Honors Biology Final Study Guide: Cell Cycle, Genetics, and Cell Structure
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What are the seven characteristics of all living things?
The seven characteristics are: 1) Growth and development, 2) Reproduction, 3) Response to stimuli, 4) Metabolism, 5) Homeostasis, 6) Cellular organization, and 7) Adaptation through evolution.
What is the difference between independent variables, dependent variables, and constant variables?
Independent variables are manipulated by the researcher, dependent variables are measured in response to changes in the independent variable, and constant variables remain unchanged throughout the experiment.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
Qualitative data describes characteristics or qualities (e.g., color, texture), while quantitative data involves numerical measurements (e.g., height, weight). Examples of qualitative data: 1) Color of a flower, 2) Texture of a surface, 3) Taste of food. Examples of quantitative data: 1) Height of a plant (cm), 2) Number of leaves, 3) Temperature (°C).
What is the difference between a constant variable and a control group in an experiment?
A constant variable is kept the same throughout the experiment to ensure that the results are due to the independent variable, while a control group is a baseline group that does not receive the experimental treatment. Keeping certain variables constant is important to ensure valid results.
What are the functions, monomers, polymers, and examples of macromolecules?
1) Carbohydrates: Functions - energy storage; Monomers - monosaccharides; Polymers - polysaccharides; Examples - starch, glycogen. 2) Proteins: Functions - structure, enzymes; Monomers - amino acids; Polymers - polypeptides; Examples - enzymes, hemoglobin. 3) Nucleic Acids: Functions - genetic information; Monomers - nucleotides; Polymers - DNA, RNA; Examples - DNA, RNA. 4) Lipids: Functions - energy storage, cell membranes; Monomers - fatty acids and glycerol; Polymers - triglycerides; Examples - fats, oils.
What are the functions of enzymes?
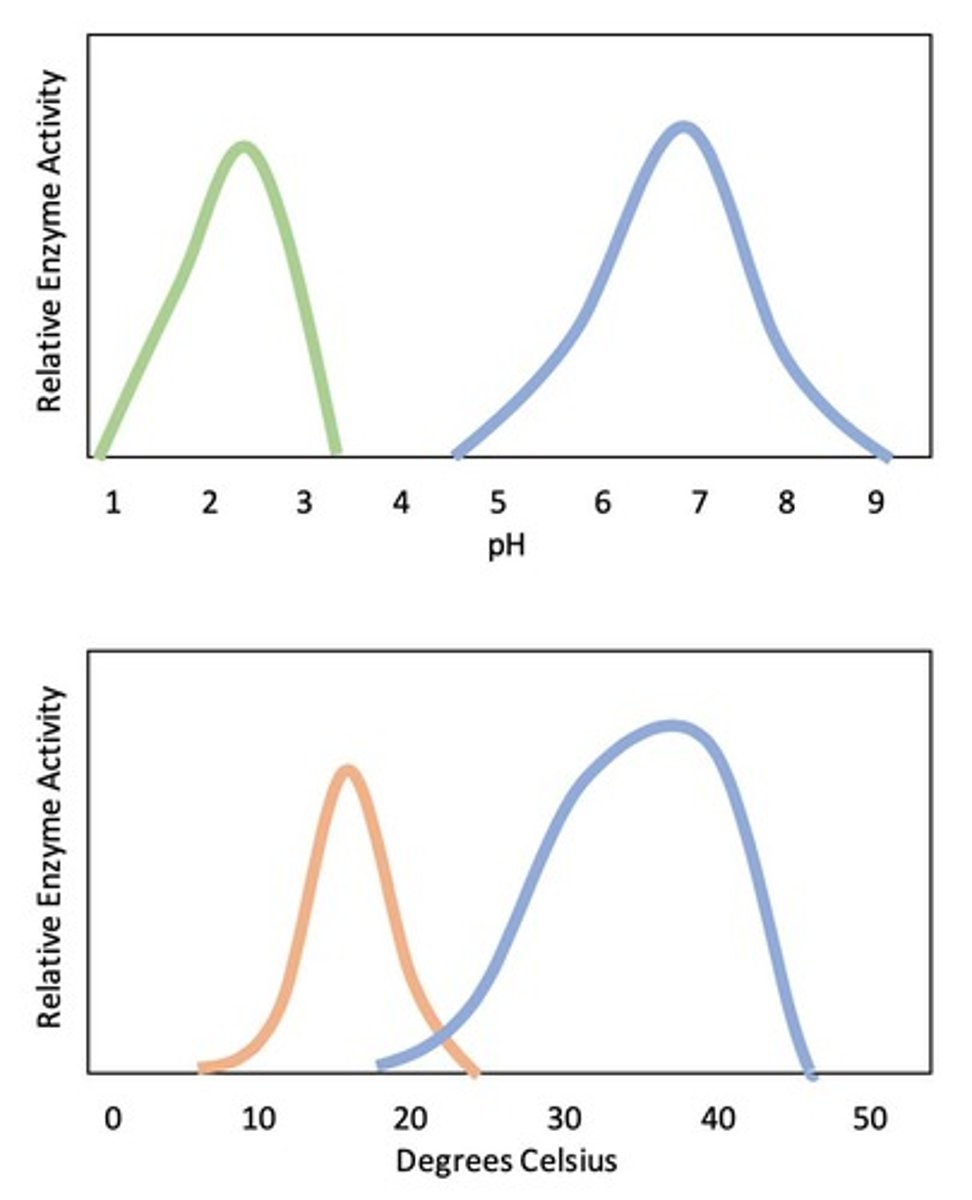
Enzymes act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. Factors affecting enzyme activity include temperature, pH, and substrate concentration.
What are the properties of water?
Water has several important properties: 1) Polarity - water molecules have a partial positive and negative charge; 2) Adhesion - water molecules stick to other substances; 3) Cohesion - water molecules stick to each other; 4) Density - ice is less dense than liquid water; 5) Solvency - water is a universal solvent.
What is the cell theory?
The cell theory states that: 1) All living organisms are composed of cells, 2) The cell is the basic unit of life, and 3) All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
What are the two main types of cells?
