Credit Test 2 Past Paper Questions
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
1
New cards
Caudal mediastinum includes trachea
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
false
2
New cards
Where is the right kidney located?
cranial, lies against the liver at the level of T13
3
New cards
Where is the left kidney located?
L1-L3
4
New cards
Acute bronchitis: on the radiogram we see alveolar pattern
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
false
5
New cards
Maximal of vertebral heart score for Irish wolfhound is 11.5
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
false
6
New cards
Write me a lung pattern in lobar pneumona
alveolar
7
New cards
Cranial mediastinum include silhouette of heart
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
false
8
New cards
Negative bronchogram is typical for bronchial pattern
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
false
9
New cards
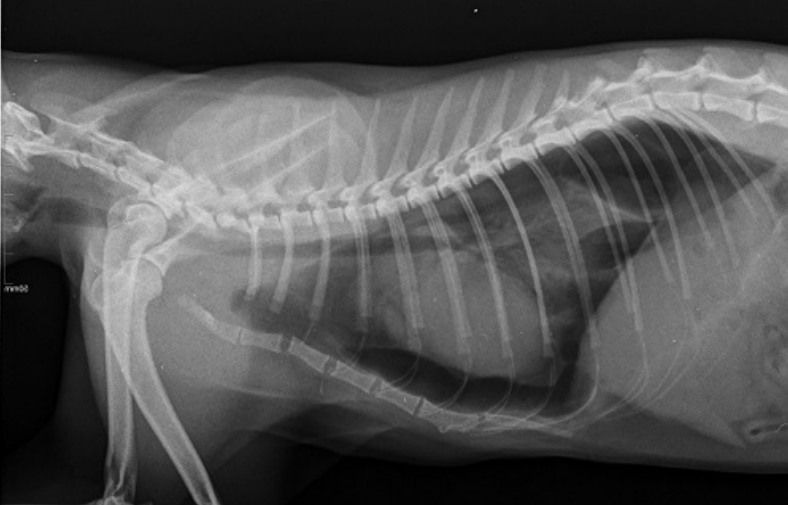
Radiographic report: pathology, status of trachea, heart, lung, etc.
cat, latero lateral position
X ray of the thorax
nice and clear radiolucent trachea
big radiolucent zone between the long and the sternum which indicate
many air present
the lung are compressed
many air radiolucent zone present in triangular shape on the dorsal
caudal next to the diaphragma
this is a pneumothorax
X ray of the thorax
nice and clear radiolucent trachea
big radiolucent zone between the long and the sternum which indicate
many air present
the lung are compressed
many air radiolucent zone present in triangular shape on the dorsal
caudal next to the diaphragma
this is a pneumothorax
10
New cards
Cardiomegaly: vertebral heart score is 9.8
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
false
11
New cards
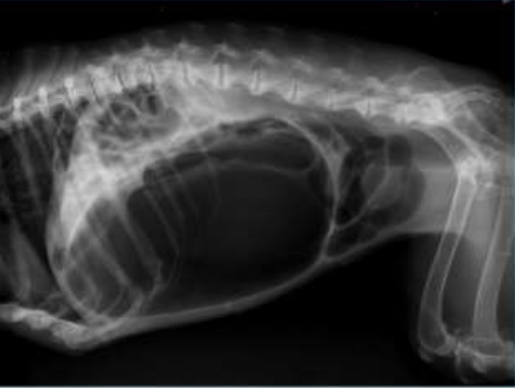
Radiographic Report
Lateral projection, right side
Pathology: spondylosis deformans all lumbar vertebrae, dilated stomach due to stomach torsion pushing the intestine dorsally and cranially), lots of gas in the large intestine
Pathology: spondylosis deformans all lumbar vertebrae, dilated stomach due to stomach torsion pushing the intestine dorsally and cranially), lots of gas in the large intestine
12
New cards
Write me the nae of positive contrast medium for cystography
non-ionic organic iodine through catheter
13
New cards
Dose of positive nonresportion contrast medium for digestive apparatus is 350-1000 ml/kg
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
false
14
New cards
Barium sulfate is positive contrast medium for normograde urography
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
false
15
New cards
Write me correct VHS for dog
8.5-10.6
16
New cards
X-ray study: Physiological size of cat's kidney is 2 cm
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
false
17
New cards
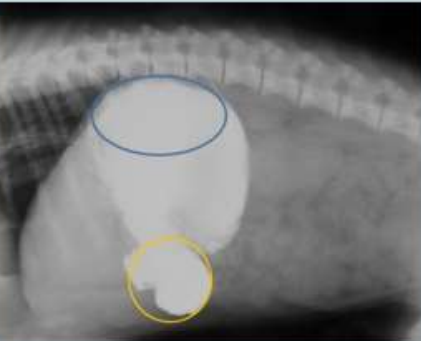
Write me name of blue and yellow parts
Blue: fundus
Yellow: Pylorus
Yellow: Pylorus
18
New cards
Which is ectopic ureter and name two common types?
ureter not entering urinary bladder in trigonum, but at different site (vagina, rectum, uterus);
- Extramural bypasses the bladder completely, and ureters enters at urethra or vagina.
- Intramural enters the bladder at correct location, but tunnels down the wall of urethra before
opening
- Extramural bypasses the bladder completely, and ureters enters at urethra or vagina.
