Chap 3: Biological Bases of Behaviour
5.0(1)Studied by 36 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Source: Barron's AP Psychology
Last updated 10:59 PM on 1/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
Neuroanatomy
The study of the parts and functions of neurons
2
New cards
Neurons
Individual nerve cells
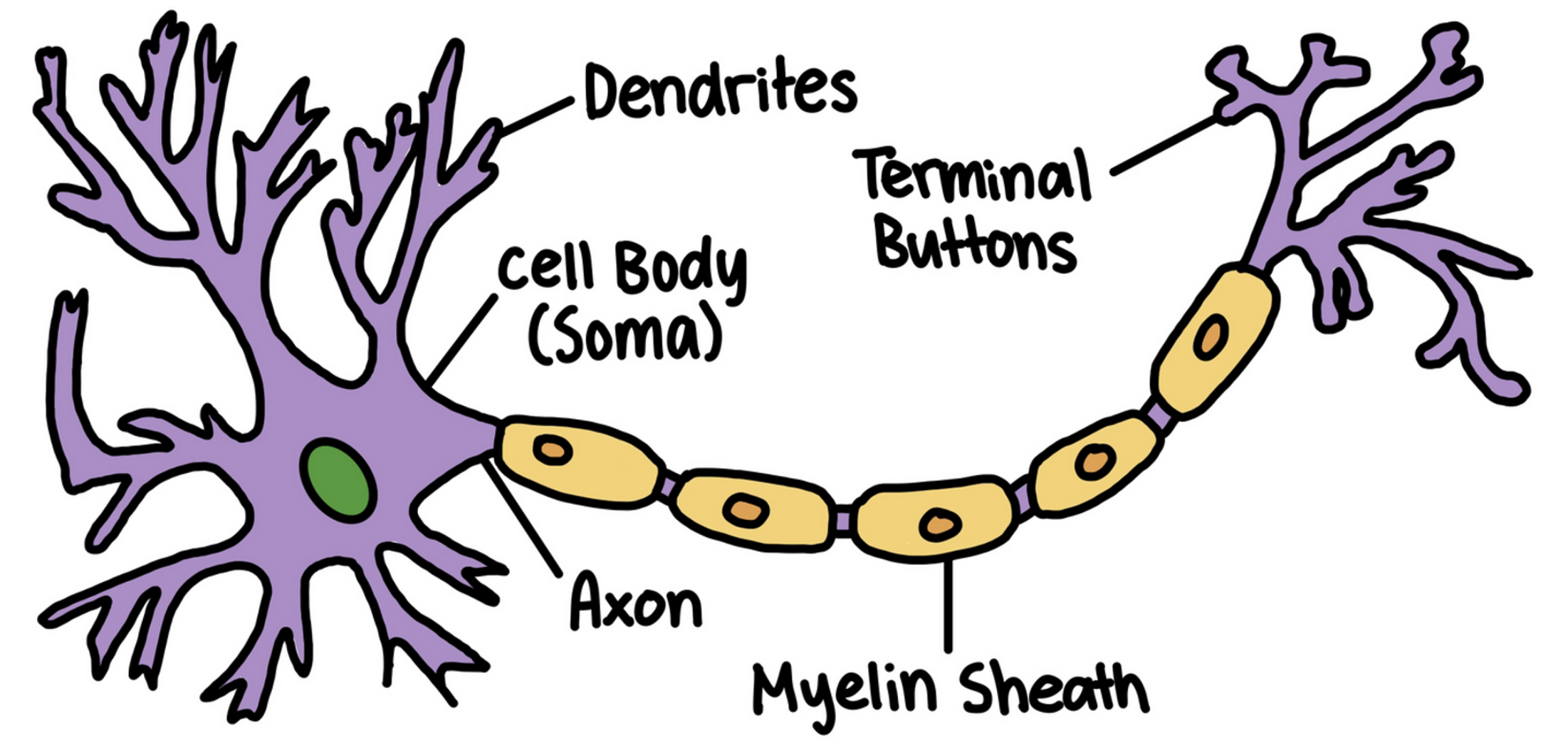
3
New cards
Dendrites
* Root-like parts of the cell that stretch out from the cell body.
