MECH 3542 Key Points 1
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Thermal expansion
The change in size or volume of a material as a result of temperature variations, characterized by the coefficient of thermal expansion denoted by alpha.
Shrink-fit assemblies
Assemblies created by heating and cooling parts to expand or contract their geometry for fitting purposes.
Melting point
The temperature at which a material transitions from a solid to a liquid state.
Heat of fusion
The amount of heat energy required at the melting point for a material to transition from a solid to a liquid state.
Solidus and liquidus temperatures
The temperatures at which melting begins and ends for alloys, with the material being a mix of solid and molten metals in between.
Thermal diffusivity calculation
The thermal conductivity, higher in metals due to free electrons, influences the material's ability to conduct heat.
Ohm’s law
The relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in a circuit, expressed as V=IR.
Resistivity
The material's property defining its resistance to current flow, varying with temperature and increasing in metals with temperature.
Conductivity
The reciprocal of resistivity, indicating a material's ability to conduct electricity.
Semiconductors
Materials with resistivity between insulators and conductors, like silicon.
Electrolyte
A solution containing ions for conducting electricity.
Electrodes
Points where current enters and leaves an electrolyte solution in electrochemical processes.
anode
Anode: Positively charged electrode where oxidation happens in an electrochemical cell, which donates electrons to the solution
Cathode
Negatively charged electrode which is plated in the electrochemical process
Toughness
Energy that a material can absorb before failure/area under the total stress-strain curve
Stiffness
Ability to resist stretching ot deflecting under load
Resilience
Energy that a material can absorb in the elastic range/area under the elastic region of the stress-strain curve
Hardness
Ability to resist plastic deformation
Ductility
Ability to accept plastic deformation
Proportional limit
The point on a stress-strain curve where elastic deformation becomes non-linear
Thermoplastic
Polymers that become viscous liquids when heated to moderate temperatures. They can be melted and reused without significant degradation.
Thermoset
Polymers which are highly crosslinked, and cannot tolerate repeated heating cycles. If heated, thermosets degrade rather than soften
Elastomers
Polymers that exhibit extreme elastic extensibility under low mechanical stress.
Name three thermosets
Phenolic, epoxy, polyesters
What are the two categories of elastomers?
Natural rubber and synthetic rubber
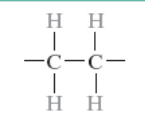
What is the monomer for polyethylene?
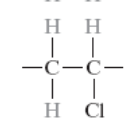
What is the monomer for polyvinyl chloride?
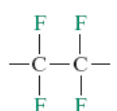
What is the monomer for polytetrafluoroethylene?
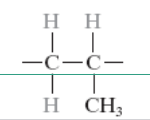
What is the monomer for polypropylene?
What is the monomer for polystyrene?
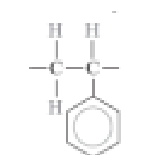
What is the monomer for PMMA?
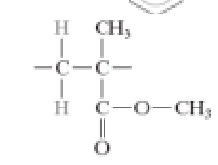
What is the structure of nylon 6,6?
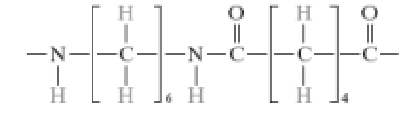
What is addition polymerization?
Double bonds between carbon atoms in ethylene monomers are made to open up with a chemical catalyst, so they can join with other monomers. Only monomers will join onto ends of the polymers. It is faster than step polymerization.
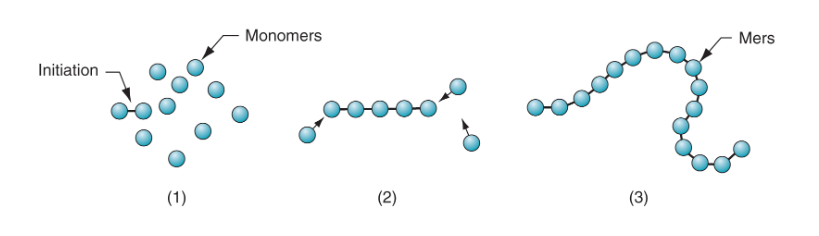
What is step polymerization?
Two reacting monomers come together to form a new molecule. Reactant molecules continue to combine with the first polymer formed, and so on. Smaller polymers will also join to form larger polymers. It is slower than addition polymerization.
What do the following polymer structures look like: Linear, branched, crosslinked?
