the living world
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
Ecosystem
A natural system made of plants, animals, and their physical surrounding environment
Biotic components
Living components of an ecosystem Smallsuch as plants and animals
Abiotic components
Non living components of an ecosystem like rocks and soil
Small scale ecosystem
Also called habitat
E.g. garden, fish tank, tree
Global scale ecosystem
Also called a biome
E.g. tropical rainforest, desert, tundra
Food chain
The sequence of who eats what in an ecosystem to obtain nutrients and energy
Food web
A number of food chains joined together in one habitat. It shows how an organism doesnt eat just one thing
Autotroph
Organisms that use photosynthesis to provide energy for themselves
Also known as producers
Heterotroph
Organisms that consume other organisms for energy
Also known as consumers
Trophic level
The position of an organism it occupies in the food chain
Lost energy in ecosystems
At each trophic level energy is lost
Only 10% of energy on average is passed onto the next trophic level
Organisms respire, move, excrete matter
Each process loses energy
What does an ecosystem depend on?
1. Flow of energy between consumers and detritivores
2. Recycling of matter via the nutrient cycle
Detritivores
Eat and break down detritus (small bits of dead organisms) for decomposers to feed on
Decomposer
Eat microscopic dead or decaying organisms
Break these down into simple molecules using chemicals and then absorb the nutrients
