BIO 11 - Viruses & Cells
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
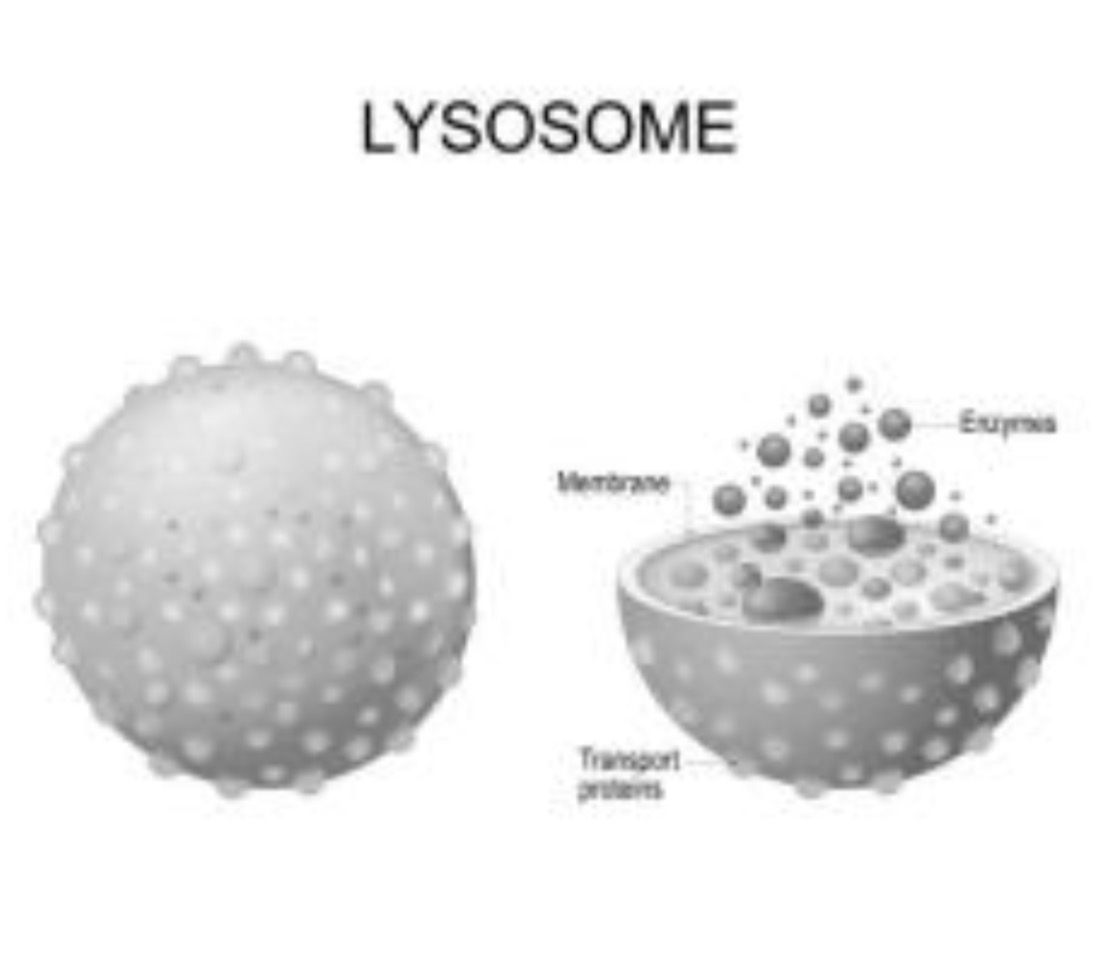
Lysosomes
These have a low pH and hydrolytic enzymes for breaking down cellular debris, ingested materials, bacteria, and viruses. Nicknamed "suicide sac" causes cell death, a process termed apoptosis
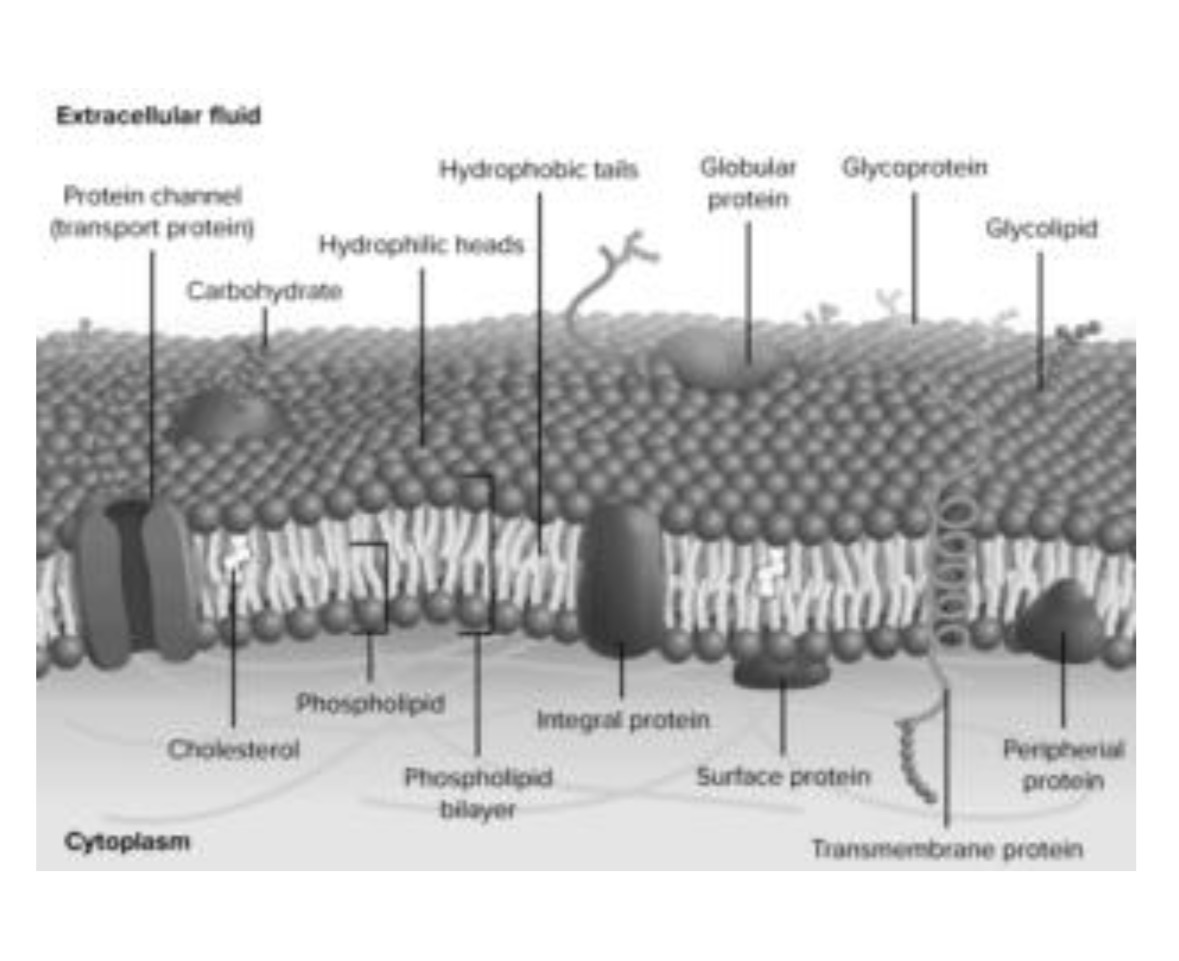