* Grow to make synaptic connections with other neurons
* Grow to make synaptic connections with other neurons
4
New cards
Cell Body (Soma)
Contains the nucleus and other parts of the cell needed to sustain its life
5
New cards
Axon
Wire-like structure ending in the terminal buttons that extends from the cell body
6
New cards
Myelin Sheath
A fatty covering around the axon of some neurons that speeds neural impulses
7
New cards
Terminal Buttons
The branched end of the axon that also contains neurotransmitters
8
New cards
Neurotransmitters
* Chemicals contained in terminal buttons that enable neurons to communicate
* Fit into receptor sites on the dendrites of neurons like a key into a lock
* Fit into receptor sites on the dendrites of neurons like a key into a lock
9
New cards
Synapse
Space between the terminal buttons of one neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron
10
New cards
Receptor Sites
A place on the dendrites where neurotransmitters fit into
11
New cards
Absolute Threshold
The amount of neurotransmitters needed for firing
12
New cards
Action Potential
When a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body
13
New cards
All-or-none principle
A neuron either fires completely or it does not fire at all
14
New cards
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Excite the next cell into firing
15
New cards
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Inhibit the next cell from firing
16
New cards
Acetylcholine
* A neurotransmitter involved in motor movement
* Lack of acetylcholine is associated with Alzheimer’s disease
* Lack of acetylcholine is associated with Alzheimer’s disease
17
New cards
Dopamine
* A neurotransmitter involved in motor movement and alertness
* Lack of dopamine is associated with Parkinson’s disease
* An overabundance of dopamine is associated with schizophrenia
* Lack of dopamine is associated with Parkinson’s disease
* An overabundance of dopamine is associated with schizophrenia
18
New cards
Endorphins
A neurotransmitter involved in pain control and addictions
19
New cards
Serotonin
* A neurotransmitter involved in mood control
* Lack of serotonin is associated with clinical depression
* Lack of serotonin is associated with clinical depression
20
New cards
GABA
* An important inhibitory neurotransmitter
* Involved in seizures and sleep problems
* Involved in seizures and sleep problems
21
New cards
Glutamate
* Excitatory neurotransmitter
* Involved in memory, migraines, and seizures
* Involved in memory, migraines, and seizures
22
New cards
Norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter involved in alertness/arousal, can cause depression
23
New cards
Afferent Neurons (Sensory)
Take information from senses to brain
24
New cards
Interneurons
Once info reaches the brain or spinal cord, interneurons take the messages and send them elsewhere in the brain or onto efferent neurons
25
New cards
Efferent Neurons (Motor)
Take information from the brain to the rest of the body
26
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Consists of brain + spinal cord (all nerves encased in bones)
27
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
* All nerves not encased in bone
* Somatic and autonomic nervous systems
* Somatic and autonomic nervous systems
28
New cards
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary muscle movements
29
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System
* Controls automatic functions of our body
* Controls response to stress
* Contains parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems
* Controls response to stress
* Contains parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems
30
New cards
Sympathetic Nervous System
* Mobilizes body to respond to stress
* Alert system - accelerates some functions (e.g. heartbeat) but conserves resources needed for a quick response by slowing down other functions (e.g. digestion)
* Alert system - accelerates some functions (e.g. heartbeat) but conserves resources needed for a quick response by slowing down other functions (e.g. digestion)
31
New cards
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Causes body to slow down AFTER a stress response (break pedal)
32
New cards
Reflexes
Reactions that occur the moment sensory impulses reach the spinal cord
33
New cards
Accidents
By observing the brain damage and behaviour after an accident, researchers can determine the functions the damaged part played in behaviour.
