ANFS345 Exam 4
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fall 2025 animal physiology, taking questions from in-class assignments and quizzes, trying to come up with my own as well
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Where does glycolysis occur?
The cytosol of the cell
How many NADH molecules does glycolysis generate?
2
What is the PRODUCT in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is GLUCOSE?
G6P
What is the ENZYME in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is GLUCOSE?
Hexokinase
What ENERGY is used in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is GLUCOSE?
1 ATP is used
What is the PRODUCT in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is G6P?
F6P
What is the PRODUCT in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is F6P?
F1,6DP
What is the PRODUCT in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is F1,6DP?
DHAP and GAP
What is the PRODUCT in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is DHAP?
GAP
What is the PRODUCT in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) GAP (GA3P)?
(2x) 1,3DPG
What is the PRODUCT in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) 1,3DPG?
(2x) 3PG
What is the PRODUCT in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) 3PG?
(2x) 2PG
What is the PRODUCT in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) 2PG?
(2x) PEP and H2O
What is the PRODUCT in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) PEP?
(2x) Pyruvic Acid
What is the ENZYME in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is F6P?
PFK
What is the ENZYME in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) GAP?
GAPDH
What is the ENZYME in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) 1,3DPG?
PGK
What is the ENZYME in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) 2PG?
Enolase
What is the ENZYME in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) PEP?
PK, Pyruvate Kinase
What ENERGY is produced in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) GAP?
(2x) NADH
What ENERGY is produced in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) PEP?
(2x) ATP
What ENERGY is produced in glycolysis when the SUBSTRATE is (2x) 1,3DPG?
(2x) ATP
How much ATP can be produced from 1 molecule of NADH?
2.5 ATP
How much ATP can be produced from 1 molecule of FADH?
1.5 ATP
In the Krebs Cycle, what does the Isocitrate to aKG reaction produce?
NADH
In the Krebs Cycle, what does the aKG to succinyl CoA reaction produce?
NADH
In the Krebs Cycle, what does the succinyl CoA to succinate reaction produce?
GTP
In the Krebs Cycle, what does the succinate to fumarate reaction produce?
FADH
In the Krebs Cycle, what does the malate to oxaloacetate reaction produce?
NADH
The enzyme _______ is needed to convert phosphoenolpyruvic acid to pyruvic acid
pyruvate kinase
The substrate _______ is required for glycolysis to begin.
glucose
The substrate needed to initiate the Krebs cycle is
acetyl coenzyme A
Which chemical reaction of the Krebs cycle produces FADH2
Succinate to fumarate
Which molecule(s) is(are) generated during aerobic metabolism?
CO2 and H2O
The specific role of oxygen in the cell is to
act as a final electron acceptor
Which molecule does not participate in proton pumping in the mitochondria?
Succinate dehydrogenase
If 43 protons pass through the ATP synthase, _______ ATP are produced.
10
How many ATP are produced for every 4 protons moved?
1 ATP
If a cell loses its mitochondria, the net number of ATP molecules that can be produced from one glucose molecule is
2 ATP (only glycolysis is possible).
Which is the correct order of events leading to the luteinizing hormone surge in rabbits?
Copulation stimulates sensory neurons in the cervix → neuronal impulses release norepinephrine → GnRH stimulates anterior pituitary cells to secrete LH → a surge of LH stimulates ovulation in the ovaries
Which aspect of reproduction is not typically studied by physiologists?
Sexual Selection
Which is the best example of postnatal provisioning?
Lactation
Which statement regarding human female gametes is true?
All primary oocytes are formed during fetal life
Which animal(s) menstruate(s)?
Humans and Gorillas
The physiological trigger for the onset of menstruation in humans is caused by
degeneration of the corpus luteum, resulting in a lack of progesterone for the support of the endometrium.
The enzyme responsible for converting androgens to estrogens is
aromatase
Which statement regarding estrogen during the follicular phase is true?
Along with follicle-stimulating hormone, estrogen stimulates the
proliferation and development of the follicles.
