Bone Diseases of the Jaw
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
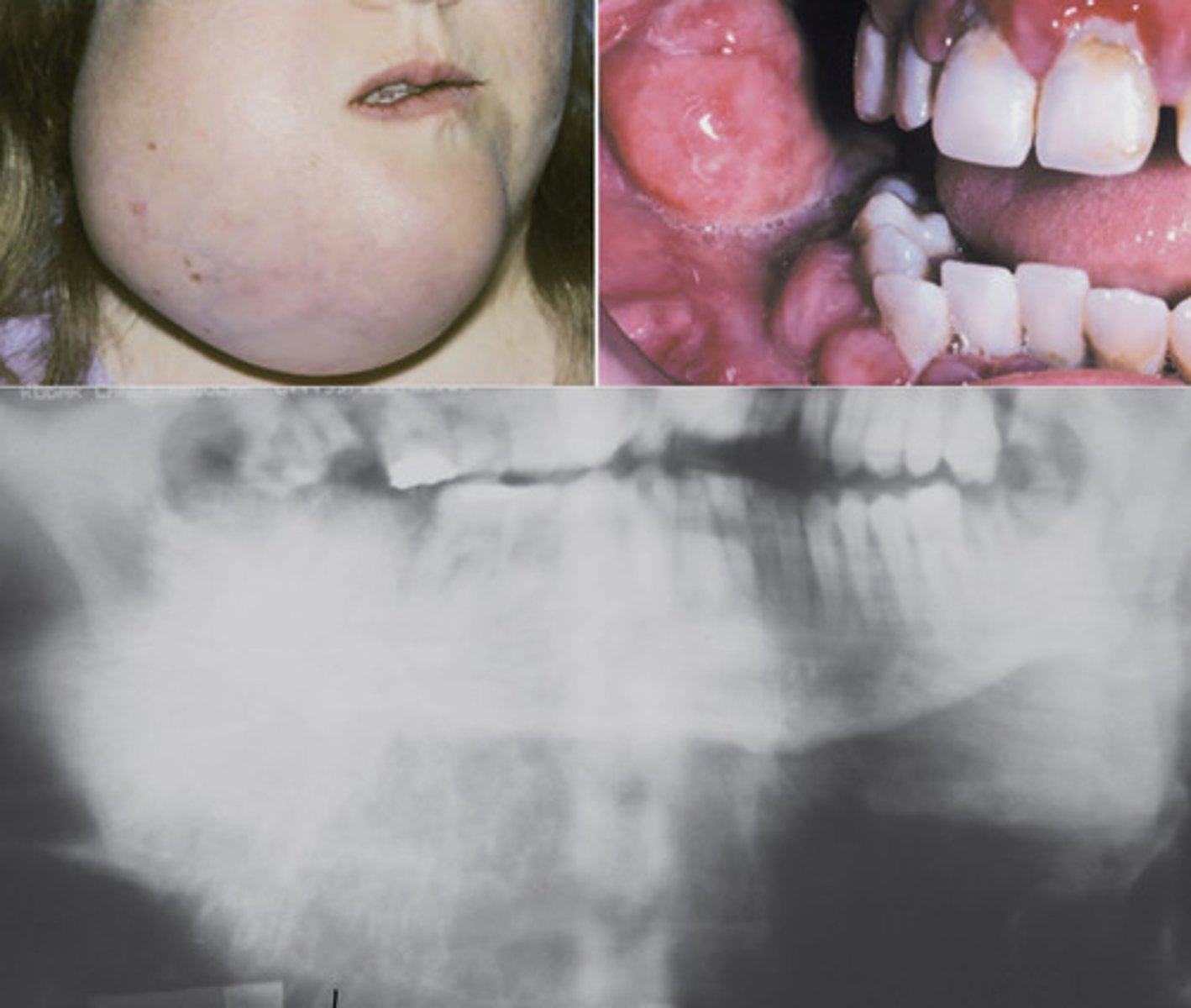
Cherubism
males
5
Bilateral/symmetric
Genetic Disorder,
Rare, inherited autosomal dominant Mendelian disorder
100% prevalence in?
Onset by age?