- Intramural enters the bladder at correct location, but tunnels down the wall of urethra before
opening
19
New cards
Fundus of stomach is VD position on left side of patient
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
true
20
New cards
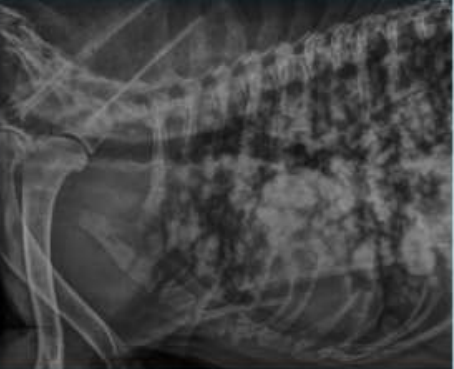
Radiographic report
Lateral projection
Adult dog
radiolucent trachea
increased radiopacity in lungs showing nodular lung patterns
circular densities - metastatic reaction
Adult dog
radiolucent trachea
increased radiopacity in lungs showing nodular lung patterns
circular densities - metastatic reaction
21
New cards
On 30 day pregnancy we can count the skulls on the radiograph
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
false
22
New cards
Is radiolucent mass between the colon descendens and the vertebrae in the LL position of the patient?
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
true
23
New cards
Types of tracheal collapse
congenital
acquired
extrathoracic (during inspiration)
intrathoracic (during expiration)
acquired
extrathoracic (during inspiration)
intrathoracic (during expiration)
24
New cards
Describe the main radiological symptoms of pneumothorax on radiograph in LL position
heart is raised from the sternum
gap between caudodorsal lung margin and spine
increased opacity of the lungs
gap between caudodorsal lung margin and spine
increased opacity of the lungs
25
New cards
Write the pulmonary patterns
normal
alveolar
interstitial (structured/nodular or unstructured)
bronchial
mixed (bronchointerstitial)
vascular
alveolar
interstitial (structured/nodular or unstructured)
bronchial
mixed (bronchointerstitial)
vascular
26
New cards
Describe radiologically the chest cavity effusion
there will be a radio-opaque area either at the ventral end of the thoracic cavity (VD) or filling the entire cavity. Borders are barely visible but there is "scalloping" of lung edges due to retraction from thoracic wall
27
New cards
What passes through the cranial mediastinum?
lymph nodes
trachea
trachea
28
New cards
What contrast agent and what dose would you use during the examination of GIT?
Positive contrast: sciabarium per os or per rectum 12 ml/kg or iodine if there are perforations in GIT
Negative contrast: 30-300 ml of air
Negative contrast: 30-300 ml of air
29
New cards
Where is physiologically located spleen on the radiograph in VD position?
caudal to the stomach, connected to left abdominal cavity
30
New cards
Stomach of a dog is located at:
cranial abdomen
31
New cards
What is pneumoperitoneum?
air in the peritoneum of the abdominal cavity
32
New cards
What are the caused of pneumoperitoneum?
puncture of the peritoneum
air trapped during surgery
gas produced by bacterial infection
air trapped during surgery
gas produced by bacterial infection
33
New cards
What passes through the retroperitoneal space?
ureters, kidneys, vena cava caudalis, abdominal aorta, sublumbar lymph nodes, prostate gland, urinary bladder neck
34
New cards
What is the physiological renal size?
dogs: 2.5-3x the size of L2
entire cats: 2.1-3.2 x the size of L2
neutered cats: 1.9-2.6x the size of L2
entire cats: 2.1-3.2 x the size of L2
neutered cats: 1.9-2.6x the size of L2
35
New cards
What density do ureters have on the radiograph, and what do we call their point of entry into the bladder?
soft tissue (not visible)
ostium ureteris on trigona vesicae
ostium ureteris on trigona vesicae
36
New cards
What contrast medium would you use to study radiolucent foreign bodies in the urinary bladder?
nonionic organic iodine 10mg/kg BW
37
New cards
How and where is physiologically visible the full urinary bladder on the radiograph?
extraperitoneal with caudal pointing neck. The body of the bladder will hang cranio-ventrally and be more rounded when full
38
New cards
From which day can we diagnose pregnancy in bitches radiologically, and why?
45
ossification of foetuses begins then
ossification of foetuses begins then
39
New cards
How is pyometra visible on LL radiograph?
Dilation of the uterine horns seen as convoluted soft tissue opacity extending cranially to the mid-abdomen and displacing the jejunal loops yet more cranially
Enlargement of the uterine body is recognised as a tubular soft tissue opacity between the colon and the bladder, displacing the descending colon dorsally
Enlargement of the uterine body is recognised as a tubular soft tissue opacity between the colon and the bladder, displacing the descending colon dorsally
40
New cards
Mediastinum: what runs through it?
lymph nodes
blood vessels
trachea
eosophagus
vasosympathetic trunk
blood vessels
trachea
eosophagus
vasosympathetic trunk
41
New cards
What can we see in the caudal mediastinum?
plica vena cava
oesophagus
oesophagus
42
New cards
Time for barium to reach to colon
a. >60
b. 60-90
c. 90+ (3-5 hours)
a. >60
b. 60-90
c. 90+ (3-5 hours)
90+ (3-5 hours)
43
New cards
How long should an animal be starved prior to radiogram of GIT?
