Translation and Mutation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
proteins
polymers of amino acids
protein functions
enzymes, transporters, communication, build cell structures
a protein’s function
is determined by its structure
primary structure
linear sequence of amino acids in a protein
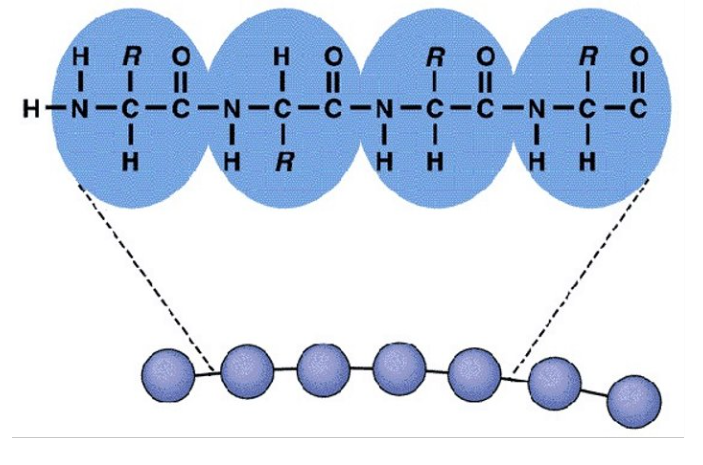
amino acids
covalently connected by peptide bonds through carboxyl groups
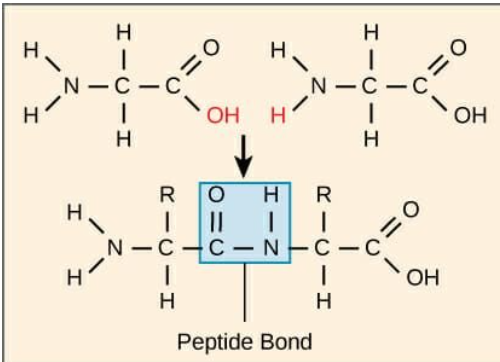
peptides
are short amino acid chains
polypeptides
are long chains of amino acids
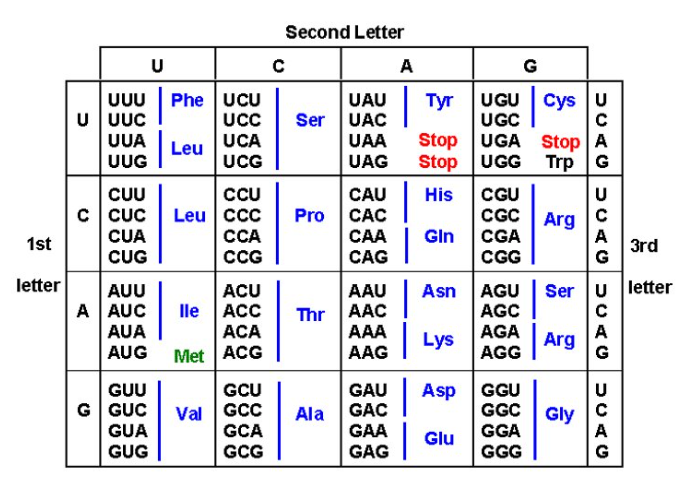
amino acids are coded for
on mRNA
multiple codons
for each amino acid
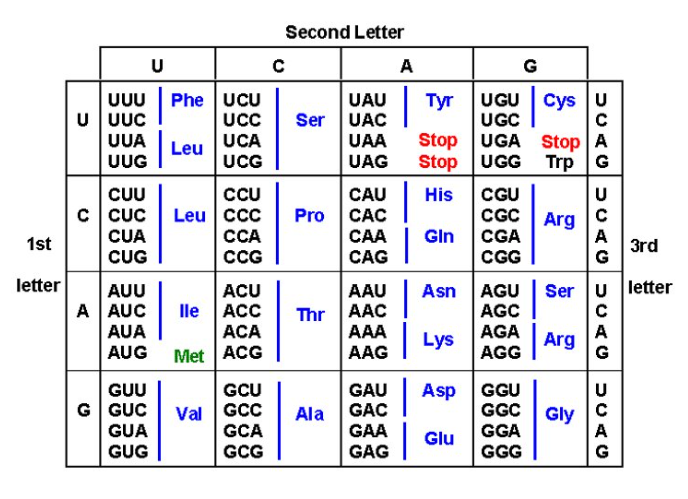
each amino acid
has its own tRNA determined by mRNA sequence