___________ mandibular swelling (can involve mx)
Cherubism
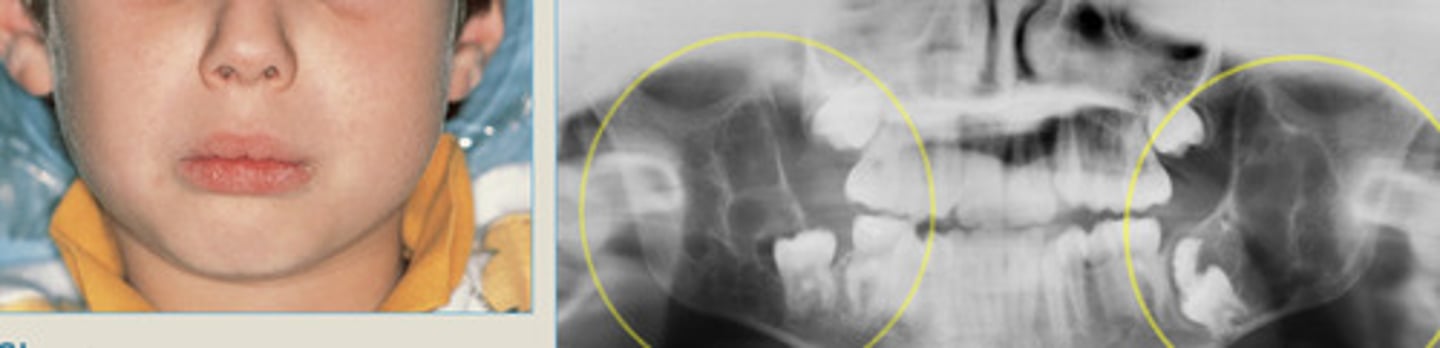
Cherubism
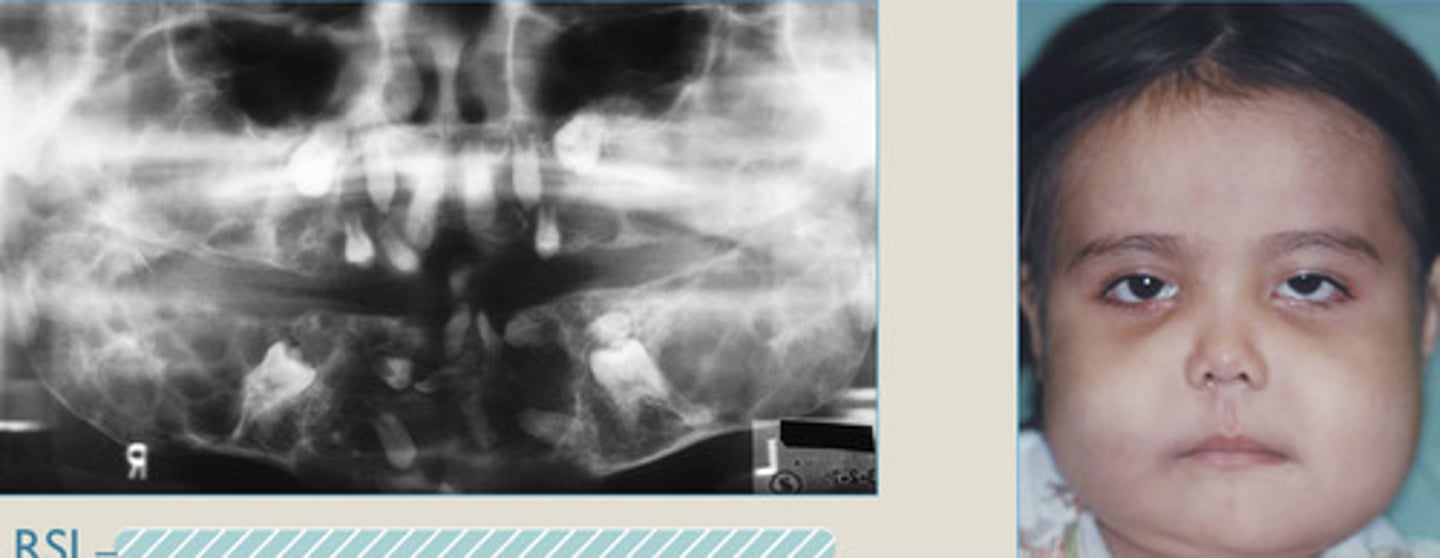
Cherubism
bilateral/symmetric, MN involvement
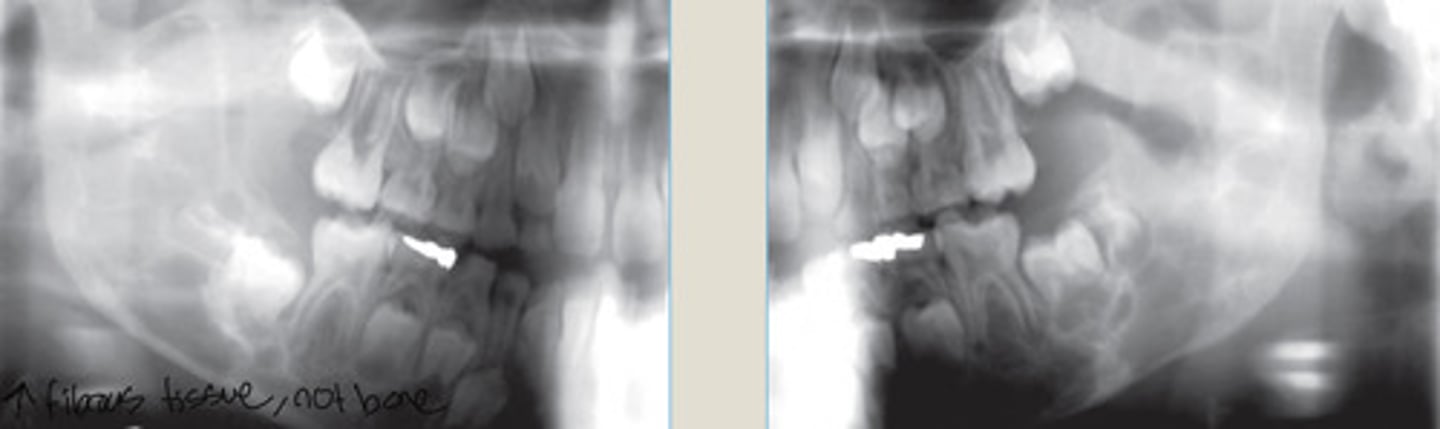
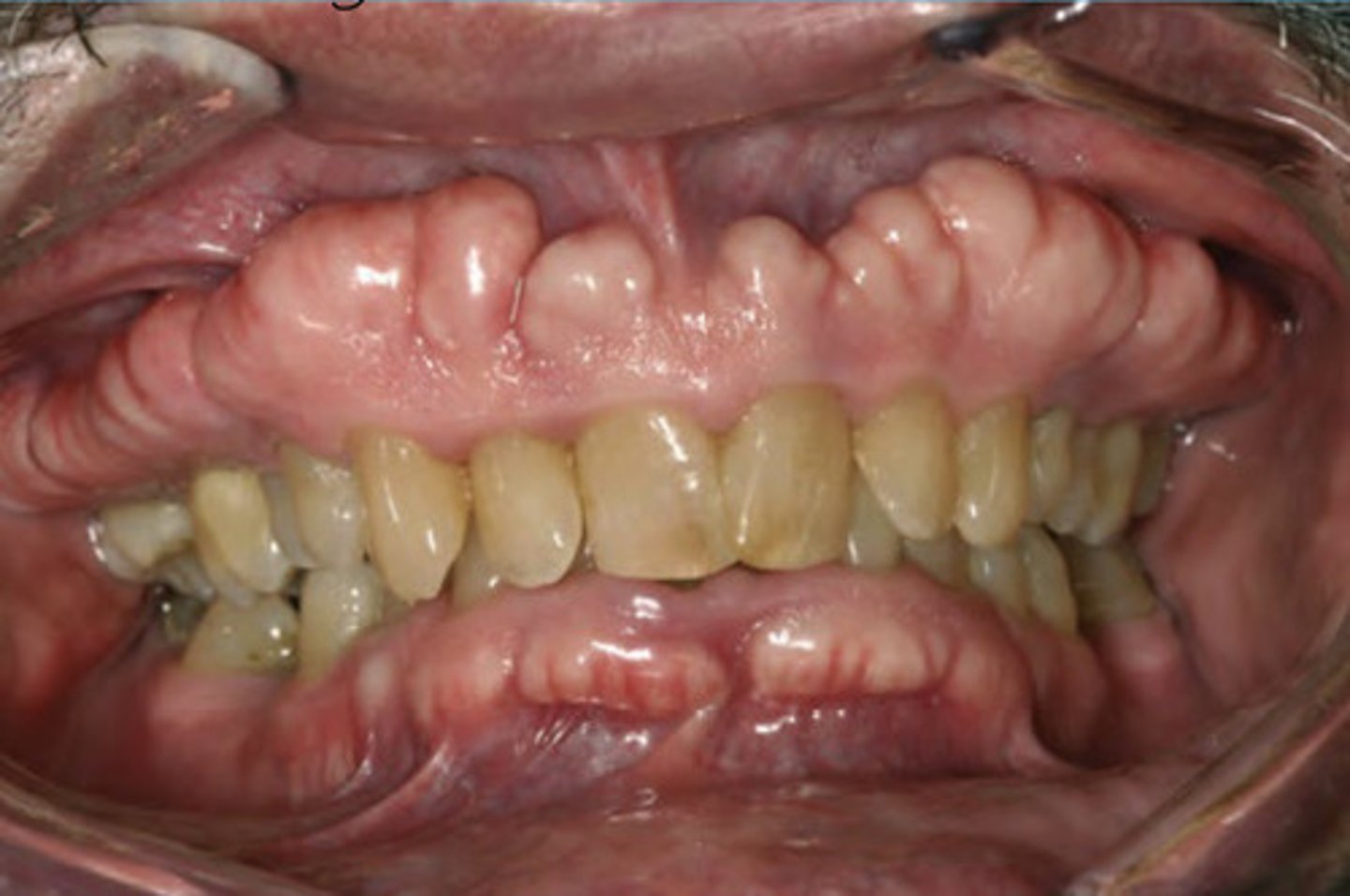
