Understanding Drug Addiction and Its Mechanisms
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
What is the relationship between medicine and drugs?
All medicine are drugs, but not all drugs are medicine.
What are psychoactive drugs?
Drugs that influence subjective experience and behavior by acting on the nervous system.
How does drug administration affect drug action?
The route of administration influences the rate and degree to which the drug reaches its site of action.
What are the three main routes of drug administration?
Ingestion (oral)
injection (subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous)
inhalation
What is a disadvantage of intravenous drug administration?
It delivers the drug directly to the brain, making effects strong and fast, with no opportunity to counteract overdose or allergic reactions.
How are drugs absorbed when inhaled?
through capillaries in the lungs.
What is the blood-brain barrier?
A barrier that prevents certain substances from entering the brain from the bloodstream.
What are some mechanisms of drug action?
Binding to synaptic receptors, influencing neurotransmitter synthesis, transport, release, or deactivation, and affecting chemical reactions in postsynaptic neurons.
How is drug metabolism primarily conducted?
By enzymes in the liver, which eliminate a drug's ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
What is drug tolerance?
Decreased sensitivity to a drug due to exposure, requiring more of the drug to achieve the same effect.
What is cross tolerance?
Exposure to one drug can produce tolerance to similar drugs, such as alcohol and benzodiazepines.
What is drug sensitization?
Increasing sensitivity to a drug, also known as inverse tolerance.
What is withdrawal syndrome?
An adverse physiological reaction following the sudden elimination of a drug, with symptoms opposite to the drug's effects.
What distinguishes physical dependence from psychological dependence?
Physical dependence involves withdrawal symptoms and tolerance, while psychological dependence involves loss of control over drug use despite adverse consequences.
What is drug abuse?
Drug use that leads to problems, such as loss of effectiveness in society or behavioral psychopathology.
Define drug dependence.
A maladaptive pattern of drug use leading to significant impairment or distress, associated with difficulty in controlling drug-taking behavior.
What is the biopsychosocial model of substance abuse?
A model that considers biological, psychological, and social factors in understanding substance abuse and dependence.
What is the difference between drug use and drug dependence?
Drug use is taking a psychoactive substance for non-medical purposes
drug dependence is a state of needing a drug to function normally.
What can happen to the body during drug withdrawal?
The body has made changes to compensate for the drug's presence, leading to adverse reactions when the drug is suddenly eliminated.
What are some symptoms of withdrawal syndrome?
Symptoms are typically the opposite of the drug's effects and vary in severity depending on the drug and pattern of use.
