6.1 - 6.2 Inquiry into Biology (Bio 20)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
Last updated 5:34 AM on 2/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
Homeostasis
* The dynamic constancy of the internal environment
* is a dynamic equilibrium (always fluctuating)
* if the part of our body is concerned w/ reproduction it is most likely concerned w/ homeostasis
* to maintain a constant internal environment our body has sensors that measure each condition. the sensors constantly monitor these conditions and relay them to a control centre (often a region of the brain or spinal cords but can also be endocrine glands)
* the control centre receives messages from several sensors and then determines whether the value of the condition is deviating from the set point.
* when deviation occurs (stimulus), the integrating centre sends a message to increase or decrease the activity of particular effectors
* effectors are usually muscles or glands and can change the value of the condition in question back to the “set point” (response)
* negative feedback loops maintain a state of homeostasis by correcting deviations form a set point.
* ie) a sensor detects a change that disrupts a balanced state and signals a control centre. the control centre then activates an effector which reverse the change and restores the balanced state
* is a dynamic equilibrium (always fluctuating)
* if the part of our body is concerned w/ reproduction it is most likely concerned w/ homeostasis
* to maintain a constant internal environment our body has sensors that measure each condition. the sensors constantly monitor these conditions and relay them to a control centre (often a region of the brain or spinal cords but can also be endocrine glands)
* the control centre receives messages from several sensors and then determines whether the value of the condition is deviating from the set point.
* when deviation occurs (stimulus), the integrating centre sends a message to increase or decrease the activity of particular effectors
* effectors are usually muscles or glands and can change the value of the condition in question back to the “set point” (response)
* negative feedback loops maintain a state of homeostasis by correcting deviations form a set point.
* ie) a sensor detects a change that disrupts a balanced state and signals a control centre. the control centre then activates an effector which reverse the change and restores the balanced state
2
New cards
Nucleic Acids
function:
1) direct cell growth & department of cells
2) expression and transfer of genetic code
subunit: nucleotides (4 different types)
types of nucleic acids:
* RNA: ribonucleic acid - involved in the making of proteins
* DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid: in the nucleus, contains genetic info for building cells/protein
1) direct cell growth & department of cells
2) expression and transfer of genetic code
subunit: nucleotides (4 different types)
types of nucleic acids:
* RNA: ribonucleic acid - involved in the making of proteins
* DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid: in the nucleus, contains genetic info for building cells/protein
3
New cards
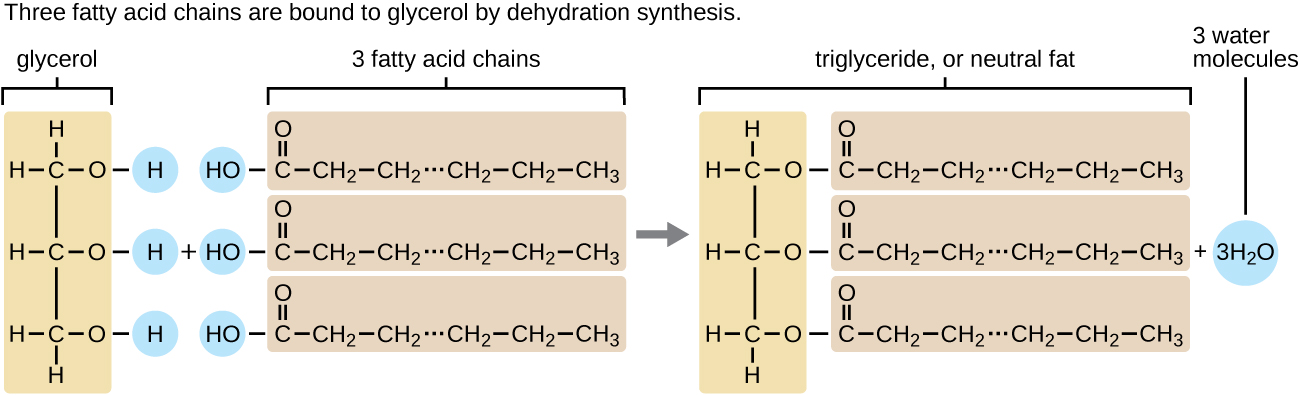
Lipids
function:
1) phospholipid bilayer (cell membrane)
2) energy storage → butter, oil, lard (fats&oils)
3) steroids → form sex hormones (estrogen&testosterone)
subunit: 3 fatty acids & glycerol
saturated fatty acids: do not have any double bonds between any carbons (solid at room temp)
unsaturated fatty acids: at least one double bond between the carbons (liquid at room temp)
* add drop on paper and if it doesn’t absorb completely and is translucent then lipids are present
1) phospholipid bilayer (cell membrane)
2) energy storage → butter, oil, lard (fats&oils)
3) steroids → form sex hormones (estrogen&testosterone)
subunit: 3 fatty acids & glycerol
saturated fatty acids: do not have any double bonds between any carbons (solid at room temp)
unsaturated fatty acids: at least one double bond between the carbons (liquid at room temp)
* add drop on paper and if it doesn’t absorb completely and is translucent then lipids are present
4
New cards
Proteins
function:
1) used in muscle, transport, (carrier proteins), antibodies, etc…
2) make up most cellular structures
subunit: amino acids
* 20 amino acids; 11 are synthesized by the body but 9 must come from your diet
* add biuret reagent (blue) and if colour changes to violet proteins are present and if it changes to pink peptides are present
1) used in muscle, transport, (carrier proteins), antibodies, etc…
2) make up most cellular structures
subunit: amino acids
* 20 amino acids; 11 are synthesized by the body but 9 must come from your diet
* add biuret reagent (blue) and if colour changes to violet proteins are present and if it changes to pink peptides are present
5
New cards
Carbohydrates
* types of carbohydrates
1) monosaccharides: one simple sugar, eg. glucose
2) disaccharides: two simple sugars, eg. maltose
3) polysaccharides: many linked simple sugars
* starches: energy in plants
* glycogen: animals energy
* cellulose: used iin the cell wall of plant cells
* add iodine solution and if sample changes to blue/black carbohydrates are present
* subunits: sugars, polymers of glucose
* function: energy storage
* eg. of macromolecules: suagrs, starches, and glycogen
\
1) monosaccharides: one simple sugar, eg. glucose
2) disaccharides: two simple sugars, eg. maltose
3) polysaccharides: many linked simple sugars
* starches: energy in plants
* glycogen: animals energy
* cellulose: used iin the cell wall of plant cells
* add iodine solution and if sample changes to blue/black carbohydrates are present
* subunits: sugars, polymers of glucose
* function: energy storage
* eg. of macromolecules: suagrs, starches, and glycogen
\
6
New cards
Vitamins & Minerals
* are not macromolecules
* are essential tot he structure and function of all cells
* only needed in small amounts
* vitamins: organic compounds. functions include - coenzymes, used for tissue development, & growth
* minerals: inorganic compounds, functions include - chemical reaction, bones, hemoglobin, & hormones
* are essential tot he structure and function of all cells
* only needed in small amounts
* vitamins: organic compounds. functions include - coenzymes, used for tissue development, & growth
* minerals: inorganic compounds, functions include - chemical reaction, bones, hemoglobin, & hormones
7
New cards
Sugars (mono/disaccharides)
* add benedict’s solution to the sample
* green: very low
* yellow: low
* yellow/orange: moderate
* orange: high
* red/orange: very high
* green: very low
* yellow: low
* yellow/orange: moderate
* orange: high
* red/orange: very high
8
New cards
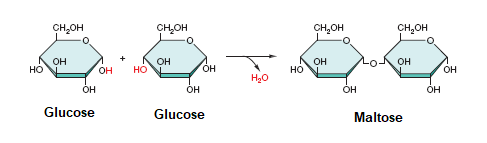
Dehydration Synthesis
* removes water from 2 or more subunits to make a macromolecule
* to form a bond between subunits, an ‘H’ and an ‘OH’ are removed from the subunits to form water, & the subunits bond together
* Removes H2O and H2O is a product
* to form a bond between subunits, an ‘H’ and an ‘OH’ are removed from the subunits to form water, & the subunits bond together
* Removes H2O and H2O is a product
9
New cards
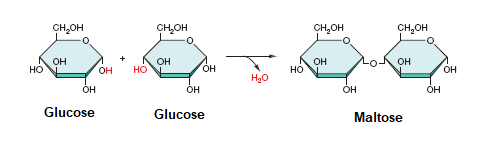
Hydrolysis
* breaks the covalent bonds in macromolecules by adding water
* a molecule of H2O us added, one ‘H: bonds to one subunit & ‘OH’ bonds to another
* a molecule of H2O us added, one ‘H: bonds to one subunit & ‘OH’ bonds to another
10
New cards
Simple Sugars & Polysaccharides
simple sugars: a carbohydrate molecule with three to seven carbon atoms (and the corresponding # of hydrogen and oxygen atoms) - this is called a monosaccharide and a disaccharide is two of these
polysaccharides: a complex carb that consists of many linked simple sugars
* starches (energy in plants)
* glycogen (energy in animals)
* cellulose (used in the cell wall)
polysaccharides: a complex carb that consists of many linked simple sugars
* starches (energy in plants)
* glycogen (energy in animals)
* cellulose (used in the cell wall)
11
New cards
Macromolecules
a large, complex assembly of organic molecules; four categories of macromolecules are carbs, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
12
New cards
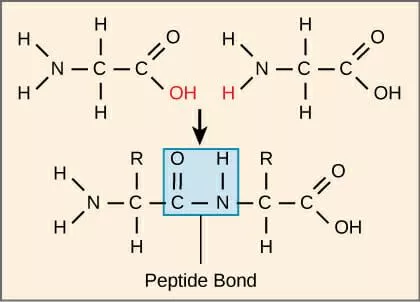
Peptide bonds
bond between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another protein
13
New cards
Catalysts
A chemical that speeds up a chemical reaction but is not used up in the reaction.