The two main types of cells are prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, and eukaryotic cells, which have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
What is the fluid mosaic model?
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of cell membranes as a flexible layer of lipid molecules with embedded proteins that can move laterally within the layer.
What is DNA replication?
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA before cell division, involving unwinding the double helix and synthesizing new complementary strands.
What are the roles of enzymes in DNA replication?
Key enzymes include helicase (unwinds the DNA), DNA polymerase (synthesizes new DNA strands), and ligase (joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand).
What is the central dogma of biology?
The central dogma of biology describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein, encompassing the processes of transcription and translation.
What is a point mutation?
A point mutation is a change in a single nucleotide in DNA, which can lead to changes in the corresponding amino acid in a protein. Examples include substitution, insertion, and deletion mutations.
What is the difference between trisomy and monosomy?
Trisomy is the presence of an extra chromosome (three copies of a chromosome), while monosomy is the absence of one chromosome (only one copy instead of two). Trisomy often has more severe effects than monosomy.
What is a pedigree chart?
A pedigree chart is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance of phenotypes of a particular gene or organism and its ancestors, used to analyze inheritance patterns.
What is the difference between autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant pedigrees?
In autosomal recessive pedigrees, the trait can skip generations and is expressed only when an individual has two copies of the recessive allele. In autosomal dominant pedigrees, the trait appears in every generation and requires only one copy of the dominant allele to be expressed.
Why can females never have a Y-linked disorder?
Females have two X chromosomes and no Y chromosome, so they cannot inherit Y-linked disorders, which are only passed on through the Y chromosome from father to son.
What is the difference between exons and introns?
Exons are the coding regions of a gene that are expressed in the final mRNA, while introns are non-coding regions that are removed during RNA splicing.
What are macromolecules?
Large, complex molecules essential for life, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What properties of water contribute to its unique characteristics?
Water's properties include polarity, adhesion, cohesion, density, and solvency, which are crucial for biological processes.
What is the significance of the optimum temperature or pH for enzymes?
The optimum temperature or pH is where enzyme activity is maximized; beyond this, enzymes can denature, sharply reducing reaction rates.
What are the three parts of the Cell Theory?