Tori and Exostoses
Localized Protuberances of excess dense cortical bone due to local factors in genetically susceptible host.
May be due to Excessive physical forces on jaws
Torus Palatinus
very firm
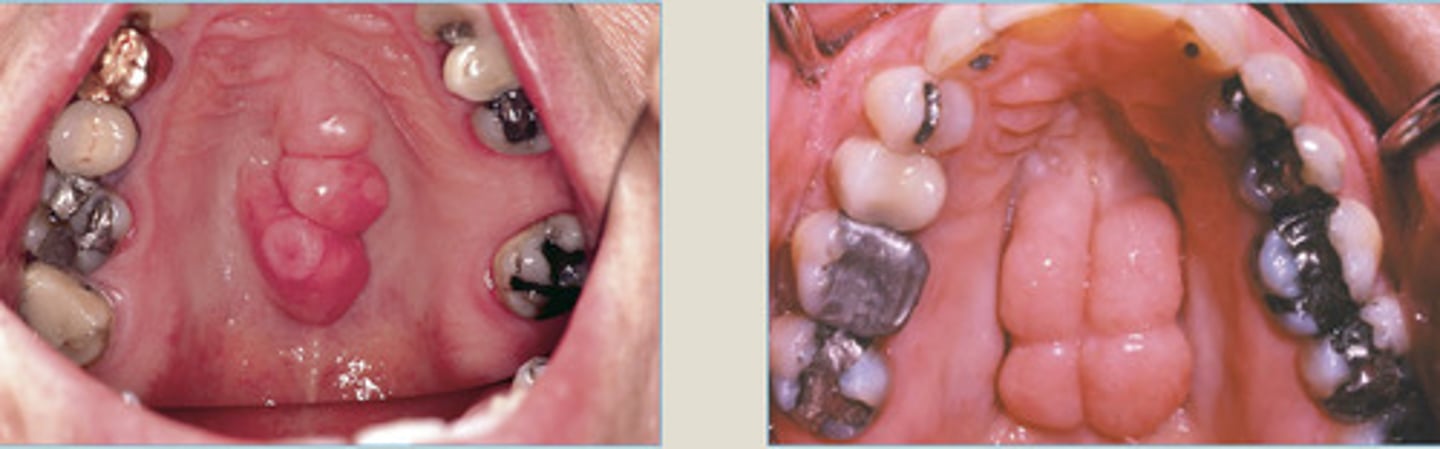
Torus Palatinus
