AP Pysch - Development Unit
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
cross sectional research
a research design that compares groups of people who differ in age but are similar in other important characteristics for a cognitive study
longitudinal research
a research design in which the same individuals are studied (over time) for a long time
ACE (adverse childhood experiences)
traumatic events that happen between the ages of 1 and 17. effects relationships people form throughout their lifespan, it impacts you later as you are developing
Achievement
established identity
zygote
fertilized egg
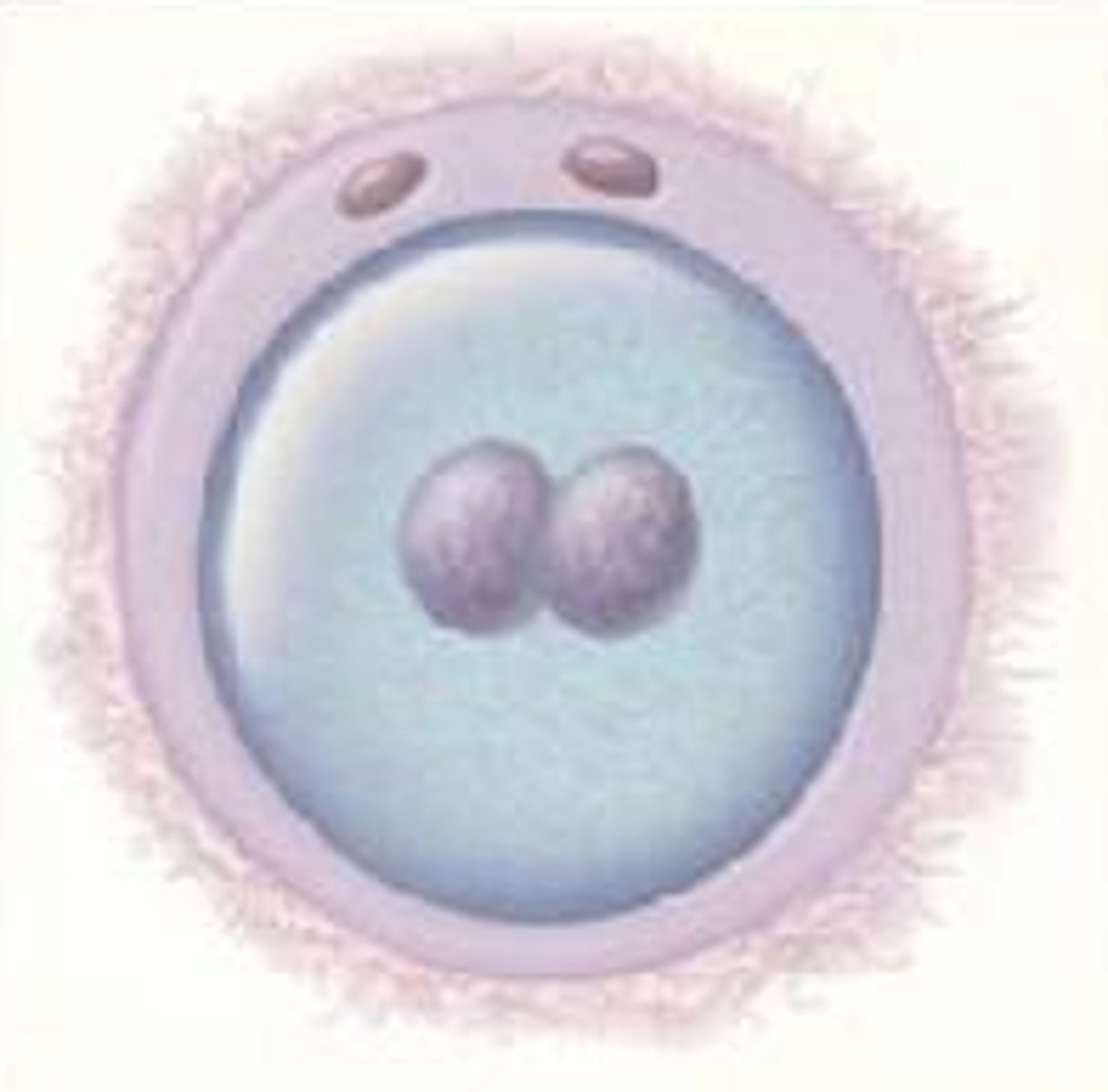
embryo
the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month
fetus
the developing human organism from 9 weeks after conception to birth
teratogens
agents that damage the process of development, they reach the fetus and cause birth defects
examples: drugs, alcohol, bacteria, viruses, chemicals
maternal illness, genetic mutations, hormones, environmental factors
Foreclosure
Committing to a goal because of parents, a goal the parents chose for them
Diffusion
no commitment in anywhere shape or form and NOT trying to figure it out, has no idea what to do in life
maturation
unfolding of natural/innate biological patterns, biological growth processes that enables changes in behavior, uninfluenced by experience
Adolescents develop a sense of identity through…
Diffusion, Foreclosure, Achievement, Moratorium
social clock
culturally preferred timing of social events, when certain things should have happened according to society such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement
temperament
an infants emotional activity, how do they react to people
Moratorium
trying to make a choice and figure out what you’re going to do in life
rooting
a reflex in which a newborn turns its head in response to a gentle stimulus on its cheek
Authoritarian
they made the rules and nothing else goes, my way or the highway, super strict
contact comfort
study with monkeys, babies prefer comfort over food
babinski
fanning and curling toes when foot is stroked
moro/startle reflex
throwing back the head and extending the arms, then rapidly drawing them in, in response to a loud sound or sudden movement
grasping (palmar reflex)
to take hold of somebody or something firmly, especially with the hand
school age
children play together, engage with friends via play
imprinting
the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life
critical periods
The time window in which something must be acquired. increased sensitivity to environment in order to master skill or task
separation anxiety
child is stressed of leaving the person that is their typical caregiver
strange situation
babies either develop a secure attachment or insecure attachment
secure attachment
an infant is happy to see mother after separation
insecure attachment
children do not trust their caregivers consistently and may show resistance or avoidance towards them