* does not increase temperature and can be recovered unchanged when the reaction is complete
* function by lowering the amount of energy needs to initiate a reaction.
* does not increase temperature and can be recovered unchanged when the reaction is complete
* function by lowering the amount of energy needs to initiate a reaction.
14
New cards
Enzymes
A protein molecule that acts as a catalyst to increase the rate of a reaction is called an enzyme.
* enzymes have a 3d shape that is specific to the kind of reactant with which it can combine
* the enzyme physically fits with a specific substrate-its reactant molecule.
* enzymes have a 3d shape that is specific to the kind of reactant with which it can combine
* the enzyme physically fits with a specific substrate-its reactant molecule.
15
New cards
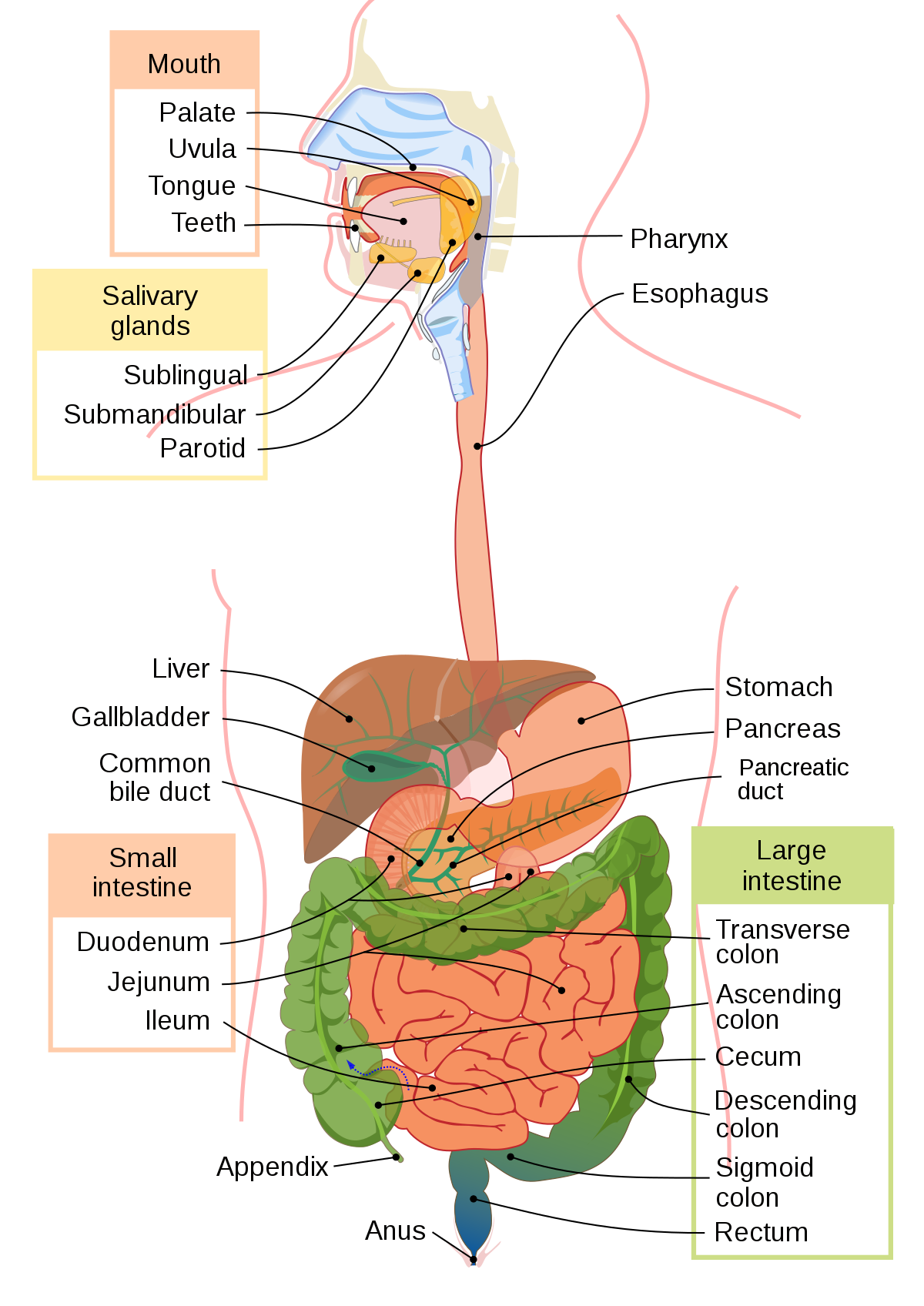
Accessory Organs
Structures that aid digestion but don’t contain food
* Salivary Glands
* Liver
* Gall Bladder
* Pancreas
* Salivary Glands
* Liver
* Gall Bladder
* Pancreas
16
New cards
The Digestive Tract
Organs that contain the food
* Mouth
* Esophagus
