2- Arthropods
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2- Arthropods
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What does arthropod mean?
Jointed foot
What type of parasites are arthropods?
Ectoparasites
Where do ectoparasites live?
On the outside of the host
Why are arthropods important in veterinary medicine?
They cause skin disease and transmit parasites and infectious diseases.
What material makes up the arthropod exoskeleton?
Chitin
What type of circulatory system does arthropods have?
Open circulatory system.
What is the blood-like fluid in arthropods called?
Hemolymph
What are the two major arthropod groups of veterinary importance?
Insecta and Acarina
How many legs do insects have?
6 legs (3 pairs)
What are the three body parts of insects?
Head
Thorax
Abdomen
Name examples of insects of veterinary importance.
Fleas
Flies
Lice
Others: roaches, grasshoppers, beetles, moths, butterflies, ants, bees, wasps.
What are the two main body regions of Acarina?
Capitulum (mouth parts)
Abdomen
What is the capitulum?
The mouthparts (fused head and thorax)
What is metamorphosis?
The process of development from egg to adult.
What are the two types of metamorphosis?
Simple and Complex
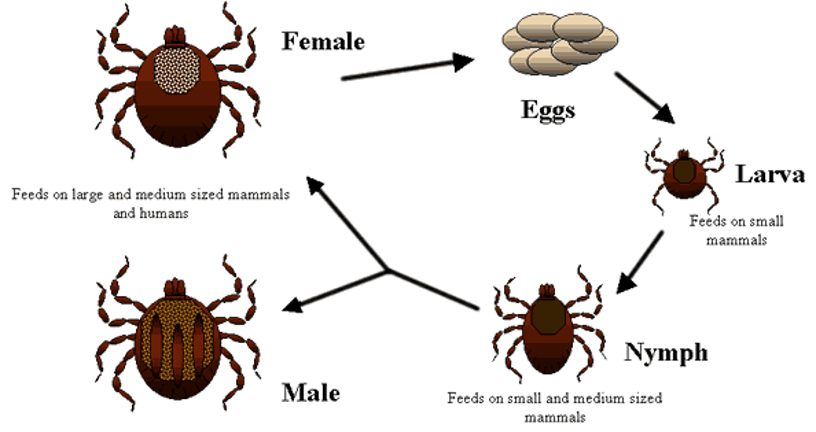
What are the stages of simple metamorphosis?
Egg —> nymph —> adult

What does a nymph look like?
A smaller version of the adult
Which arthropods have simple metamorphosis?
Ticks and lice
What are the stages of complex metamorphosis?
Egg —> Larva —> Pupa —> Adult
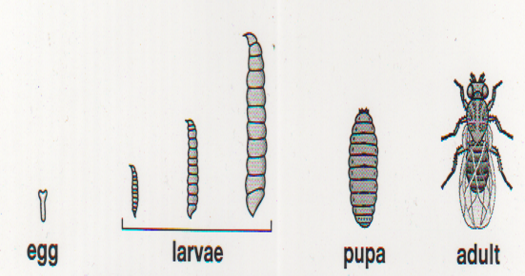
Which arthropods have complex metamorphosis?
Fleas and Flies
Which arthropod transmits tapeworms?
Fleas
Which arthropods commonly transmit bacterial diseases?
Ticks
Which arthropods commonly cause mange?
Mites
Which arthropods are usually host-specific and live their entire life on the host?
Lice
What is a hemocoel?
The body cavity of arthropods where hemolymph bathes internal organs in an open circulatory system.
What does dioecious mean?
Males and Females are separate individuals.
Arthropods belong to which two important subphyla in parasitology?
Mandibulata and Chelicerata
Which classes are in Subphylum Mandibulata?
Insecta, Crustacea, and Myriapodia
Which class belongs to Subphylum Chelicerata?
Acarina (ticks and mites)
Why is Class Crustacea important in parasitology?
They act as intermediate hosts for several parasites.
Name crustaceans
Crayfish, aquatic copepods, freshwater crustaceans.
What parasites are associated with crustaceans?
Paragonimus, Diphyllobothrium, Spirometra, Dracunculus
What organisms are in Class Myriapodia?
Centipedes and Millipedes.
What does “no metamorphosis” mean?
No pupal stage; development is:
Egg —> larva —> nymph —> adult