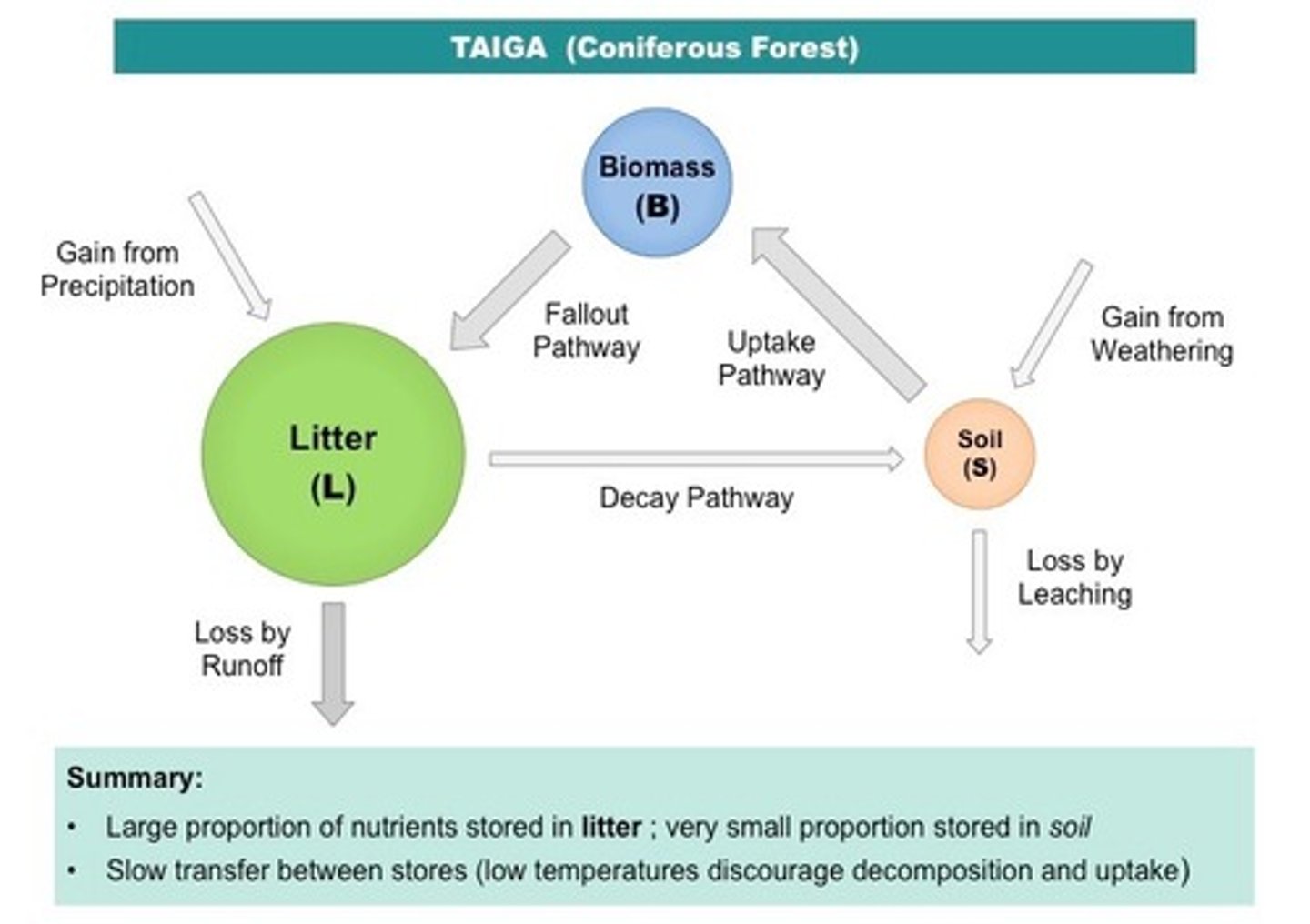
Gersmehl diagram
Epping forest - type of ecosystem
Deciduous forest
Interdependent:
Every organism rely on every other to survive
Epping forest - Climate
July average: 19 degrees
January average: 6 degrees
Usually quite rainy in summer and winter
Epping forest - nutrient cycle
Trees are deciduous so lose leaves in autumn
Decompsers and detritivores work on leaves
Nutrients in leaves are converted to humus in the soil
This supports plant growth, in which fruits are fed on by consumers
Epping forest - gersmehl diagram
Circles:
Large Biomass
Medium Soil
Low Litter
Arrows:
From B to L: Low leaves falling
To L: Minerals from rainfall
From L: Low runoff
From L to S: High decomposing
From S: High leaching
To S: Medium weathered rock
From S to B: Medium uptake by plants of nutrients
Epping forest: management
Dead wood left to rot to promote fungi, which is a decomposer in the nutrient cycle
Grassy areas left uncut to promote butterflies
Biking areas clearly marked to prevent damage
How can changes in an ecosystem occur
Naturally or human
Global or local
Ecological impacts in the absence of wolves in yellowstone
Elk pop began to rise
This caused conditions in the park to decline:
Deciduous, woody species such as aspen and cottonwood began to decline due to overgrazing
Coyote pop increased which led to reduction of pronghorn pop
Ecological impacts after the reintroduction of wolves in yellowstone
Elk pop declined
This led previously overgrazed fauna to flourish
