have been cultured (USE GLOVES AND GOWN)
* disease requiring contact precaution: multi drug resistant organisms, scabies and herpes simplex virus, and draining wounds where they have been cultured (USE GLOVES AND GOWN)
66
New cards
what is airborne isolation
* this is used when known or suspected contagious diseases can be transmitted via small droplets or particles that’re suspended in the air
* this type requires negative pressure rooms with high efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration system
* people need to wear N95 mask (needs to be fitted)
* diseases that require this: varicella, rubella/measles, TB
* this type requires negative pressure rooms with high efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration system
* people need to wear N95 mask (needs to be fitted)
* diseases that require this: varicella, rubella/measles, TB
67
New cards
what is droplet isolation
* this is used when known contagious disease can be transmitted through large droplet suspended in the air (coughing, sneezing, or talks)
* diseases that use this: pharyngeal diphtheria, mumps, rubella, pertussis, scarlet fever, meningococcal sepsis, and influenza
* diseases that use this: pharyngeal diphtheria, mumps, rubella, pertussis, scarlet fever, meningococcal sepsis, and influenza
68
New cards
what is protective isolation
* this is used for patients who have a compromised immune systems (protects the patients from microorganisms)
* diseases that need this: immunosuppression, including leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, aplastic anemia, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, and severe sepsis
* patients rooms need positive pressure HEPA filtration, anyone entering needs a mask and wash hands, nothing alive in the room or fresh fruits/veggies in the room
* diseases that need this: immunosuppression, including leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, aplastic anemia, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, and severe sepsis
* patients rooms need positive pressure HEPA filtration, anyone entering needs a mask and wash hands, nothing alive in the room or fresh fruits/veggies in the room
69
New cards
what is medical asepsis
(often referred to as clean technique) procedures include handwashing, wearing gloves, gowning, and disinfecting
70
New cards
what is surgical asepsis
* (sterile technique) is used to prevent the introduction of microorganisms from the environment to the patient
* Surgical asepsis is used for: surgical procedures, invasive procedures such as catheterization, procedures that invade the bloodstream or break the skin, dressing changes, and wound care
* Surgical asepsis is used for: surgical procedures, invasive procedures such as catheterization, procedures that invade the bloodstream or break the skin, dressing changes, and wound care
71
New cards
what is the definition of pain
An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such
72
New cards
what does nociception mean
process when the sensation of tissue injury is conducted from the peripheral to the central nervous system
73
New cards
what is pain threshold
lowest intensity at which the brain recognizes the stimulus as pain
74
New cards
what is pain tolerance
intensity/duration of pain that a patient is able or willing to endure
75
New cards
what is acute pain
* occurs abruptly after an injury or disease, persists until healing occurs, and often is intensified by anxiety or fear
* lasts LESS THAN 6 months
* lasts LESS THAN 6 months
76
New cards
what is chronic pain
* may be malignant or nonmalignant but lasts for a prolonged period of time during prolonged tissue pathology or pain that persists beyond the normal healing period for an acute injury or disease
* lasts MORE THAN 6 months
* lasts MORE THAN 6 months
77
New cards
what is nociceptive pain
Physiologic pain in response to trauma, injury, or inflammation
78
New cards
what is visceral pain
inner pain with the organs (appendix, pancreas, bowels)
79
New cards
what is somatic pain
outer pain with the body (skin, muscles, bones, and joints)
80
New cards
what is neuropathic pain
pain with the nerves
81
New cards
what is phantom pain
brain receives pain message from area of amputation
82
New cards
what is psychogenic pain
no physical cause but can be caused by mental, emotional, or behavioral factors
83
New cards
what are (physiologic) vital sign changes for acute pain
* increased blood pressure, heart rate, increased respirations
* diabetics have increased blood glucose due to stress or pain
* diabetics have increased blood glucose due to stress or pain
84
New cards
what are the types of pain assessment tools to use
* 10cm visual analog scale (0-10)
* Wong-baker faces pain scale
* the nonverbal pain scale
* SOCRATES (site, onset, character, radiation, associations, time course, exacerbating relieving factors, severity)
* Wong-baker faces pain scale
* the nonverbal pain scale
* SOCRATES (site, onset, character, radiation, associations, time course, exacerbating relieving factors, severity)
85
New cards
what is the purpose for documenting and what is documenting
to describe facts clearly and concisely to improve communication
* ´the written, or electronically generated, information about a patient that describes the patient, the patient’s health, and a care and service provided, including the dates of care.
* ´the written, or electronically generated, information about a patient that describes the patient, the patient’s health, and a care and service provided, including the dates of care.
