Chemistry - Chapter 6
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
energy
law of conservation of energy
capacity to do work or produce heat, a state function
energy can be converted from one form to another, but can be neither created nor destroyed
types of energy
radiant energy: comes from the Sun and is Earth’s primary energy source
thermal energy: energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules
chemical energy: energy stored within the bonds of chemical substances
nuclear energy: energy stored within the collection of neutrons and protons in the atom (nucleus)
potential energy: energy available by virtue of an object’s position, energy due to position or composition
kinetic energy: energy due to the motion of the object and depends on the mass of the object and its velocity
heat vs. temperature
involves the transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature differences, not a state function
a measure of thermal energy, not equal to thermal energy
work
state function
force acting over a distance, not a state function
a property that does not depend in any way on system’s past or future, only the present, energy is a state function, work and heat are not
universe
surroundings
system
contains surroundings and system
include everything else in the universe
part of universe where attention is at
endothermic reaction
heat flow is into system
thermal energy is transferred from surroundings to system
energy is absorbed from surroundings
system is positive
if temperature increases, rate of reaction increases
(energy on the reactants side of a chemical reaction)
exothermic reaction
heat flow is out of system
thermal energy is transferred from system to surroundings
energy is released from system
system is negative
if temperature increases, rate of reaction increases
(energy on the products side of a chemical reaction)
thermodynamics vs. thermochemistry
the study of energy and its interconversions, the study of the effects of work, heat, and energy on a system
the study of heat change in chemical reactions
heat energy equation
Q = m c △T
Q: energy transferred (J)
m: mass (g)
c: specific heat capacity (4.184 for water, 0.451 for iron, 0.900 for aluminum)
△T: temperature change (C)
J / C = calories
convert if unit for temperature and calories are not the same
4 quantities of thermodynamics
temperature (T)
internal energy (U)
entropy (S)
heat (Q)
classical thermodynamics vs. statistical thermodynamics
concerns the relationships between bulk properties of matter
seeks to explain those bulk properties of matter in terms of constituent atoms
laws of thermodynamics according to British scientist C.P. Snow
you can’t win
you can’t break even
you can’t get out of the game
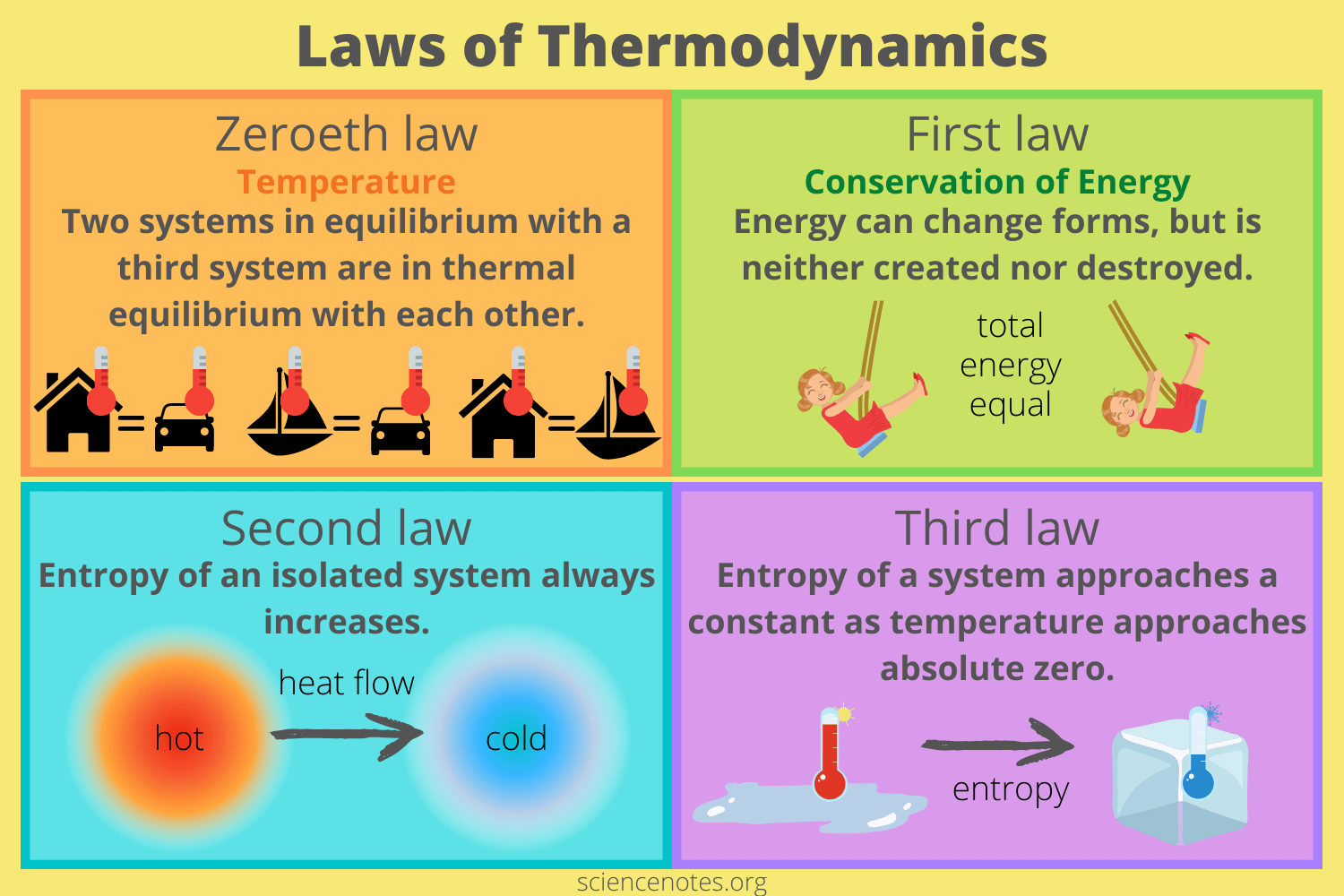
1st law of thermodynamics
energy can be converted from one form to another, but can be neither created or destroyed
an extension of the law of conservation of energy
the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system
△U = Q ± W
2nd law of thermodynamics
entropy of an isolated system always increases, heat flows spontaneously from a hot object to a cold object (spontaneously meaning without the assistance of external work)
every effort put forth, no matter how efficient, will have a tiny bit of waste
3rd law of thermodynamics
no system can reach absolute zero
this is why the Kelvin temperature scale is used, not only is the internal energy proportional to temperature, but you never have to worry about dividing by zero in an equation
0th law of thermodynamics
two systems in thermal equilibrium with a third system and in thermal equilibrium with each other
internal energy
the sum of the potential and kinetic energies of all the “particles” in the system
thermodynamic quantities
consists of two parts: number gives the magnitude of change, sign indicates the direction of flow
sign reflects the system’s point of view
endothermic process: q is positive
exothermic process: q is negative
system does work on the surroundings: W is negative
surroundings do work on the system: W is positive
1st law terminology
adiabatic: no heat transferred (Q = 0) (specifically for closed, isolated, insulated systems)