Plasma Membrane
Controls what enters and exits the cell, is semi-permeable and includes a phospholipid bilayer.
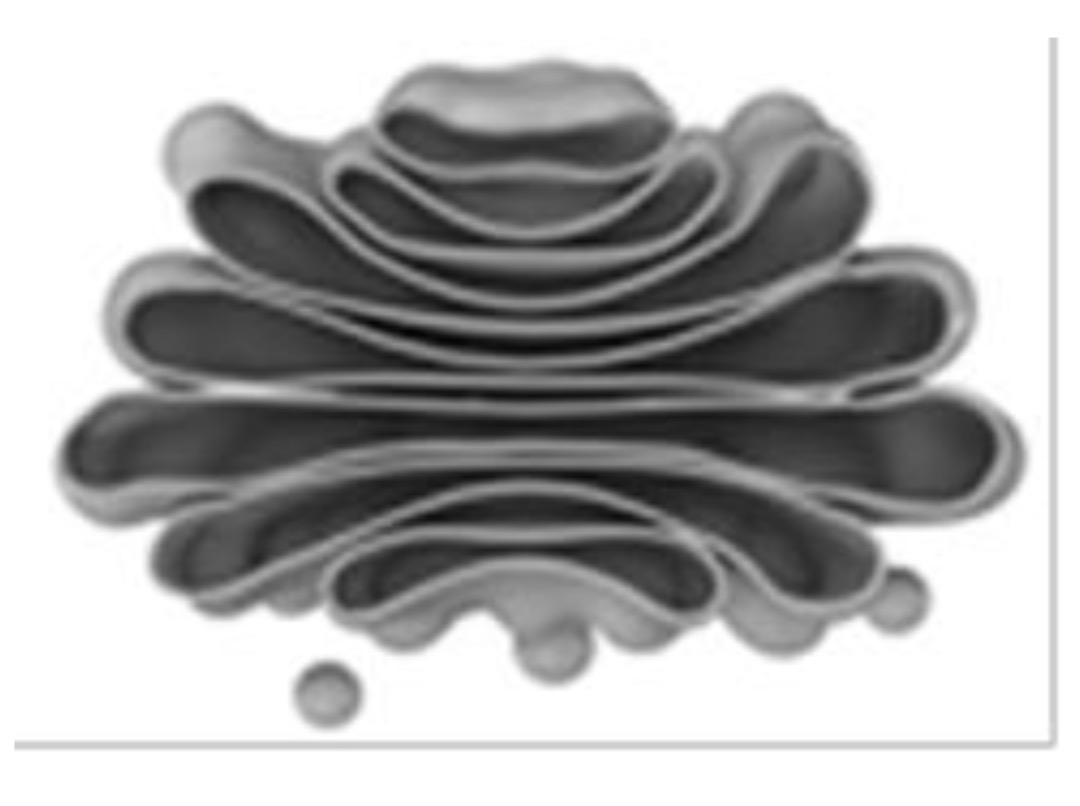
Golgi Apparatus
Sorts and packages proteins and Lipids destined for other organelles, the plasma membrane, and secretion beyond the cell.
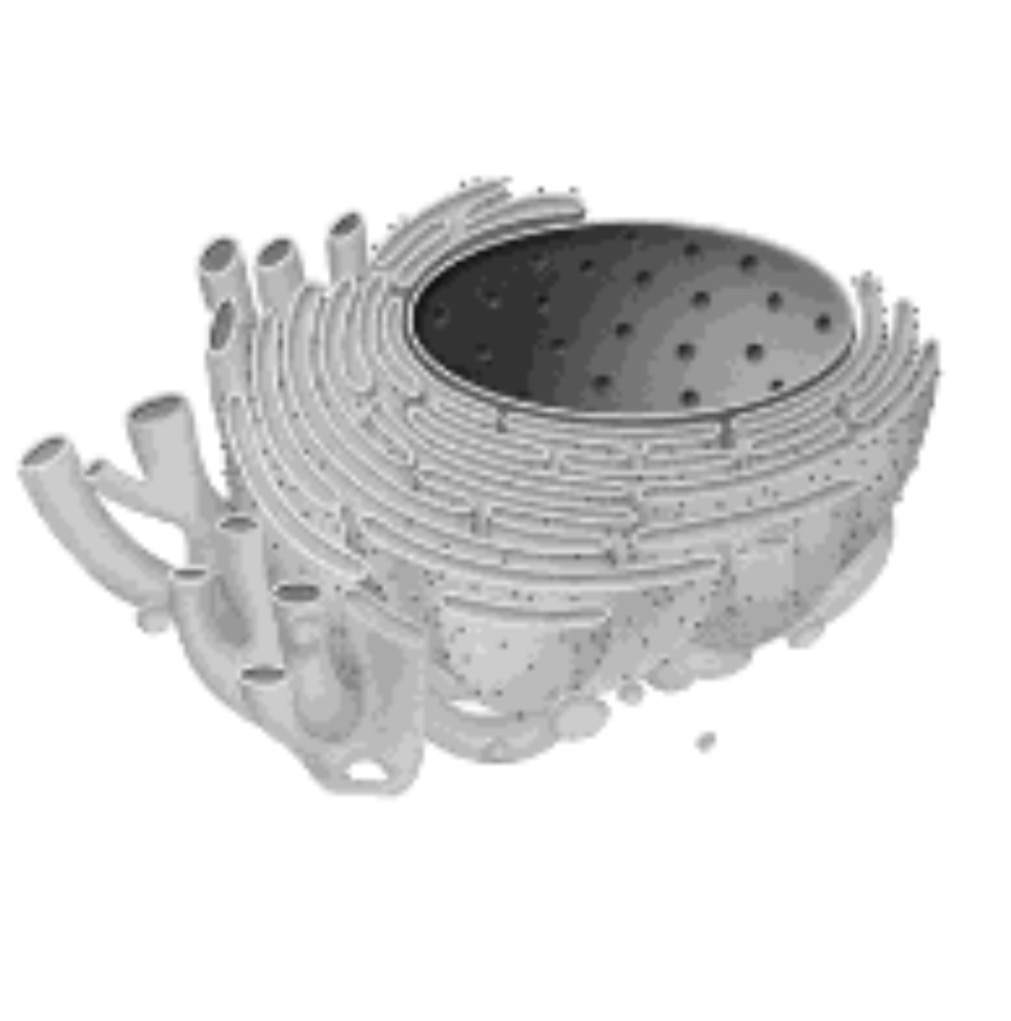