Sperm are produced in the
seminiferous tubules
The _______ cells support and regulate spermatogenesis
Sertoli
Which statement about the mammalian vomeronasal organ is true?
It mostly detects pheromones and other chemical signals
The molecule that absorbs light is called a
Photopigment
The ear drum is contained in the
Middle ear
Sound travels in the following order
Ear drum > Hammer > Anvil > Stapes
Beat perception and synchronization within 120 to 140 beats/min in rats is processed via the
auditory cortex
Bitter taste may signal the presence of
Toxins
The gustatory system is designed to identify ______________ main classes of taste
5
The sensors for smell are mostly located in the
Olfactory epithelium
The vertical pupils in the cat allow it to see
certain regions in its visual field in very high clarity
What is true about dogs?
They inhale and exhale out of two different openings in the nose
Where does the Krebs cycle take place?
Mitochondria Matrix
What type of transduction does NOT include cell signaling?
Ionotropic Transduction
What type of transduction CAN include cell signaling, and is primarily secondary signaling?
Metabotropic Transduction
What type of STIMULUS do MECHANORECEPTORS perceive?
Touch, pressure, proprioception
What type of STIMULUS do VESTIBULAR RECEPTORS perceive?
Balance; body position and movement
What type of STIMULUS do OSMORECEPTORS perceive?
Osmotic Pressure
What type of STIMULUS do AUDITORY RECEPTORS perceive?
Sound
What type of STIMULUS do THERMORECEPTORS perceive?
Heating and Cooling
What type of STIMULUS do ELECTRORECEPTORS perceive?
Electric fields in water
What type of STIMULUS do PHOTORECEPTORS perceive?
Light
What type of STIMULUS do MAGNETORECEPTORS perceive?
Position or change of magnetic field
What type of STIMULUS do OLFACTORY CHEMORECEPTORS perceive?
Chemicals generally from a distance
What type of STIMULUS do TASTE CHEMORECEPTORS perceive?
Taste (Sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami)
What type of TRANSDUCTION do OLFACTORY CHEMORECEPTORS use?
Metabotropic in vertebrates, ionotropic or mixed in insects
What type of TRANSDUCTION do TASTE CHEMORECEPTORS use? (SALTY and SOUR)
Ionotropic
What type of TRANSDUCTION do TASTE CHEMORECEPTORS use? (SWEET, BITTER, and UMAMI)
Metabotropic
What type of TRANSDUCTION do MAGNETORECEPTORS use?
Unknown
What type of TRANSDUCTION do PHOTORECEPTORS use?
Metabotropic
What type of TRANSDUCTION do ELECTRORECEPTORS use?
Ionotropic
What type of TRANSDUCTION do THERMORECEPTORS use?
Ionotropic
What type of TRANSDUCTION do AUDITORY RECEPTORS use?
Ionotropic
What type of TRANSDUCTION do OSMORECEPTORS use?
Ionotropic
What type of TRANSDUCTION do VESTIBULAR RECEPTORS use?
Ionotropic
What type of TRANSDUCTION do MECHANORECEPTORS use?
Ionotropic
What does the PACINIAN CORPUSCLE sense?
Vibration
What does the RUFFINI ENDING sense?
Pressure
What does the MEISSNER CORPUSCLE sense?
Touch
What does the MERKEL DISC sense?
touch and pressure
what do the FREE NERVE ENDINGS sense?
Pain, itch, temperature
What RECEPTOR does the MERKEL DISC utilize?
Tonic Receptor
What RECEPTOR does the RUFFINI ENDING utilize?
Tonic Receptor
What RECEPTOR does the MEISSNER CORPUSCLE utilize?
Phasic Receptor
What RECEPTOR does the PACINIAN CORPUSCLE utilize?