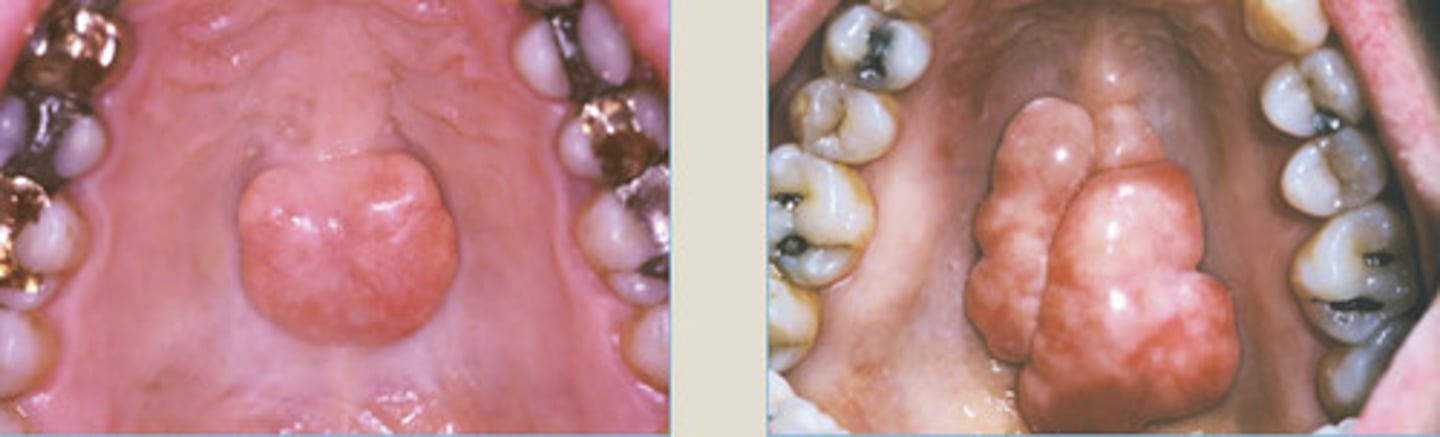
Torus Mandibularis
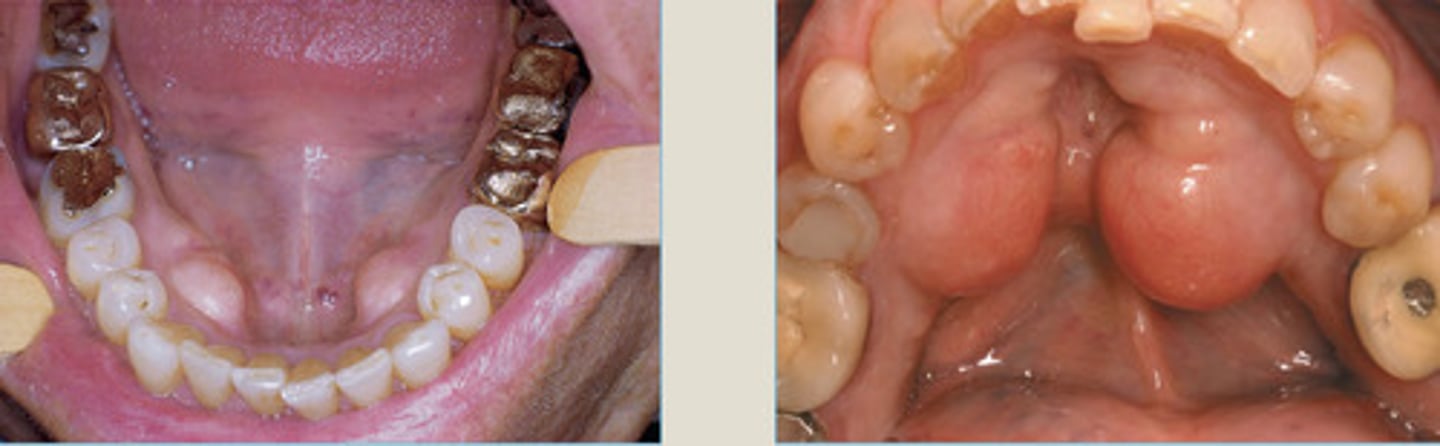
Buccal Exostoses
Buccal Exostoses
Buccal Exostoses
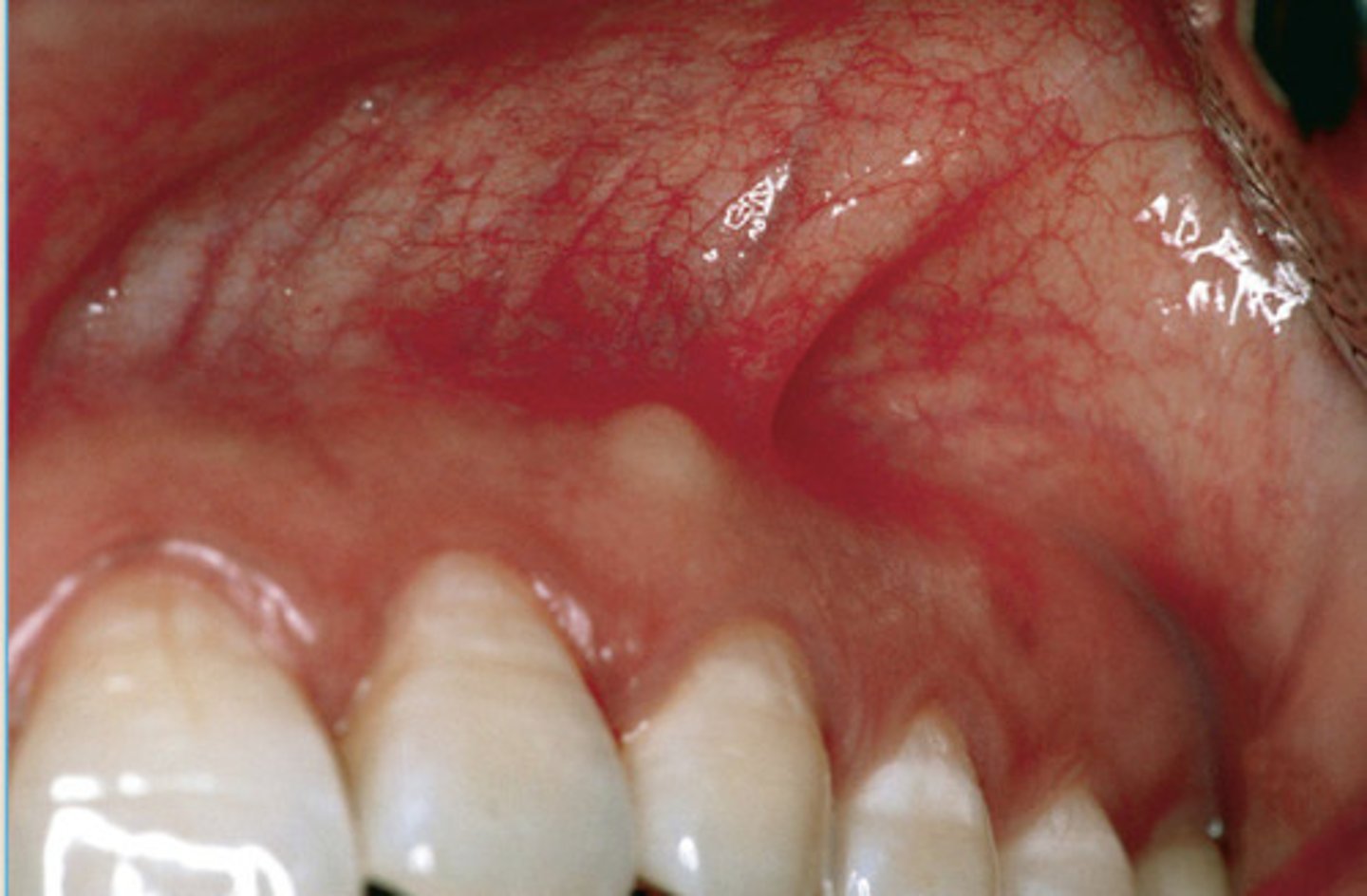
Osteomyelitis
necrosis
odontogenic
2 wks
infection spreading through bone marrow spaces.
