Science mid year exam | Secondary 4
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
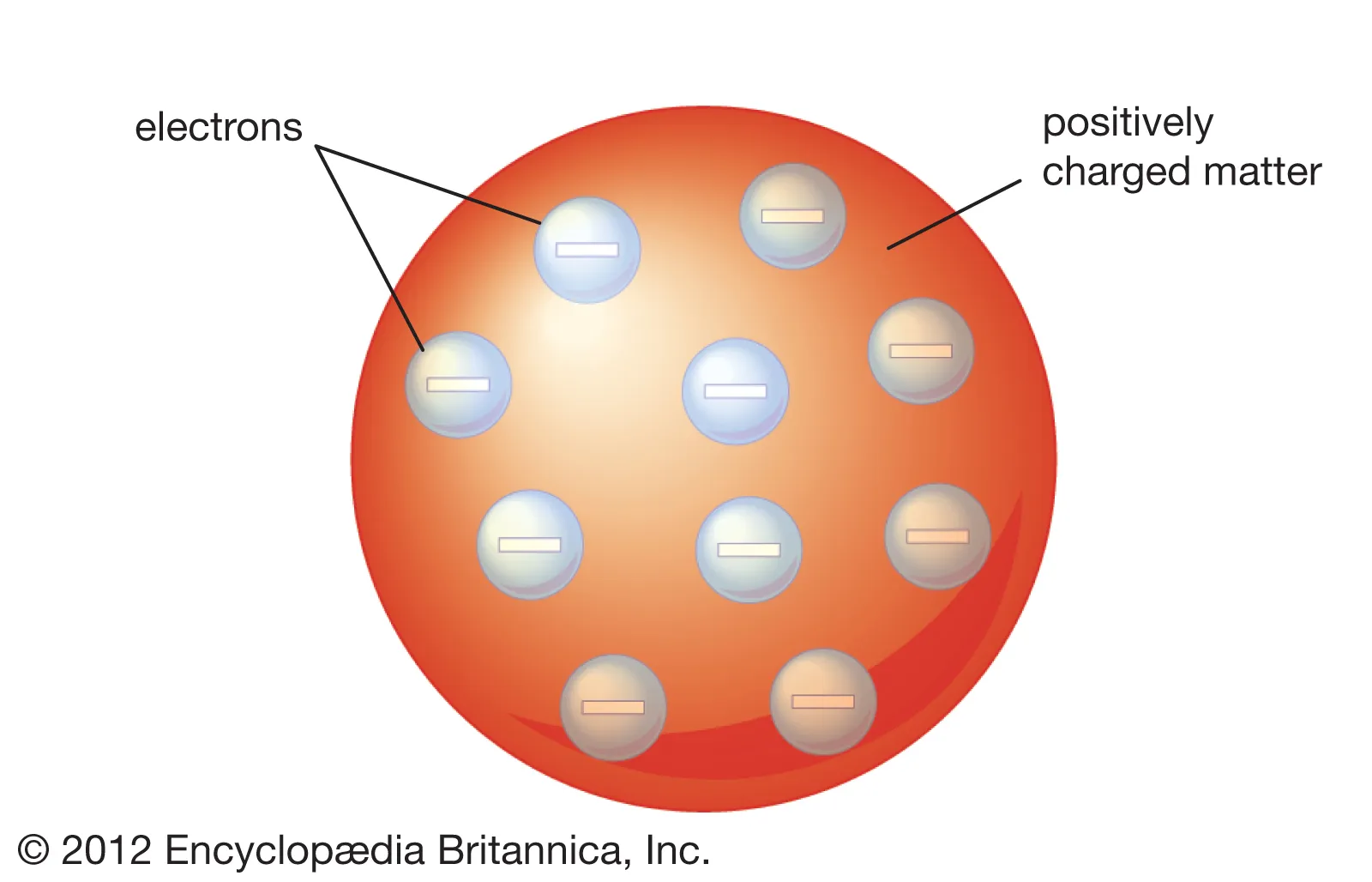
Thomson atom model
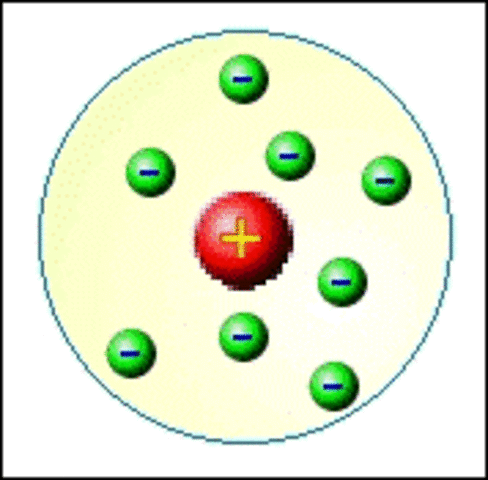
Rutherford atom model
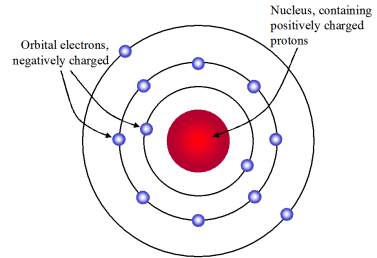
Bohr-Rutherford atom model
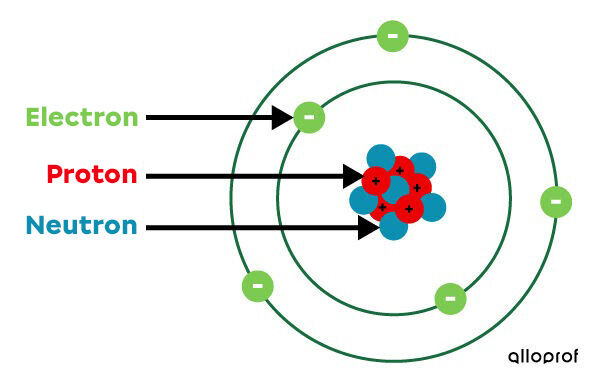
Simplified Atomic atom model
Groups
Represents valence electrons
Period
Number of rings on atom
Staircase
Metals are left, metalloids are alongst it, non-metals on right
Metal
good conductors, shiny, they are malleable
Non-metal
not shiny, poor conductors
Metalloids
Properties of metals and non-metals
Alkali Metal
Most reactive, reactive with are, always combined with other elements
Alkali Earth Metals
Excellent conductors, melting point higher than 1st group, 2nd most reactive
Halogens
Form salt when combined with alkali metals, form strong acid when combined with hydrogen, always combined with something
Noble gases
lack of reactivity, doesn’t combine with other element
Ionization/Ions
When a neutral atom or molecule becomes charged by either losing one or more electrons
Which properties lose electrons
Metals
Which properties gains electrons
Non-metals
Atomic radius
Size of a neutral atom
How do we measure the atomic radius of an atome
Increases down each group & decreases across each period
Where in the periodic table are the elements with a higher melting point& better conductivity
The middle
Isotopes
Different types of the same element. Because of different amounts of neutrons
Why do atoms bond
To be in a stable state
Octet rule
Elements gaining or losing electrons to be in a stable state
Positive Ions
lose electrons
Negative Ions
Gain electrons
Ionic bond
Metals + Non-metals
In Ionic bonds, what do the molecules end with
Ide
Covalent bond
Non-metal + Non-metal
What does a Ionic bond do
Give electrons
What does a covalent bond do
Share electrons
Diatomic elements
Covalent bonds when the same elements bond
Electric conductivity
The ability of electric currents to flow through a solution
Types of electrolytes
Acids, bases, and salts