SER - Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Makes lipids, hormones, and makes steroids for cell signaling, and stores calcium for muscle contraction.
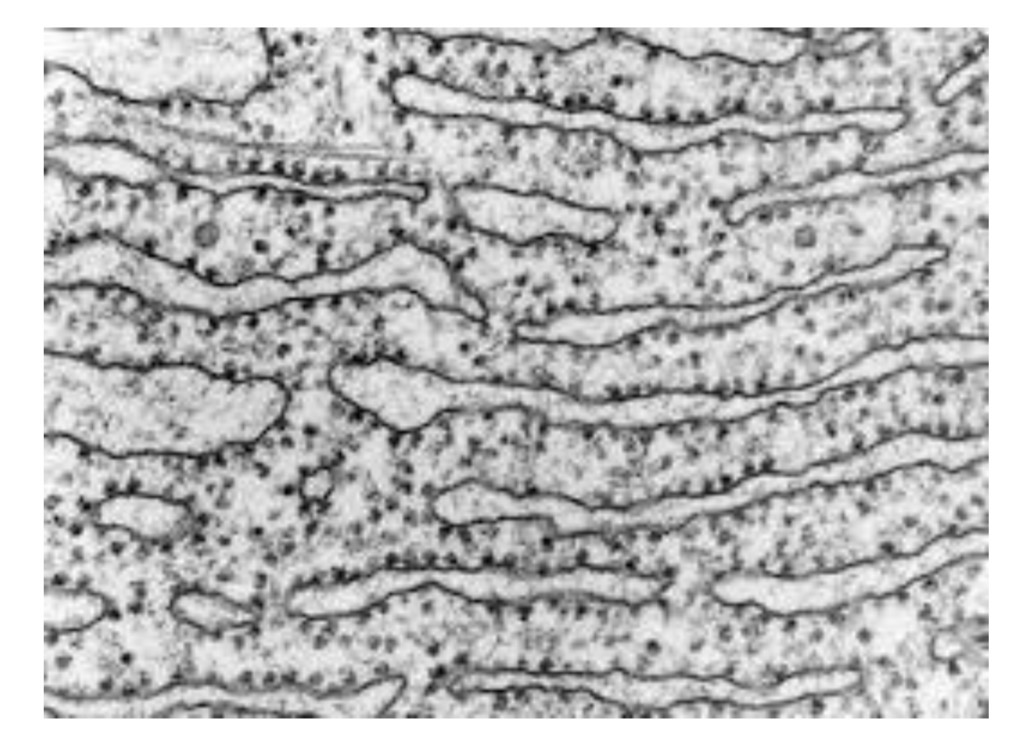
RER - Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Has ribosomes on its surface and produces proteins destined for particular organelle within the cell or plasma membrane or for secretion beyond the cell.
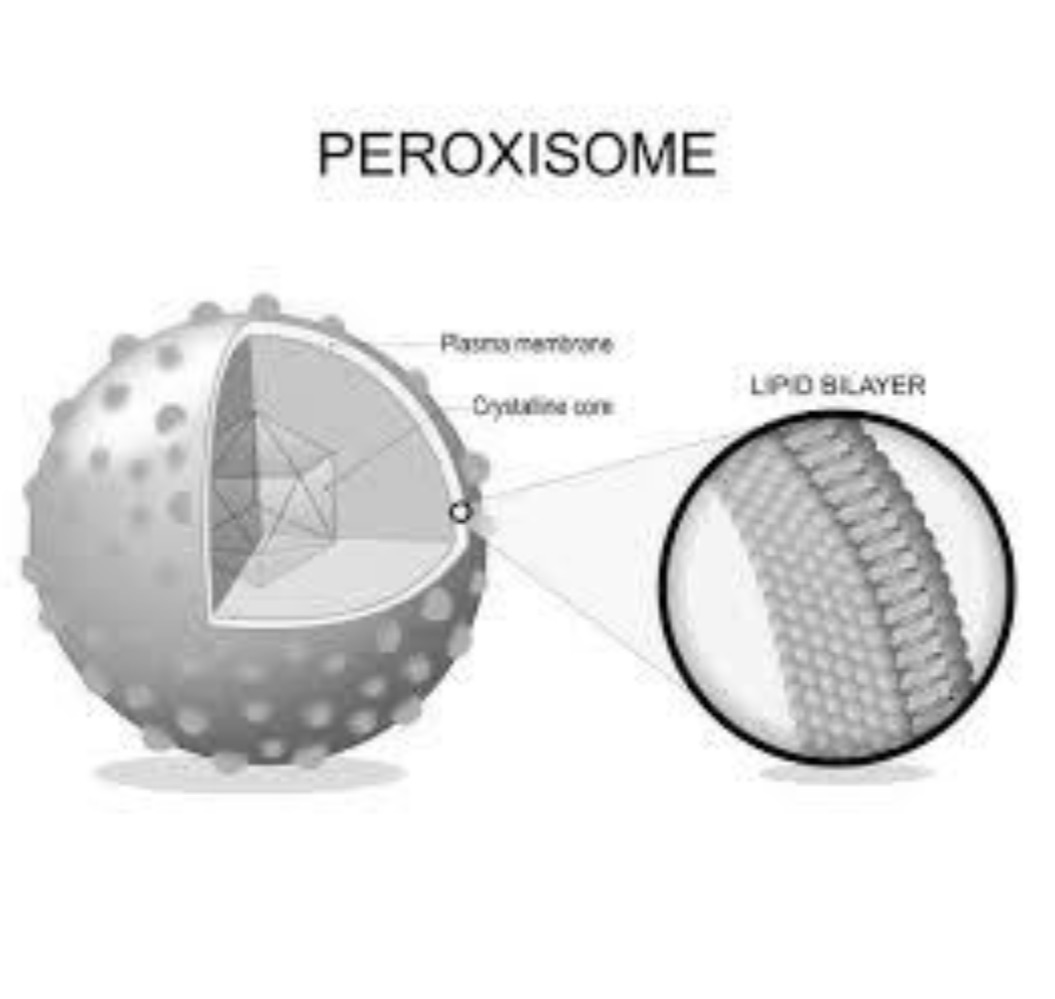
Peroxisome
Breaks down fatty acids, detoxifies alcohol, and makes cholesterol using peroxidases to break down hydrogen peroxide.
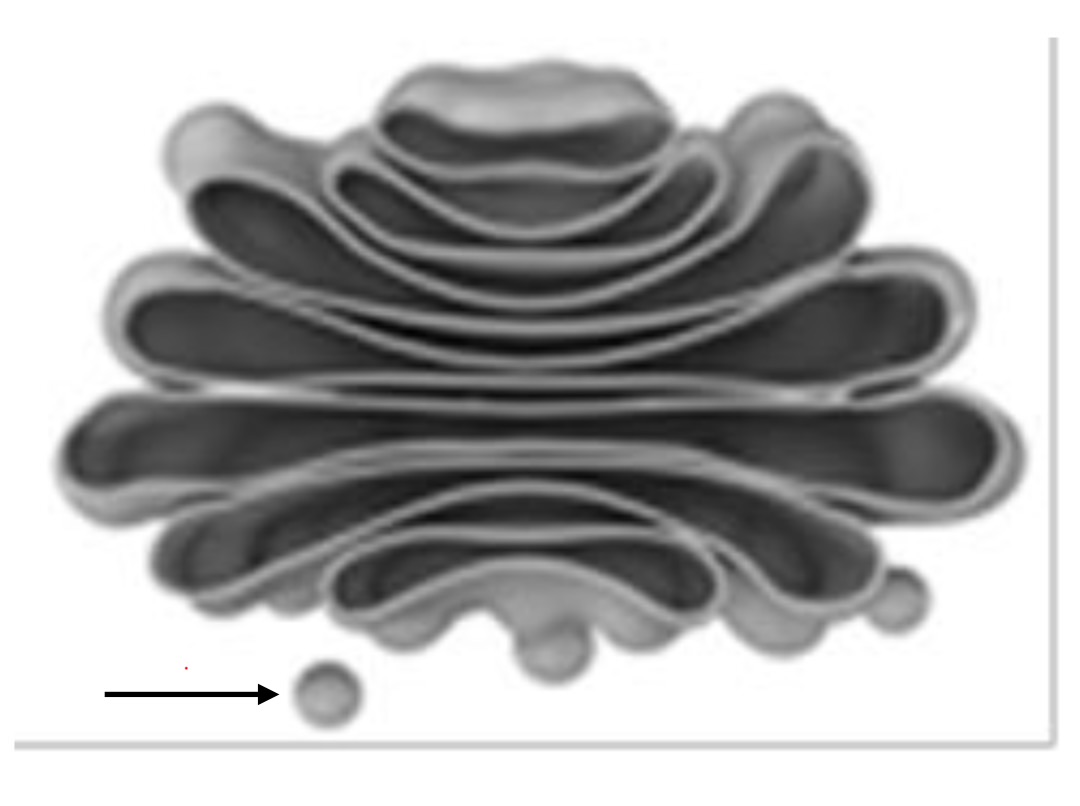
Vesicle