* Stomach
* Small Intestine
* Large Intestine
* Rectum
* Anus
* Mouth
* Esophagus
* Stomach
* Small Intestine
* Large Intestine
* Rectum
* Anus
17
New cards
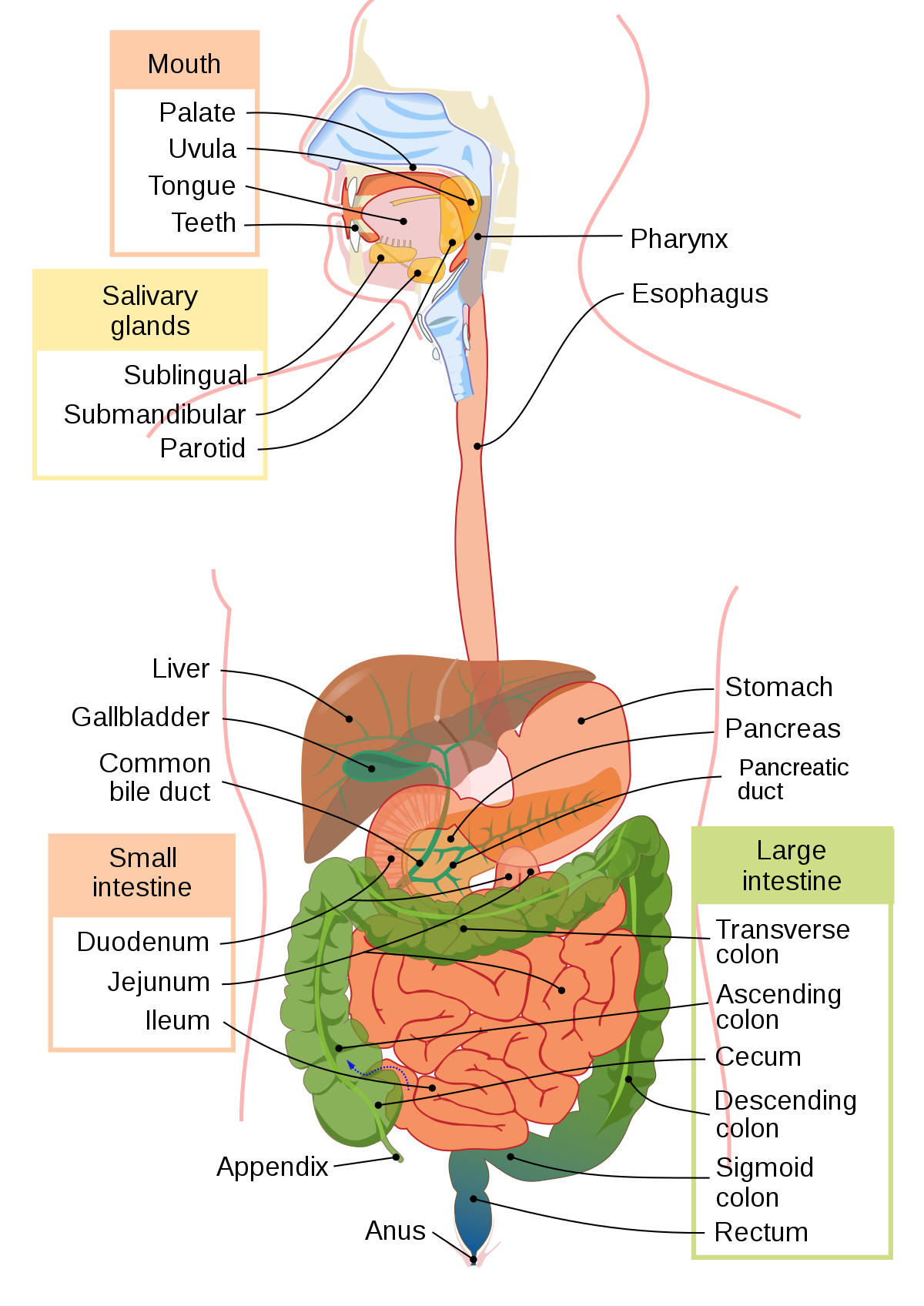
Salivary Glands
* secrete starch-digesting enzymes
* produce saliva → a mix of water & enzymes = amylase (starch → smaller carbs)
* the water in the saliva moistens food and activates taste buds
* amylase: (enzyme) polysaccharides into disaccharides
* produce saliva → a mix of water & enzymes = amylase (starch → smaller carbs)
* the water in the saliva moistens food and activates taste buds
* amylase: (enzyme) polysaccharides into disaccharides
18
New cards
Mouth
* teeth + tongue = mechanical digestion
* bolus: a mix of food and saliva
* bolus: a mix of food and saliva
19
New cards
Esophagus
* long muscular tube, the bolus stretches the esophagus; stimulates peristalsis (wave-like) muscular contractions .: pushes the bolus towards the stomach
20
New cards
Stomach
* muscular bag, rhythmic contractions. mixes bolus w/ stomach acid + enzymes (gastric juices) creating CHYME
* lined w/ mucus (or mucous) protecting it from the gastric juices
