Urinary System Anatomy and Function: Kidneys, Nephrons, and Pathways
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Urinary System
Aka The Renal System; Function: regulation of the blood by filtration and production of urine.
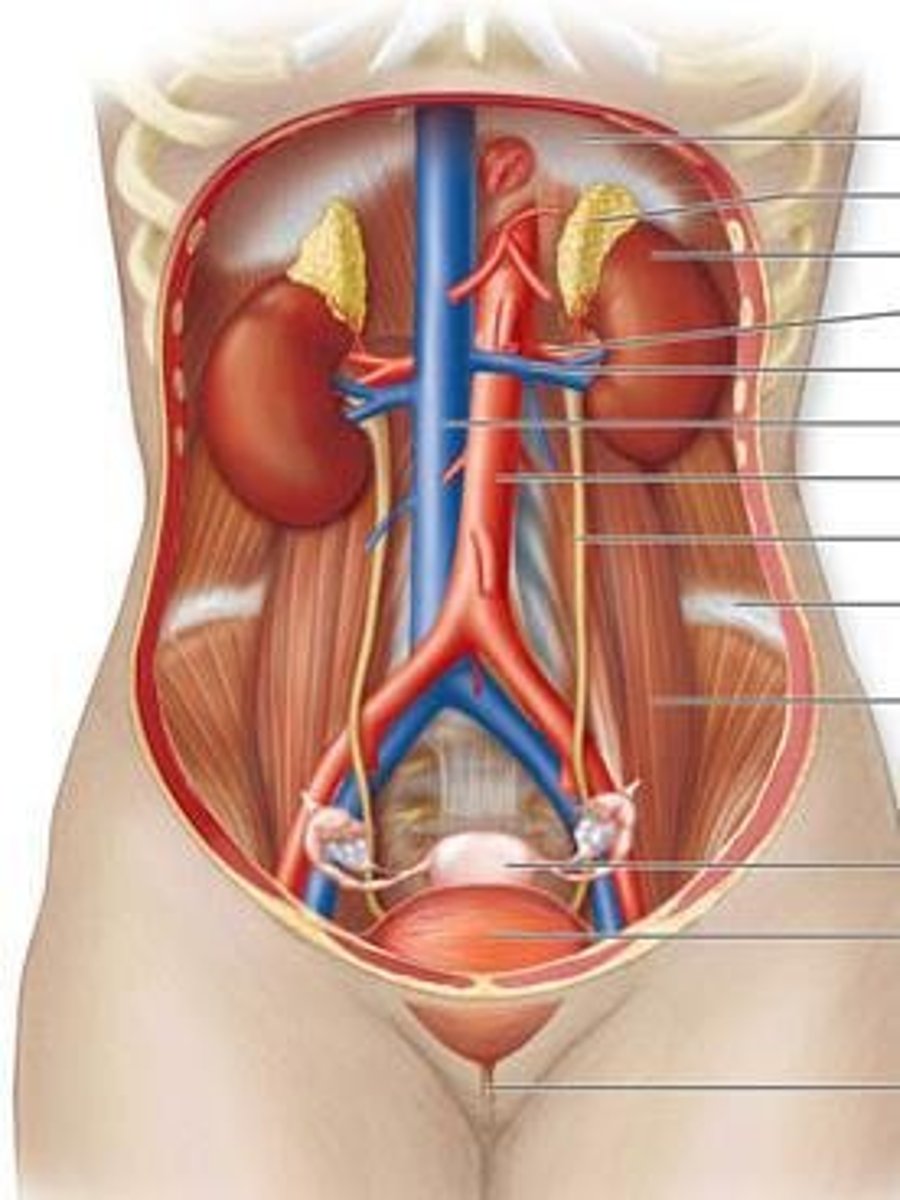
Kidney
Filter the blood; one pair (two) located along the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity.
Ureter
Transport urine to bladder.
Bladder
Store urine; contains rugae that allows for expansion.