86
New cards
what’re the purposes of patient record
* Communication
* Reimbursement
* Care Planning
* Education
* Quality Review
* Decision Analysis
* Legal
* Documentation
* Research
* Historical Documentation
* Reimbursement
* Care Planning
* Education
* Quality Review
* Decision Analysis
* Legal
* Documentation
* Research
* Historical Documentation
87
New cards
what’re important considerations for guidelines for documenting
* timing: needs the date and time of any recording
* confidentiality: keep this as a legal private record (access is restricted to health professionals)
* permanent: enteries made in dark colored black so its permanent and changes can be indicated
* signature: each recording is signed by the nurse doing the assessment/charting (needs name and title → O. Rose R.N.) → don’t walk away before logging off
* accuracy: all recordings must be accurate and correct → with facts and exact observations (quote directly, spell correctly, avoid general words, draw a line through errors needing corrected and blank spaces)
* sequence: recording events in the order they occurred (assessments, interventions, and patients response)
* appropriateness: only record info that pertains to patients health and care
* use of standard terminology: use only commonly accepted symbols, abbreviation, and terms specified by agency
* confidentiality: keep this as a legal private record (access is restricted to health professionals)
* permanent: enteries made in dark colored black so its permanent and changes can be indicated
* signature: each recording is signed by the nurse doing the assessment/charting (needs name and title → O. Rose R.N.) → don’t walk away before logging off
* accuracy: all recordings must be accurate and correct → with facts and exact observations (quote directly, spell correctly, avoid general words, draw a line through errors needing corrected and blank spaces)
* sequence: recording events in the order they occurred (assessments, interventions, and patients response)
* appropriateness: only record info that pertains to patients health and care
* use of standard terminology: use only commonly accepted symbols, abbreviation, and terms specified by agency
88
New cards
what’re the formats for nursing documentation
* Initial Nursing Assessment
* Kardex Care Plan
* Plan of Nursing Care
* Critical/Collaborative Pathways
* Progress Notes
* Flow Sheets
* Discharge and Transfer Summary
* ´Home Healthcare Documentation
* Kardex Care Plan
* Plan of Nursing Care
* Critical/Collaborative Pathways
* Progress Notes
* Flow Sheets
* Discharge and Transfer Summary
* ´Home Healthcare Documentation
89
New cards
what’re components of Flow sheets
* Graphic Sheet
* 24-Hour Fluid Balance Record
* Medication Record
* 24-Hour Patient Care Record
* 24-Hour Fluid Balance Record
* Medication Record
* 24-Hour Patient Care Record
90
New cards
what’re some problems with documentation
* 1 in 4 malpractice suits are determined on the basis of patient record
* documentation content that increases risk for legal problems (objective things)
* documentation mechanics that increases risk for legal problems
* documentation content that increases risk for legal problems (objective things)
* documentation mechanics that increases risk for legal problems
91
New cards
whats the difference between EMR and EHR
* EMR: record of one episode→ certain patients current chart
* EHR: record from different doctors and long term view
* EHR: record from different doctors and long term view
92
New cards
what is CPOE
computer physicians order entry → access via password and verification codes
* providers entering and sending treatment instructions (including medication, laboratory, and radiology orders) – via a computer application rather than paper, fax, or telephone
* providers entering and sending treatment instructions (including medication, laboratory, and radiology orders) – via a computer application rather than paper, fax, or telephone
93
New cards
what is MAR
medication administration record: a drug chart that tells you the patients 6 rights of med administration (nurse must go over them 3 times prior to giving med)
94
New cards
whatre some issues of not giving good report
When a plan is not communicated to all members of the health care team, care becomes fragmented, tasks are repeated, and delays or omissions in care often occur
95
New cards
what is SBAR and what it used for
* s: situation
* B: background
* A: assessment
* R: recommendation
* its used for communication between health care professionals
* B: background
* A: assessment
* R: recommendation
* its used for communication between health care professionals
96
New cards
what an incident report
When an unusual and unexpected event involving a patient, visitor, or staff member occurs, an incident report is completed → falls, med errors, equipment malfunctions
* not apart of medical record
* factual only, objective, nonjudgemental
* not apart of medical record
* factual only, objective, nonjudgemental
97
New cards
what the importance of using informatics in nursing
The use of information and computer technology to support all aspects of nursing practice, including direct delivery of care, administration, education, and research
* this is recognized as a specialty in nursing
* this is recognized as a specialty in nursing
98
New cards
what does DIKW stand for and what does it mean
D= data (facts)
I= information (organized data)
K= knowledge ( organized info thats meaningful)
W= wisdom (appropriate application of knowledge)
I= information (organized data)
K= knowledge ( organized info thats meaningful)
W= wisdom (appropriate application of knowledge)
99
New cards
what is BCMA used for
bar-code medication administration is used as a part of the process of med administration (fewer errors made)
100
New cards
what is stroke volume
amount of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each CONTRACTION