Elk behavior changed: less favourable habitat, browse wider so other flora species could survive
Beaver colonies increased 1 to 9 as elk browsed less on their food
Dams from beavers led to more moose, otter, birds, fish, amphibians
Rivers meander less due to less erosion as stronger tress regenerated due to less focused grazing by elk
Tropical rainforests
High temp
Heavy rainfall
These conditions creates ideal environment for plants to grow
These plants support animals
More than half of animal and plant species in the world come from TRF
Hot deserts
Around 30 degrees N/S
High pressure subtropical belts result in sinking air and no precipitation
No clouds so no sunlight blocked during day so high day temps
Low night temps as no clouds trap heat
Plants and animal need to be highly adapted to survive e.g. cacti
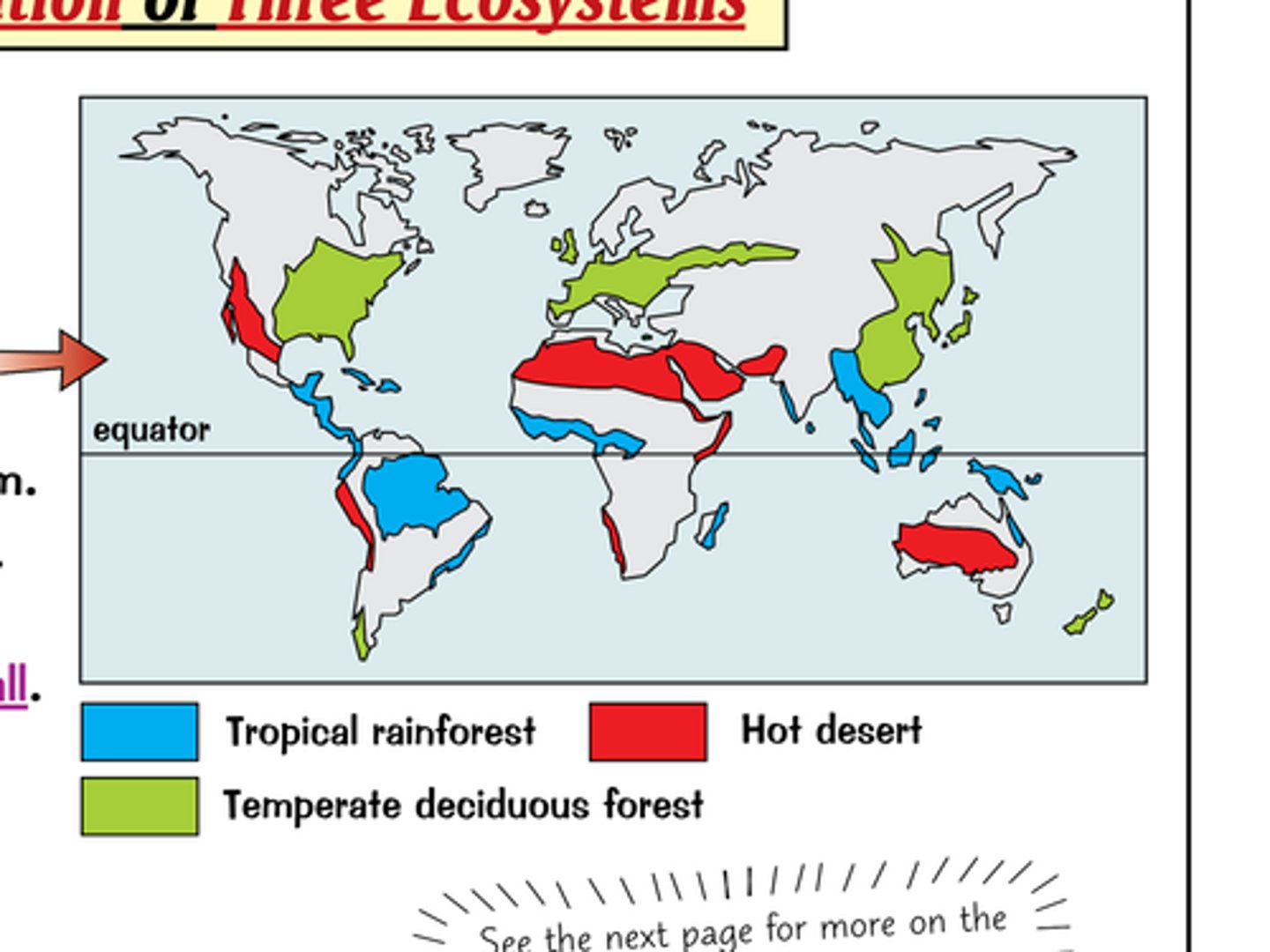
Where can you find tropical rainforests?
Tropical rainforests are located in the tropics, near the equator.
How much rain do they get?
Most rainforests get at least 75 inches of rain with many getting well over 100 inches in areas.

What's the temperature there? Would you like this climate?
Because they are close to the equator, the temperature stays between 25 and 28 degrees C for most of the year.

Which continent should you travel to find a rainforest?
To Africa, to South-east Asia or to South America.
How many percent of the animals on Earth live here?
50%. Scientists say that around half of the planet's animal and plant species live in the world's rainforests.