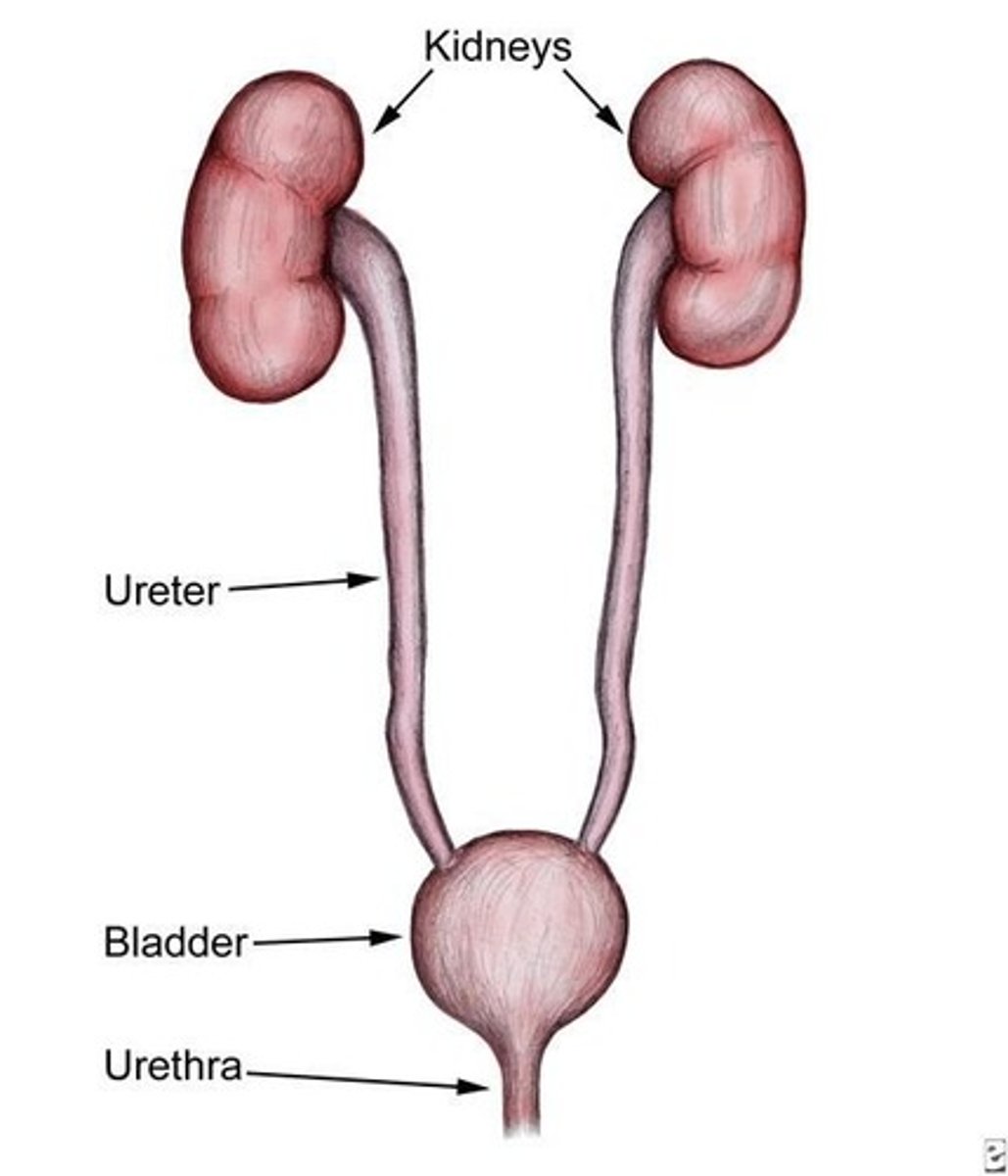
Urethra
Conveys urine from the body.
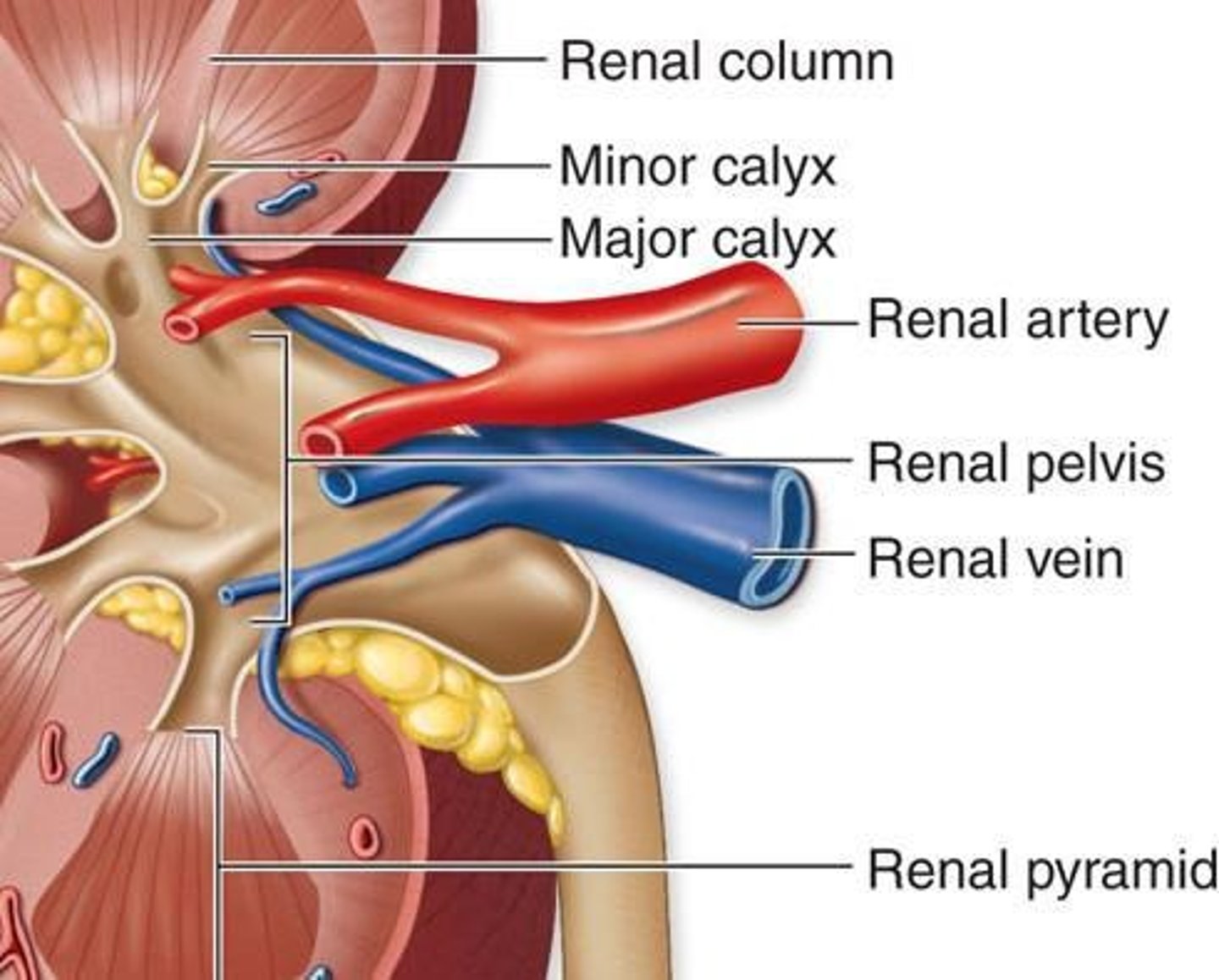
Hilum
Concave medial border where blood vessels, nerves, and ureters enter/leave the kidney.