Transport proteins throughout and between the cell and to the cell surface.
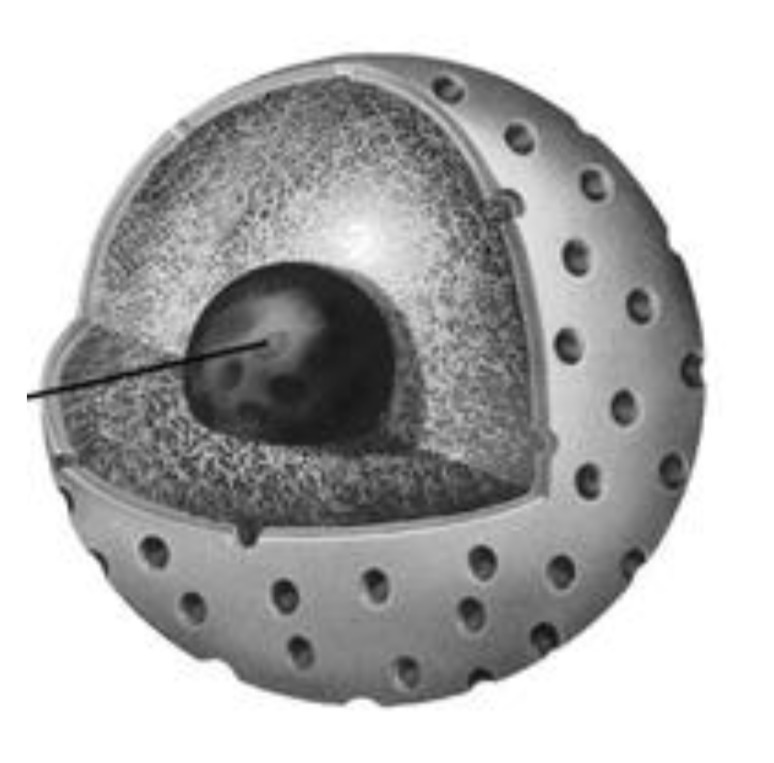
Nucleus
Stores and protects the DNA, and regulates gene expression and therefore cell function. The nucleolus synthesizes (makes) ribosomes.
Exocytosis
Vesicles that carry materials destined for secretion beyond the cell.
Endocytosis
Vesicles that helps bring in material into the cell.
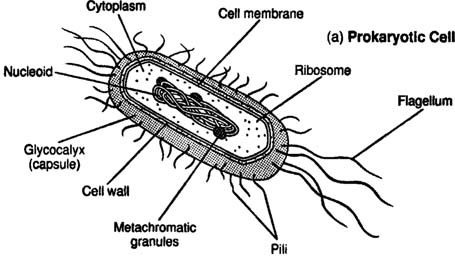
Prokaryote Cells
A cell with no (before) nucleus or membrane bound organelles.
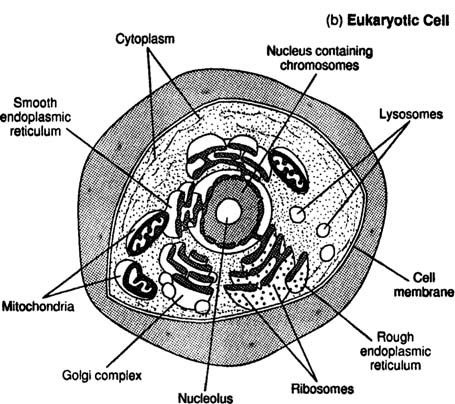
Eukaryote Cells
A cell with true nucleus and membrane bound organelles.
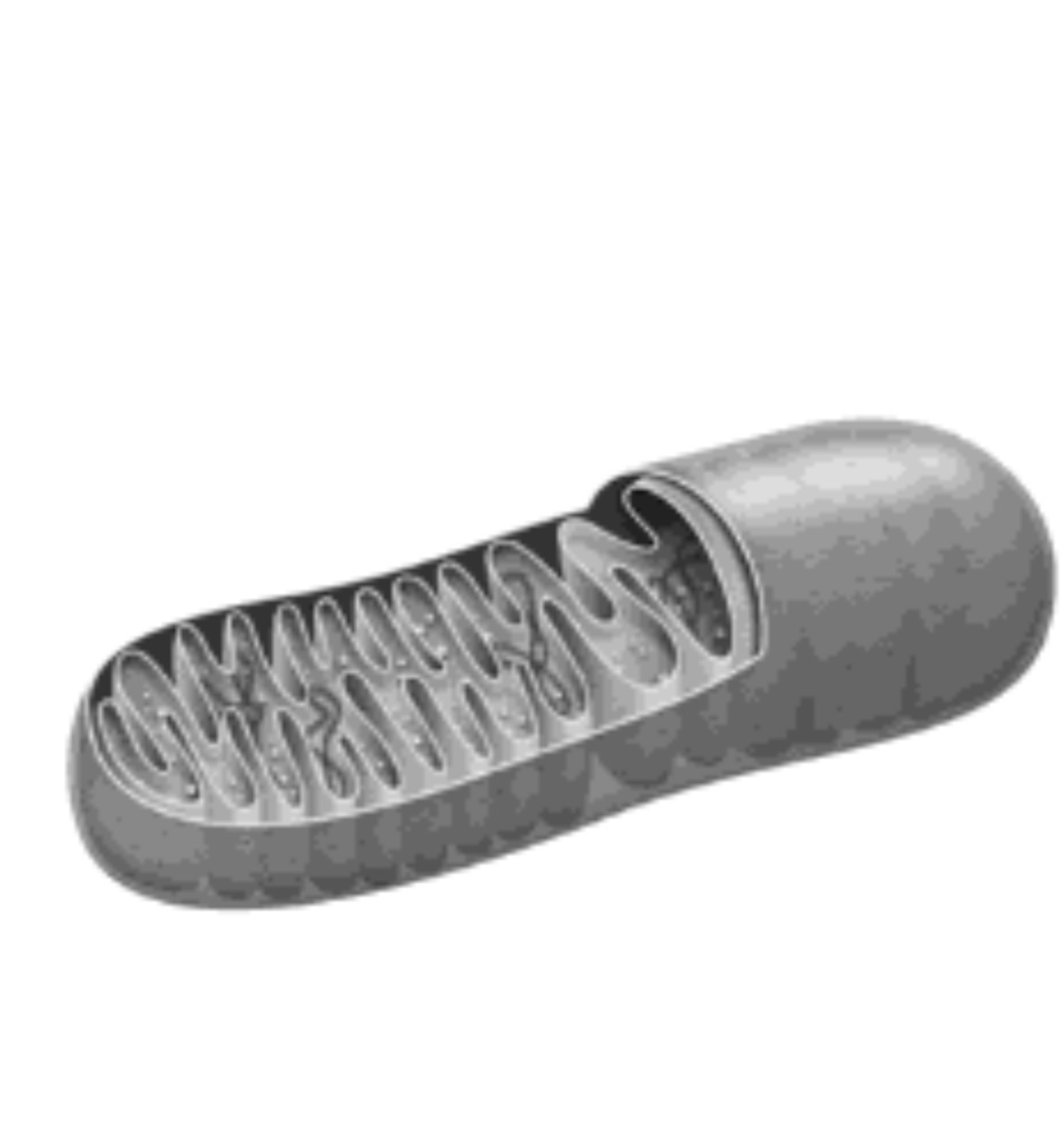