Erik Erikson
Made the theory of 8 psycho-social stages of development: theory shows how people evolve through the life span
parallel play
play side by side but not actually interacting with each other
basic trust
according to Erik Erikson, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with responsive caregivers
pretend play
children play pretend together, interacting
authoritarian parents tend to have children with _____
self esteem issues, and may develop lying habits, they tend to rebel, poor decision-makers, because of strict rules
authoritative parents tend to have children that are ______
happy, responsible, self confident, better decision makers, and successful
permissive parents tend to have children that ____
struggle academically, not responsible, don't respect authority, and report sadness and low self-esteem
uninvloved parents tend to have children that ______
struggle academically, don't respect authority, report sadness and low self-esteem, and have behavior issues
Authoritative
Yes there’s rules and consequences but also flexible
what parenting styles have a high level of control?
authoritative & authoritarian
Permissive
even if there are rules, there’s no consequence for breaking them
sensorimotor stage
babies experiencing the world through senses. object permanence
Age range: birth - 2 years
Sensorimotor Developmental Phenomena
object permanence, stranger anxiety
preoperational stage
Representing things with words and images, but lacking logical reasoning, lack of conservation, theory of mind
Age: 2-6 years
egocentric, theory of the mind, symbolic thinking, animism
preoperational stage developmental phenomena
pretend play, egocentrism, language development
stranger anxiety
the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age
symbolic thinking
ability to pretend, play make-believe, and have an imagination, use of symbols to represent the world
concrete operational stage
children have more rational and logical thinking. they gain the mental ability to comprehend mathematical transformations and conservation. conservation
Age: 7-11 years
concrete operational developmental phenomena
conservation, mathematical transformations
mathematical transformations
able to compute reversible math equations easily
conservation
the principle that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects, change in shape doesn’t mean change in quantity
formal operational stage
Abstract thinking: involving imagined realities and symbols
Age:12-adulthood
formal operational developmental phenomena
abstract logic, potential for moral reasoning, hypothetical reasoning
assimilation
integrating new information into existing cognitive schemas
example: seeing dog and thinking its a cat because 4 legs
accommodation
adapting or altering our current understandings (schemas) in response to new information that doesn’t match up existing schemas
example: a child adapts the existing schema to incorporate the knowledge that some four-legged animals are horses.