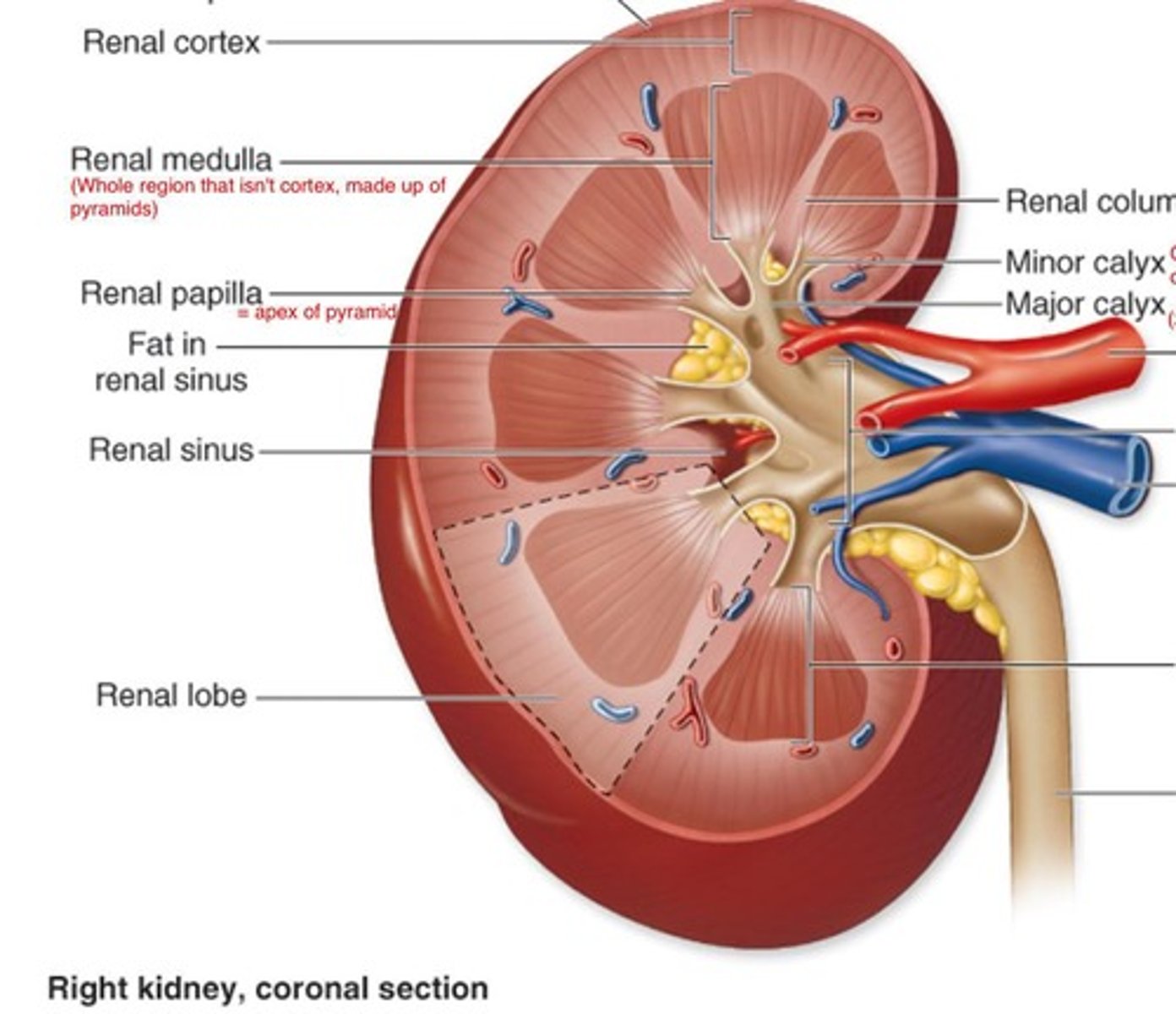
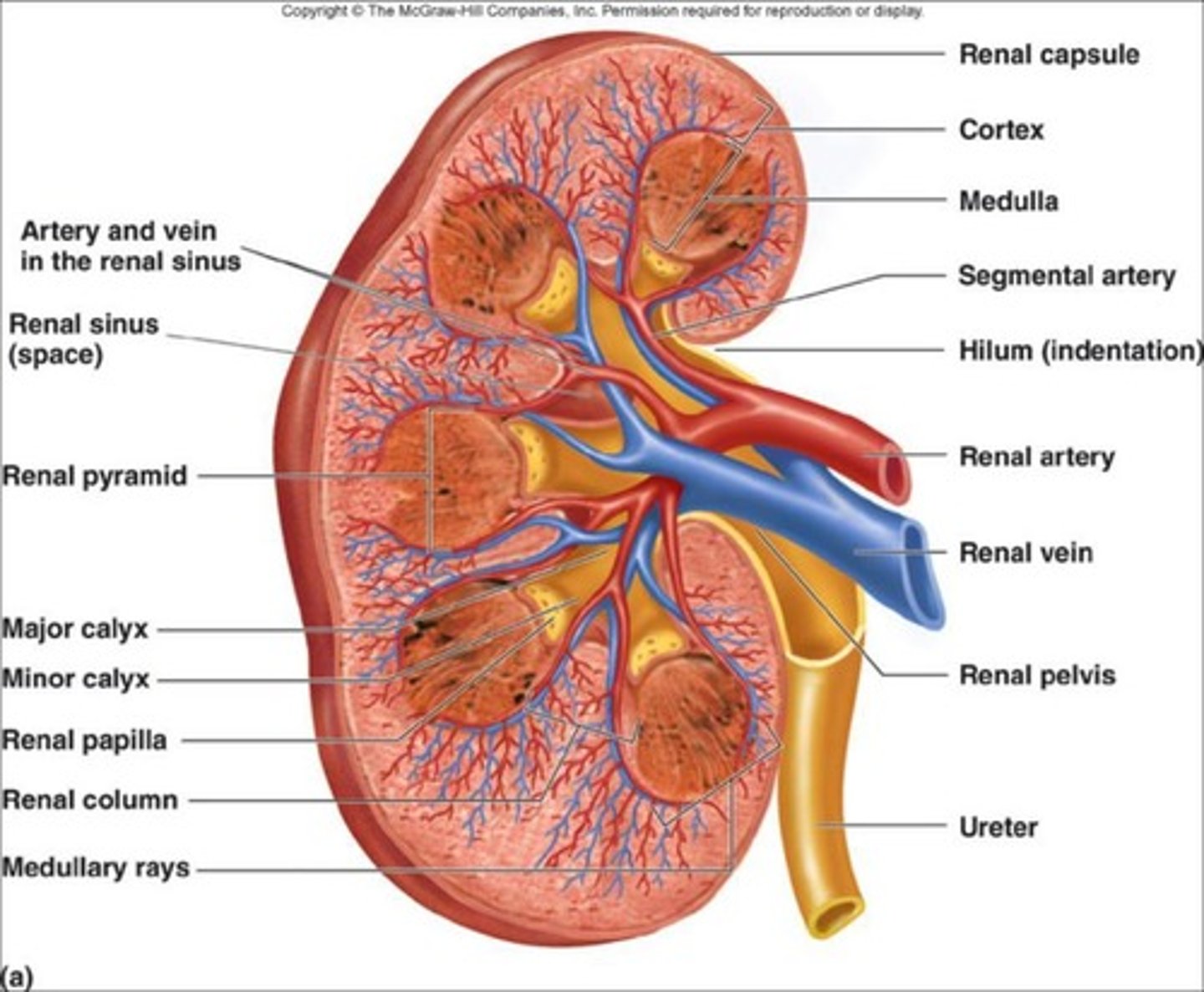
Renal Sinus
Internal space within each kidney; houses renal arteries, renal veins, lymphatic vessels, nerves, renal pelvis, renal calyces.
Renal Cortex
Outer region/layer of the kidney.
Renal Medulla
Inner region/layer of the kidney; darker shade than renal cortex; divided into renal pyramids.

Renal Columns
Extension of renal cortex into the medulla.
Renal Pyramids
Subdivision of medulla created by renal columns; there are approximately 8-15 pyramids/kidney in adults.
Renal Papilla
Tip or apex of renal pyramid; points towards renal sinus.
Corticomedullary Junction
Meeting of cortex and medulla; located at base of pyramid.
Minor Calyx
Funnel shaped space at end of renal papilla; 1 minor calyx for each renal papilla.
Major Calyx
Formed by merger of 2 or more minor calyces; each kidney contains 2-3 major calyces.
Renal Pelvis
Large funnel shaped space formed by merger of all major calyces; collects urine and transports to ureter.