Mitochondria
Known as the “power house” of the cell because it produces energy (ATP) via cellular respiration.
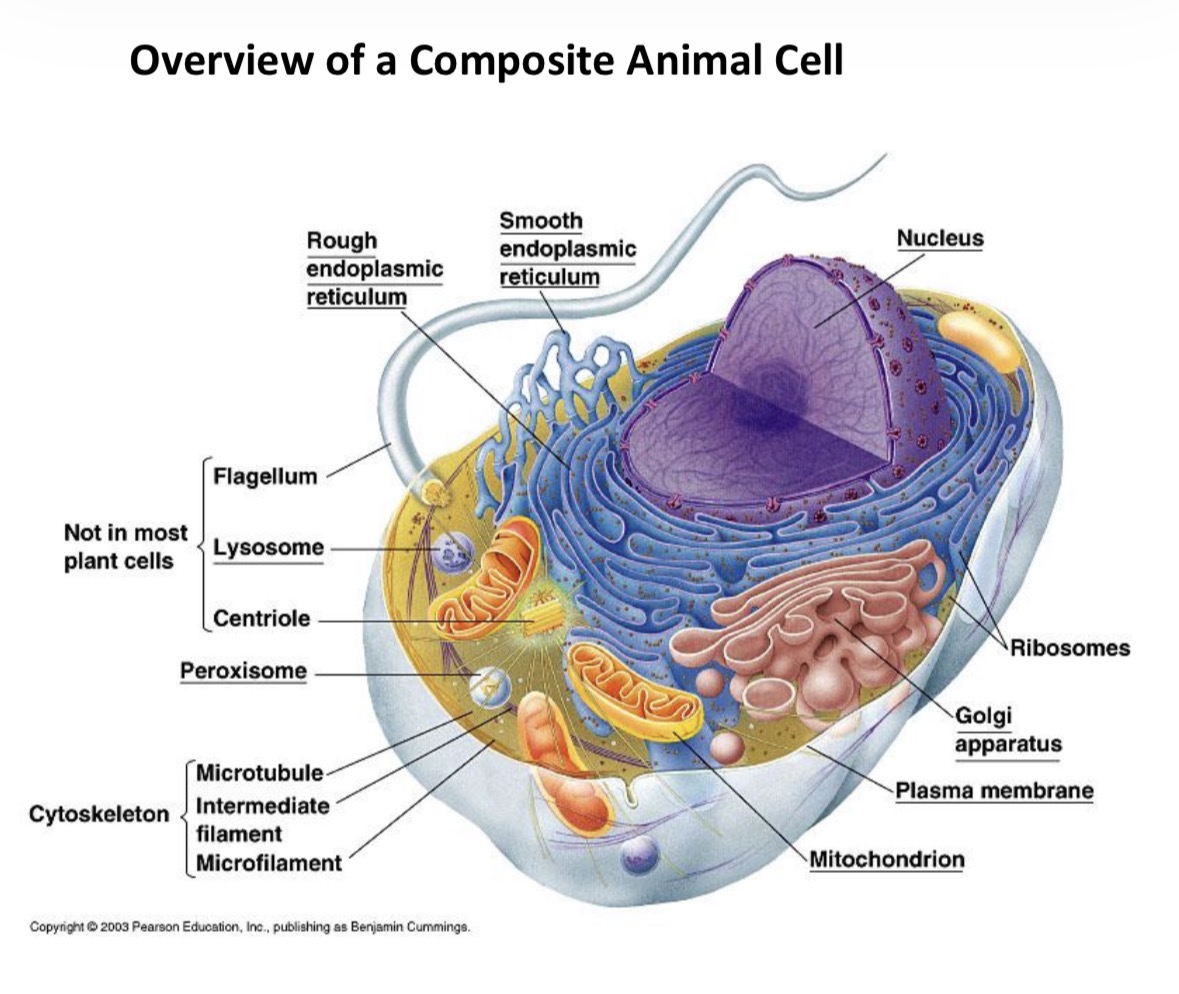
Animal Cells
A cell that does not have a cell wall, chloroplast, and its vacuole is much more smaller than in the plant cell.
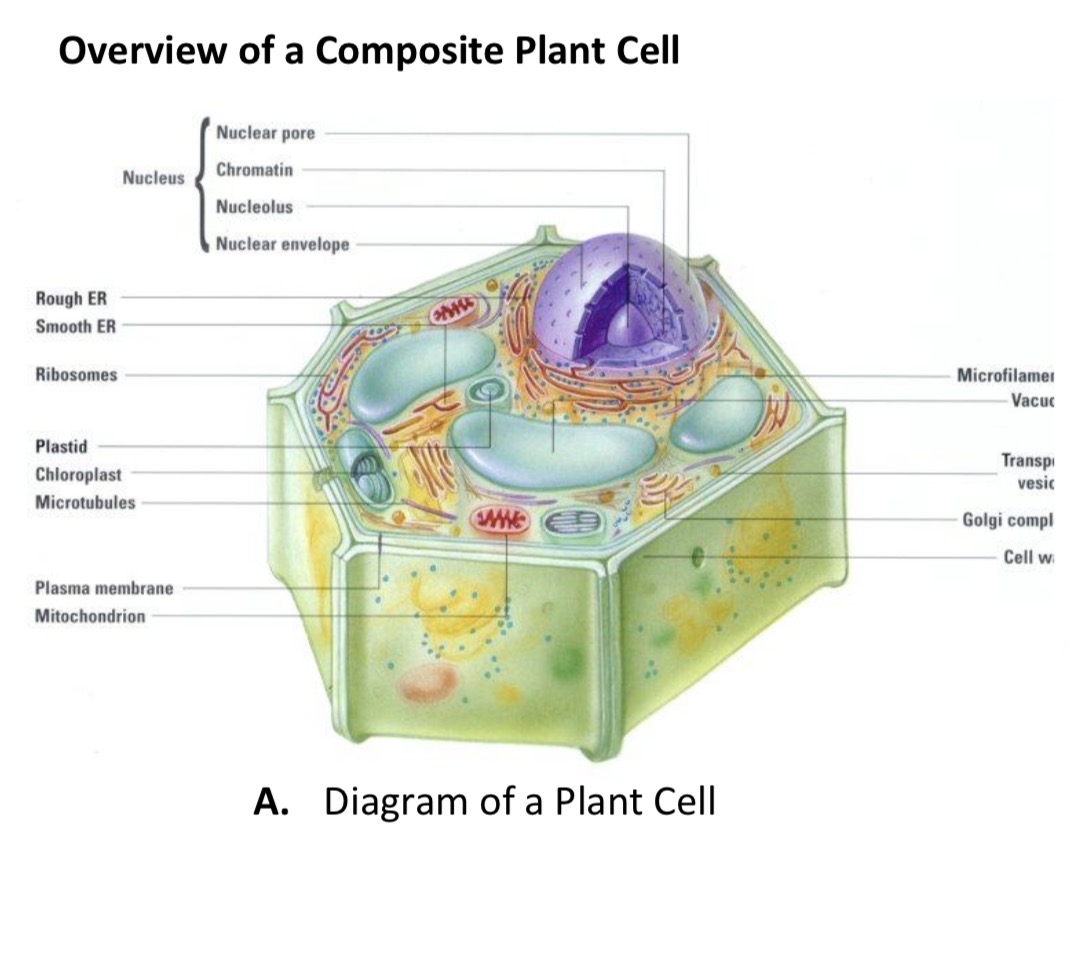
Plant Cells
A cell that has a cell wall, chloroplast for photosynthesis, and a large central vacuole, which helps it maintain its structure.
Endosymbiotic Theory
A theory that Mitochondria and chloroplast evolved from engulfing aerobic prokaryotes and photosynthetic prokaryotes.
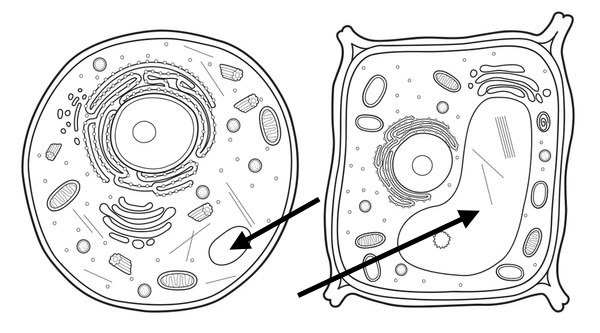
Vacuole