12 hours, 12-24 hours as needed
enema: 2-3 hours before
enema: 2-3 hours before
44
New cards
How much sciabarium should be given for radiogram of GIT?
12 mg/kg
45
New cards
Where is pylorus located?
a. right
b. middle
c. left
a. right
b. middle
c. left
right
46
New cards
Location of the spleen
a. ventrolumbar
b. ventroabdominal
c. not visible
a. ventrolumbar
b. ventroabdominal
c. not visible
ventroabdominal
47
New cards
Describe the position of the caecum
VD: located to the right of the midline at the level of L3-L4
48
New cards
What can stop contrast medium in the small intestine?
obstruction by foreign material
49
New cards
What can improve the visibility of the small intestine?
contrast medium
50
New cards
Causes of dilated oesophagus
vascular ring anomaly
megaoesophagus
foreign bodies
diverticula
hiatial hernia
stenosis
megaoesophagus
foreign bodies
diverticula
hiatial hernia
stenosis
51
New cards
What gets stuck in the oesophagus in megaesophagus?
air, fluid, food
52
New cards
Location of stomach: pylorus, body, fundus in VD
In VD projection: Dog: U-shaped, Cat: J-shaped.
Pylorus: Right
Body: Midline/left
Fundus: Left
Pylorus: Right
Body: Midline/left
Fundus: Left
53
New cards
Where is localisation of duodenum in VD position?
on left side (caudal to stomach, connected to left abdominal cavity)
54
New cards
Colon descendens ventrodorsal located:
on left side;
extends caudally to the left mid-dorsal abdomen
extends caudally to the left mid-dorsal abdomen
55
New cards
Colon transversus VD location
Extends from right to left caudal to stomach
56
New cards
Colon ascendens position in VD:
Cranially in the mid-adbomen to the right of midline
57
New cards
We see gall bladder in regular radiogram?
NO – Because of fluid silhouette effect
58
New cards
We see stomach in caudal part of abdominal cavity Lateral-Lateral?
No - Only if there is dislocation, tympany or dilatation
59
New cards
What we see in Torsion?
Stomach turns and changes position, soft tissue bands across the stomach
60
New cards
Fundus in Lateral-Lateral position is located:
Dorsally. If found ventrally there is gastric torsion.
61
New cards
How many ml of contrast medium we use for positive contrast medium to observe GIT?
Sciabarium per os 12ml/kgContrast mediums for GIT. List
62
New cards
Contrast mediums for GIT. List 2
- Skiabarium 12ml/kg bw.
- Iodine 2-3 ml/kg bw
- Double contrast: 1ml/kg barium and inflation of air.
- Iodine 2-3 ml/kg bw
- Double contrast: 1ml/kg barium and inflation of air.
63
New cards
What contrast media is used for ruptured oesophagus?
Aqueous iodine solutions should be used for perforations as they are non-toxic. Radiograph
needs to be taken immediately after administration of the contrast agent.
Liquid barium sulphate does not adhere well to the oesophageal lumen
needs to be taken immediately after administration of the contrast agent.
Liquid barium sulphate does not adhere well to the oesophageal lumen
64
New cards
Describe radiologically the chest cavity effusion:
There will be a radio-opaque area either at the ventral end of the thoracic cavity (VD) or
filling the entire cavity. Borders are barely visible but there is “scalloping” of lung edges due
to retraction from thoracic wall
filling the entire cavity. Borders are barely visible but there is “scalloping” of lung edges due
to retraction from thoracic wall
65
New cards
Effusion in AC
Liquid in abdomen. Can be classified as transudate, exudate, blood, and urine
66
New cards
Two positions to study abdominal cavity
- Ventrodorsal
- Lateral-Lateral (does not matter if left or right lateral but the view should be kept consistent
in all studies)
- Lateral-Lateral (does not matter if left or right lateral but the view should be kept consistent
in all studies)
67
New cards
What contrast medium is used for urography?
- Iodine
- Negative (air, oxygen, nitrogen)
- Positive
- Double
- Negative (air, oxygen, nitrogen)
- Positive
- Double
68
New cards
What passes through the retroperitoneal space?
Ureters, kidneys, vena cava caudalis, abdominal aorta, sublumbar lymph nodes, prostate gland
and urinary bladder neck
and urinary bladder neck
69
New cards
How and where is physiologically visible the fill uinary bladder on the radiograph
It is extraperitoneal with a caudal pointing neck. The body of the bladder will hang cranioventrally and be more rounded when full.
70
New cards
How we count babies in radiogram?
by counting skulls
71
New cards
How many ml of contrast medium we use for negative contrast medium?