Acids
“H” in the front of the formula, turns litmus paper red
Bases
“OH” in the end of the formula, turns litmus paper blue
Salts
Metals + Non-Metals, Doesn’t have “H” or “OH”
Electrolytes
Substance when dissolved in water allows electric currents to flow through it
Non-electrolytes
Non-metals + no-metals (not acids)
Physical change
It doesn’t modify the nature or characteristic properties of matter
What are some physical changes
crushing, cutting, bending
Chemical change
It modifies the nature and characteristic properties of matter
What are some chemical changes
formation of gas, precipitation, change in colour, heat and light
Combustion
A form of oxidation that releases a large amount of energy
Celullar Resporation
When glucose and oxygen make carbon dioxide and water
Photosynthesis
Solar energy, carbon dioxide and water make glucose and oxygen
Nuclear stability
Atomic nucleus to resist radioactive decay and maintain
What does the stability of a nucleus depend on
Its size and the number of neutrons it contains
Radioactivity
Unstable atoms spontaneously transforms into a more stable atom, or several more, while releasing energy
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear reaction when the nuclease of a large atom splits into one or more smaller nuclei
Nuclear Fusion
Two or more smaller nuclei join together to form a heavier nucleus
Electricity
Phenomena caused by positive and negative charges
Electric charge
Electrons are negatively charged while protons are positively charged. A negative and positive attract & two negatives/positive repel
Insulation
Prevents electric current to flow
Conduction
Transmits electric current from one part to another
Series circuits
The circuit is connected with one direction
Parallel
The circuit has multiple branches
Magnetism
It’s the property that make some things attract and repel
Law of conservation
Energy can’t be created nor destroyed. It always remains constant
Heat
the transfer of energy(change in temperature)
Temperature
How hot or cold the particle are
Endothermic
Takes energy
Exothermic
Loses energy