What are the types of drug tolerance?
Metabolic tolerance (less drug reaches the site of action)
functional tolerance (decreased responsiveness at the site of action).
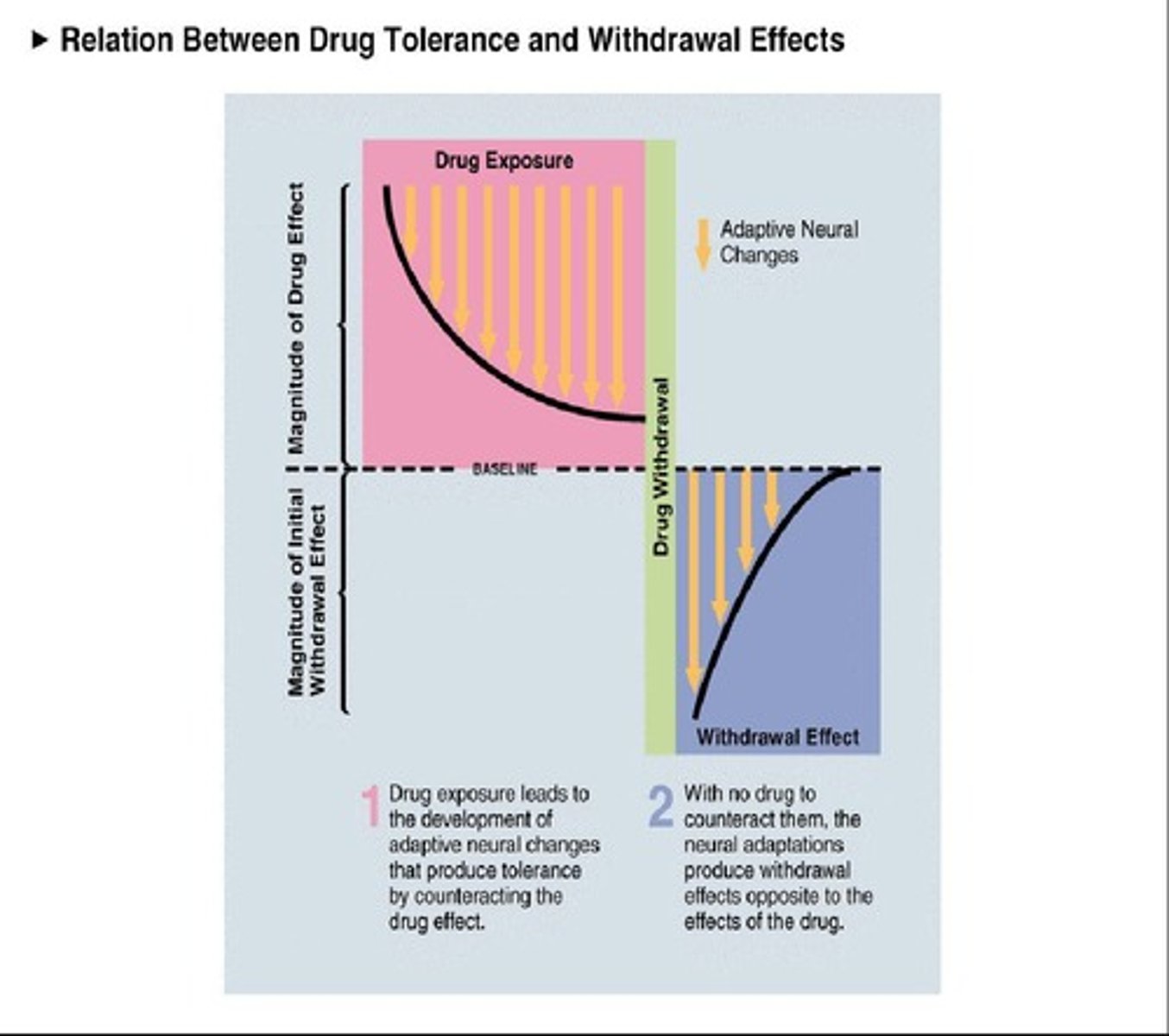
What does it mean for a drug to have a 'motivational hierarchy'?
It indicates that obtaining and using the drug dominates the organism's behavior, often at the expense of other activities.
What is an example of a drug that can be absorbed through mucous membranes?
Cocaine.
What is the significance of the liver in drug metabolism?
its enzymes terminate the action of most drugs, preventing them from passing through lipid membranes.
What defines an addict?
someone who continues to use a drug despite its adverse effects on health and social life.
Can addiction and physical dependence occur separately?
Yes, addiction and physical dependence may occur together or separately.
What may persist after withdrawal symptoms have subsided in addicts?
Addicts may still crave the drug even after withdrawal symptoms due to physical dependence have subsided.
What is contingent drug tolerance?
tolerance that develops only to drug effects that are experienced.
What is conditioned drug tolerance?
when maximal tolerance effects are seen in the environment where the drug is usually taken.
What are conditioned withdrawal effects?
withdrawal symptoms elicited by drug-related cues.
What does the Conditioned Compensatory Response Theory suggest?
It suggests that conditional stimuli predicting drug administration elicit responses opposite to the drug's unconditional effects, leading to situationally specific tolerance.
What are exteroceptive stimuli?
external, public stimuli, such as the drug-administration environment.
What are interoceptive stimuli?
internal, private stimuli, such as thoughts.
What are the main effects of depressants?
relaxation, anxiety reduction, and sleep.
Name a common stimulant and its main effect.
Cocaine is a common stimulant that produces alertness and euphoria.
What are the main effects of opiates/narcotics?
pain control and euphoria.
What are the effects of psychedelics?
alter perceptions and can cause hallucinations.
How are drugs classified in terms of legal scheduling?
Drugs are classified from Schedule I (most restricted) to Schedule V (least restricted) based on medical usage and potential for abuse.
What drugs are classified as Schedule I?
heroin, LSD, peyote, PCP, and mescaline.
What is the heritability estimate for alcohol addiction?
55%.
What are the effects of long-term tobacco use?
can lead to smoker's syndrome, increased susceptibility to respiratory infections, and various lethal lung disorders.
What is Buerger's Disease?
a condition where blood vessels become constricted, often associated with smoking.
What is the impact of quitting smoking by age 40?
can add an average of 9 years to a person's life span.
What are the withdrawal symptoms of alcohol?
tremors,
nausea,
sweating,
vomiting.
What is the effect of alcohol at moderate to high doses?
alcohol acts as a depressant, depressing neural firing.