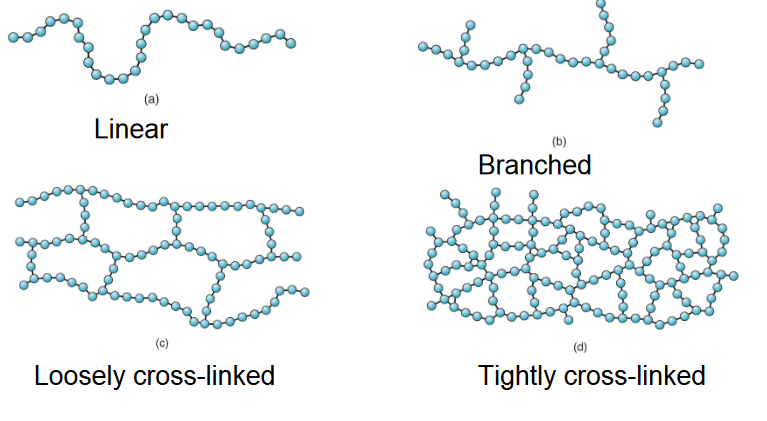
What molecular structure do thermoplastics have?
Linear or branched structure
What molecular structure do thermosets and elastomers have?
Crosslinked—thermosets are highly crosslinked, and elastomers are less crosslinked
Define degree of crystallinity
The amount of a polymer which exhibits a crystalline structure
What happens to the properties of a polymer when crystallinity is increased?
Density, stiffness, strength, and heat resistance increase. The polymer may also become more opaque.
How do the mechanical properties of thermoplastics compare to those of metals and ceramics? List 7 differences.
Thermoplastics have a lower Young’s modulus, lower tensile strength, lower hardness, and greater ductility. They also have lower density, higher coefficient of thermal expansion, and lower melting temperatures.
What happens when a thermoset is cured?
A chemical reaction occurs which causes the polymer chains to become tightly crosslinked.
What is vulcanization?
The process of curing natural rubber by increasing the degree of crosslinking within the molecular structure.
How do you calculate molecular number average and molecular weight average?
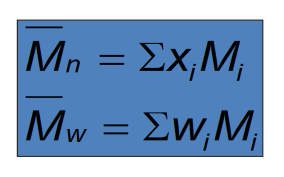
What occurs to the crystalline regions in a semicrystalline polymer when placed under tensile stress?
The crystalline regions align along the stretching direction.
Define strain rate
the measure of how quickly deformation occurs in a material. It is the change in strain over time.
What happens to the mechanical properties of thermoplastics when temperature is decreased?
Decreased ductility, increases strength, increases stiffness
What happens to the mechanical properties of thermoplastics when strain rate is increased?
Decreased ductility, increased strength, increased stiffness
Define matrix phase and dispersed phase as it relates to composites.
Matrix phase: continuous, usually softer material that houses the dispersed phase. Dispersed phase: discontinuous material surrounded by the matrix phase, added to impart some mechanical properties to the composite.
What is MMC?
Metal matrix composite, where the matrix material is a metal
What is CMC?
Ceramic matrix composite, where the matrix material is a ceramic.
What is PMC?
Polymer matrix composite, where the matrix material is a polymer.
What is an interphase in a composite?
A third material which ensures the matrix and dispersed phases can effectively bond. Bonding of the matrix and dispersed phase is crucial for the composite function.
What three factors determine composite material properties?
1) Materials used as component phases 2) Shape and dispersion of the components 3) How each phase interacts with each other
What are the 3 classifications of composites?
Fiber-reinforced, particle-reinforced, and structural
Define cermet
A metal matrix composite (MMC) with a ceramic as the dispersed phase
Define ceramic
Inorganic compound consisting of a metal/semi-metal and nonmetals
Name 4 material properties commonly associated with ceramics.
High hardness, electrically/thermally insulating, high melting temperatures, extremely low ductility
Should a metal casting mold be made smaller, the same size, or larger than the actual part dimensions? Why?
Casting molds should be made slightly larger, to account for metal shrinkage during cooling.
Define cope and drag in the metal casting process.
Cope: upper part of the metal casting mold / Drag: lower part of the metal casting mold.
What is the advantage of using an expendable mold over a permanent mold in metal casting? What is the disadvantage?
Expendable molds can produce more intricate part geometries, however they are more costly when used for high-volume production.
What is the flask in metal casting?
The container which contains the casting mold halves
What is the parting line in metal casting?
The line which separates the upper and lower half of the casting mold (separates the cope and drag)
What is a core in metal casting?
A piece of the mold placed inside the mold cavity which forms the interior geometry of the part.
What is the purpose of a riser in metal casting?
To supply liquid metal to the mold cavity, which accommodates for part shrinkage.
Name 4 defects associated with the casting process.
Metal oxide formation, gas porosity, penetration, hot tears
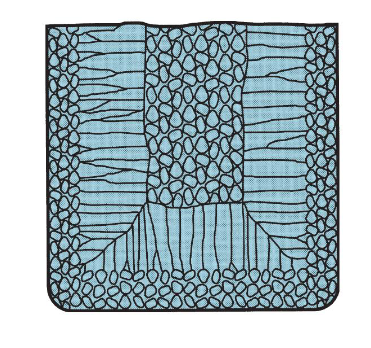
What does the grain structure of casted pure metals look like?
Randomly-oriented grains near the mold wall, large columnar grains oriented to the center of the casting.