isothermal: constant temperature
isobaric: constant pressure
isochoric: constant volume
adiabatic process
a process that transfers no heat
when a system expands adiabatically, W is positive (system does work) so △U is negative
when a system compresses adiabatically, W is negative (work is done on system) so △U is positive
Q = 0
△U = ±W
isothermal process
a constant temperature process
any heat flow into or out of the system must be slow enough to maintain thermal equilibrium
for ideal gases only
△T = 0, △U = 0
±Q = -/+W
isobaric process
a constant pressure process
△U, W, and Q are generally non-zero, but calculating the work done by an ideal gas is straightforward
ex. water boiling in a saucepan
W = ± P x △V
U = ±Q ±W
isochoric process
a constant volume process
when the volume of a system doesn’t change, it will do no work on its surroundings
ex. heating gas in a closed container
△V = 0, W = 0
△U = ± Q
W = ±P x △V
w: atm x L
expanding is -, compressing is +
1 atm x L = 101.3 J
enthalpy
H, the heat content of a chemical system, used to quantify the heat flow into or out of a system
process that occurs at constant pressure, state function
△H = Hproducts - Hreactants
enthalpy change
the amount of heat released or absorbed when a chemical reaction occurs at constant pressure, kJ/mol
endothermic reaction
energy is absorbed
energy is a reactant of the reaction
reaction vessel becomes cooler and temperature decreases
energy of products > energy of reactant
sign of △H is positive
ex. solid to liquid, liquid to gas
exothermic reaction
energy is released
energy is a product of the reaction
reaction vessel becomes warmer and temperature increases
energy of reactants > energy of products
sign of △H is negative
ex. liquid to solid, gas to liquid
calorimetry
the science of measuring heat, measures the thermal energy (heat) exchanged between the reaction (the system) and the surroundings
by measuring the change in temperature of water
△E
specific heat capacity
the energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius
molar heat capacity
the energy required to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance by one degree Celsius
constant volume calorimetry
device called a constant volume (bomb) calorimeter
system: sample is burned in oxygen gas
surroundings: calorimeter
qcal = Ccal x △T
qrxn = -qcal
use mcat when heat capacity of calorimeter is not mentioned, but when it is use the equation (m = amt of water in mL)
whatever the calorimeter received, the reaction gave away
use heat capacity to find sig figs
△Erxn can also be expressed per mole of reactant
divide qrxn by moles of reactant
data from certain experiments would not give the correct molar heats of combustion because calorimeters would not usually have that much energy
constant pressure calorimetry
constant pressure (usually 2 styrofoam coffee cups)
reaction takes place in solution inside inner cup
volume is not constant due to evaporation
qsoln = msoln x cs, soln x △T
add mass when “dissolved” or “stirred” only if temps are the same, if temps diff then do equations separate and then add
qrxn = -qsoln
△Hrxn = -qsoln / molsoln
standard enthalpy of formation (△Hf^0)
the heat change that results when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 298 K
standard enthalpy of formation of any element in its most stable form is zero
they are compiled in huge tables of thermodynamic quantities
calculating △H for a reaction
aA + bB > cC + dD
△Hrxn^0 = c (△Hf^0 (C) ) + d (△Hf^0 (D) ) - (a (△Hf^0 (A) ) + b (△Hf^0 (B) ) )
balance equation
add the products first then add the reactants, THEN subtract
ex. I2, H = 0
write if exothermic or endothermic
Hess’s Law
when reactants are converted to products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps
calculating △H for multiple reactions
work backward from the required reaction, using the reactants and products to decide how to manipulate the other given reactions at your disposal
reverse any reactions as needed to give the required reactants and products
multiply reactions to give the correct numbers of reactants and products
change the sign of and multiply △H as needed