causing______ of bone
if in the jaw: _____ origin
takes >__ wks to see lucency in radiograph
LEFT: Acute Osteomyelitis-ill defined radiolucency of the right body of the MN
RIGHT: Aute Osteomyelitis with sequestrum appearing as radiolucent in the right body of MN w/ central opaque mass of necrotic bone
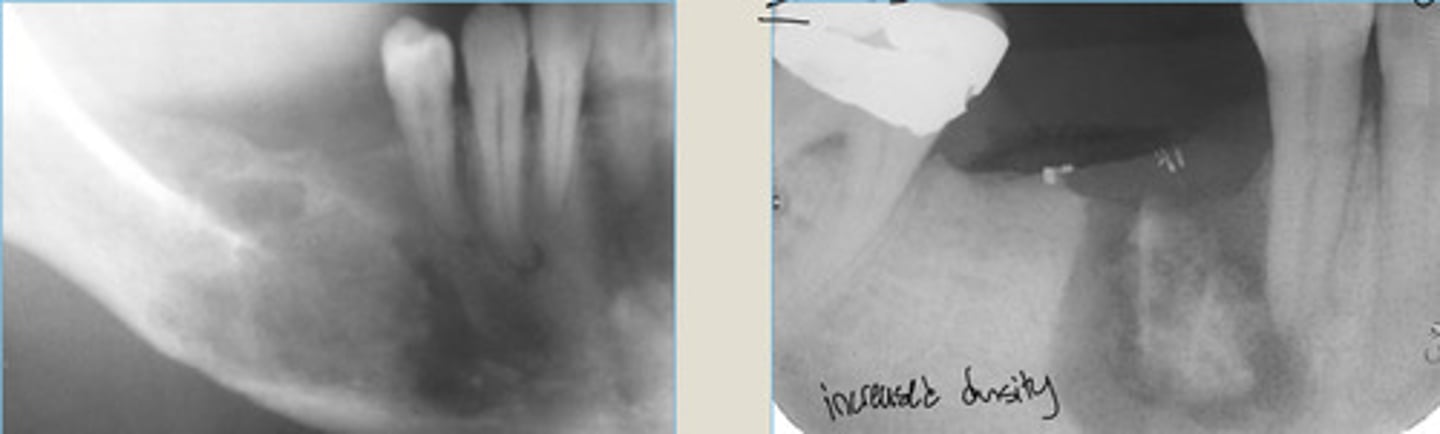
Chronic Osteomyelitis
LEFT: in region of 3rd molar extraction
RIGHT: Moth-eaten radiolucent appearance
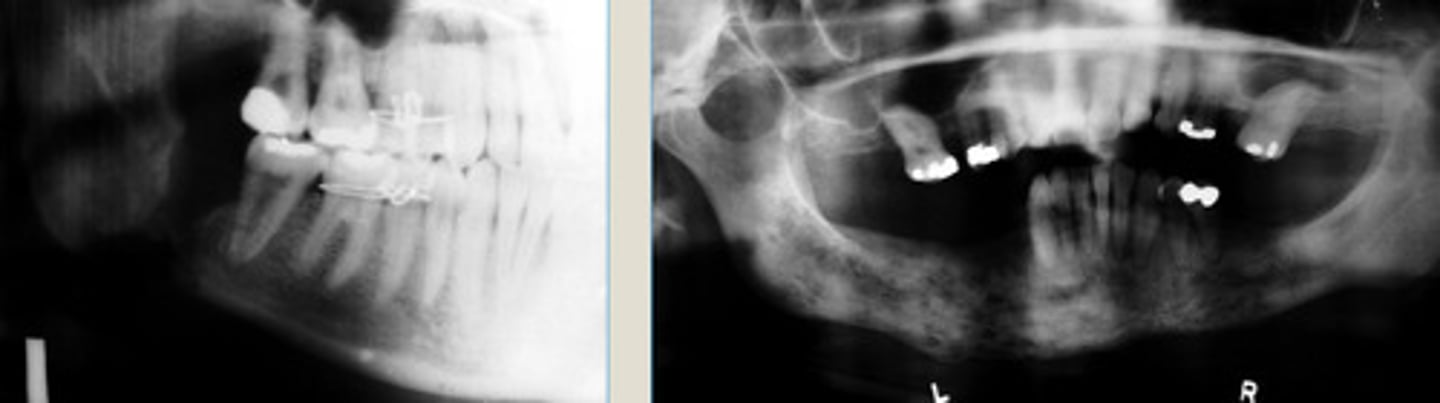
Chronic Osteomyelitis
LEFT: ill-defined lucency of right body of MN, adjacent to recent extraction site
RIGHT: Enlarged, ill-defined lucency of R. body of MN 2 yrs after initial TX
1. Eliminate source of infection
2. Surgical Drainage
3. Remove dead bone by curettage
4. Treat w/ antibiotics
Chronic Osteomyelitis TX
Condensing Osteitis
pulpal inflammation or irritation
pulpitis due to large restorations/caries that encroach on the pulp
Reactive Inflammatory lesion characterized by increased bone density at the apex of the tooth.