In which layer would you searh for monkeys?
In the canopy layer.

In which layer would you searh for snakes?
In the undercanopy layer.

Why are rainforests so important for humans?
Because they act as the Earth's lungs by producing around 40% of the world's oxygen. The rainforests also provide a number of important drugs to help sick people and cure diseases.

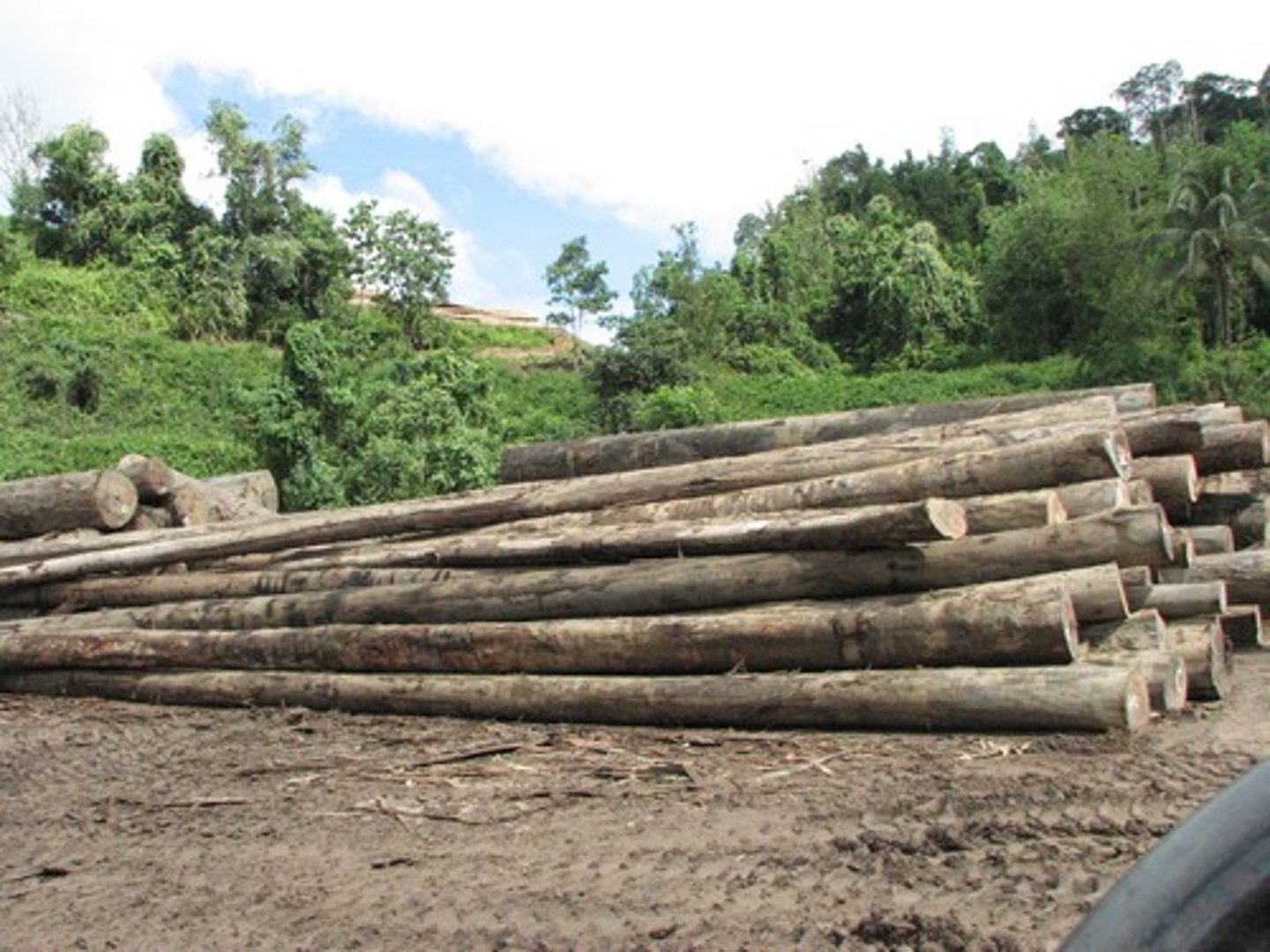
Is the territory of the rainforests growing or getting smaller?