Nephron
The microscopic functional unit of the kidney; both kidneys contain a total of 2.5 million nephrons.

Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Small tubule originating from glomerular capsule; functions to reabsorb water, nutrients, and ions from the filtrate.
Nephron Loop (Loop of Henle)
Originates at sharp bend in proximal convoluted tubule; consists of descending limb and ascending limb.
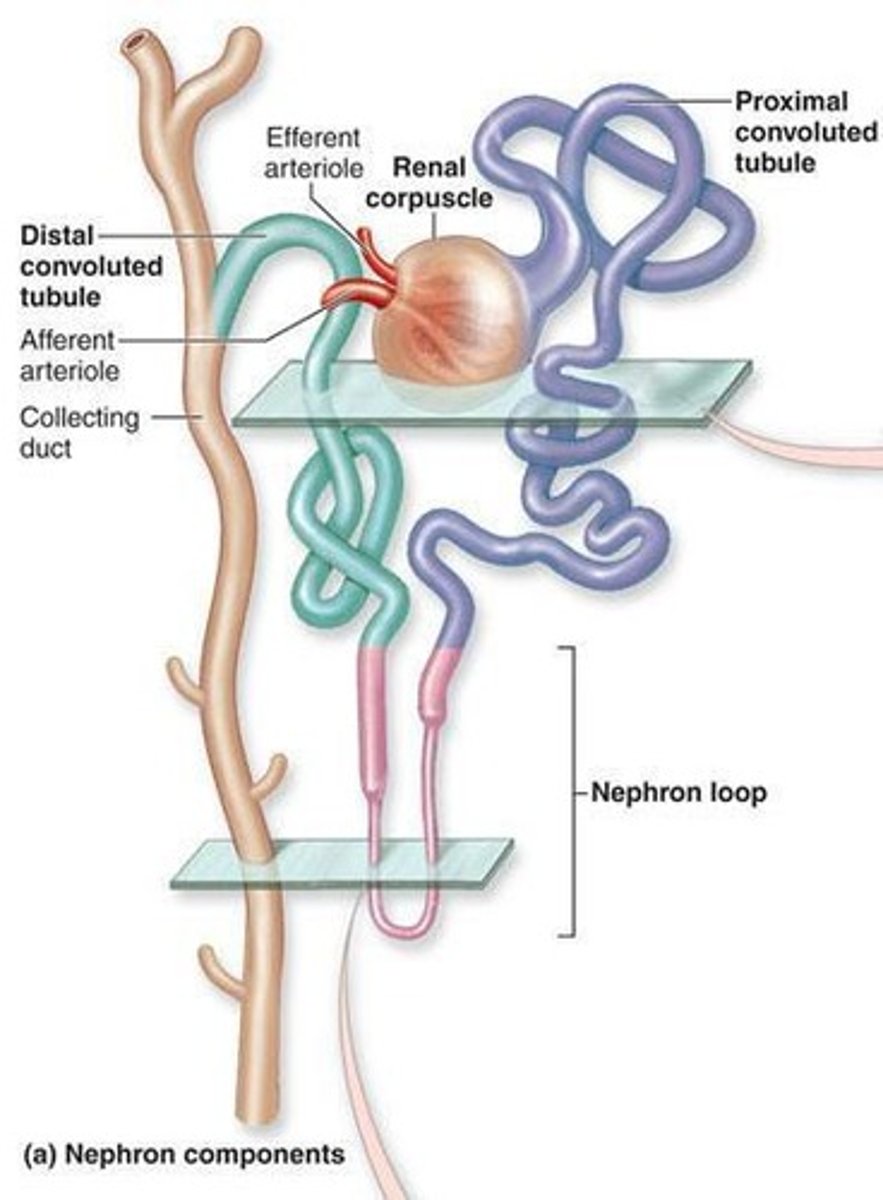
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Originates in renal cortex at end of thick ascending limb of loop of Henle; leads to collecting duct.