30-300ml of air per dog
72
New cards
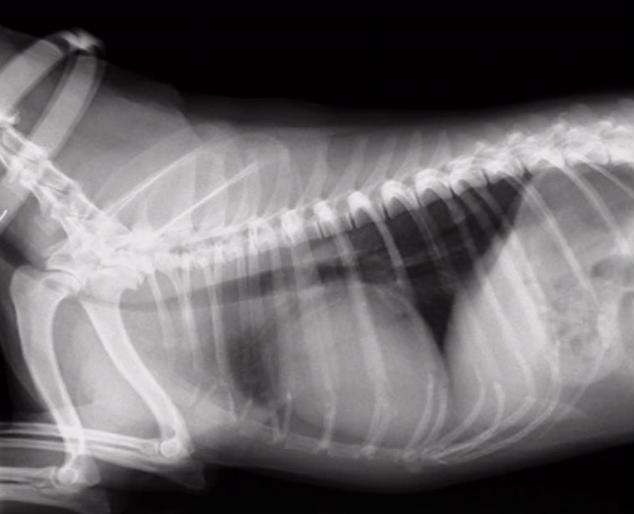
Radiographic report
Right side
o Lateral
o Dog (squared
vertebrae)
o Compression of
trachea
o Tracheal collapse in
cervical + apertura
o Diaphragm + border
o In articulatio humeri
arthrosis
o Lateral
o Dog (squared
vertebrae)
o Compression of
trachea
o Tracheal collapse in
cervical + apertura
o Diaphragm + border
o In articulatio humeri
arthrosis
73
New cards
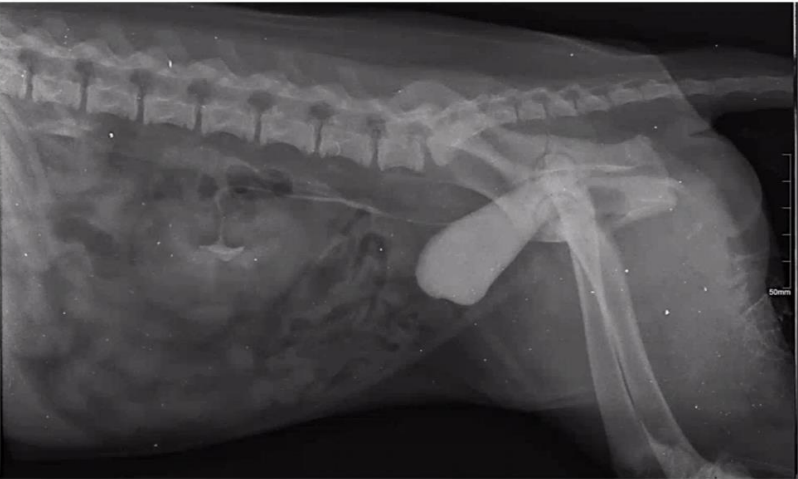
Radiographic report
LL position
o Left kidney is enlarged
o Contrast medium: positive iodine
through I.V catheter (urography)
o We can see ureters
o In retroperitoneal space only 1
trigonum
o Second ureter is running behind
trigonum pathology: ectopic no
ending
o Left kidney is enlarged
o Contrast medium: positive iodine
through I.V catheter (urography)
o We can see ureters
o In retroperitoneal space only 1
trigonum
o Second ureter is running behind
trigonum pathology: ectopic no
ending
74
New cards
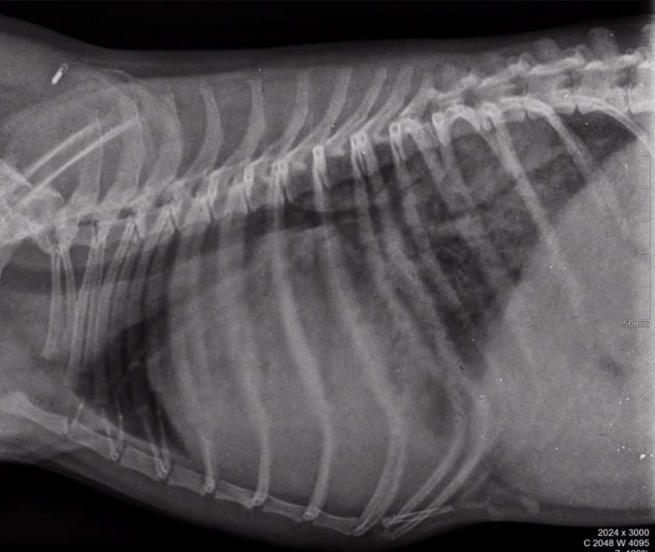
Radiographic report
LL position
Dog
o Heart is enlarged
cardiomegaly, because
it is compressing tracheal
wall
o Measurements are ok
o Alveolar lung pattern
o See only line of bronchus negative, oedema because of heart
Dog
o Heart is enlarged
cardiomegaly, because
it is compressing tracheal
wall
o Measurements are ok
o Alveolar lung pattern
o See only line of bronchus negative, oedema because of heart
75
New cards
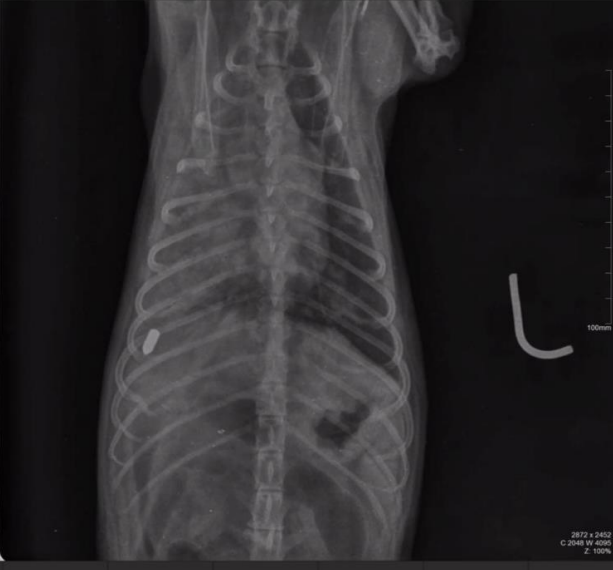
Radiographic report
VD, left, dog
o Foreign body 9-10th thoracic
vertebrae on the right side
o Foreign body is rod shaped,
radiopaque metal
o Can’t see borders on the right
side traumatic
o Alveolar part
o Foreign body harms lungs
o Foreign body 9-10th thoracic
vertebrae on the right side
o Foreign body is rod shaped,
radiopaque metal
o Can’t see borders on the right
side traumatic
o Alveolar part
o Foreign body harms lungs
76
New cards
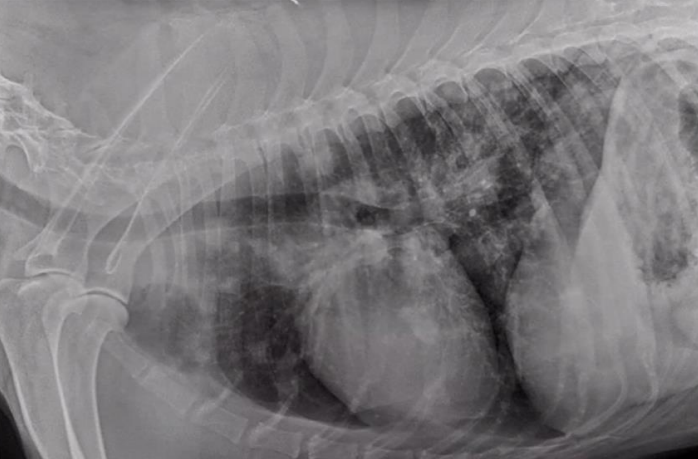
Radiographic report
. LL, dog
o Chest x-ray
o Right side
o Vertebrae are ok
o Lungs increased opacity
o Interstitial lung pattern
o 2nd tumour metastatic
o Chest x-ray
o Right side