It is getting smaller. Unfortunately, human development is killing off much of the world's rainforest. Around 40% of the world's rainforests have already been lost.

Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world or a particular habitat.
Deforestation
The chopping down and removal of trees to clear an area of forest, usually because of business needs
Logging
The business of cutting down trees and transporting the logs to sawmills.
Loss of biodiversity
An environmental impact of deforestation
Medicines as a result of deforestation
could be lost due to deforestation including Reserpine, a drug which can be used to treat people with high blood pressure.
Indigenous Tribes as a result of deforestation
Lose their homelands when developments take place
Soil erosion
Happens as trees no longer protect the soil through interception
Flooding
can increase as there is less interception
Improving transportation
means easier access to raw materials like minerals and timber.
Economic benefits of deforestation
are selling hardwoods like mahogony and allowing farming
Nutrient cycle as a result of deforestation
is damaged during deforestation as there is no loger litter to decompose
Mineral Deposits in trf deforestation
including bauxite, iron ore, manganese, gold, silver and diamonds can be exploited and sold
Undergrowth layer
The rainforest layer where trees grow up to 5 metres. Much of the sunlight is blocked by the canopy only 1-2% of sunlight
Understorey layer
below the canopy layer; usually shrubs and smaller trees - 17m and only 2-5% of sunlight where plants rarely grow above 10m in height
canopy layer of tropical rainforests
This layer of a rainforest contains the majority of the largest trees, typically 30-45 m tall. The densest areas of biodiversity are found here, a more or less continuous cover of foliage formed by adjacent treetops. It is home to 50 percent of all plant species, suggesting that perhaps half of all life on Earth could be found there. Epiphytic plants attach to trunks and branches, and obtain water and minerals from rain and debris that collects on the supporting plants. The fauna is similar to that found in the emergent layer, but more diverse. A quarter of all insect species are believed to exist in this layer and 90% of all trf organisms are found here - 29m in height
emergent layer of tropical rainforests
This layer of a tropical rainforest contains a small number of very large trees , which grow above the general canopy, reaching heights of 45-55 m. They need to be able to withstand the hot temperatures and strong winds that occur above the canopy in some areas. trees can grow 25 to 45m in height and many leaves have flexible bases to face towards the sun and pointed tipped leaves for rain to drip off
Uses of TRF - chocolate
cacao tree native to amazon rainforest
Uses of TRF - rivers
can be used as a Hydroelectric energy source
Uses of TRF - rice
2nd most produced food crop in the world which originates from trf regions across the globe
estimated amount of forest lost every year
size of england
fraction of medicines with ingredients derived from trf species
¼
total damage cost of forest loss for global economy
12 trillion dollars
deforestation activities causing forest to be cleared
Road building, settlement of population growth and commercial farming
sustainable management
management that meets the needs of the present population without endangering the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
selective logging
The cutting out of trees which are mature or inferior, to encourage the growth of the remaining trees in a forest or wood.
conservation and education of trf
rainforest can be preserved conservation areas
ecotourism of trf
introduce people to the natural world
income benefits the gov for protecting trf
income for indigenous
Debt reduction
Countries are relieved of some of their debt in return for protecting their rainforests.
Where is Malaysia?
Southeast Asia, it consists of peninsular Malaysia and the island of Borneo
How much of Malaysia is covered and by what?
67% of Malaysia is covered in tropical rainforests.
What are the causes of deforestation in Malaysia (7) ?
Logging
Road Building
Energy Development - Dam building
Mineral extraction
Urbanisation from population pressure
Subsistence farming
Commercial farming - palm oil
Why did logging occur in Malaysia?