Membrane-bound storages organelles in cells that holds materials like water, nutrients, or waster. In plants additionally stores pigments and toxins. It is much more larger than its counter part in the animal cell.
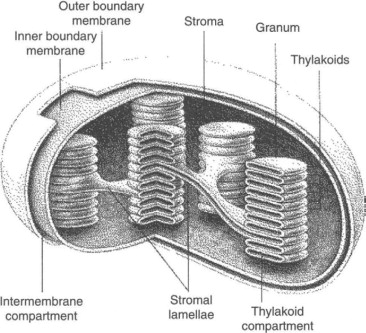
Chloroplast
An organelle only found in plants where photosynthesis happens using sunlight to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water.
Cell Wall
Provides extra support and structure to the exterior of the plant cell.
Cellular Respiration
A process of breaking down glucose and oxygen to produce (ATP) along with carbon dioxide and water as waste.
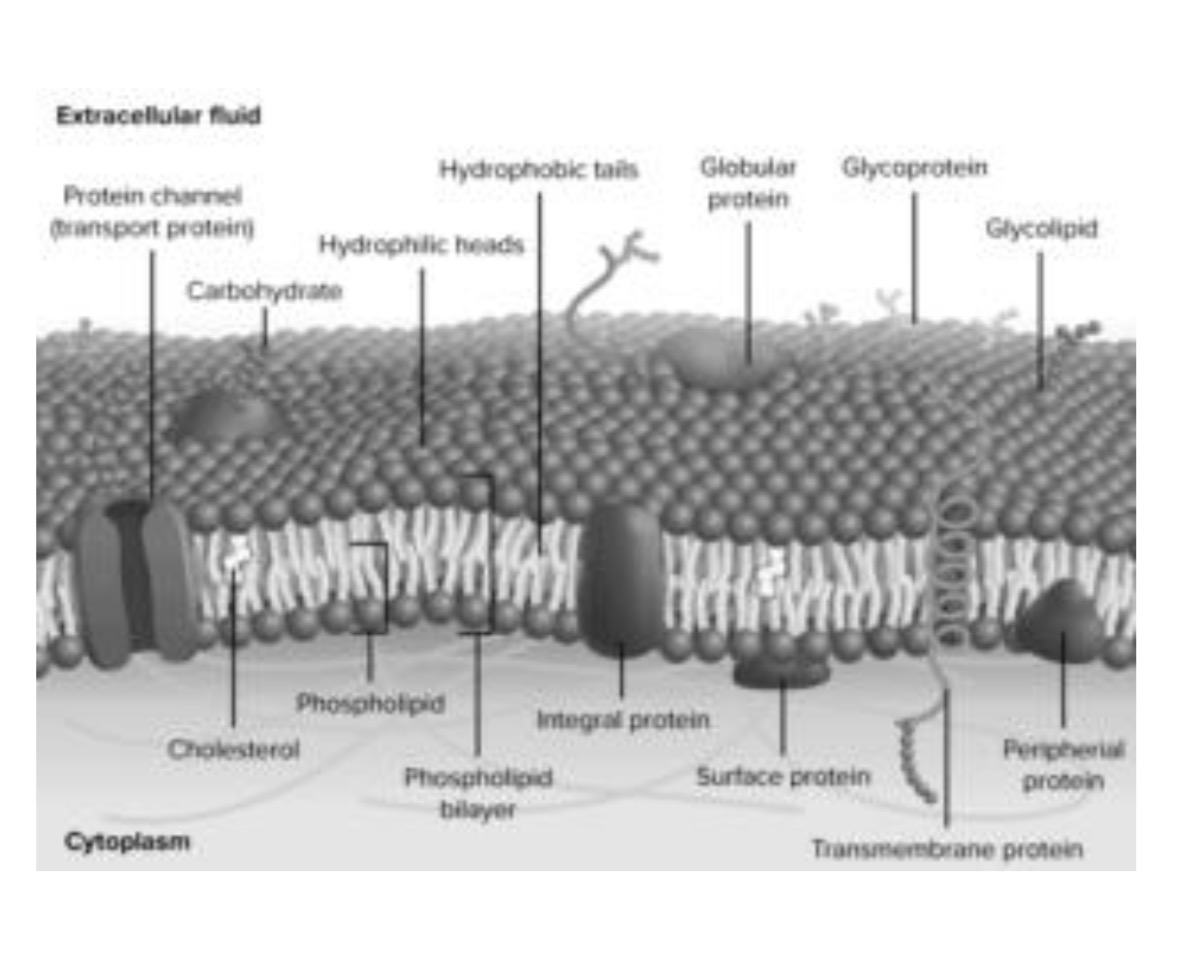
Fluid Mosaic Model
As phospholipids are as described as “liquid-like” and a mixture of proteins float through out it.