* lined w/ mucus (or mucous) protecting it from the gastric juices
21
New cards
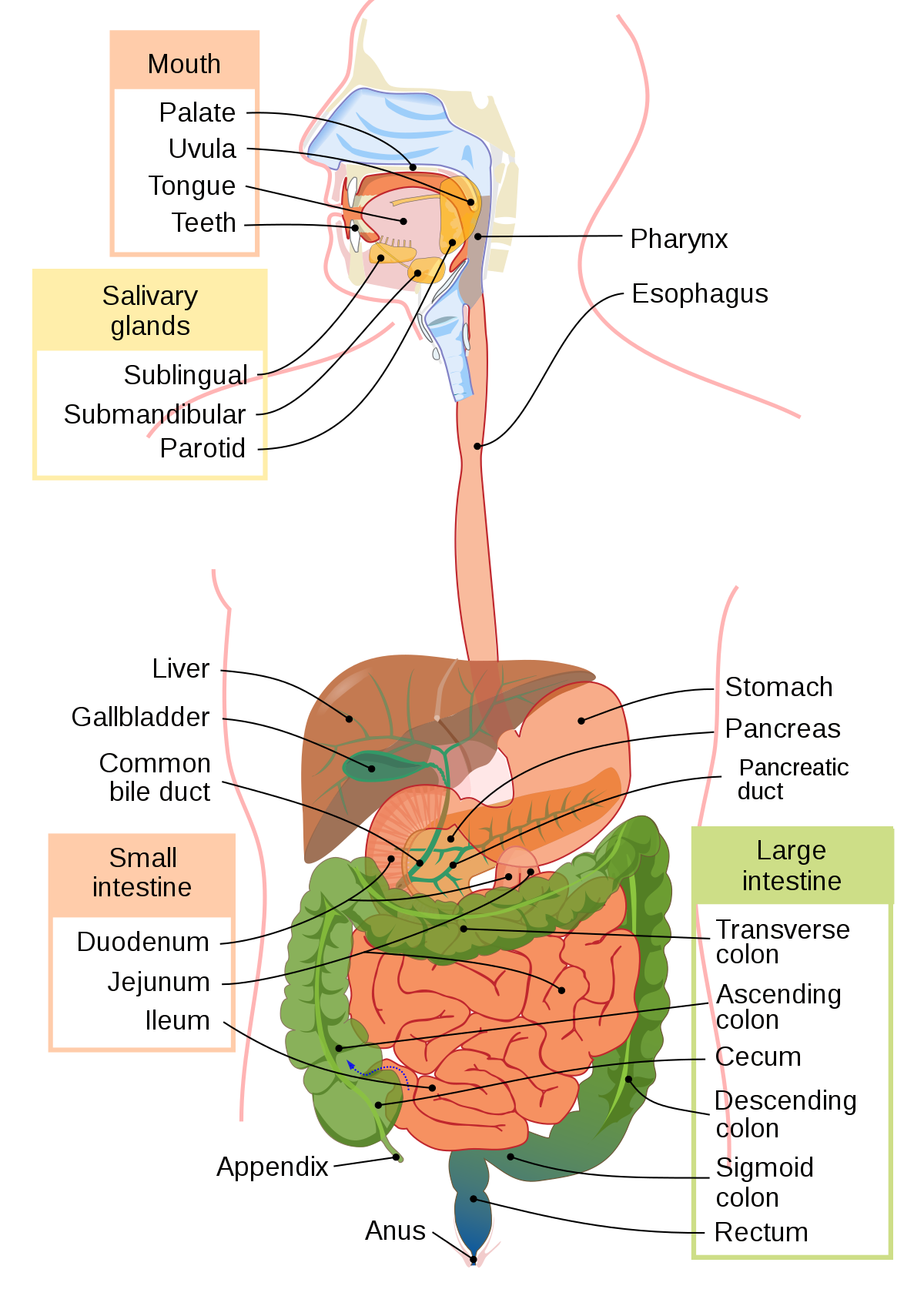
Small Intestine
* complete digestion
* pH of 9
* 90% of absorption → villi and microvilli, which increase surface area
* contains 3 sections
* duodenum: digestion & absorption
* jejunum: absorption
* ileum: absorption
* Secretin: (hormone) - stimulates the pancreas and gall bladder
* Enterkinase: converts trypsinogen into trypsin
\-secretes enzymes that digest macromolecules; absorbs hydrolyzed molecules into bloodstream
* pH of 9
* 90% of absorption → villi and microvilli, which increase surface area
* contains 3 sections
* duodenum: digestion & absorption
* jejunum: absorption
* ileum: absorption
* Secretin: (hormone) - stimulates the pancreas and gall bladder
* Enterkinase: converts trypsinogen into trypsin
\-secretes enzymes that digest macromolecules; absorbs hydrolyzed molecules into bloodstream
22
New cards
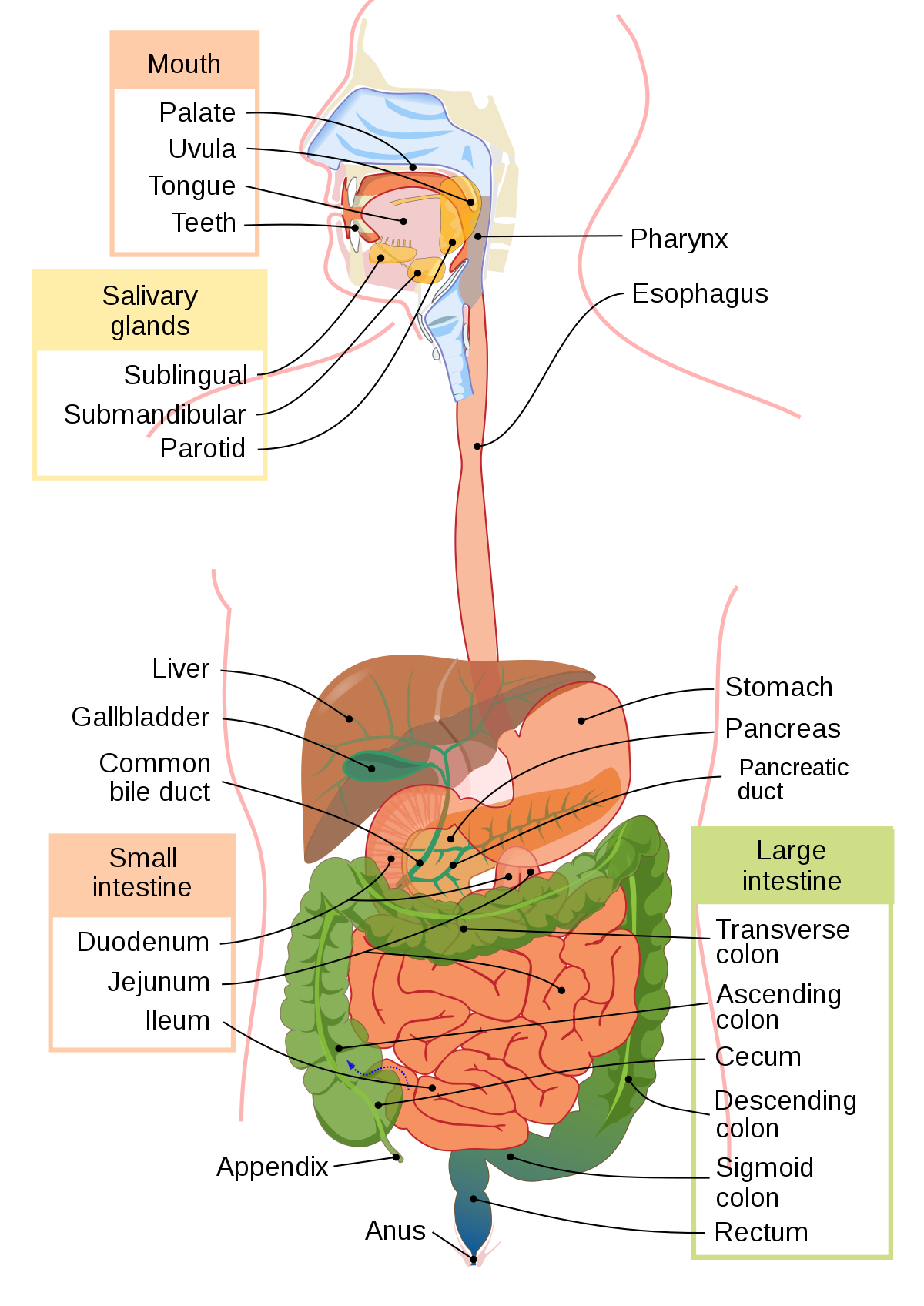
Large Intestine
* approx. 1.5m in length w/ a wider diameter
* function: concentrate and eliminate waste by