What is the effect of alcohol at low doses?
can simulate neural firing and facilitate social interaction.
What is the time frame for convulsive activity after alcohol withdrawal?
15-30 hours.
What condition may occur 24-48 hours after alcohol withdrawal and how long can it last?
Delirium tremens, which may last 3-4 days.
What syndrome is associated with chronic alcohol use and can lead to memory issues?
Korsakoff's syndrome.
What severe liver condition can result from heavy alcohol use?
Cirrhosis.
What is fetal alcohol syndrome?
A condition that affects children of mothers who are heavy alcohol users during pregnancy.
What is the primary psychoactive constituent of marijuana?
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol).
What is the endogenous transmitter associated with marijuana?
Anandamide.
What are the effects of high doses of marijuana on memory?
They impair short-term memory and interfere with tasks involving multiple steps.
How does the addiction potential of marijuana compare to that of alcohol and tobacco?
Marijuana has a low addiction potential, and its long-term negative effects are far less severe than those associated with alcohol and tobacco.
What are the characteristics of Sativa strains of marijuana?
Uplifting and energetic effects, cerebral, spacey or hallucinogenic, best suited for day use.
What are the characteristics of Indica strains of marijuana?
Relaxing and calming effects, body buzz or 'couch lock', best suited for night use.
What are some adverse effects of heavy marijuana use?
Respiratory problems, potential heart attack triggers in susceptible individuals, and possible correlation with schizophrenia.
What medicinal uses does marijuana have?
Treats nausea, blocks seizures, dilates bronchioles in asthmatics, decreases severity of glaucoma, and reduces some forms of pain.
What is the primary effect of cocaine and its derivatives?
They increase neural and behavioral activity.
What is crack cocaine?
A potent, cheap, and smokable form of cocaine.
What are the effects of cocaine binges?
They may lead to cocaine psychosis, resembling paranoid schizophrenia.
What is a common effect of amphetamines?
They produce effects similar to cocaine and can also lead to psychosis.
What are the medicinal uses of opiates like morphine and codeine?
used as analgesics (painkillers)
treatment of cough and diarrhea.
What motivates individuals to continue using opiates despite the risks?
The rush following IV injection, tolerance, physical dependence, and the desire to avoid withdrawal.
What is methadone used for in heroin addiction treatment?
It binds to opiate receptors, produces less pleasure, is administered orally, and prevents withdrawal.
What are the two biopsychological theories of addiction discussed?
Physical-dependence theory
positive-incentive theories.
What does the incentive-sensitization theory suggest about drug addiction?
value of addictive drugs increases with use, while the hedonic value decreases due to tolerance.
What are the three fundamental causes of relapse?
Stress,
priming (single exposure),
environmental cues.
What did Olds and Milner discover about brain circuitry related to addiction?
They discovered that brain circuitry exists that reinforces behaviors, leading to stimulation of brain 'pleasure centers'.
What are the two pathways in the mesotelencephalic dopamine system?
nigrostriatal pathway
mesocorticolimbic pathway.
What is the major reward pathway for intracranial self-stimulation and addictive drugs?
The mesocorticolimbic pathway, including the nucleus accumbens.
What is the relationship between intracranial self-stimulation and dopamine release?
Intracranial self-stimulation is often associated with an increase in dopamine release in the mesocorticolimbic pathway.
How do dopamine agonists and antagonists affect intracranial self-stimulation?
Dopamine agonists tend to increase intracranial self-stimulation, while dopamine antagonists tend to decrease it.
What effect do lesions of the mesocorticolimbic pathway have on intracranial self-stimulation?
tend to disrupt intracranial self-stimulation.