schemas
cognitive structure, framework that organizes and interprets information
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
social development psychologists
Harry Harlow, Konrad Lorenz, Mary Ainsworth, Erik Erikson, Diana Baumrind
cognitive development psycologists
Jean Piaget & Lev Vygotsky
Jean Piaget
Known for his theory of cognitive development in children
Lev Vygotsky
most famous for social development theory (of child cognitive development)
scaffolding
the support for learning and problem solving that encourages independence and growth
zone of proximal development
the area where they are learning. the area between what a child has already learned and what they are about to learn if they receive proper guidance and instruction
More Knowledgeable Other
we turn to a More Knowledgeable Other (MKO) as we learn tasks and skills
example of a MKO
parent, teacher, or other adult
trust vs. mistrust
infants learn to trust when they are cared for, parents fulfilling the needs of a child
trust = needs met, mistrust = no needs met
autonomy vs. shame & doubt (2-3 years old)
a toddler learns to do things independently, they express self control, say no, and try to do things themselves; failure causes parents to shame and doubt them
initiative vs. guilt (4-5 years)
child finds independence in planning, playing and other activities. The child has more responsibility, and asks why all the time. parents make them feel bad for asking questions
industry vs. inferiority (6 - 11 years)
the child learns to be productive, they go through hard work and learning. How are teachers and parents making the child feel when they’re getting, or not getting, what they’re learning
identity vs. role confusion (adolescence)
which teenagers and young adults search for and become their true selves, who am i, trying to figure out identity, looks to role models and peer groups to develop plans for the future
intimacy vs. isolation (young adulthood)
individuals form deeply personal relationships, marry, begin families. learning to share yourself and finding someone to share yourself with
generativity vs. isolation (Middle Adulthood)
have found meaning in work or parenthood. thinking if you have done enough or not, responsibility for next generation, have they accomplished something worth while, volunteering and giving back to the community
integrity vs. despair (Late Adulthood)
those near the end of life look back and evaluate their lives. fulfillment, pride, regret, happy or sad, what would they have done differently
primary sex characteristics
the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) needed for sexual reproduction
secondary sex characteristics
non-reproductive sexual characteristics, such as female breasts and hips, male voice getting deeper, and body hair
menarche
the first menstrual period
"Storm and Stress"
G. Stanley Hall's phrase for the intense moodiness, emotional sensitivity, and risk-taking tendencies that characterize the life stage he labeled adolescence
imaginary audience
adolescents belief that they are the focus of everyone else's attention and concern, everybody is watching them, they feel like they’re under constant surveillance
personal fable
type of thought common to adolescents in which young people believe themselves to be unique and protected from harm, that no one understands what you’re going through
menopause
cessation of menstruation, women’s inability to reproduce
five stages of grief
1. Denial
2. Anger
3. Bargaining
4. Depression
5. Acceptance
crystalized intelligence
facts and knowledge that have accumulated over time; tends to increase with age
example of crystallized intelligence
Reading comprehension and vocabulary exams
fluid intelligence
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood, declines as people age
example of fluid intelligence
solving puzzles and coming up with problem-solving strategies
Alzeheimer's Disease (AD)
A progressive disease that destroys the brain's neurons, gradually impairing memory, thinking, language, and other cognitive functions
gender stereotypes
overgeneralizations about the behavior of people based on their gender, rooted in society and developed as societal norms
sex
the biological/genetic distinction between females and males. child’s sex is genetically determined by father
gender
socially influenced characteristics by which people define male and female. attitudes, feelings, and behavior, that a given culture associates with a person’s biological sex
Homosexuality
gay (studies shown genetic predisposition, twin studies)
X chromosome
The sex chromosome found in both men and women. Females have two X chromosomes; males have one.
Y chromosome
the sex chromosome found only in males
sexual orientation
a person's romantic and emotional attraction to another person. based on genetics, prenatal hormones, and social influences
gender identity
personal sense of being male or female (or neither or combo)
testosterone
Male sex hormone
gender roles
expected behaviors, attitudes, and traits for men and women, can be based on culture
Sexualization
the acts or processes whereby an individual or group is seen as sexual in nature or persons become aware of their sexuality
morality of women
idea from Carol Gilligan that women strive to survive, but self-sacrifice for goodness, and believe in nonviolence
why did Gilligan disagree with Kohlberg?
he only worked with white males