7. Ketones and Aldehydes
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What are the similarities between Ketones and Aldehydes?
Both have general formula
CₙH₂ₙO
Both have a carbonyl functional group
Lower boiling points/Higher solubility
NO H bonding
What are the differences between Ketones and Aldehydes?
position of carbonyl in molecule
Aldehyde Structure
carbonyl group attached to at least one hydrogen
usually at end of molecule
Ketone Structure
carbonyl carbon connected to 2 carbons
middle of molecule
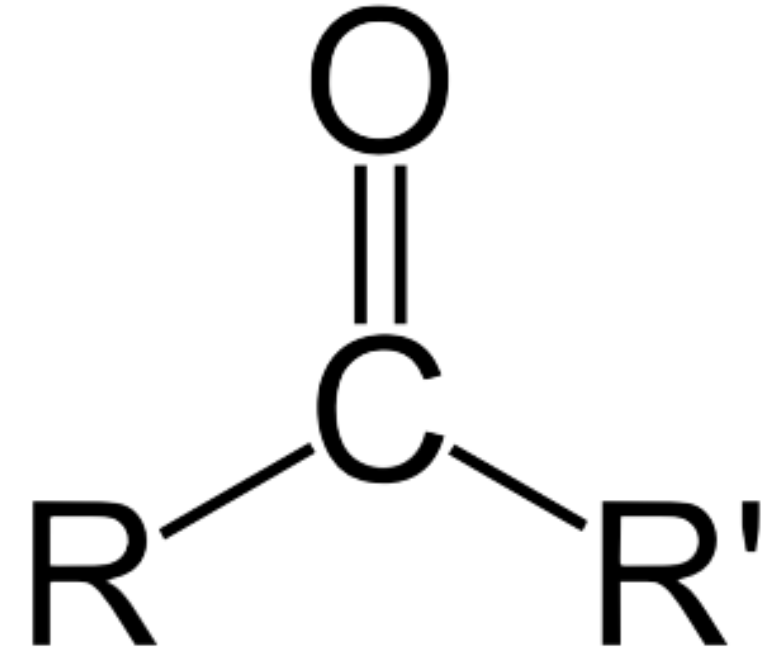
How to Name Aldehydes
prefix is # of carbons (alkane)
ending goes from -e → -al
no position numbers since carbonyl is always carbon 1
How to Name Ketones
prefix is # of carbons (alkane) + position of the carbonyl
ending goes from -e → -one
if your ketone has two carbonyl groups: name, location, -dione/-trione
How are aldehydes and ketones created?
controlled oxidation of alcohols
How are aldehydes and ketones controlled in oxidizing reactions?
oxidizing agents (oxygen-rich compounds)
represented by [O]
What is the flow of oxidation for primary alcohols?
primary alcohol → aldehyde → carboxylic acid
orange → green
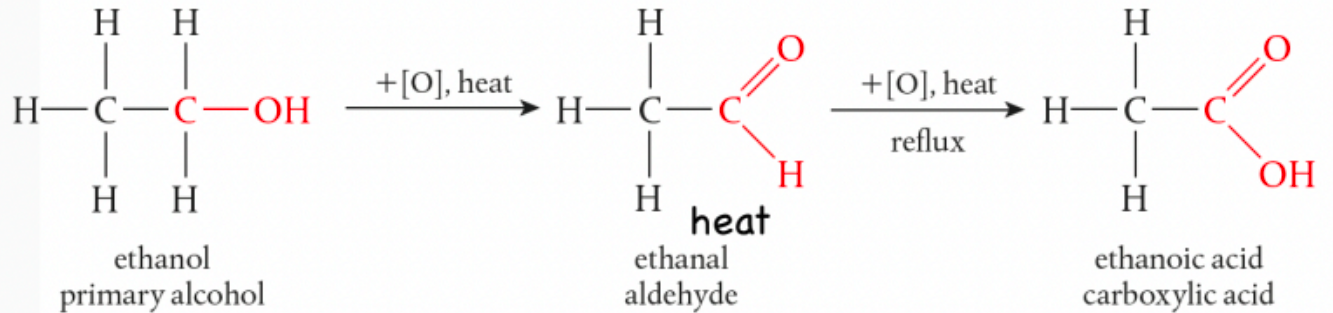
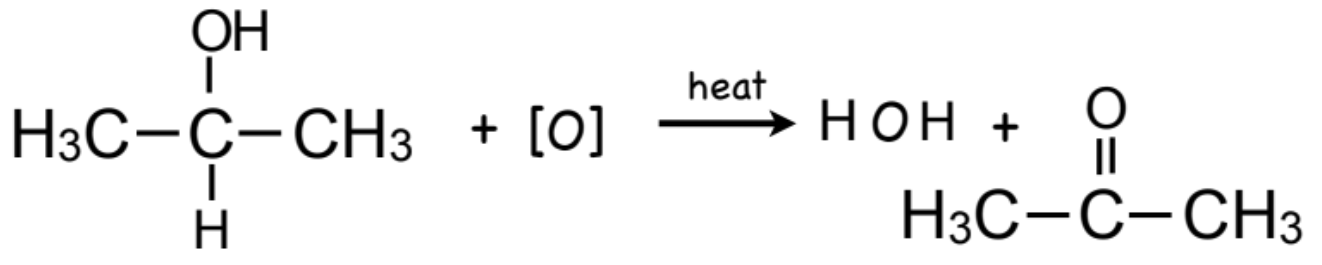
What is the flow of oxidation for secondary alcohols? What is their colour change?
secondary alcohol → ketone
orange → green
What is special about teritary alcohols?
they do not oxidized
How do you obtain aldehyde from a primary alcohol?
stop the reaction by removing aldehyde from the reaction before it becomes carboxylic acid
How do you obtain aldehyde from a primary alcohol?
leave the aldehyde for prolonged period of time
Use apparatus for reflux (a distillation techinque)
Tell me about Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
use a suitable reducing agent (NaBrH₄) in an aqueous alcoholic solution or lithium aluminum hydride
in anhydrous conditions
followed by an aqueous acid (carboxylic acid)
Complete the statement: both reagents produce the _______ ion,…
both reagents produce the hydride ion, H⁻, which acts as nucleophile on electron-deficient carbonyl carbon
Reduction of a carboxylic acid produces…
an aldehyde
Reduction of an aldehyde produces…
a primary alcohol
Reduction of a ketone produces a…
secondary alcohol