1) absorbing H20 + salt into the blood
2) bacteria: use waste material to make vitamins (K + B12); break it down further
3) form and expel feces (cellulose & fibre)
\-absorbs water and salts; passes remaining undigested material and some water out of the body
* function: concentrate and eliminate waste by
1) absorbing H20 + salt into the blood
2) bacteria: use waste material to make vitamins (K + B12); break it down further
3) form and expel feces (cellulose & fibre)
\-absorbs water and salts; passes remaining undigested material and some water out of the body
23
New cards
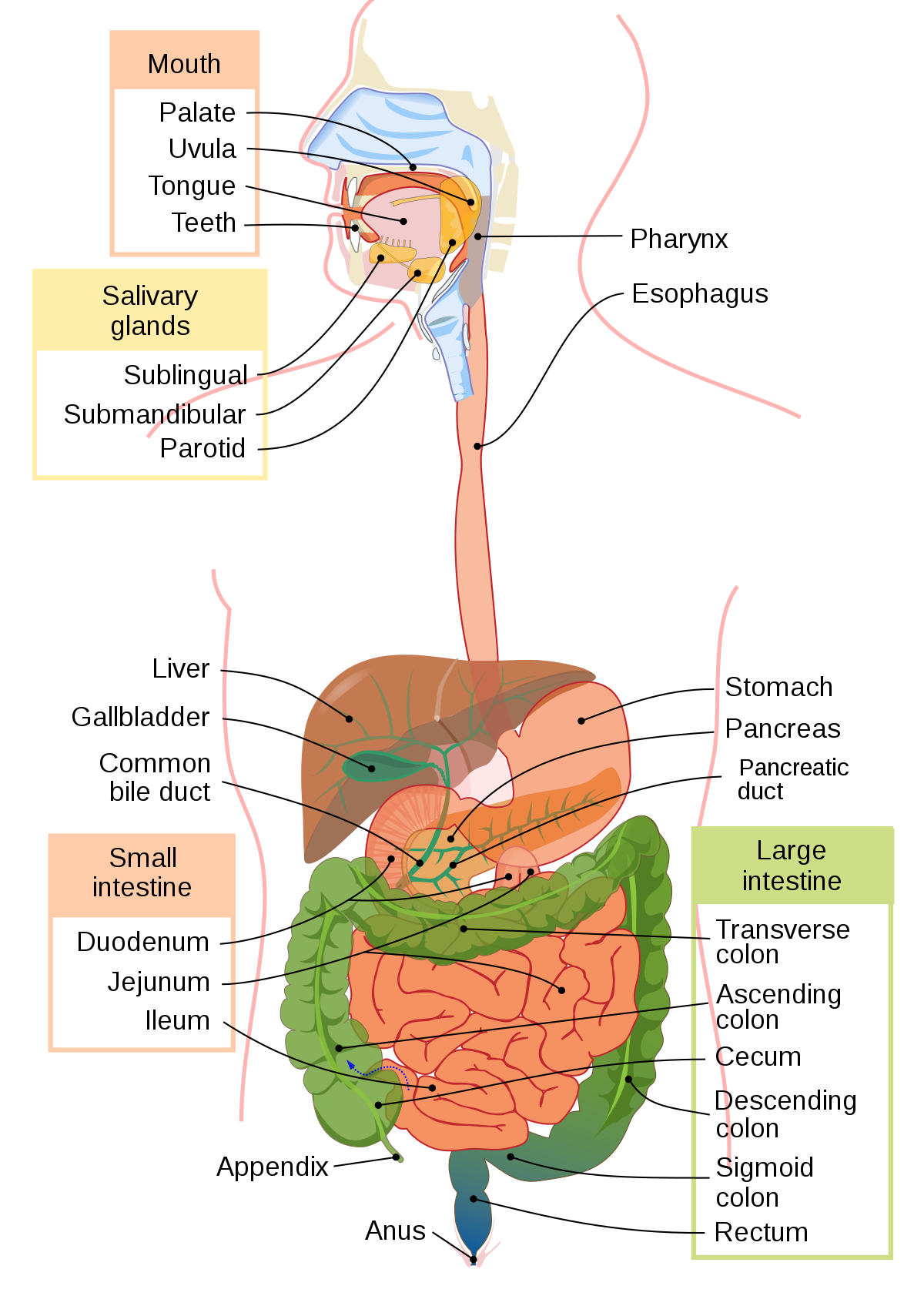
Rectum
* Can hold on to the feces when you pass gas
* stores waste prior to elimination
* stores waste prior to elimination
24
New cards
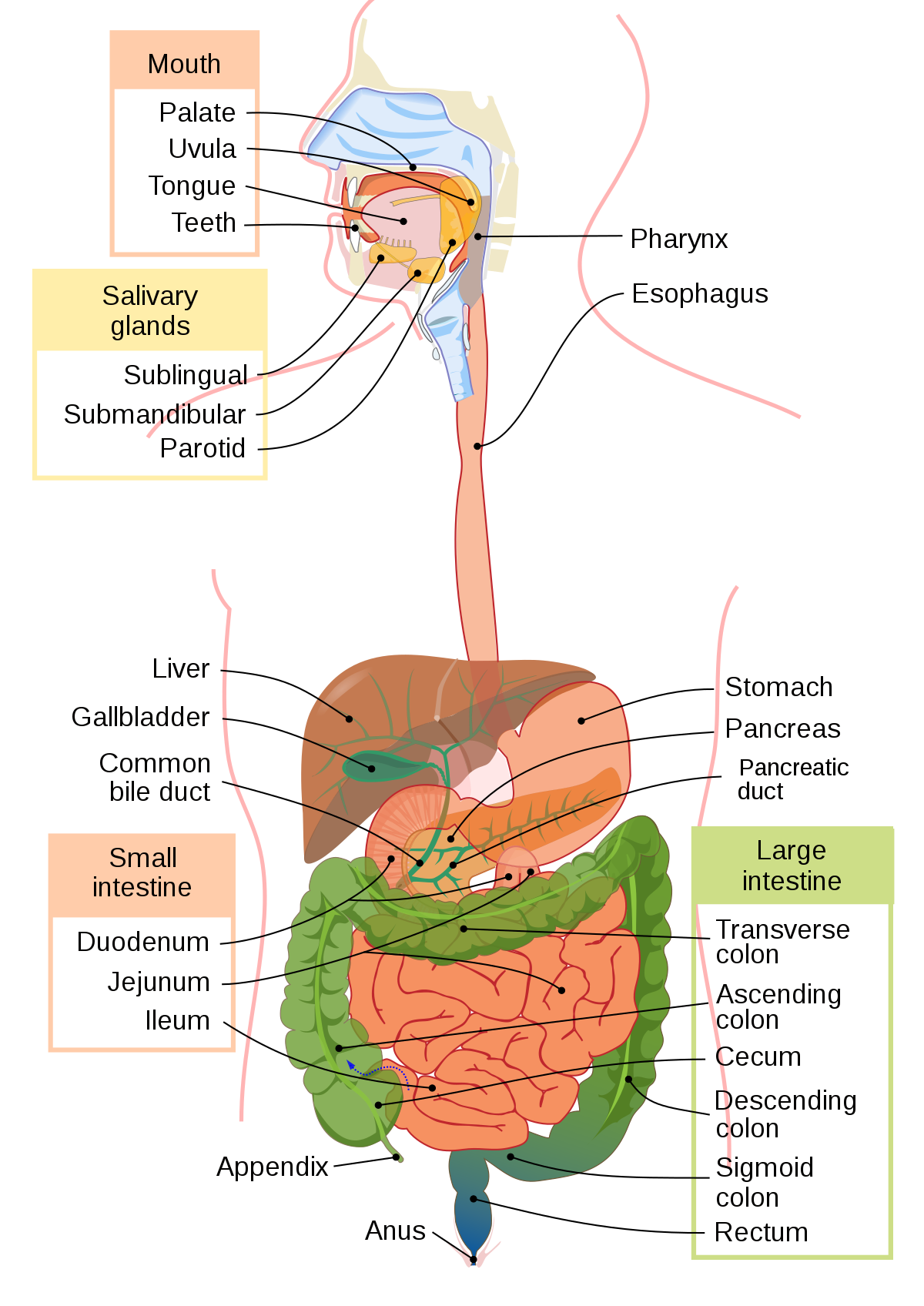
Anus
* Releases the feces, controlled by the 2 sphincters (one can be consciously control and one is controlled by the nervous system)
* Holds rectum closed; opens to allow elimination
* Holds rectum closed; opens to allow elimination
25
New cards
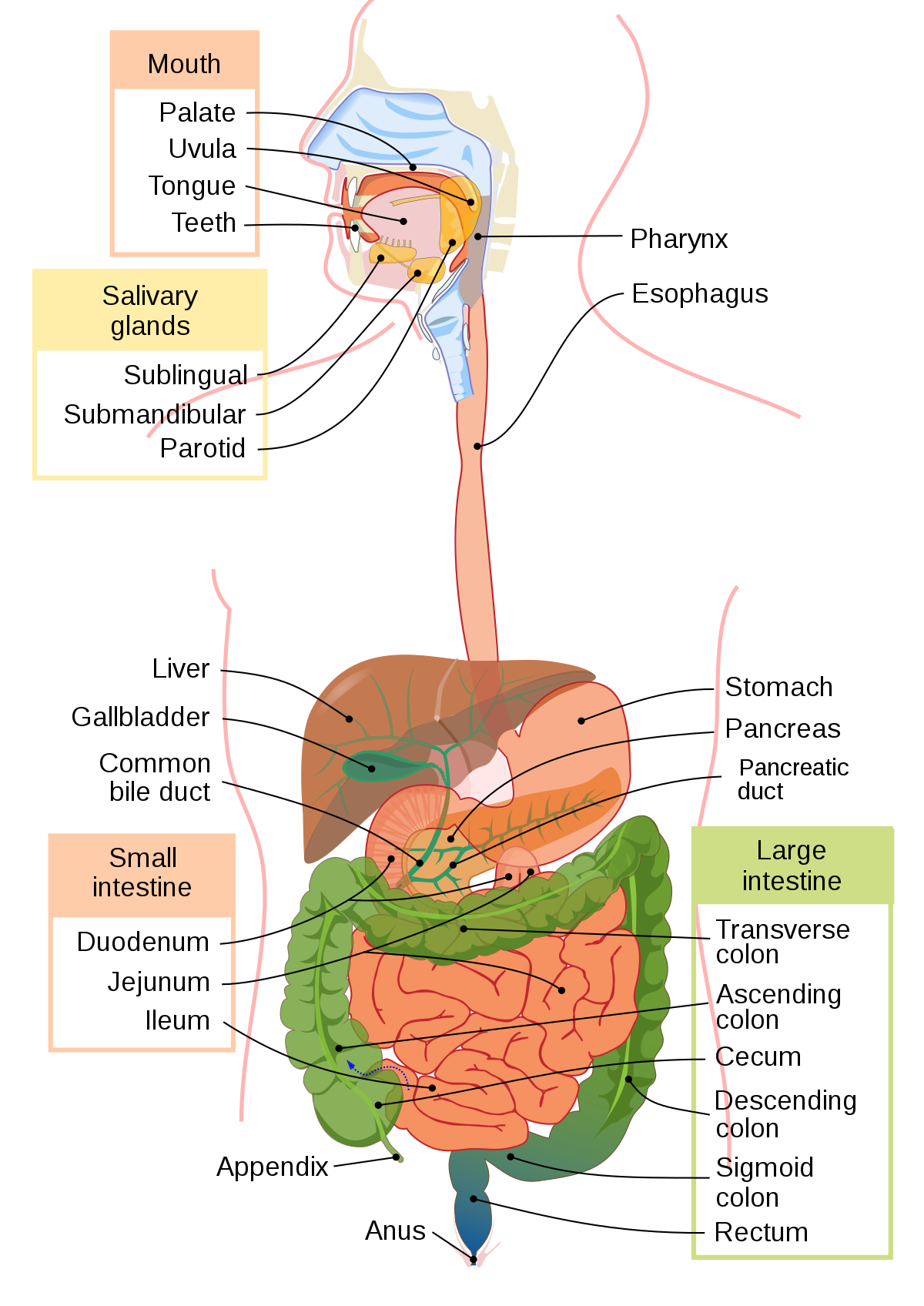