In 1980s, Malaysia was largest exporter of tropical wood so clear felling was taking place on a wide scale
What is clear felling?
Absolute clearance of all trees from an area leaving bare soil and destroying habitats
What dam has been built?
The Bakun Dam in Sarawak which cleared 700km^2 of forest
Why has mining caused deforestation?
Due to open-cast mining which requires large amounts of trees, soils and bedrock to be cleared.
What is palm oil?
- Type of vegetable oil which gives food smooth texture
- Used in 50% of supermarket products - e.g. ice cream
Why is Malaysia linked with palm oil?
Malaysia is the largest exporter in this growing industry and has around 90% of the world's oil palm trees.
Benefits of palm oil farming?
It directly provides employment for 1 million people in Malaysia.
It contributes to 10% of Malaysia's total exports.
Costs of palm oil farming?
Intentional forest fires to destroy huge areas of forest and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions
Between 70,000 to 200,000 children are estimated to work on plantations.
What were the impacts of deforestation for Malaysia (3)?
Soil Erosion
Loss of Biodiversity
Contribution to climate change
What were the impacts of deforestation for Malaysia (4)?
Loss of Biodiversity
What were the impacts of deforestation for Malaysia (4)?
Contribution to climate change
What were the impacts of deforestation for Malaysia (4)?
Economic Development
What is soil erosion?
The removal of soil which acts as an important part of ecosystems present.
How does it contribute to climate change?
Deforestation reduces the amount of carbon trees store which increases CO2 emissions.
Trees give off moisture from transpiration - so lack of trees causes drier climate
Economic benefits of deforestation (2)?
An increase in number of jobs because land will be used for commercial/industrial processes.
Improved infrastructure opens up areas for development and tourism.
Economic losses of deforestation (3)?
Fires can destroy forests as well as cause harmful pollution.
Number of tourists may decrease
Rising temperatures may ruin some crops from growing such as tea, fruits and flowers.
Desertification
where semi-arid areas/drylands is gradually turned into desert.
Where does desertification usually happen?
On the edges of an existing desert
When it rains, what may happen that leads to the degradation of soil(desertification)?
Instead of the water being absorbed by the soil, it runs off the surface(surface runoff).
What is the degradation of soil a result of?
Decreased fertility and structure.
What is a result of soil degradation?(desertification)
Harder to grow crops/natural vegetation
Why would the soil be exposed to hot sun and rain in desertification?
There are no plants/natural vegetation to intercept those factors.
The heat bakes the soil to the point where it _______.
cracks
Physical Reasons for desertification
soil erosion-soil exposed to wind and rain
Physical Reasons for desertification - natural occurrences
natural occurrences-droughts for example
Human Reasons for desertification(3)
Overcultivation-the need to produce more food, this exhausts the soil
Anthropogenic climate change-slight climate changes can lead to a big impact, as to increase global temperatures would set the stage for hot desert climate
Overgrazing-the pressure on semi-fragile areas could lead to desertification as too many animals exceed vegetation limits
Social effects of desertification
20 million people in Sahel region of Africa faced hunger in 2014(source:UN)
Loss of species affects medicinal availability
Population pressure stopped traditional nomadic farming - soil drained intensively of nutrients, thus infertile/poor soil and regular crop failure
Economic effects of desertification
UN required 2 billion in food aid due to desertification
Environmental effects of desertification
Loss of vegetation, thus damage to animal habitats
Less tree cover and more grasses which protects the soil less
Plant adaptations to TRF(buttress roots)
buttress roots-large roots growing above the grounnd from the stem of their trunk-this is to provide them with stability so they do not fall over
Plant adaptations to TRF(lianas)
lianas-wind themselves around rainforest trees and climb high - this is to reach available sunlight
Plant adaptations to TRF(drip tip)
drip tips-the pointed end of a leaf - directs water away from the middle of the leaf
Plant adaptations to TRF(waxy leaves)
waxy leaves-waxy waterproof coating on leaf surface - helps water run off easier to preevent them from being weighed down