34
New cards
Lesions
* The removal or destruction of part of the brain
* Observe behaviour afterwards to determine function of that part of the brain
* **Frontal Lobotomy** (In the past, lesioning of frontal lobe was used to make the patients calm and relieve symptoms)
* Observe behaviour afterwards to determine function of that part of the brain
* **Frontal Lobotomy** (In the past, lesioning of frontal lobe was used to make the patients calm and relieve symptoms)
35
New cards
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
* Detects brain waves
* Examine what type of waves the brain produces during different stages of consciousness and use this information to generalize about brain function.
* Examine what type of waves the brain produces during different stages of consciousness and use this information to generalize about brain function.
36
New cards
Computerized Axial Tomography Scan (CAT or CT)
* Several X-ray cameras that rotate around the brain and combine all the pictures into a detailed 3D picture
* Only show structure, not the functions or activity
* Only show structure, not the functions or activity
37
New cards
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
* Uses magnetic fields to measure the density and location of brain material.
* Only show structure, not functions or activity
* Only show structure, not functions or activity
38
New cards
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
* Shows what areas of the brain are most active during certain tasks
* Measures how much of a certain chemical parts of the brain are using
* Measures how much of a certain chemical parts of the brain are using
39
New cards
Functional MRI (fMRI)
* Combines elements of MRI and PET scans
* Show details of brain structures with information about blood flow in the brain
* Show details of brain structures with information about blood flow in the brain
40
New cards
Hindbrain
* Controls basic biological functions that keep us alive
* Contains medulla, pons, and cerebellum
* Contains medulla, pons, and cerebellum
41
New cards
Medulla
Part of hindbrain that controls blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing
42
New cards
Pons
Part of hindbrain that controls facial expressions
43
New cards
Cerebellum
Part of hindbrain that coordinates habitual muscle movements
44
New cards
Midbrain
Coordinates simple movements with sensory information
45
New cards
Reticular Formation
A netlike connection of cells throughout the midbrain that controls general body arousal and the ability to focus our attention
46
New cards
Forebrain
* Controls thought and reason (what makes us human)
* Contains thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus
* Contains thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus
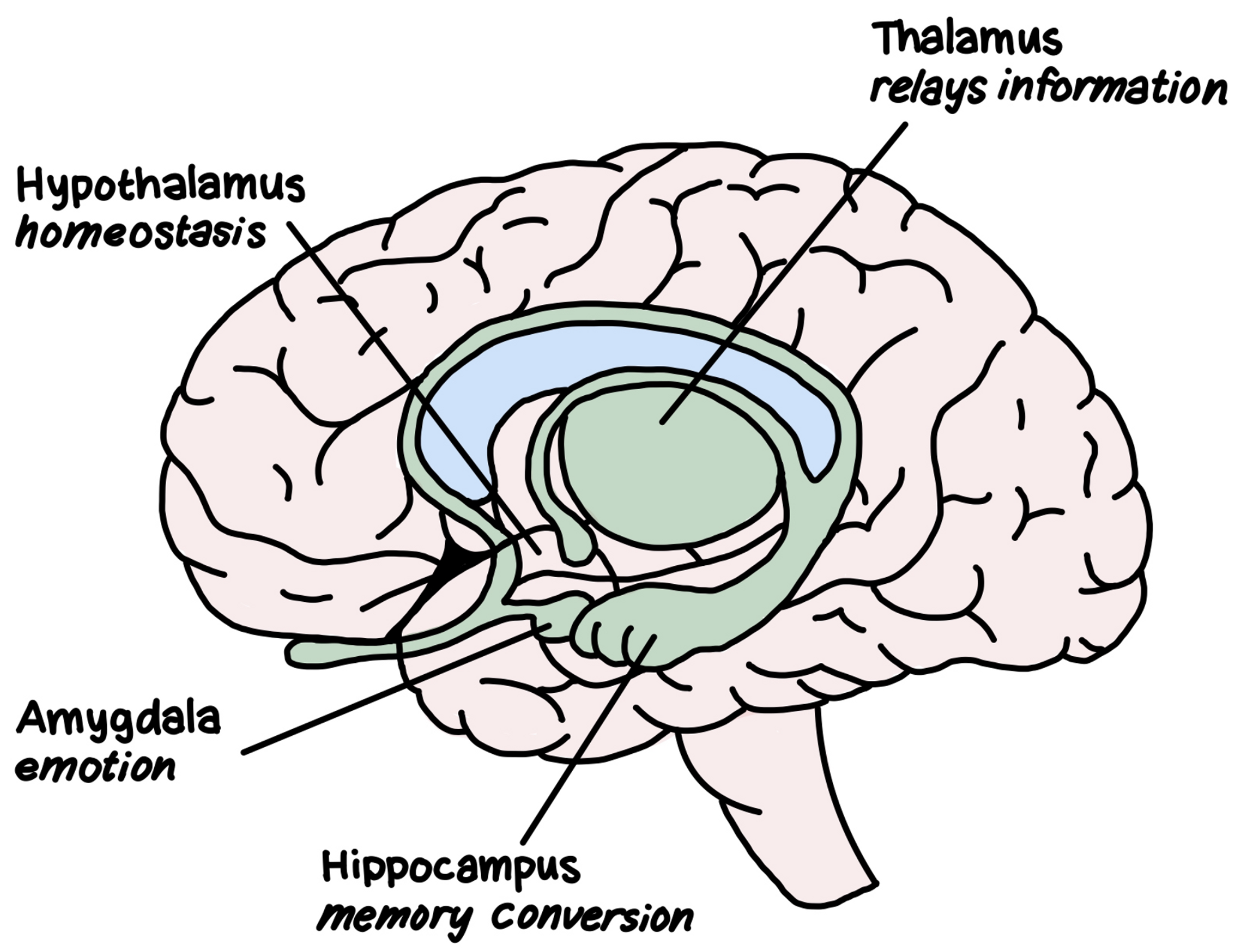
47
New cards
Thalamus
Receives the sensory signals coming up the spinal cord and sends them to the appropriate areas in the rest of the forebrain
48
New cards
Hypothalamus
* Metabolic functions
* e.g. body temperature, sexual arousal (libido), hunger, thirst, and the endocrine system