B.) Pathogen

D.) I, III, and IV, only

B.) Icosaheldral

D.) Contains a membrane coat stolen from the host cell

B.) Complex virus

A.) DNA or RNA protected by protein coat

B.) Unique and allow them to bind only to specific host proteins

C.) Lyric and Lysogenic

C.) Attachment

D.) Lysogenic cycle

A.) Excision

C.) Lysis

A.) Prokaryotes evolved first

C.) Prokaryote cell with no nucleus or membrane bound organelles

C.) 10-100 micrometers in size

D.) Endosymbiotic Theory

A.) All cell contains DNA

B.) I, III, and IV, only

B.) Ribosomes, vesicle, mitochondria, nucleus

D.) lysosomes

B.) H₂O₂
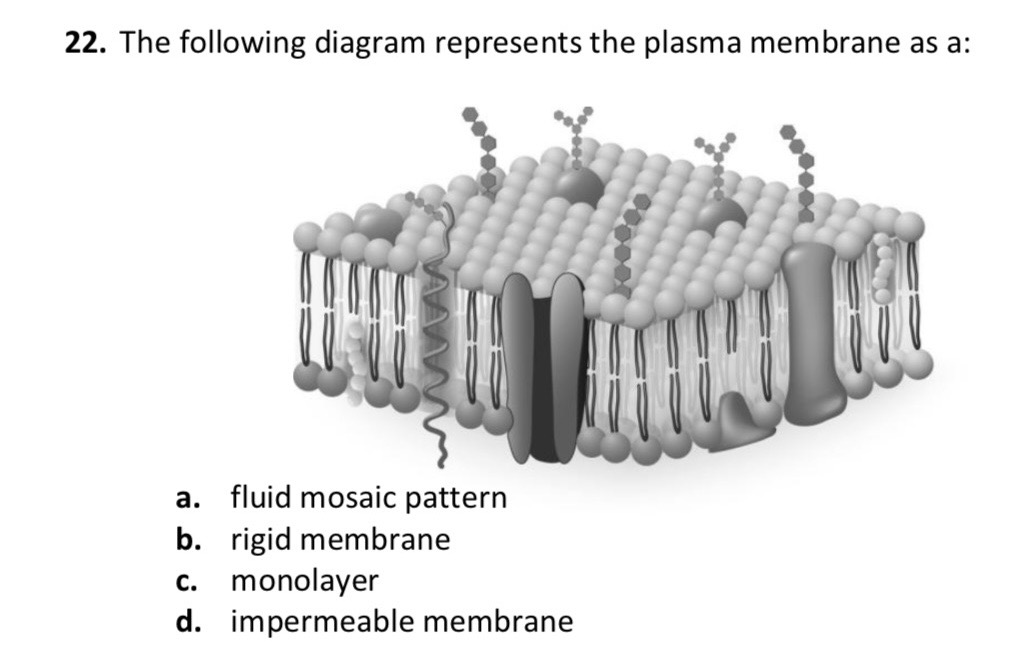
A.) Fluid mosaic pattern

B.) uncharged and hydrophobic

D.) Golgi apparatus
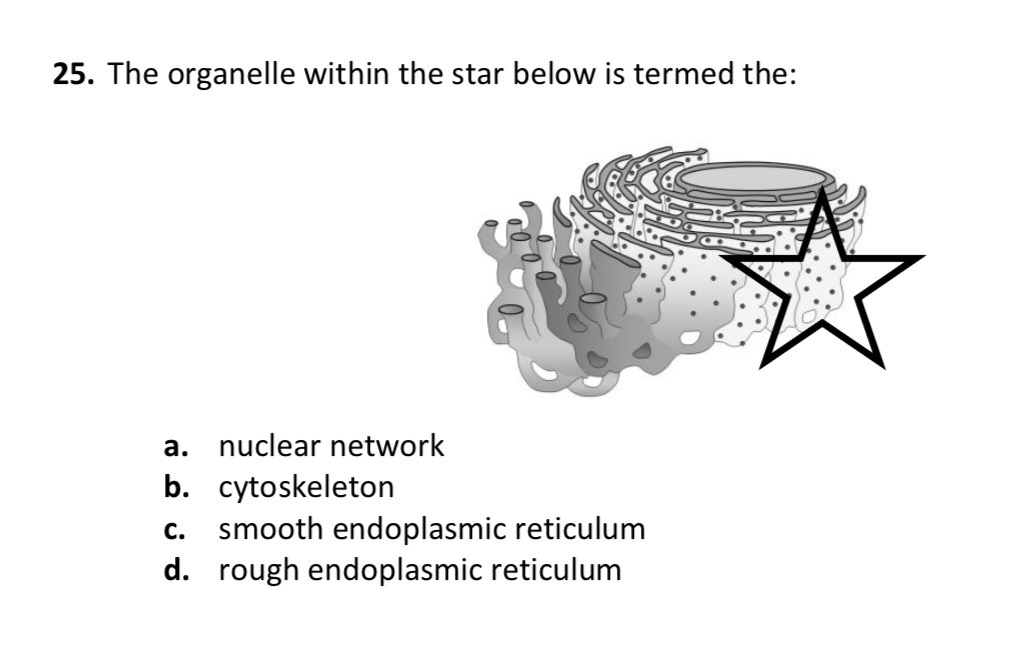
D.) Rough endoplasmic reticulum

D.) Protects DNA and makes ribosomes

D.) Secreting antibodies

C.) A Cristae, and produces ATP

C.) Both a and b

A.) Semipermeable

D.) Endocytic vesicle

C.) I, II, and III, only

D.) Thylakoid

D.) Cytosal and refers to glucose breaking

C.) Pyruvate which is then the input of the Krebs cycle

D.) Electron carriers involved in either cellular respiration or photosynthesis
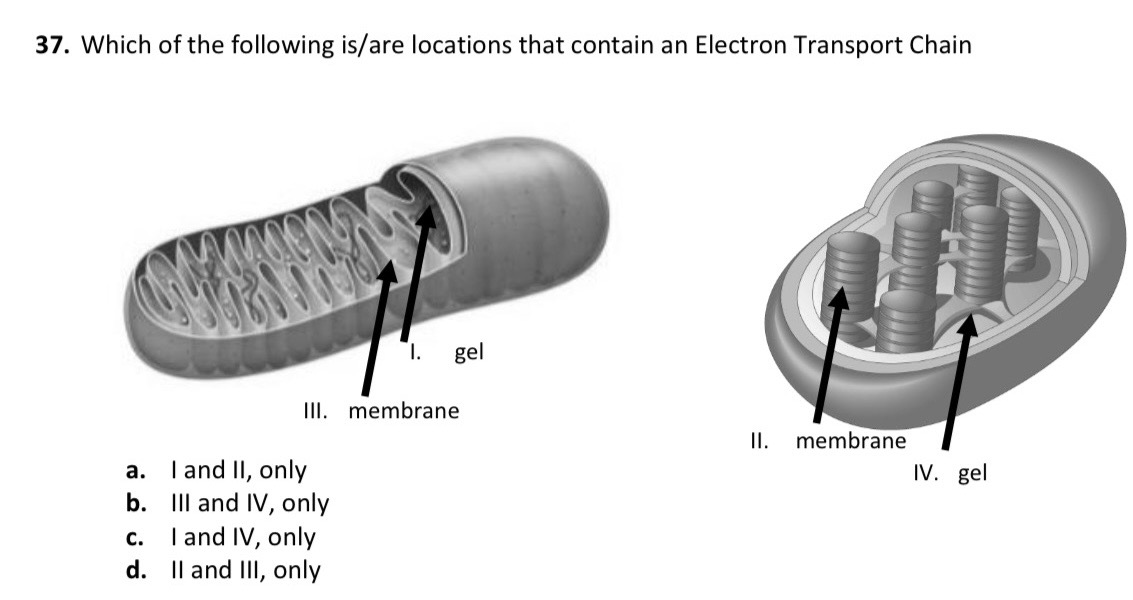
D.) II and III, only
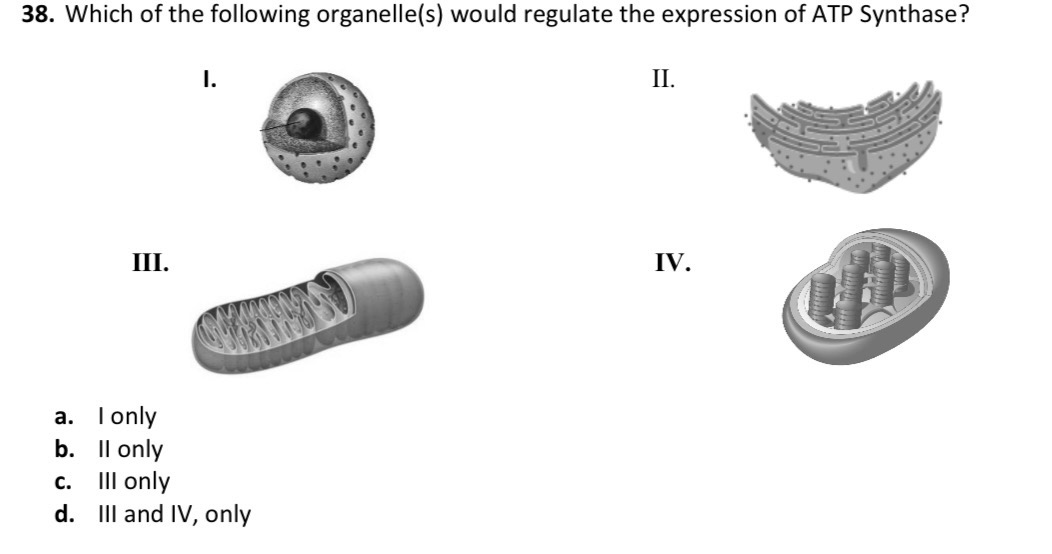
A.) I only