o Vertebrae are ok
o Lungs increased opacity
o Interstitial lung pattern
o 2nd tumour metastatic
77
New cards
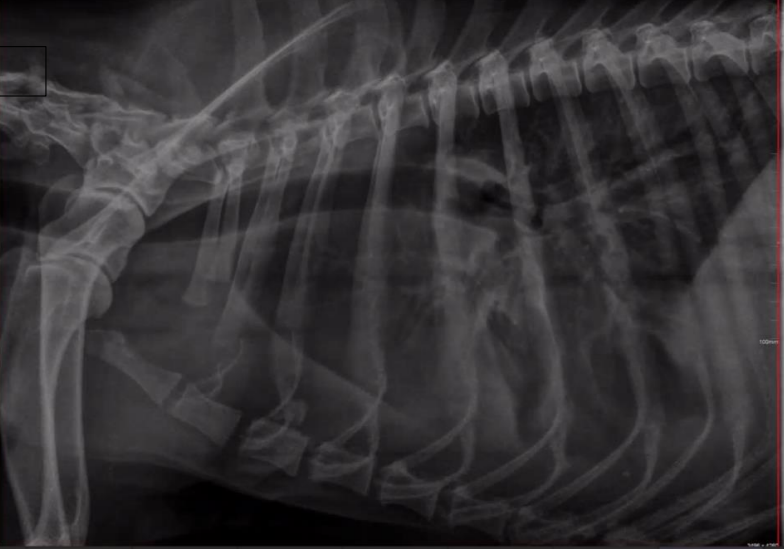
Radiographic report
Thoracic cavity
o Lateral side
o Trachea in good position, borders are not clear
o Heart is not clearly visible
o Trachea is pushing dors. In the cranial mediastinum
o Lungs: I can see the vessels + structures -> free liquid in the thoracic cavity (maybe exudate, transudate or blood)
o Lateral side
o Trachea in good position, borders are not clear
o Heart is not clearly visible
o Trachea is pushing dors. In the cranial mediastinum
o Lungs: I can see the vessels + structures -> free liquid in the thoracic cavity (maybe exudate, transudate or blood)
78
New cards
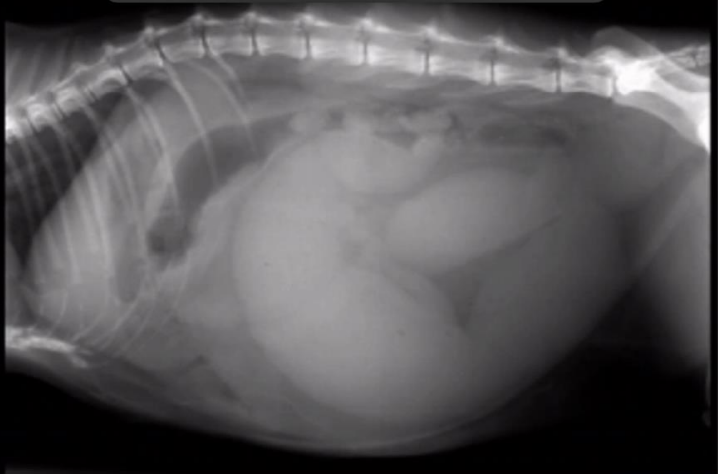
Radiographic report
Dog, LL, abdominal cavity
o Abdomen disc
o Uterus pyometra
o Tubular mass radiopaque
o Pushing colon/stomach cranially
o Abdomen disc
o Uterus pyometra
o Tubular mass radiopaque
o Pushing colon/stomach cranially
79
New cards
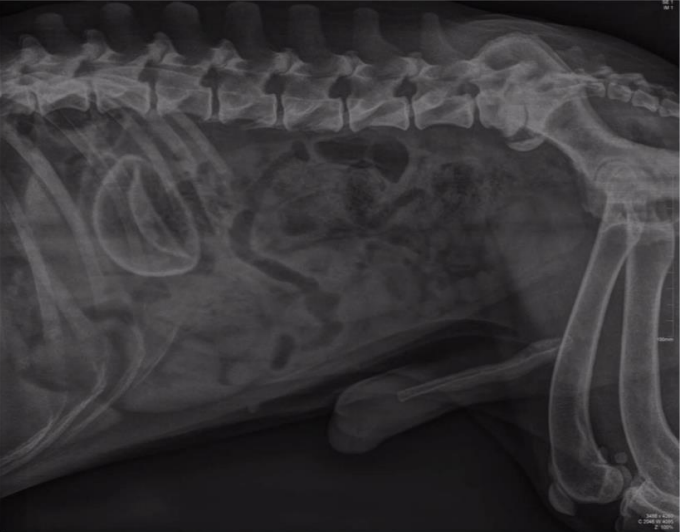
Radiographic report
Lateral, male, abdominal cavity
o Liver + spleen good, no changes
o Loops of intestine have little gas, colon ascendens is ok
o L- sacral min. + new bone spondylosis deformans + fusion (min.intrav.space)
o Foreign body, NOT be confused with kidney
o Liver + spleen good, no changes
o Loops of intestine have little gas, colon ascendens is ok
o L- sacral min. + new bone spondylosis deformans + fusion (min.intrav.space)
o Foreign body, NOT be confused with kidney
80
New cards
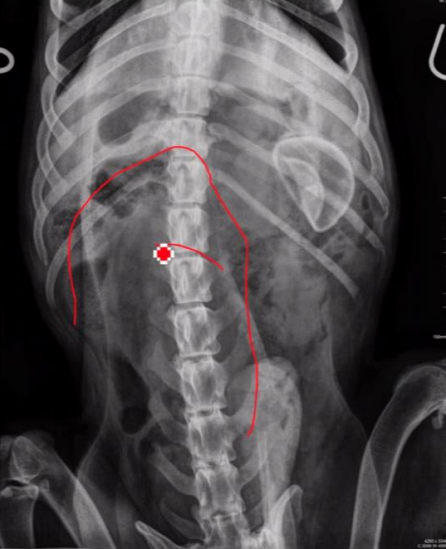
Radiographic report
VD, male, abdominal cavity
o See colon and loops of
small intestine
o Foreign body is
radioopaque, NOT be
confused with kidney
o See colon and loops of
small intestine
o Foreign body is
radioopaque, NOT be
confused with kidney
81
New cards
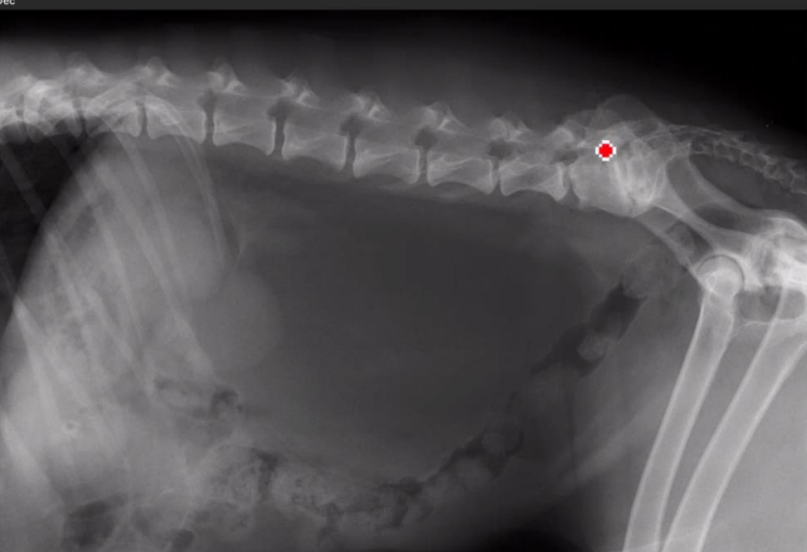
Radiographic report
Lateral, dog, abdominal cavity
o Colon descendes is displaced we can see
faeces
o Big mass, because we can see border of other organs (radiopacity of fat)
o Kidneys no good position
o Stomach is pushing on the diaphragm (pushed cranially)