1. All living organisms are composed of cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of life. 3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
What distinguishes eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells do not.
What is passive transport?
The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy, including diffusion and osmosis.
What is active transport?
The movement of substances against their concentration gradient, requiring energy, often through protein pumps.
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA is a double helix composed of nucleotides, each containing a sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What are point mutations?
Genetic mutations that involve a change in a single nucleotide, which can affect protein synthesis.
What is a Punnett square?
A diagram used to predict the genetic outcomes of a cross between two organisms.
What is a karyotype?
A visual representation of an individual's chromosomes, used to identify chromosomal abnormalities.
What is the role of RNA in protein synthesis?
RNA serves as a template for protein synthesis, with different types of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA) playing distinct roles.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell, maintaining homeostasis.
What are feedback loops?
Biological mechanisms that regulate processes; positive feedback amplifies a response, while negative feedback reduces it.
What is the significance of surface area to volume ratio in cells?
A higher surface area to volume ratio increases efficiency in nutrient uptake and waste removal.
What are the stages of meiosis?
Meiosis consists of two rounds of division (meiosis I and II) resulting in four haploid cells from one diploid cell.
What is a frameshift mutation?
A genetic mutation caused by insertions or deletions of nucleotides that alters the reading frame of the gene.
What is the function of checkpoints in the cell cycle?
Checkpoints monitor and regulate the progression of the cell cycle, preventing uncontrolled cell growth and cancer.
What is the role of enzymes in DNA replication?
Enzymes such as helicase, DNA polymerase, and ligase facilitate the unwinding, synthesis, and sealing of DNA strands.
What is the difference between dominant and recessive traits?
Dominant traits are expressed in the phenotype even if only one allele is present, while recessive traits require two copies to be expressed.
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
Isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
simple diffusion
movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration with no fancy stuff
faciltated diffusion
process of diffusion in which molecules pass across the membrane through cell membrane channels
endocytosis and exocytosis
moving materials in or out of the membrane
types of excoytosis
phagocytosis (large clumps), pinocytosis (liquids)
primary active transport
active transport that moves ions or small molecules across a membrane and may create a difference in charge across that membrane
Enzymes are controlled by
Optimum PH / Tempature
Polarity
Molecules having uneven distribution of charges
Carbohydrates
monosaccharides/ Primary energy source/ short-term storage
Lipids
glycerol and fatty acids/ Long-term energy stroage
Proteins
amino acids/Enzymes/immunity/ cell signaling chemical
nucleic acids
DNA, RNA, nucleotides / Protein syntehtis
Varaible
A factor that can change durring an experiment
Constant Variable
The variable that doesn't change
control group
the group that does not receive the experimental treatment.
Prophase
chromosomes visible
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase
chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
Telophase
turns back into chromatids
What do checkpoints in the cell cycle do?
checks to insure cell is growing, duplicating dna & makes sure cell is functioning
Interphase 1
homologous chromosomes x2
phrophase 1 (meiosis)
Crossing over occurs
Metaphase 1
chromies in middle
anaphase 1
homologous chromosomes separate, but sister chromatids do not separate
Cytokenis 1
2 new haploid cells yayayya
Meiosis 2
So like in anaphase it turns into 4 haploid daughter cells whoopee
gene regulation
ability of an organism to control which genes are transcribed in response to the environment
Helicase
unzipper
DNA polymerase
x2 dna mollecules
Primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer.
Ligase
glues that shi tg
Trimosomy
x3 of a certian chromie
mRNA (messenger RNA)
encodes protiennnnn
What is the function of rRNA?
where da amino acids assemble
tRNA (transfer RNA)
carries amino acids to the ribosome
Monosomy
-1 chromie
Haploid
1 copy of each chromosome
Diploid
2 copies of each chromosome
How can you treat cancer?
surgery, radiation, chemotherapy
regulatory proteins
proteins involved in the expression of control genes
universal solvent
water
Cohesion property
the tendency of molecules of the same kind to stick together
ester bond
when fatty acids are joined to a glycerol
peptide bond
covalent bond formed between amino acids
glycosidic bond
covalent bond between two monosaccharides