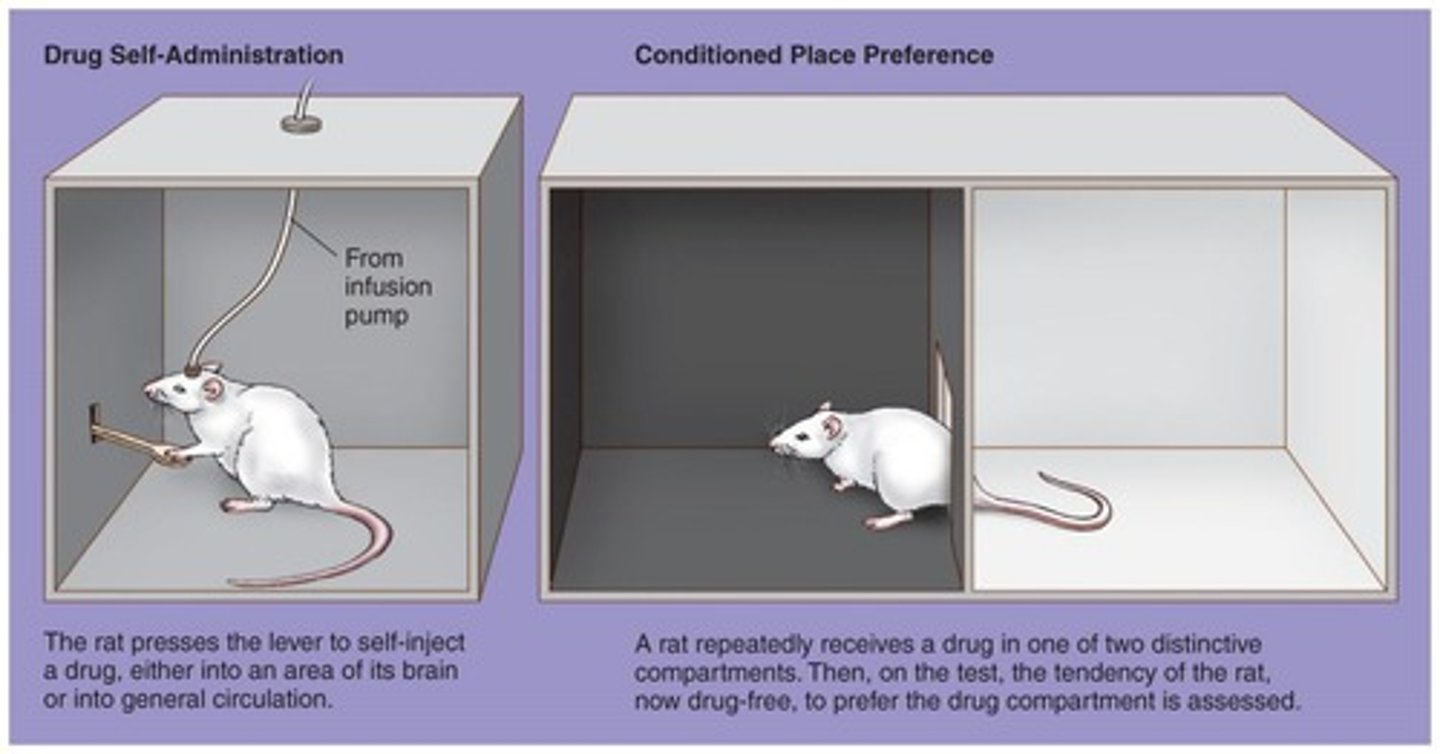
What are the two key methods for measuring drug-produced reinforcement in laboratory animals?
1. Drug self-administration paradigm using cannulas to the bloodstream.
2. Conditioned place-preference where lab animals choose to spend more time in compartments where drugs were administered.
dopamine ROLE in drug addiction
It interfere with self-stimulation and reduce the reinforcing effects of food.
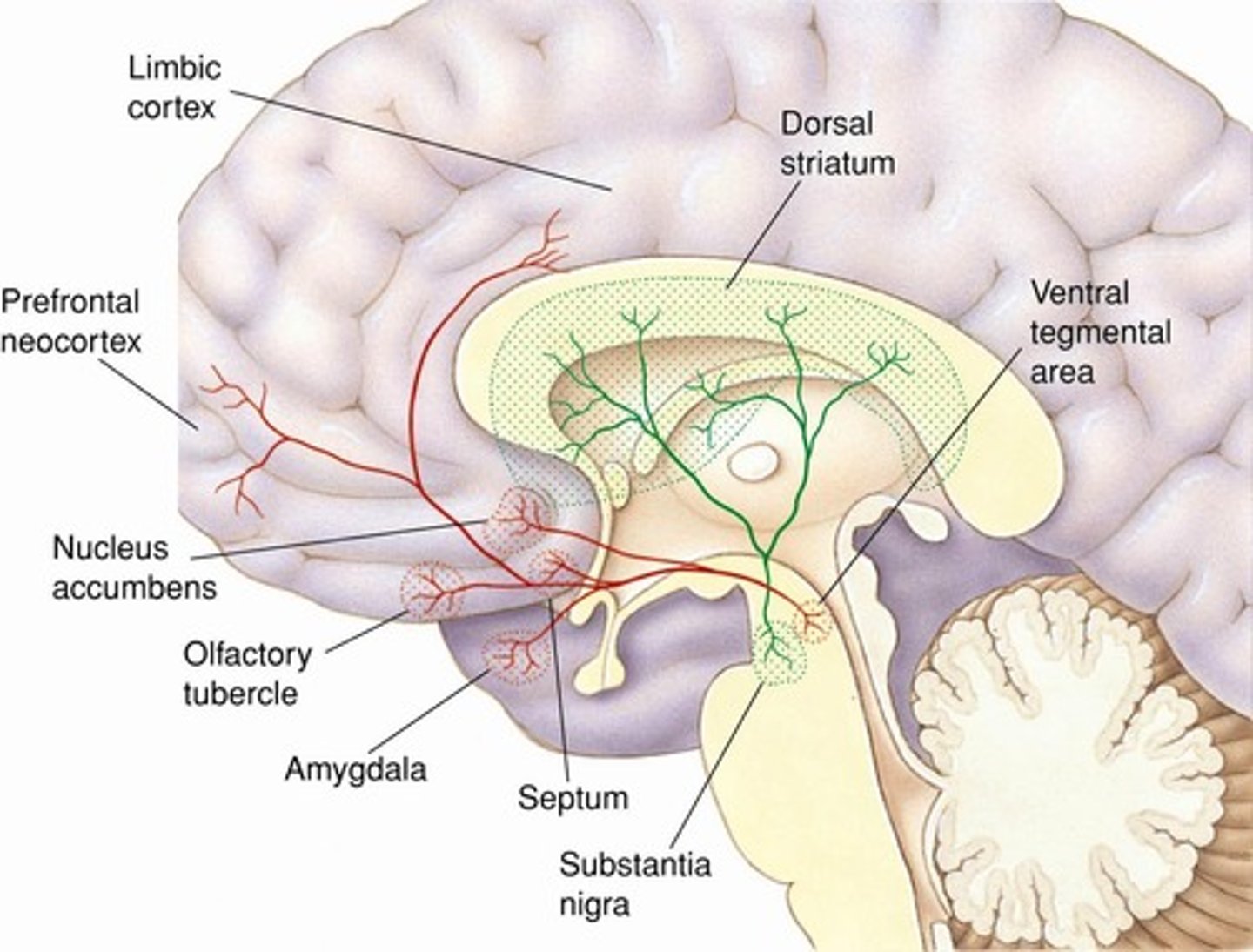
What is the primary role of the nucleus accumbens in drug addiction?
important in drug addiction, as animals self-administer microinjections of addictive drugs into it.
the brain's reward center. Drugs cause a huge dopamine surge here, making drug use feel intensely pleasurable and reinforcing the habit.
What happens when drugs are microinjected into the nucleus accumbens?
it produces conditioned place preferences.
It makes a place associated with drugs feel good, even without the drugs.
What are the effects of lesions in the nucleus accumbens or ventral tegmental area?
may result in no drug self-administration or drug-related place preference.
What is the relationship between dopamine and both addictive drugs and natural reinforcers?
Both self-administration of addictive drugs and natural reinforcers result in increased dopamine in the nucleus accumbens.
What do PET displacement studies indicate about dopamine during drug intake?
dopamine increases in the nucleus accumbens during drug intake are correlated with self-reported 'high' and euphoria.
How does overall dopamine function differ in human addicts?