Pancreas
\-Releases bicarbonate ions (HCO3), neutralizes the gastric juices and increases the pH and also has lots of enzymes
\-Manufactures enzymes to digest macromolecules; secretes bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid that enters the small intestine
* releases pancreatic juices into the small intestine
* pancreatic juices include:
* Bicarbonate Ions: neutralizes
* Lipase: (enzyme) - breaks down fats
* Trypsinogen: becomes trypsin peptides into shorter chains of amino acids
* Erepsin: short chains of amino acids into amino acids
* disaccharase: disaccharides into monosaccharides
\-Manufactures enzymes to digest macromolecules; secretes bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid that enters the small intestine
* releases pancreatic juices into the small intestine
* pancreatic juices include:
* Bicarbonate Ions: neutralizes
* Lipase: (enzyme) - breaks down fats
* Trypsinogen: becomes trypsin peptides into shorter chains of amino acids
* Erepsin: short chains of amino acids into amino acids
* disaccharase: disaccharides into monosaccharides
26
New cards
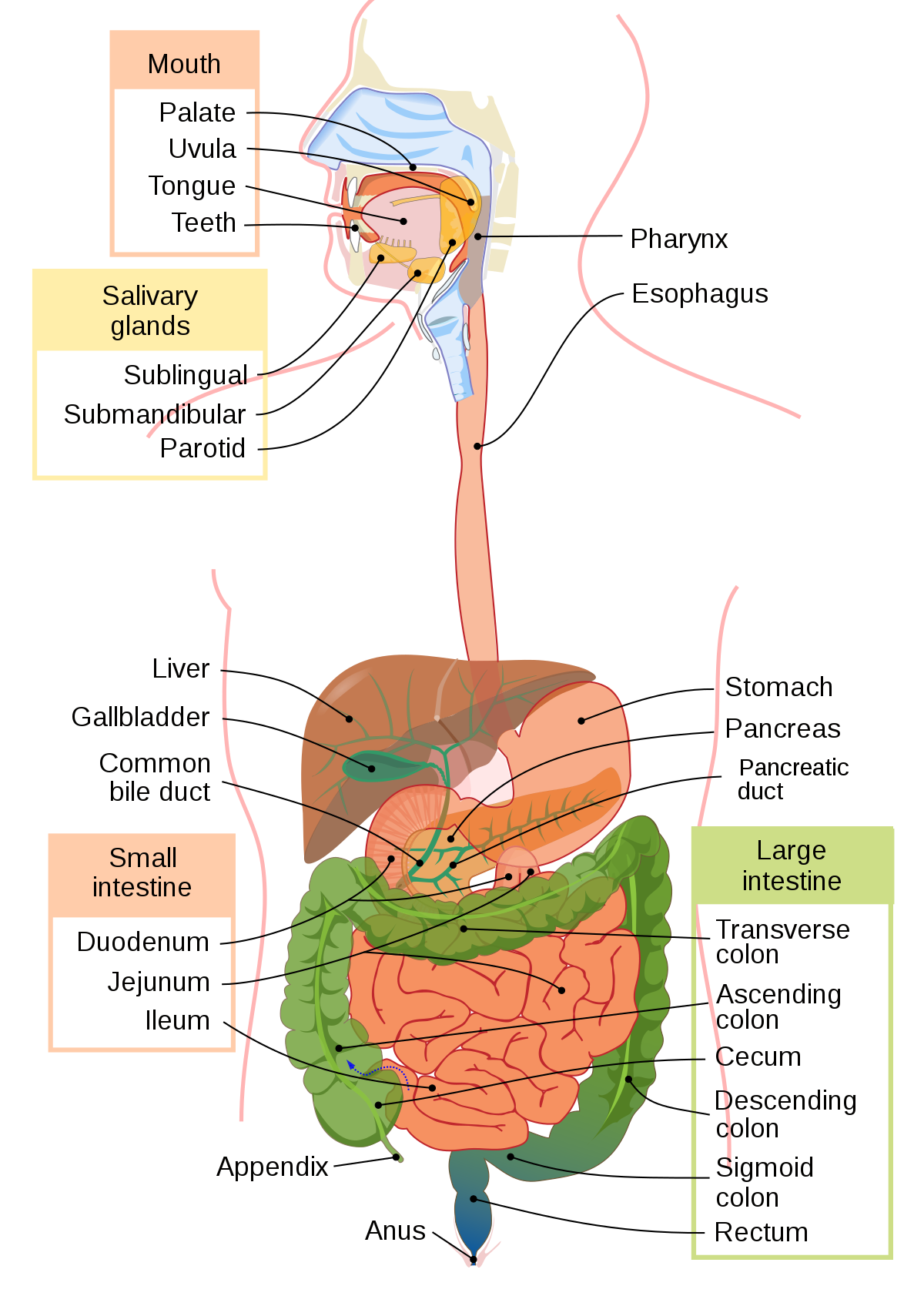
Gall Bladder
Stores bile and releases it into the small intestine
27
New cards
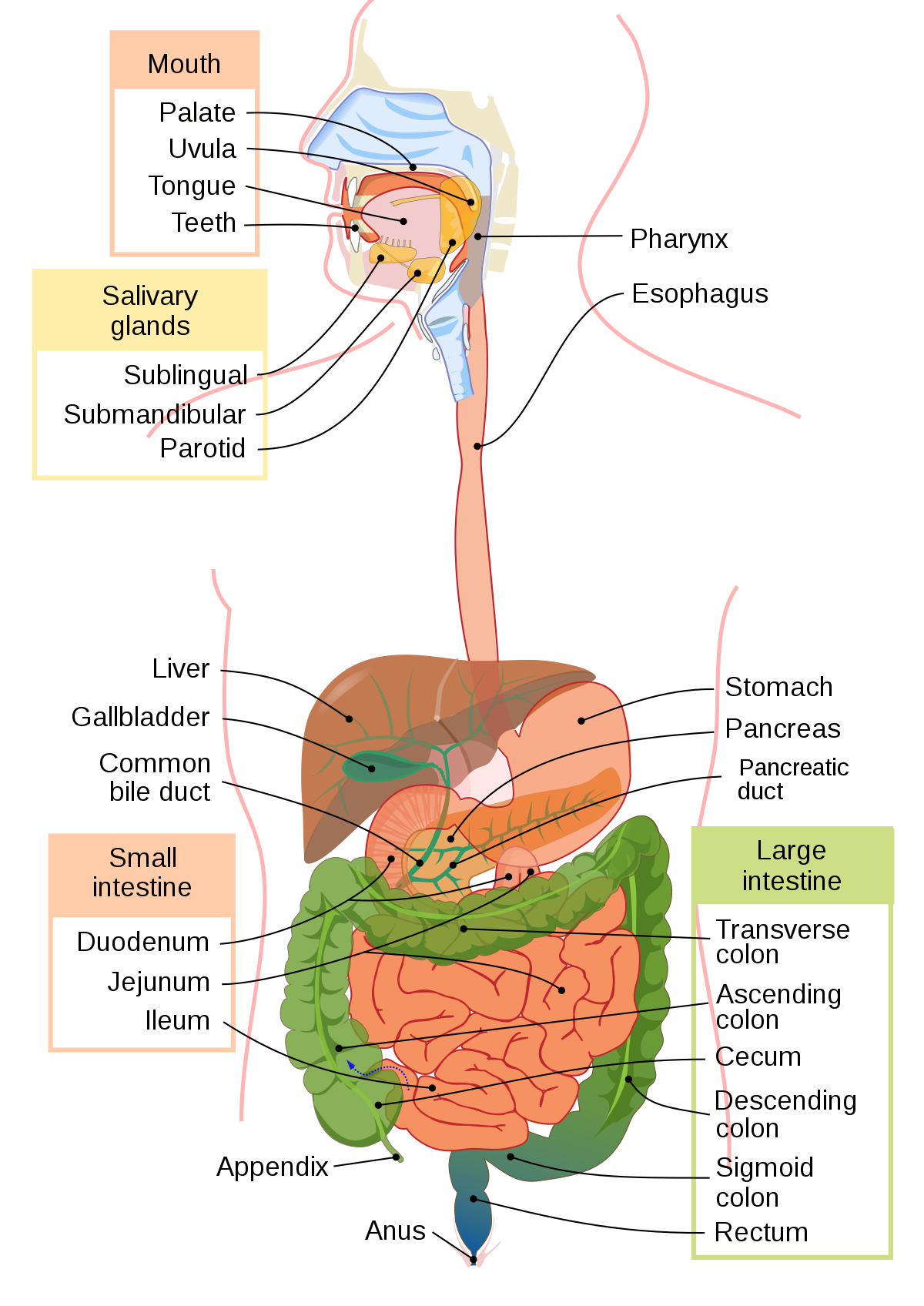
Liver
* stores glycogen
* secretes bile salts
* emulsifies fats/lipids: taking large fat droplets and breaking it into smaller droplets; to increases surface area
* Release bile which emulsifies fats (physical digestion)
* secretes bile salts
* emulsifies fats/lipids: taking large fat droplets and breaking it into smaller droplets; to increases surface area
* Release bile which emulsifies fats (physical digestion)
28
New cards
Pharynx
opening at the back of the mouth to the trachea (wind pipe) & esophagus
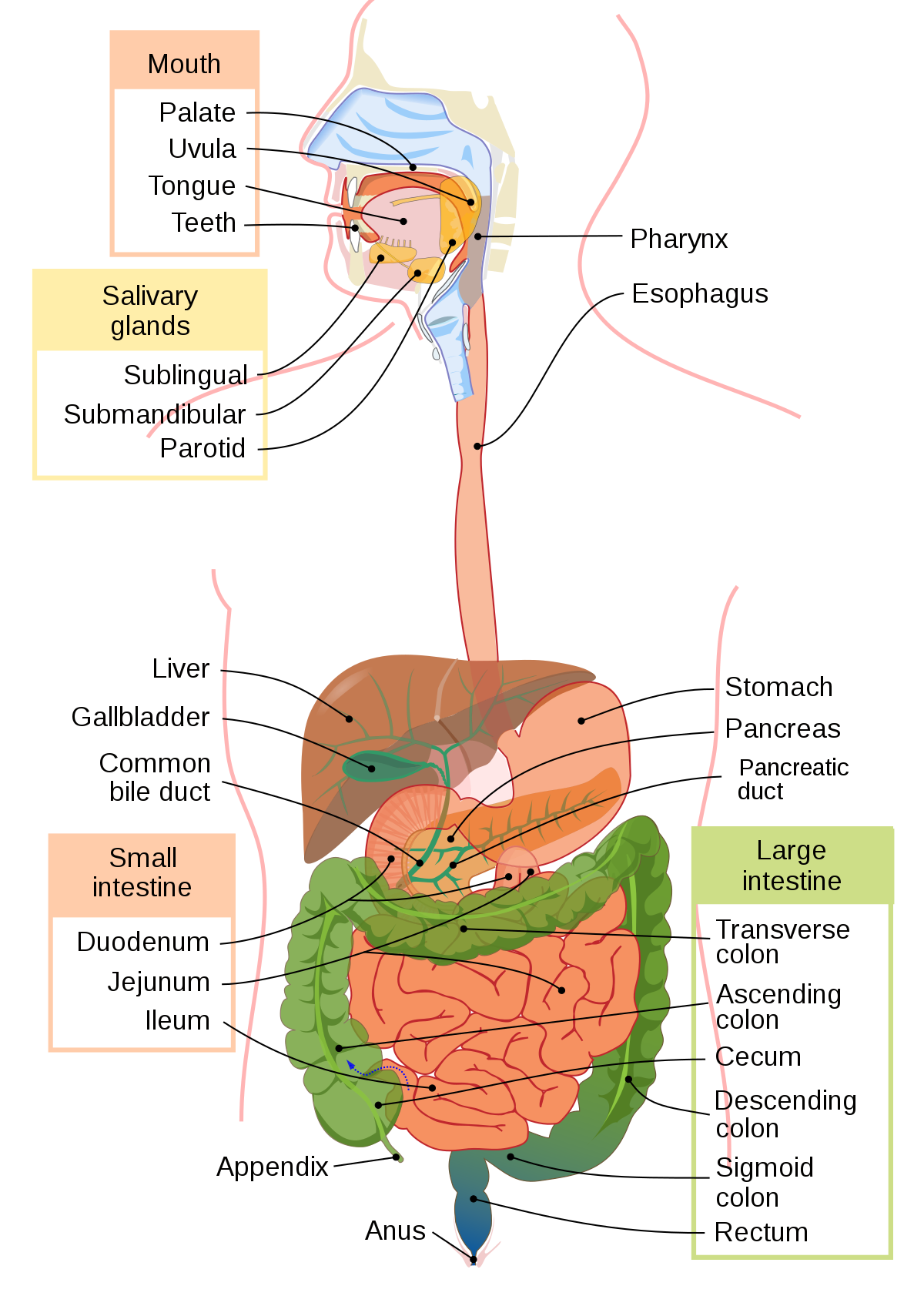
29
New cards
Epiglottis
closes the trachea when swallowing food
30
New cards
Salivary Amalyse
* Salivary amylase is a glucose-polymer cleavage enzyme that is produced by the salivary glands.
31
New cards
Bile
Bile is a fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile helps with digestion. It breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can be taken into the body by the digestive tract.