Stimulated by chronic, low grade:
Usually starts in bone at/around tooth that has _____ due to?
Any age, any tooth
No bone symptoms (tooth may be symptomatic)
No bondy expansion
Clinical features of Condensing Osteitis
1. Variable opacity around apex
2. Joins with lamina dura
3. Blending border
4. Tooth with large restoration/caries
5. NO radiolucent rim
Rad features of Condensing Osteitis
Condensing Osteitis
well defined, no radiolucent rim
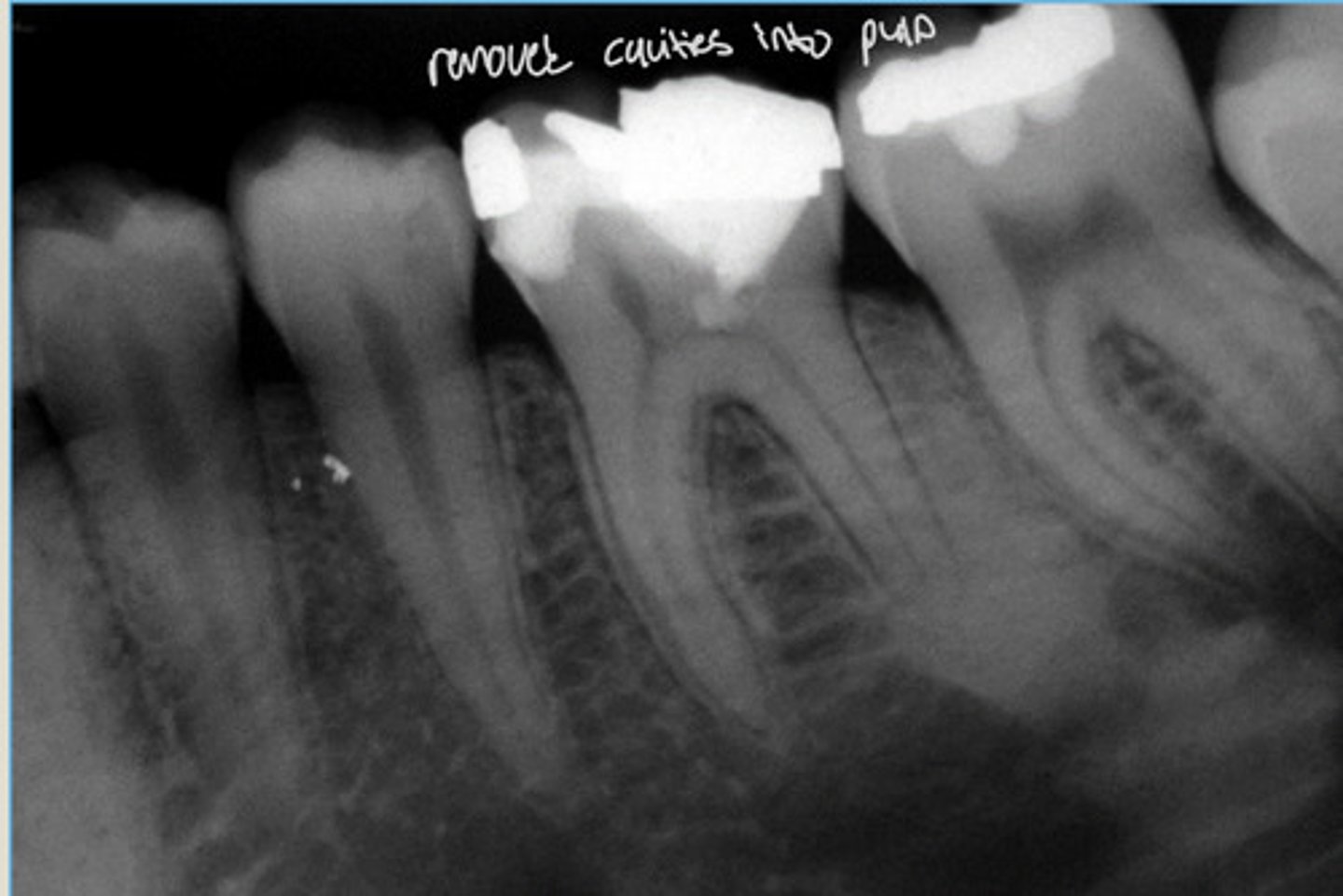
Condensing Osteitis
RIGHT: bone scar following extraction of affected tooth
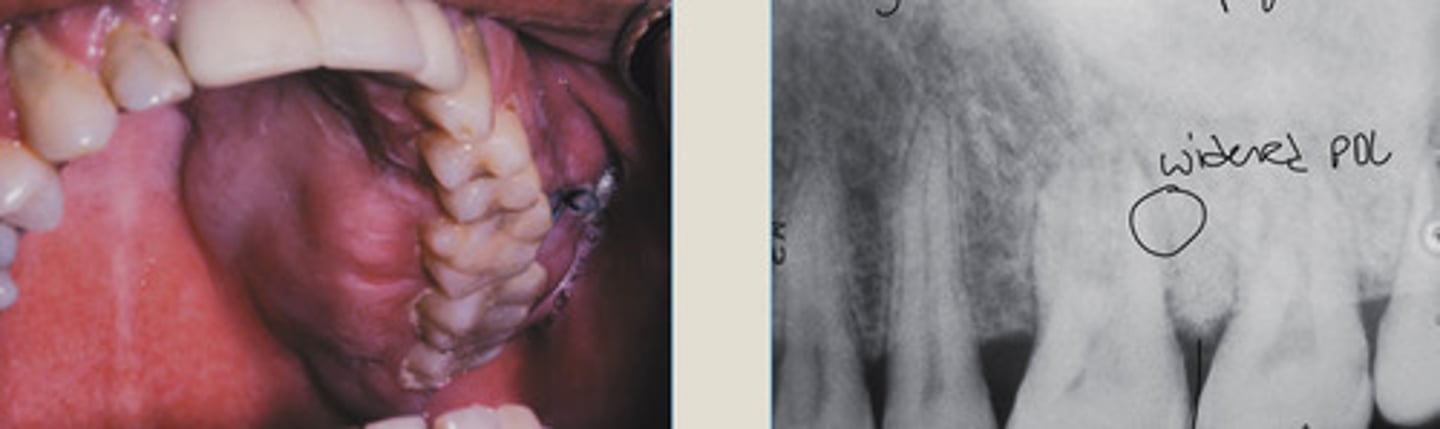
Increased density of both root apices of nonvital 1st M
Widened PDL