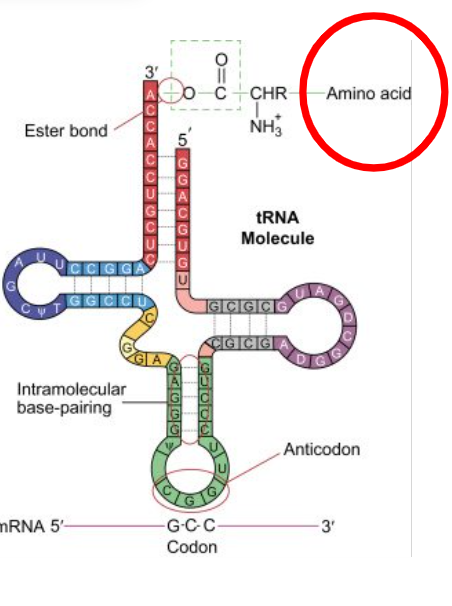
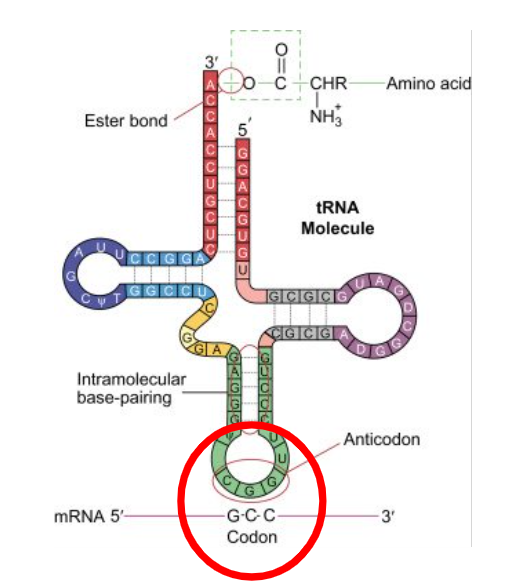
codon on mRNA binds to
the anticodon on tRNA
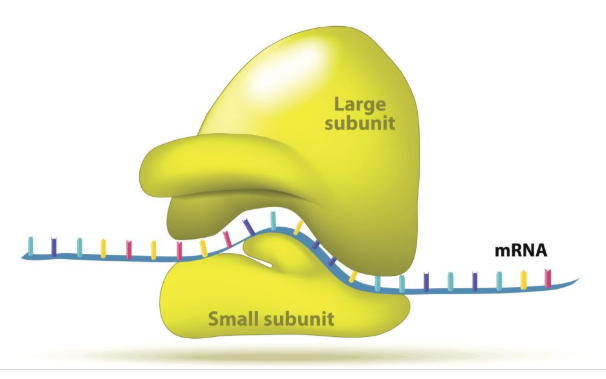
before translation begins
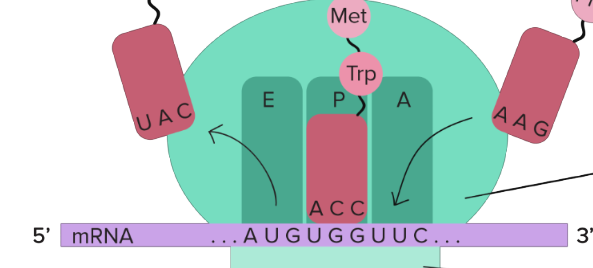
ribosome assembles
shine-Dalgarno sequence
ribosome binds here on mRNA
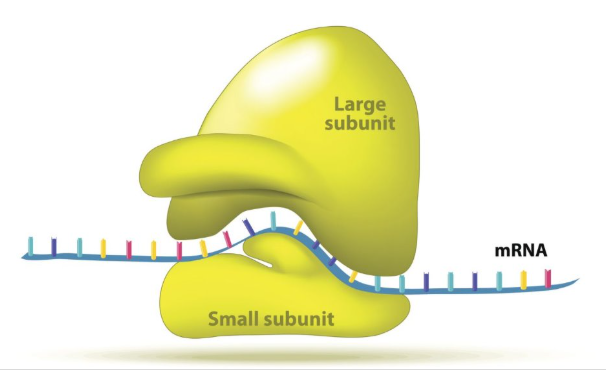
large subunit of ribosome
50S
small subunit of ribosome
30S
large subunit contains
three sites for tRNA
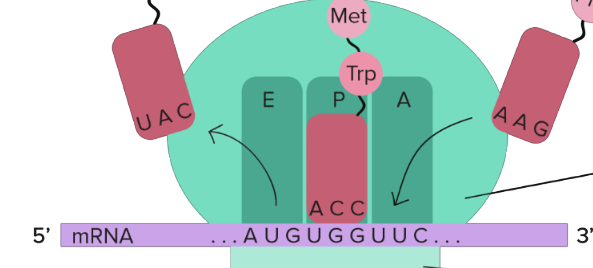
tRNAs carrying amino acids
fit into sites on large subunit
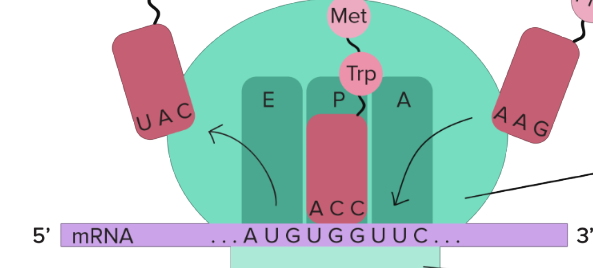
A site of large subunit
amino acids arrive here
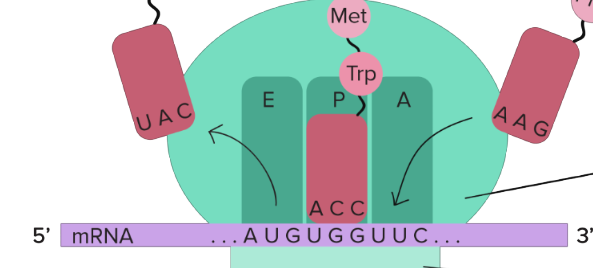
P site of large subunit
peptides are made here, where growing polypeptide is found