* e.g. body temperature, sexual arousal (libido), hunger, thirst, and the endocrine system
49
New cards
Amygdala
Vital to experiences of emotion
50
New cards
Hippocampus
Processes memory to be permanently stored in other areas of the cerebral cortex
51
New cards
Cerebral Cortex
* Grey wrinkled surface of the brain (layer of densely packed neurons)
* Contains 8 lobes, 4 in each hemisphere (frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal)
* Overtime, the dendrites of the neurons grow and connect with other neurons to form the complex neural web
* Contains 8 lobes, 4 in each hemisphere (frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal)
* Overtime, the dendrites of the neurons grow and connect with other neurons to form the complex neural web
52
New cards
Fissures
Wrinkled surface of the cerebral cortex to increase surface area
53
New cards
Hemispheres
* The two halves of the brain (right and left)
* Theories: Left = logic and sequential tasks, Right = spatial and creative tasks
* Theories: Left = logic and sequential tasks, Right = spatial and creative tasks
54
New cards
Contralateral Control
* LEFT hemisphere: sensory and motor functions of RIGHT half of body
* RIGHT hemisphere: sensory and motor functions of LEFT half of body
* RIGHT hemisphere: sensory and motor functions of LEFT half of body
55
New cards
Brain Lateralization
* Specialization of function in each hemisphere
* Research is done by examining split-brain patients
* Research is done by examining split-brain patients
56
New cards
Split-brain
* Corpus callosum is cut to treat severe epilepsy
* Operation pioneered by **Roger Sperry** and **Michael Gazzaniga**
* Cannot orally report info only in the right hemisphere since spoken language is in the left hemisphere
* Operation pioneered by **Roger Sperry** and **Michael Gazzaniga**
* Cannot orally report info only in the right hemisphere since spoken language is in the left hemisphere
57
New cards
Association Area
Any area of the cerebral cortex that is not associated with receiving sensory information or controlling muscle movements
58
New cards
Frontal Lobes
Large areas of the cerebral cortex located at the top front part of the brain behind the eyes
59
New cards
Prefrontal Cortex
* Anterior / front of frontal lobe
* Critical role in thought directing process
* Critical role in thought directing process
60
New cards
Broca’s Area (Paul Broca)
* Frontal lobe
* Responsible for controlling muscles involved in producing speech
* Responsible for controlling muscles involved in producing speech
61
New cards
Wernicke’s Area (Carl Wernicke)
* Temporal lobe
* Responsible for understanding of spoken and written language
* Responsible for understanding of spoken and written language
62
New cards
Motor Cortex
* Thin, vertical strip at the back of the frontal lobe
* Sends signals to our muscles, controlling our voluntary movements
* Top of the body is controlled by neurons at the bottom of this cortex, progressing down the body as you go up the cortex
* Sends signals to our muscles, controlling our voluntary movements
* Top of the body is controlled by neurons at the bottom of this cortex, progressing down the body as you go up the cortex