D.) Microtubules

B.) Actin

C.) In storms while light-dependent reactions occur on the thylakoid

D.) Attached ribosome → RER → vesicle → Golgi → vesicle → plasma membrane
Evidence of Endosymbiotic Theory
Mito & Chlora have a double membrane
Mito & Chlora is size = to aerobic & photosynthetic prokaryote
They have their own unique DNA & ribosomes
The DNA & ribosomes are more similar to prokaryote DNA & ribosomes than nuclear
The DNA & ribosomes reproduce similarly to prokaryote cells (binary fission)
What are 7 Eurocentric characteristic of living things?
H - Homeostasis
A - Aquire Materials & Energy
R - Reproduce
O - Order
G - Growth
A - Adapt
S - Stimuli
What is the 3 tenets of the Cell Theory?
The cell is the smallest unit of life
All living things are made up of one or more cells
All cells came from pre-existing cells
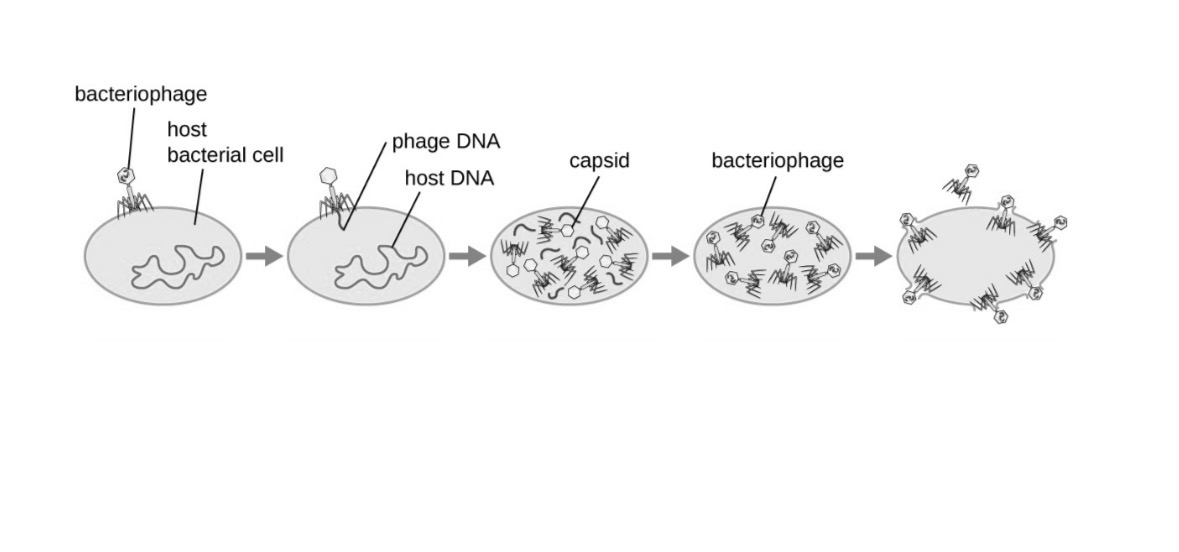
Lytic
A viral reproduction process where a virus infects a host cell, makes copies of itself, and then causes the cell to burst (lyse), releasing new viruses.
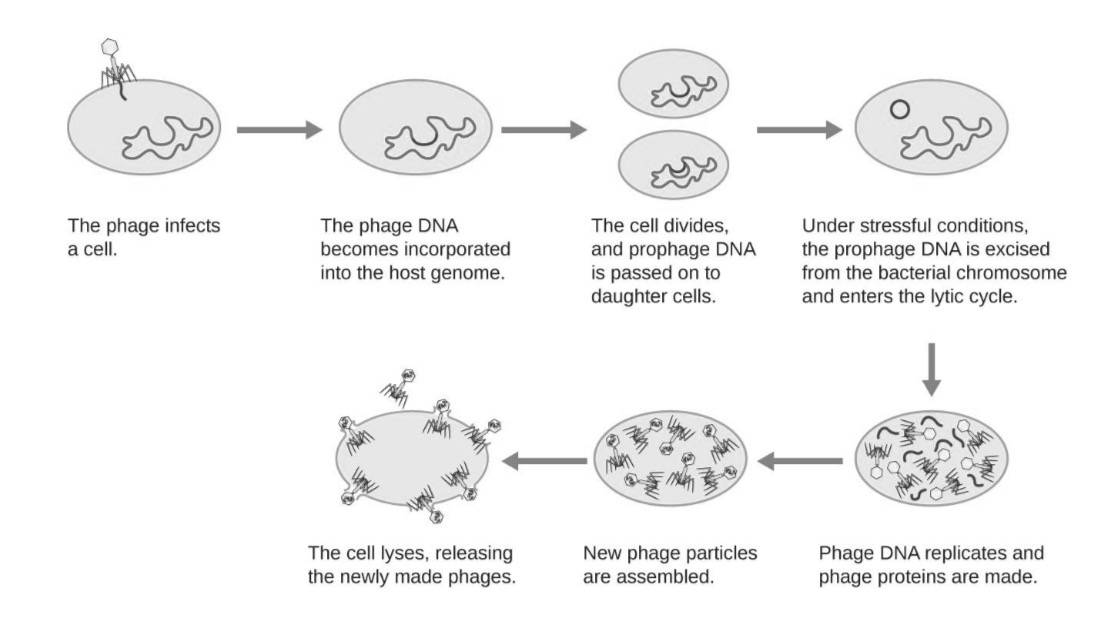
Lysogenic
Is a viral reproduction process where the virus inserts its DNA into the host cell’s DNA and remains inactive for a while, copying along with the host cell without killing it immediately.