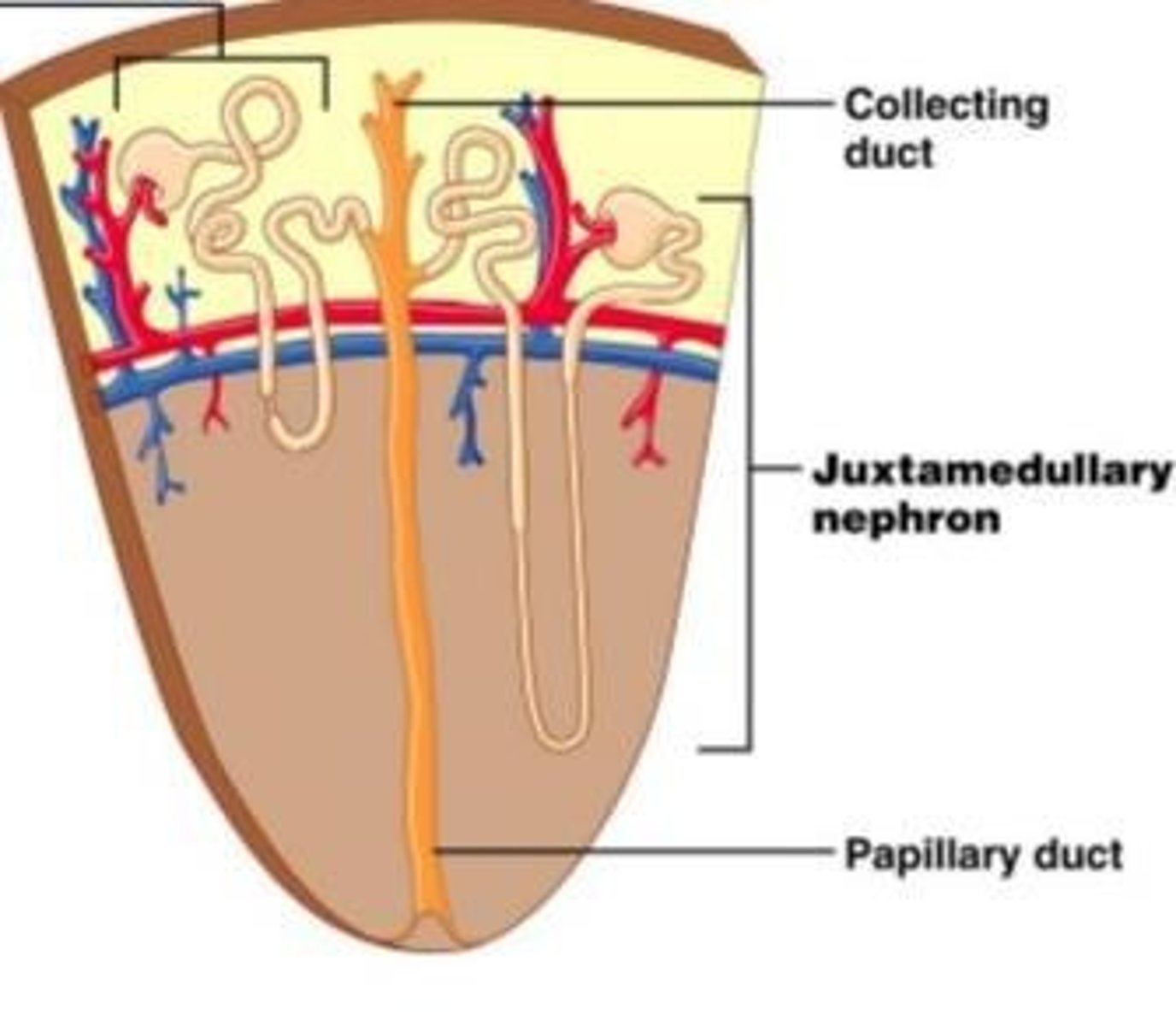
Collecting Duct
Collects fluid from distal convoluted tubules; runs through medulla towards renal papilla.
Cortical nephron
85% of nephrons; most of nephron lies in the renal cortex; has short loop of Henle.
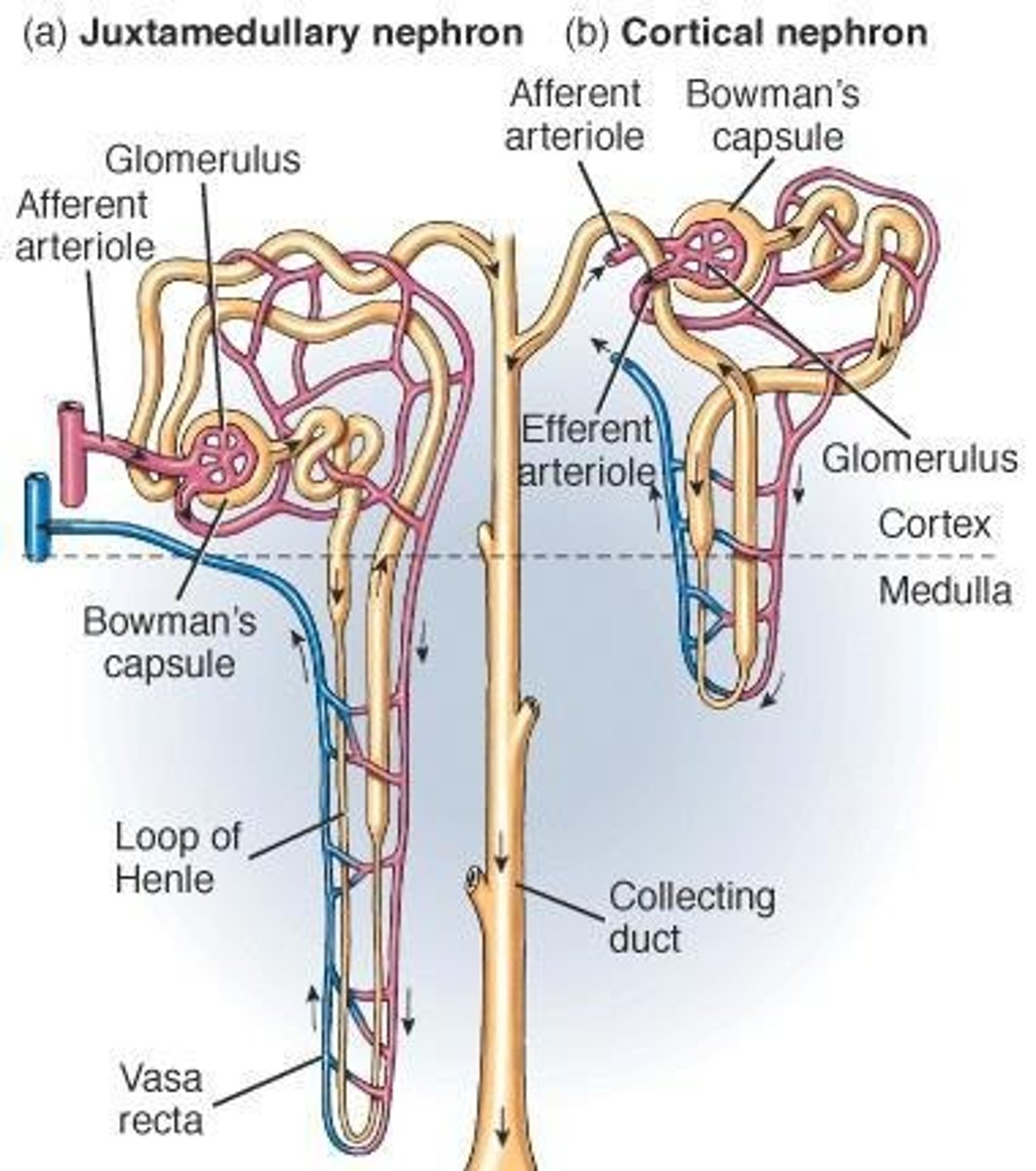
Juxtamedullary nephrons
Renal corpuscle lies next to corticomedullary junction; have long loops that extend deep into the medulla.
Peritubular capillaries
Capillaries that surround the PCT and DCT in renal cortex.

Vasa recta
Capillaries that surround the Nephron loop in renal medulla.
Renal Artery
Blood supply to kidneys.
Segmental Artery