63
New cards
Parietal Lobes
* Located behind the frontal lobe but still on the top of the brain
* Contains the sensory cortex
* Contains the sensory cortex
64
New cards
Sensory Cortex
* A thin, vertical strip that receives incoming touch sensations from the rest of our body
* Top of sensory cortex receives sensations from the body of the body and vice versa
* Top of sensory cortex receives sensations from the body of the body and vice versa
65
New cards
Occipital Lobes
* At the very back of our brain, farthest from our eyes
* Interpret messages from our eyes in our **visual cortex**
* Impulses from right half of each retina are processed in the visual cortex in the right occipital lobe
* Impulses from left half of each retina are processed in the visual cortex in the left occipital lobe
* Interpret messages from our eyes in our **visual cortex**
* Impulses from right half of each retina are processed in the visual cortex in the right occipital lobe
* Impulses from left half of each retina are processed in the visual cortex in the left occipital lobe
66
New cards
Temporal Lobes
* Process sound sensed by our ears (**auditory cortex**)
* Sound received by either ear is processed in both auditory cortices
* Damage to this area affects ability to interpret spoken language (Wernicke’s area)
* Sound received by either ear is processed in both auditory cortices
* Damage to this area affects ability to interpret spoken language (Wernicke’s area)
67
New cards
Brain Plasticity
The ability of the nervous system to change its activity in response to intrinsic or extrinsic stimuli by reorganizing its structure, functions, or connections.
68
New cards
Endocrine System
* A system of glands that secrete hormones that affect many different biological processes in our bodies
* Controlled by hypothalamus
* Controlled by hypothalamus
69
New cards
Adrenal Glands
* Produce adrenaline
* Signals body to prepare for fight or flight (autonomic nervous system - involuntary responses)
* Signals body to prepare for fight or flight (autonomic nervous system - involuntary responses)
70
New cards
Ovaries and Testes
* Produce sex hormones
* Levels of estrogen and testosterone may explain gender differences (Developmental Psychology)
* Levels of estrogen and testosterone may explain gender differences (Developmental Psychology)
71
New cards
Monozygotic Twins
Identical twins (same genetic material)
72
New cards
Thomas Bouchard
* Studied monozygotic twins raised in different families to see if traits were nature or nurture
* Criticized because twins share the same physical characteristics, thus causing others to treat them in similar ways (effective psychological environment).
* Criticized because twins share the same physical characteristics, thus causing others to treat them in similar ways (effective psychological environment).
73
New cards
Turner’s Syndrome
Single X chromosome instead of a 23rd pair
74
New cards
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
Extra X chromosome, thus XXY pattern
75
New cards
Down Syndrome
Extra chromosome on 21st pair