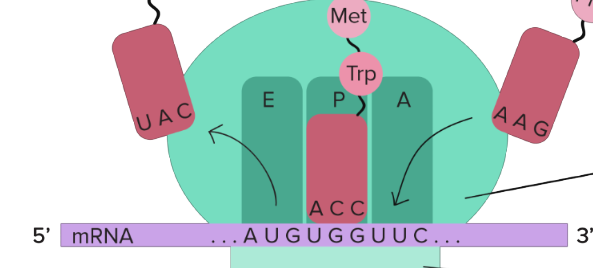
ribosomes have
peptidyl transferase activity carried out by rRNA that act as ribozymes
E site
where empty tRNA exits the ribosome
methionine
start codon
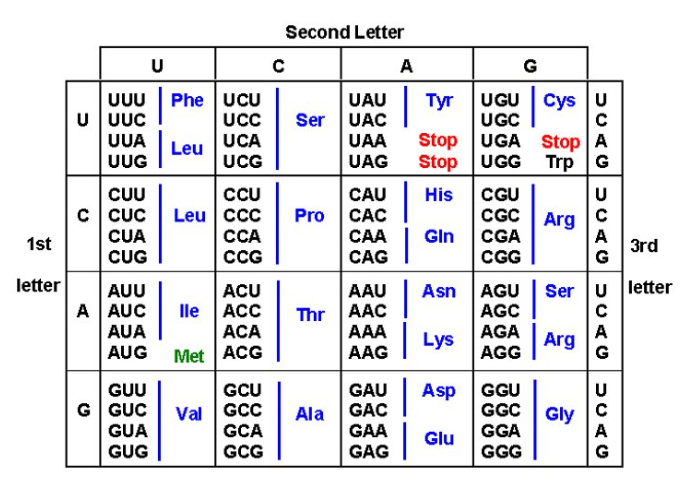
stop codons
end translation
point mutation
single nucleotide is switched
silent mutation
mutation that has no affect
missense mutation
mutation that changes amino acid sequence
nonsense mutation
mutation that stops translation
proofreads
rn polymerase cannot correct mistakes
frameshift mutation
whole base is inserted or removed
thymine dimers
cause dna polymerase to stall, occur when exposed to UV radiation, can be repaired or cut out
mutagens
ionizing radiation, reactive oxygen species, intercalating agents