NO radiolucent rim
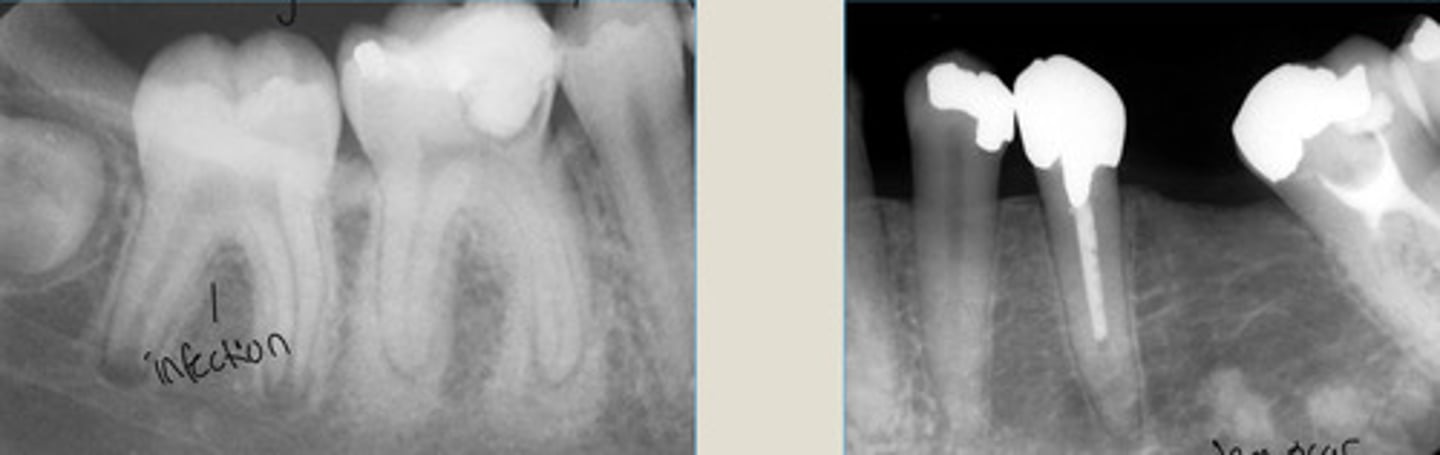
Idiopathic Osteosclerosis
Increased bone density at the apex of a healthy tooth
MORE common than Condensing Osteitis
AGE: adolescent/young adult + persists for life
SITE: Post. MN
Asymptomatic
NO bony expansion
Clinical Features of Idiopathic Osteosclerosis
AGE?
SITE?
SYMPTOMS?
BONY EXPANSION?
Idiopathic Osteosclerosis
LEFT: bone sclerosis btwn apical to roots 1st + 2nd molars
Large area of radiopacity fusing with lamina dura
NO TX
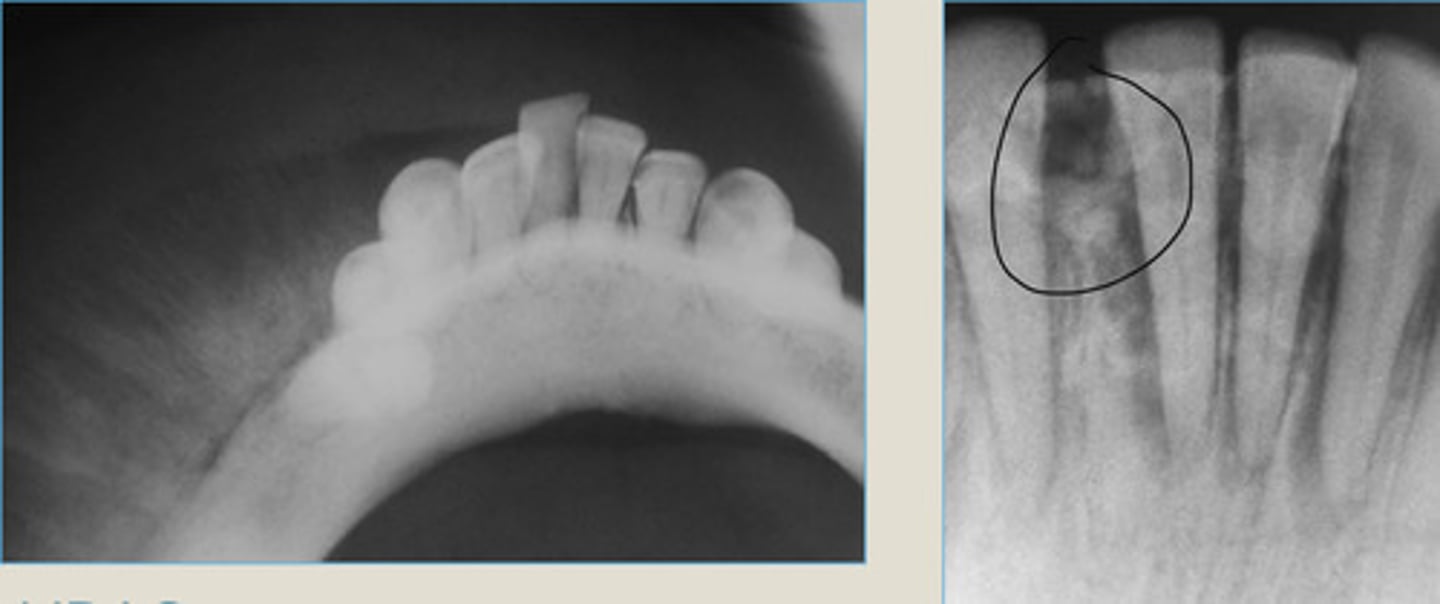
1. Early osteolytic stage = radiolucent
2. Intermediate blastic stage = mixed with lucent rim
3. Mature stage = opaque with lucent rim