Extremely Phasic Receptor
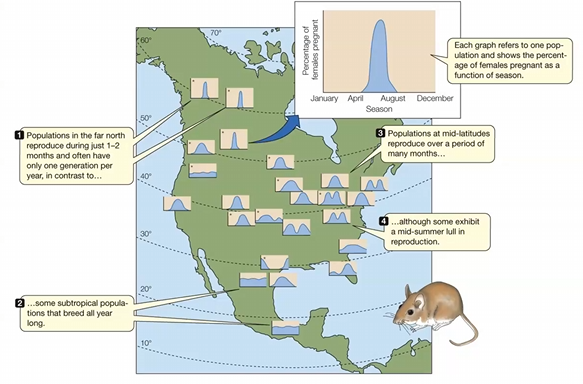
The graphs in the figure represent the
percentage of pregnant females as a function of the season.
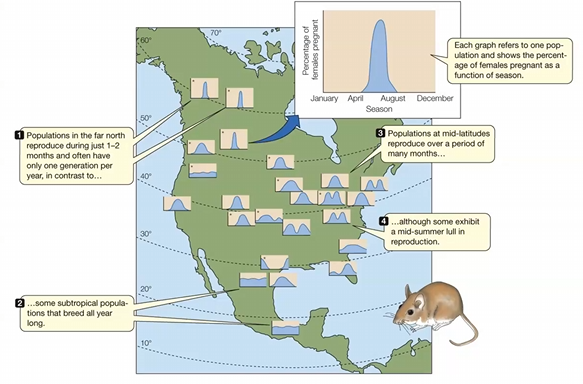
Which conclusion can be drawn from the information in the figure?
Populations at high latitudes reproduce during just 1–2 months.
Upon ovulation, the ruptured follicle next transforms to
Mature corpus luteum
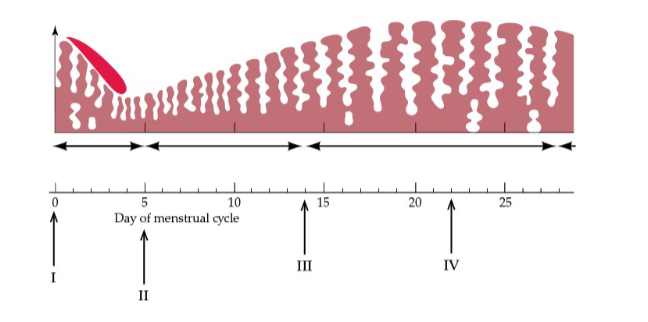
What process is occurring at arrow III in the figure?
Ovulation and Estrus
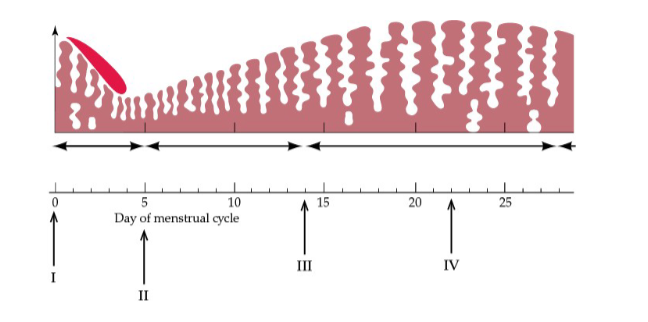
What process is occurring at arrow I in the figure?
Menstruation
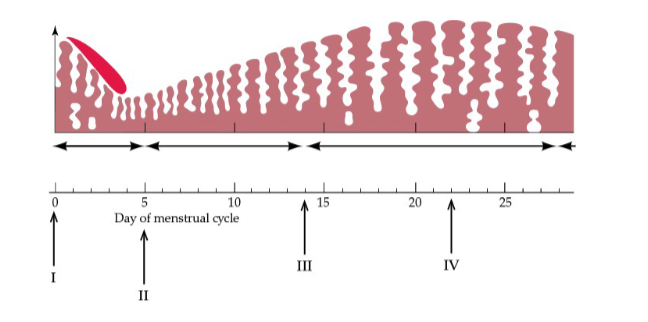
Which of the following hormones would not be surging at the time of arrow III in the figure?
FSH and Progesterone