Branch to superior/inferior regions of kidney.
Interlobar Artery
Flows between adjacent lobes.
Arcuate Artery
Flows along cortico-medullary junction.
Interlobular Artery
Branches off of arcuate artery into the cortex.
Afferent Arteriole
Enters microscopic filtering units of the kidney.
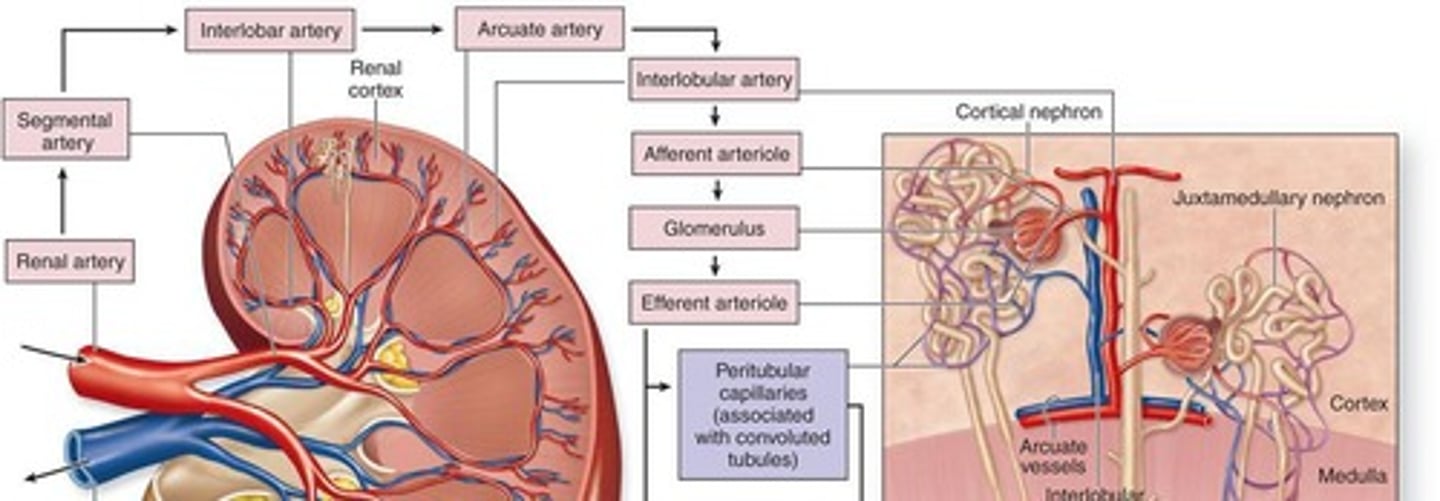
Glomerulus
Location of blood filtration where liquid, ions, and waste leave the blood stream.

Efferent Arterioles
Leave the glomerulus.
Interlobular Vein
Drains blood from peritubular capillaries and vasa recta.
Arcuate Vein
Located along the cortico-medullary junction.
Interlobar Vein
Flows between adjacent lobes.
