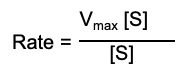FUNCHEM 20: Catlaysis, Enzymes and Michaelis-Menten equation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is a catalyst?
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of chemical reaction without being used up in the reaction
What is the role of functional group in enzye
The functional group in the active site of the enzyme assist in balancing the bond breaking parts of the mechanism with the bond making parts
Anything that disrupts this structure will reduce the enzyme catalytic power
Explain the Lock and Key Theory of the enzyme
Active Site within the structure of each enzyme
It has a specific shape, which gives each enzyme its specificity
Only molecules of the right shape can be a substrate for the enzyme
The enzyme and the substrate slot together forming a complex
In this complex the substrate reacts at a lower activation energy
This may be due to the bonds within it being deformed and stressed in the complex making them more likely to react.
Once the reaction has been catalyzed, the product is no longer in the right shape to be in the active site and the complex breaks up, releasing the product and freeing the enzyme for further catalytic action
Explain the Induced-fit theory
Enzyme undergoes conformational change as the substrate approaches and start to bind
Proteins are flexible molecules whose overall structure is maintained by weak intermolecular interactions.
At any given time, these can be disrupted by small changes in their vicinity
The enzyme and substrate must still have complementary surfaces
Why is enzyme temperature dependent?
Hydrophobic interactions and salt bridges break as the increase in temperature causes the enzyme’s structure to “wiggle around”
Why are enzymes ph dependent?
salt bridges depend on ionic charges for their bonding power
Anything that neutralizes such charge will destroy the salt bridges and make the folded structure of enzyme less stable.
Increase of ph- will take an H+ from an NH3+ group and neutralize its charge
Decrease in ph- will put an H+ on a COO-.
How do you find Km, the Michaelis- Menten constant
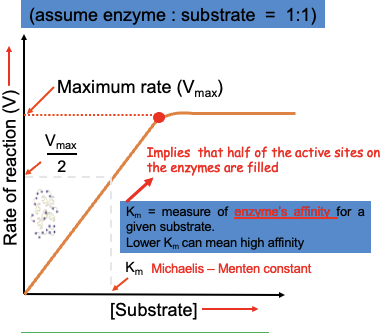
What is the Michaelis Menten equation

What is the rate equation that relates to the Michaelis Menten Equation

At low substrate concentration it is a first order reaction, what’s the rate
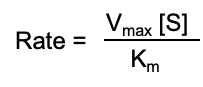
At high substrate concentration- it is a zero order reaction
what’s the rate equation