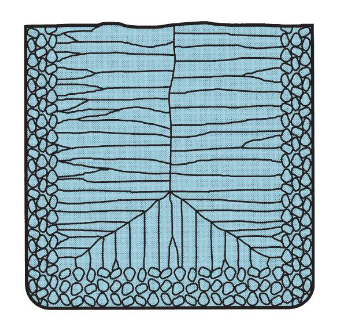
What does the grain structure of casted alloys look like?
Segregated randomly-oriented grains in the center, randomly-oriented grains near the wall, and columnar grains in between.
What is the equation for determining solidification time in casting?
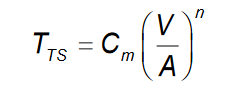
What is the equation that relates the solidification time between the mold and the riser in the casting process?
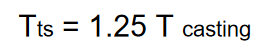
List 3 basic types of sheet metal forming processes
Cutting (shearing, blanking, punching), Bending, Drawing
Define cold working
Metal forming process that takes place at room temperature
Define warm working
Metal forming process that takes place above room temperature, but below the recrystallization temperature
Define hot working
Metal forming process which occurs above the recrystallization temperature (approx. half the melting temperature)
For creating threads, which process if preferred: turning or rolling? Why?
Threads should be rolled, as this gives them better strength and is better suited to high production volume
What material properties are desirable for metal forming
Low yield strength and high ductility
What is the equation to calculate flow stress in the plastic region?
where K is the strength coefficient and n is the strain hardening exponent
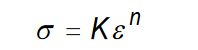
What are 4 advantages of cold forming?
Better accuracy, better surface finish, strain hardening increases strength/hardness, no heat input required
What are 3 disadvantages of cold forming?
Higher power input required, surfaces must be clean, strain hardening limit the extent of forming
What are 3 advantages of hot working?
Lower power input required, properties of product are isotropic, no strain hardening occurs
What are 4 disadvantages of hot working?
Lower dimensional accuracy, higher energy input is required, oxidation is a concern, and shorter tool life
Why is friction undesirable in metal forming?
metal flow is reduced, higher power input is required, tools wear faster
What are the benefits of adding lubrication in metal forming?
Reduced friction, better tool life, better surface finish, removes heat from tooling
Define bulk deformation in metal working
Metal forming operations which cause significant shape change through plastic deformations
Define rolling (metalworking process)
Work thickness is reduced by compressive forces exerted by rolls
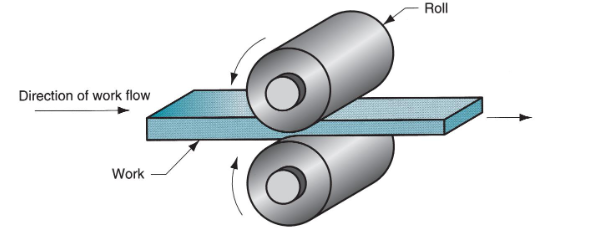
Define rolling draft, and how it is calculated
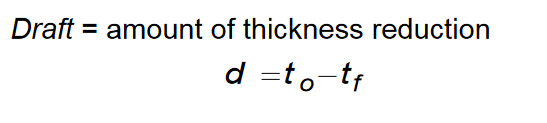
Define rolling reduction, and the equation to calculate it
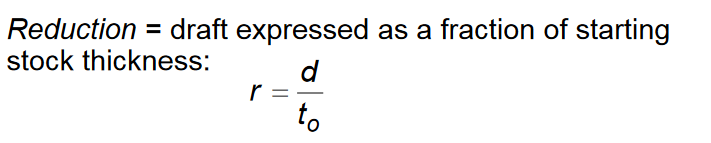
Define forging (metalworking process)
Deformation process where work is compressed between two dies
Name 7 machining operations
Turning, drilling, milling, shaping, planing, broaching, sawing
What is the equation to calculate chip thickness ratio?
Note: chip ratio is always less than one, because chip thickness after cut is always greater than the original
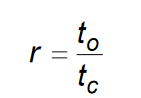
What is the equation for calculating machining shear strain?

What are the four basic types of chips in machining?
Discontinuous, continuous, continuous with built-up edge, serrated chip
What is the Merchant equation, and what does it signify?
To increase the shear plane angle, we must increase the rake angle or reduce the friction angle, or reduce the friction coefficient

Define turning
A material removal process using a single point cutting tool, which removes material from a rotating workpiece
Define milling
Machining operation where work is fed past a rotating tool with multiple cutting edges
Define drilling
Machining operation where a drill bit rotates relative to the workpiece. Relative velocity at the drill point is zero, thus no cutting takes place by the turning motion alone—a large thrust force is required to form the hole
What are the three modes of tool failure?
Fracture, temperature, gradual wear
What are the two types of gradual tool wear?
Crater wear (occurs on top rake face) and flank wear (occurs on flank)
What is the Taylor tool life equation?

What are the three most important properties when selecting tooling material?
Toughness, hot hardness, wear resistance
Define brazing
Joining process where filler metal is used to permanently join parts, but no melting of base metals occurs