AP Bio Unit 1
4.8(4)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From Princeton Review Book
Last updated 2:11 AM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
Elements
substances that connot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means
2
New cards
isotopes
when some atoms have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons
3
New cards
compound
when two or more individual elements are combined in a fixed ratio
4
New cards
ionic bond
formed between two atoms when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
5
New cards
ions
charged forms of an atom
6
New cards
covalent bonds
formed when electrons are shared between atoms
7
New cards
nonpolar covalent
when electrons are shared equally between atoms
8
New cards
polar covalent
when electrons are shared unequally
9
New cards
polar
molecules that have partially positive and partially negative charges
10
New cards
hydrogen bonds
weak chemical bonds that from when a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom
11
New cards
cohesion
the ability of water molecules sticking together
12
New cards
transpiration
when water molecules evaporate from a leaf, pulling on neighboring water molecules drawing up the molecules enabling water to move up the stem
13
New cards
adhesion
water molecules sticking to other substances
14
New cards
capillary action
when cohesion and adhesion occurs in thin vessels
15
New cards
acidic solution
when it contains a lot of hydrogen ions (H+)
16
New cards
basic solution
when it contains a lot of hydroxide ions (OH-)
17
New cards
alkaline
a basic solution
18
New cards
pH scale
a scale that is numbered from 1 to 14 measuring the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution
19
New cards
acidic range on the pH scale
20
New cards
basic range on the pH scale
>7
21
New cards
neutral pH range
7
22
New cards
organic compounds
molecules that contain carbon and oxygen
23
New cards
inorganic compounds
molecules that do not contain carbon molecules
24
New cards
polymers
Large molecules made up of repeating units called monomers
Ex. proteins
Ex. proteins
25
New cards
monomers
building blocks of polymers
26
New cards
dehydration synthesis
when a water molecule is lost and a larger compound is formed
27
New cards
hydrolysis
when water breaks the bond between the two monomers
28
New cards
Carbohydrates
organic compounds that contain Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
CHO
CHO
29
New cards
monosaccharides
one sugar
30
New cards
disaccharides
two sugars
31
New cards
polysaccharides
many sugars
32
New cards
glycosidic linkage
when two monosaccharides are joined
33
New cards
Proteins
organic molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen atoms
perform most of the work in you cells
perform most of the work in you cells
34
New cards
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
35
New cards
four important parts of an amino acid
1. amino group (NH2)
2. Carboxyl group (COOH)
3. Hydrogen
4. R-group
36
New cards
hydrophobic
non-polar and uncharged molecules that don’t like water
37
New cards
hydrophilic
polar and uncharged molecules that like water
38
New cards
dipeptide
when two amino acids join
39
New cards
peptide bond
when two amino acids bond
40
New cards
polypeptide
when a group of amino acids joins together in a string
41
New cards
protein
when a polypeptide chain twists and folds on itself forming a three-dimensional structure
42
New cards
primary structure
when the amino acids are in a linear sequence
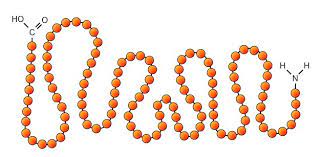
43
New cards
secondary structure
when the polypeptide forms either an alpha helix or a beta-pleated sheet
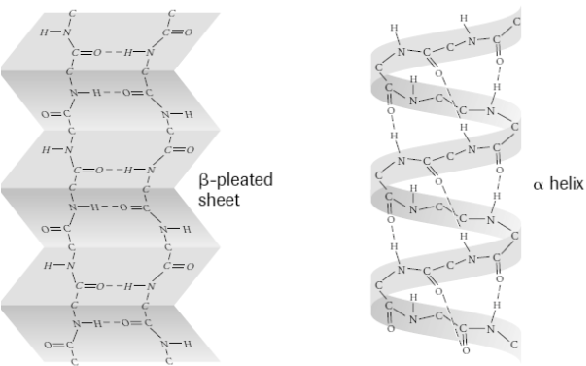
44
New cards
tertiary structure
when the polypeptide reshapes so that the r-groups interact with each other
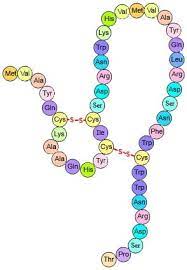
45
New cards
quaternary structures
when different polypeptide chains interact with each other
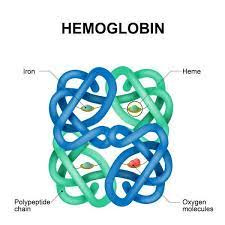
46
New cards
chaperone proteins (chaperonins)
proteins involved in the folding of other proteins that help it fold properly and make the process more efficient
47
New cards
Lipids
organic molecules consisting of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and sometimes phosphorus
function as structural components of cell membranes, energy storage and insulation, and signaling molecules
function as structural components of cell membranes, energy storage and insulation, and signaling molecules
48
New cards
saturated fatty acid
a fatty acid with hydrogens along its long carbon chain, no double bonds
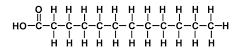
49
New cards
unsaturated fatty acids
when there is a double bond in the chain so not all carbons have two hydrogens
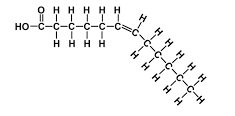
50
New cards
phospholipids
lipids that contain two fatty acid" “tails” and one negatively charged phosphate “head”
51
New cards
amphipathic molecule
a molecule that has both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region
Ex. phospholipids
Ex. phospholipids
52
New cards
Cholesterol
a four-ringed molecule that is found here and there in a membrane
type of lipid, increases membrane fluidity except at high temperatures when it helps to hold things together instead
type of lipid, increases membrane fluidity except at high temperatures when it helps to hold things together instead
53
New cards
Nucleic Acid
an organic compound that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen as well as sometimes phosphorus
54
New cards
nucleotides
make up nucleic acids
55
New cards
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
a polymer of nucleic acids that contains the hereditary “blueprints” for all life
56
New cards
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
a polymer of nucleic acids that is essential for protein synthesis