Renal Vein
Drains blood from the kidneys into the Inferior Vena Cava to return to the heart.
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
Combination of cells that monitor blood pressure so that urine can accommodate any changes.
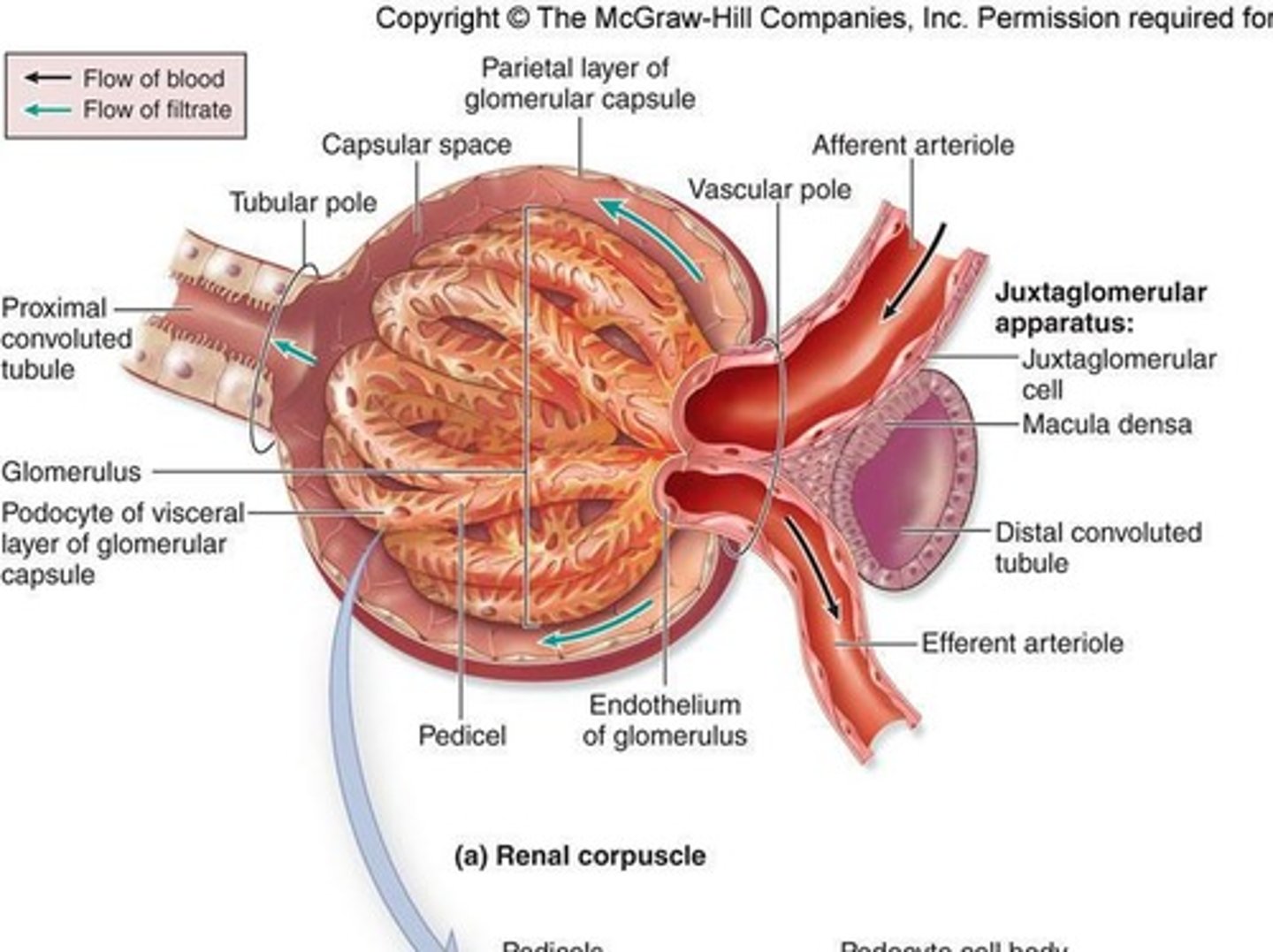
Juxtaglomerular Cells
Cells present in the wall of the afferent arteriole.
Macula Densa
Cells present in the wall of the distal convoluted tubule that contain receptors to monitor decreased blood pressure.
Renin
Released by Juxtaglomerular cells, causing a cascade of reactions leading to blood vessel constriction and raising blood pressure.
Transitional Epithelium
Mucosa that accommodates changes in volume.
Urinary Bladder
Expandable muscular sac that serves as a reservoir for urine.
Rugae
Folds in the bladder that allow stretching.
Trigone
Imaginary triangle that connects 2 ureter and 1 urethral openings.
Internal Urethral Sphincter
Smooth muscle, involuntary superior urethral sphincter surrounding the neck of the bladder.
External Urethral Sphincter
Skeletal muscle, voluntary inferior urethral sphincter.
Female Urethra
3-5 cm long, transports urine to outside body.
Male Urethra
18-20 cm long, transports urine and semen to outside body, has 3 regions: Prostatic, Membranous, and Spongy.