diminished in human addicts, except during drug or drug cue exposure.
What is the function of increased dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens?
Increased dopamine levels are related to the experience of reward, as ventral tegmental neurons fire in response to stimuli at a rate proportional to their reward value.
Drugs cause a huge dopamine rush in your brain's reward center, making you feel great
How can neutral stimuli affect dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens?
Neutral stimuli that signal the impending delivery of a reward can trigger dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens.
What psychological complexities are associated with addiction?
Addiction is psychologically complex, with addicts showing poor decision making and lack of self-control, suggestive of a role for the prefrontal cortex.
What non-adaptive behaviors may be related to drug addiction?
Drug addiction may be related to compulsive eating, gambling, sexual behavior, kleptomania, shopping, etc.
Which other neurotransmitters are involved in addiction besides dopamine?
Other neurotransmitters involved include glutamate, endogenous opioids, norepinephrine, GABA, and endocannabinoids.
What brain structures are involved in the initial drug taking process?
mesocorticolimbic pathway (nucleus accumbens)
prefrontal lobes
amygdala
What brain structures are associated with craving and compulsive drug use?
dorsal striatum and hypothalamic stress circuits
What factors contribute to relapse in addiction?
priming doses (prefrontal cortex)
drug-associated cues (amygdala),
stress (hypothalamic stress circuits).