o Opacity of kidney (diff.opacity)
o It is FAT LIPOMA
o Big fat mass
o L-S connection stenosis, decreased space
o Colon descendes is displaced we can see
faeces
o Big mass, because we can see border of other organs (radiopacity of fat)
o Kidneys no good position
o Stomach is pushing on the diaphragm (pushed cranially)
o Opacity of kidney (diff.opacity)
o It is FAT LIPOMA
o Big fat mass
o L-S connection stenosis, decreased space
82
New cards
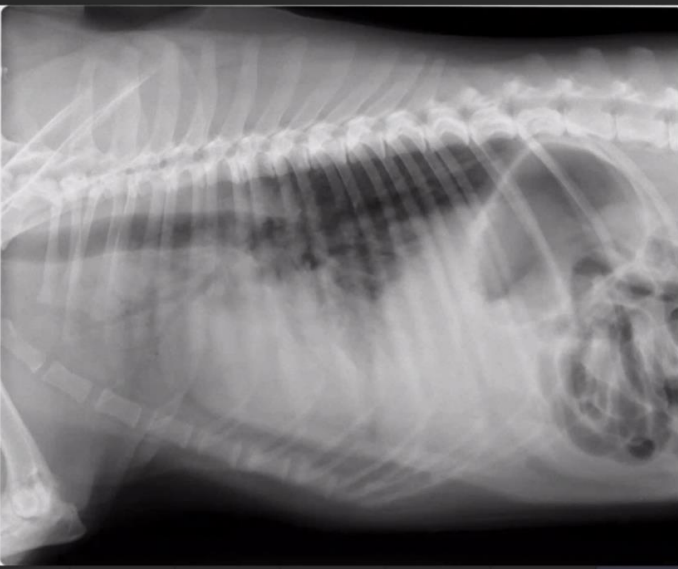
Radiographic report
Dog, LL, not clear organs
o Cant see border of diaphragm
o No free liquid
o We can see the bronchus alveolar lung pattern
o Cant see border of diaphragm
o No free liquid
o We can see the bronchus alveolar lung pattern
83
New cards
Pyloric part of stomach in VD position is on left side of body
a. True
b. False
a. True
b. False
False
84
New cards
in fibrosis of lung tissue: on the radiograph we see: interstitial pattern
a. True
b. False
a. True
b. False
True
85
New cards
For kidney evaluation we use negative contrast material and application will be in the kidney's pelvis
a. True
b. False
a. True
b. False
False
86
New cards
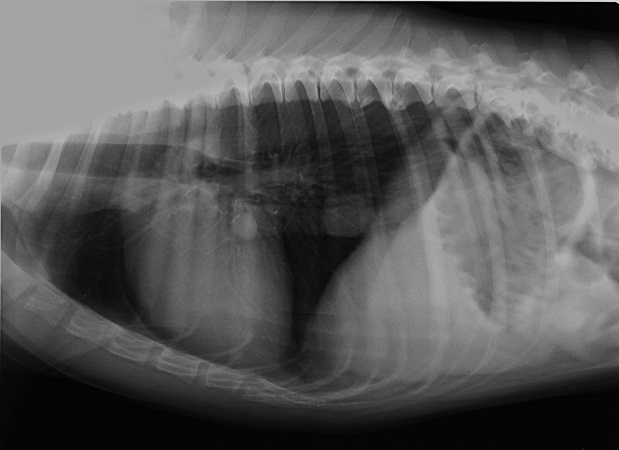
Latero-lateral position, dog, interstitial lung pattern
a. True
b. False
a. True
b. False
True
87
New cards
mark the correct size of the kidneys in the breed St. Bernard dog
a. 4.5-5.5 times larger than L7
b. 4.5-5.5 times larger than L2
c. 2.5-3 times larger than L7
d. 2.5-3 times larger than L2
a. 4.5-5.5 times larger than L7
b. 4.5-5.5 times larger than L2
c. 2.5-3 times larger than L7
d. 2.5-3 times larger than L2
2.5-3 times larger than L2
88
New cards
The middle mediastinum contains the silhouette of the heart
a. True
b. False
a. True
b. False
True
89
New cards
Normal time period for normograde urography radiography examination is: after application, next 1 hour after application, next 3 hours after application and 5 hours after application
a. True
b. False
a. True
b. False
False
90
New cards
Cranial mediastinum include cranial lung lobe
a. True
b. False
a. True
b. False
False
91
New cards
Select the correct answer:
a. Latero-lateral position, dog, female, spondylosis deformans in lumbo-sacral connection, full urinary bladder
b. Latero-lateral position, dog, male, spondylosis deformas in lumbo-sacral connection, radiopaque foreign body in intestine
c. Latero-lateral position, dog, female, spondylosis deformans in lumbo-sacral connection, torsion of stomach
d. Latero-lateral position, dog, male, spondylosis deformans in lumbo-sacral connection, abdominal effusion
a. Latero-lateral position, dog, female, spondylosis deformans in lumbo-sacral connection, full urinary bladder
b. Latero-lateral position, dog, male, spondylosis deformas in lumbo-sacral connection, radiopaque foreign body in intestine
c. Latero-lateral position, dog, female, spondylosis deformans in lumbo-sacral connection, torsion of stomach
d. Latero-lateral position, dog, male, spondylosis deformans in lumbo-sacral connection, abdominal effusion
Latero-lateral position, dog, male, spondylosis deformans in lumbo-sacral connection, abdominal effusion
92
New cards
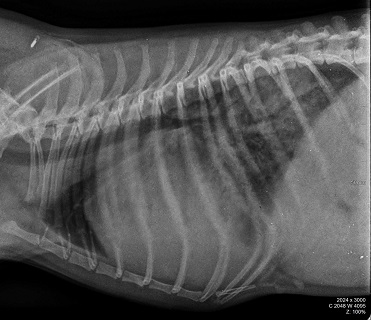
Radiographic report
LL position
Dog
enlarged cardiac silhouette (cardiomegaly or pericardial effusion)
alveolar lung pattern
Dog
enlarged cardiac silhouette (cardiomegaly or pericardial effusion)
alveolar lung pattern
93
New cards
Oedema of lung has alveolar pattern:
a. True
b. False
a. True
b. False
True
94
New cards
Acute bronchitis: mark me correct lung pattern
a. without pattern
b. bronchial
c. alveolar
d. intersticial
a. without pattern
b. bronchial
c. alveolar
d. intersticial
without pattern
95
New cards
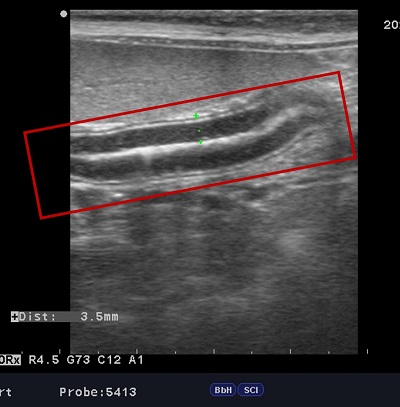
Radiographic anatomy - ultrasonography - write me name of organ (red zone)
(longitudinal) small intestine
96
New cards
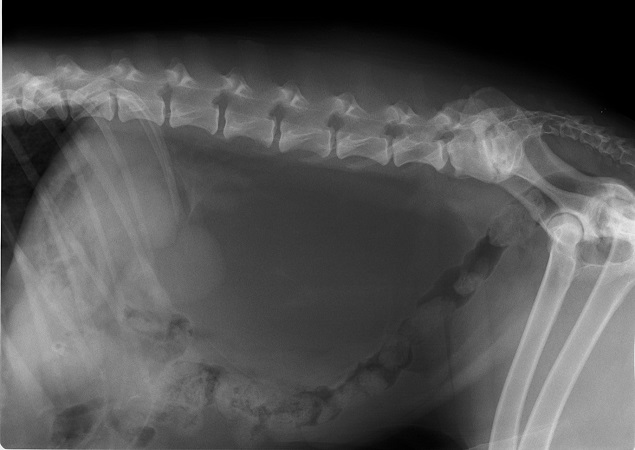
Select the correct answer
a. latero lateral position, dog, male, pathology radiopaque mass as soft tissue in the sublumbal part - gigantic sublumbal lymph node
b. laterolateral position, abdominal mass radiopacity as soft tissue in retroperitoneal space
c. laterolateral position, enormously filled bladder, lumbosacral stenosis, spondylosis deformans lumbal vertebrae L2-3
d. laterolateral position, lumbosacral stenosis, spondylosis deformans L-S