32
New cards
Gastrin
* a hormone
* in the stomach
* secreted by the stomach into the blood to stimulate the release of gastric juices and muscle contractions
* in the stomach
* secreted by the stomach into the blood to stimulate the release of gastric juices and muscle contractions
33
New cards
Protease
* in the small intestine
34
New cards
Carbohydrase
* sucrase
* maltase
* lactase
* in the small intestine
* maltase
* lactase
* in the small intestine
35
New cards
CCK
36
New cards
Esophageal & Pyloric Sphincter
* esophageal sphincter is a door way that comes b4 the stomach
* pyloric sphincter comes after the stomach
* pyloric sphincter comes after the stomach
37
New cards
Appendix
* ? may have good bacteria or involved with immune system
38
New cards
Mechanical & Chemical Digestion
Mechanical: physical breakdown (eg. chewing)
Chemical: chemical breakdown (ie. hydrolysis)
Chemical: chemical breakdown (ie. hydrolysis)
39
New cards
Gastric Juices
* HCL: kills any microbes; activates pepsinogen
* Pepsinogen: reacts w/ the HCL to become pepsin
* Pepsin: enzyme (protein → peptides)
* Rennin: coagulate milk protein (slows down the movement)
* Pepsinogen: reacts w/ the HCL to become pepsin
* Pepsin: enzyme (protein → peptides)
* Rennin: coagulate milk protein (slows down the movement)
40
New cards
Salivary Amylase
* enzyme acts in the mouth
* pH = 7
* substrate (food) digested: starch and glycogen
* products of digestion: maltose (disaccharide)
* origin of enzymes: salivary glands
* pH = 7
* substrate (food) digested: starch and glycogen
* products of digestion: maltose (disaccharide)
* origin of enzymes: salivary glands
41
New cards
Pancreatic Amylase
* enzyme acts in the small intestine
* pH = 8
* substrate (food) digested: starch and glycogen
* products of digestion: maltose
* origin of enzymes: pancreas
* pH = 8
* substrate (food) digested: starch and glycogen
* products of digestion: maltose
* origin of enzymes: pancreas
42
New cards
Carbs (sucrase, maltase, lactase)
* enzymes act in the small intestine
* substrate (food) digested:
* sucrase - sucrose
* maltase - maltose
* lactase - lactose
* products of digestion:
* sucrase - glucose + fructose
* maltase - glucose
* lactase - glucose + galactose
* origin of enzymes: small intestine
* substrate (food) digested:
* sucrase - sucrose
* maltase - maltose
* lactase - lactose
* products of digestion:
* sucrase - glucose + fructose
* maltase - glucose
* lactase - glucose + galactose
* origin of enzymes: small intestine
43
New cards
Pancreatic lipase
* enzymes act in the small intestine
* pH = 8
* substrate (food) digested: lipids
* products of digestion: fatty acids and glycerol
* origin of enzymes: pancreas
* pH = 8
* substrate (food) digested: lipids
* products of digestion: fatty acids and glycerol
* origin of enzymes: pancreas
44
New cards
Proteases (pepsin, trypsin, chymotrypsin)
* where enzyme acts:
* pepsin - stomach (pH = 1-2)
* trypsin & chymotrypsin - small intestine (pH = 8)
* substrate (food) digested:
* pepsin - protein
* trypsin & chymotrypsin - peptides
* products of digestion:
* pepsin - peptides
* trypsin & chymotrypsin - smaller peptides
* origin of enzymes:
* pepsin - stomach
* trypsin & chymotrypsin - pancreas
* pepsin - stomach (pH = 1-2)
* trypsin & chymotrypsin - small intestine (pH = 8)
* substrate (food) digested:
* pepsin - protein
* trypsin & chymotrypsin - peptides
* products of digestion:
* pepsin - peptides
* trypsin & chymotrypsin - smaller peptides
* origin of enzymes:
* pepsin - stomach
* trypsin & chymotrypsin - pancreas
45
New cards
peptidases
* enzymes act in the small intestine
* pH = 8
* substrate (food) digested: peptides
* products of digestion: smaller peptides and amino acids
* origin of enzymes: pancreas and small intestine
* pH = 8
* substrate (food) digested: peptides
* products of digestion: smaller peptides and amino acids
* origin of enzymes: pancreas and small intestine
46
New cards
Nucleases
* enzyme acts in the small intestine
* pH = 8
* substrate (food) digested: nucleic acids
* products of digestion: nucleotides and components
* origin if enzymes: pancreas
* pH = 8
* substrate (food) digested: nucleic acids
* products of digestion: nucleotides and components
* origin if enzymes: pancreas
47
New cards
Nucleosidase’s
* enzyme acts in the small intestine
* pH = 8
* substrate (food) digested: nucleotides
* products of digestion: bases, sugars, and phosphates
* origin of enzyme: small intestine
* pH = 8
* substrate (food) digested: nucleotides
* products of digestion: bases, sugars, and phosphates
* origin of enzyme: small intestine
48
New cards
Small Intestine (macromolecules)
* Complex Carbs: Polysaccharides and Disaccharides (Carboghydrases: pancreatic amylase, sucrase, maltase, and lactase)\] → Monosaccharides
* Proteins: Smaller peptides {Proteases: trypsin & chymotrypsin} → Peptides {Peptidases} → Amino acids
* Fats: fat droplets {bile} → fat droplets(emulsified) {Lipases} → Glycerol and fatty acids
* Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA {Nucleases} → Nucleotides {Nucleosidase’s} → Nitrogen-containing bases, sugars, and phosphates
* Proteins: Smaller peptides {Proteases: trypsin & chymotrypsin} → Peptides {Peptidases} → Amino acids
* Fats: fat droplets {bile} → fat droplets(emulsified) {Lipases} → Glycerol and fatty acids
* Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA {Nucleases} → Nucleotides {Nucleosidase’s} → Nitrogen-containing bases, sugars, and phosphates
49
New cards
Organic Molecules
* always contain carbon and hydrogen
* the chemistry of carbon accounts for the formation of the very large variety of organic molecules found in living things
* the chemistry of carbon accounts for the formation of the very large variety of organic molecules found in living things
50
New cards
Enzyme Function
51
New cards
Factors affecting enzyme activity
52
New cards
Absorption of Glucose in the SI
starch (polysaccharide) → enzyme → disaccharide → enzyme → glucose (monosaccharide) → active transport into cells on intestinal wall → blood vessel
* starts in the mouth w/ salivary amylase
* hydrochloric acid denatures so digestion stops
* chyme enters small intestine & pancreatic amylase completes digestion of starch in2 disaccharides
* other carbohydrases hydrolyze the disaccharides in2 monosaccharides
* monosaccharides absorbed via active transport in2 villi to enter blood stream then to the liver then to all body cells
* starts in the mouth w/ salivary amylase
* hydrochloric acid denatures so digestion stops
* chyme enters small intestine & pancreatic amylase completes digestion of starch in2 disaccharides
* other carbohydrases hydrolyze the disaccharides in2 monosaccharides
* monosaccharides absorbed via active transport in2 villi to enter blood stream then to the liver then to all body cells
53
New cards
Absorption of Amino Acids in the SI
Proteins → enzymes → peptides → amino acids → active transport into cells of intestinal wall → blood vessel
\[using protein enzymes\]
* in the stomach, pepsin breaks proteins into polypeptides
* the polypeptides are broken down by trypsin and chymotrypsin which hydrolyze the peptide bonds between amino acids resulting in short peptide chains
* peptidases split the peptide chains into single amino acids
* amino acids are absorbed via active transport into the villi of the small intestine
* the blood stream carries the amino acids to the liver
\[using protein enzymes\]
* in the stomach, pepsin breaks proteins into polypeptides
* the polypeptides are broken down by trypsin and chymotrypsin which hydrolyze the peptide bonds between amino acids resulting in short peptide chains
* peptidases split the peptide chains into single amino acids
* amino acids are absorbed via active transport into the villi of the small intestine
* the blood stream carries the amino acids to the liver
54
New cards
Absorption of Lipids in the SI
fat → bile → emulsification into triglyceride → enzymes → glycerol & fatty acids → diffusion → triglycerides → protein-coated triglycerides → lymph vessel
\[using lipase enzymes\]
* fats arrive in the small intestine which triggers bile to emulsify them into a fine suspension
* emulsification is a physical process bc the bonds that join glycerol & fatty acids are not hydrolyzed
* lipase breaks down fats into glycerol and fatty acids and absorbed by the villi by diffusion
* triglycerides are reassembled and coated w/ proteins to make them soluble by entering lymph vessels
* lymph vessels: drain near the heart into the blood stream to be distributed to body cells
\[using lipase enzymes\]
* fats arrive in the small intestine which triggers bile to emulsify them into a fine suspension
* emulsification is a physical process bc the bonds that join glycerol & fatty acids are not hydrolyzed
* lipase breaks down fats into glycerol and fatty acids and absorbed by the villi by diffusion
* triglycerides are reassembled and coated w/ proteins to make them soluble by entering lymph vessels
* lymph vessels: drain near the heart into the blood stream to be distributed to body cells
55
New cards
Regulation of the Digestive System
* coordinated by nervous system (sight + smell) and endocrine system (hormones)
* when food enters your stomach, it secrete gastrin, stomach releases gastric juices and start muscle contractions
* when stomach pH decreases you stop releasing gastrin (negative feedback loop)
* when the chyme enters the small intestines, duodenum releases secretin, CCK, and GIP; act on the stomach to stop contractions
* CCK: stimulate pancreatic secretions & gall bladder
* secretin: will stimulate bicarbonate ions from the pancreas
* when food enters your stomach, it secrete gastrin, stomach releases gastric juices and start muscle contractions
* when stomach pH decreases you stop releasing gastrin (negative feedback loop)
* when the chyme enters the small intestines, duodenum releases secretin, CCK, and GIP; act on the stomach to stop contractions
* CCK: stimulate pancreatic secretions & gall bladder
* secretin: will stimulate bicarbonate ions from the pancreas