a. latero lateral position, dog, male, pathology radiopaque mass as soft tissue in the sublumbal part - gigantic sublumbal lymph node
b. laterolateral position, abdominal mass radiopacity as soft tissue in retroperitoneal space
c. laterolateral position, enormously filled bladder, lumbosacral stenosis, spondylosis deformans lumbal vertebrae L2-3
d. laterolateral position, lumbosacral stenosis, spondylosis deformans L-S
laterolateral position, lumbosacral stenosis, spondylosis deformans L-S
97
New cards
ULTRASOUND: Acoustic enhancement is artefact: produced by structures in the body which reflect or absorb nearly 100% of the ultrasound beam
a. True
b. False
a. True
b. False
False
98
New cards
Radiographic report
LL position
Male dog
urinary bladder with negative contrast is very dorsal in comparison to normal position
masses with radiopacity as soft tissue in ventral abdomen pushing the urinary bladder dorsally
confirmation with ultrasound
Male dog
urinary bladder with negative contrast is very dorsal in comparison to normal position
masses with radiopacity as soft tissue in ventral abdomen pushing the urinary bladder dorsally
confirmation with ultrasound
99
New cards
When the torsion of stomach by 180 degrees is:
a. pylorus is right side of patient and dorsally
b. pylorus is left side of patient and ventrally
c. pylorus is right side of patient and ventrally
d. pylorus is left side of patient and dorsally
a. pylorus is right side of patient and dorsally
b. pylorus is left side of patient and ventrally
c. pylorus is right side of patient and ventrally
d. pylorus is left side of patient and dorsally
pylorus is left side of patient and dorsally
100
New cards
Write the physiological position of the cecum in the dog in VD and LL position
a. VD-right side of patient LL-medially
b. VD-left side of patient LL-medially
c. VD-left side of patient LL-ventrally
d. VD-right side of patient LL-ventrally
a. VD-right side of patient LL-medially
b. VD-left side of patient LL-medially
c. VD-left side of patient LL-ventrally
d. VD-right side of patient LL-ventrally
VD-right side of patient LL-medially