root end and PDL in all stages
Cemento-osseous Dysplasia:
Reactive/dysplastic fibro-osseous lesions
3 types go through same three stages:
Can always see _____ + _____ in all stages
1. Teeth Vital
2. Common in Ant. MN of adults (40 yrs)
3. STRONG Female Predilection
4. STRONG African American Predilection
5. NO symptoms
6. Lucent > Opaque progression
6 Clinical Features of Periapical Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia
Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
Lesions confined to the periapices of MN anterior teeth
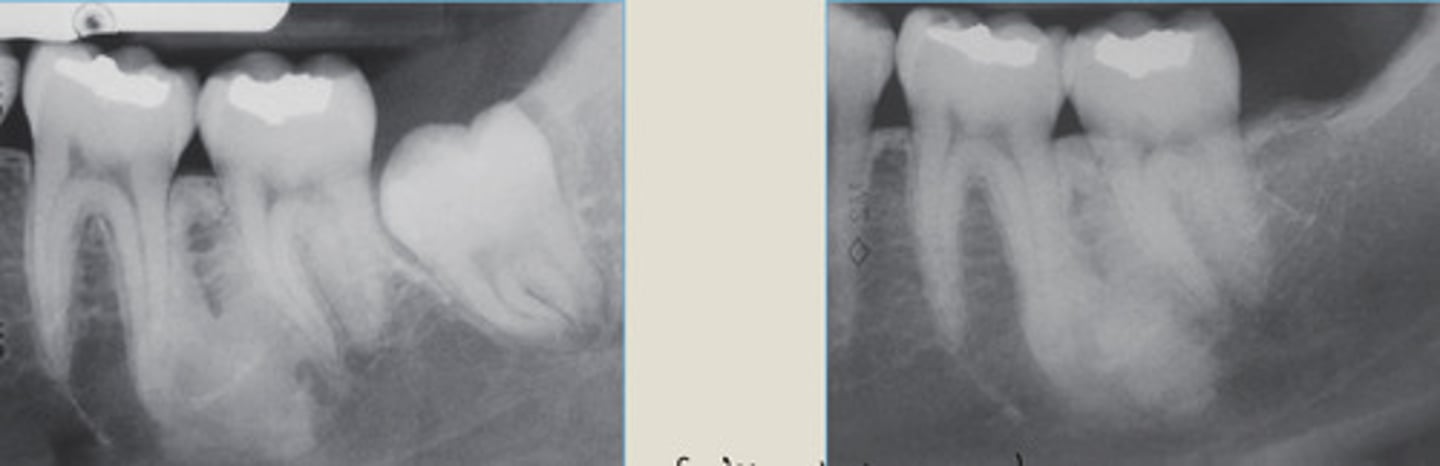
Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
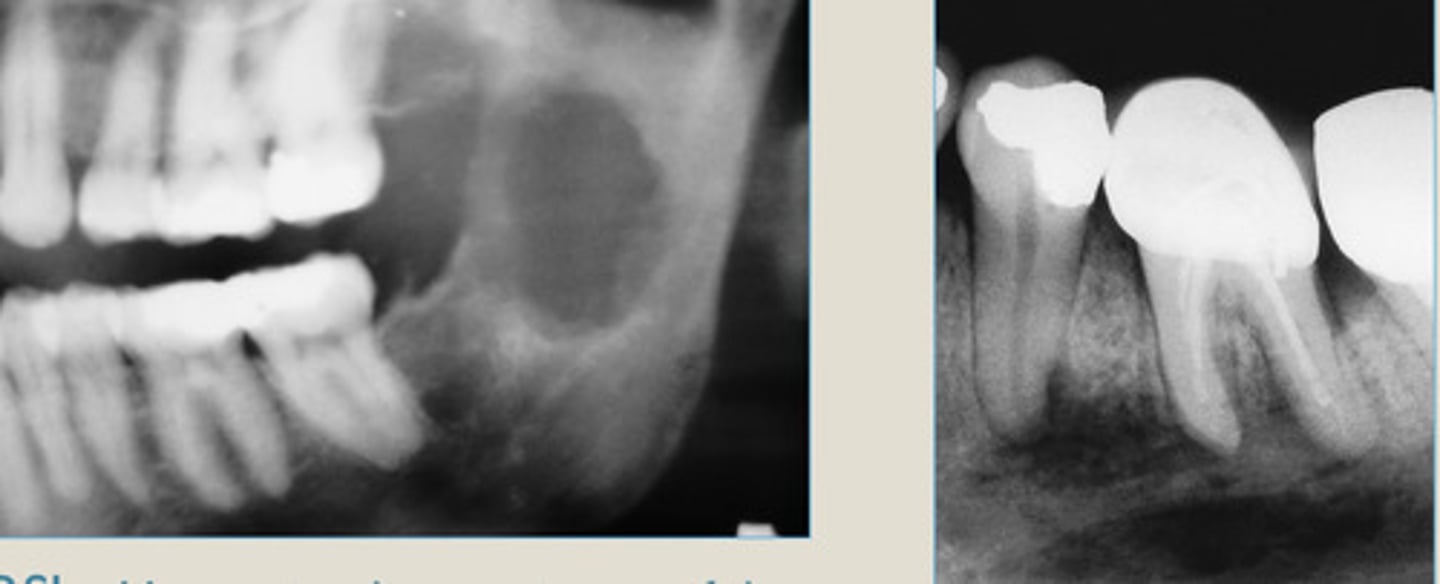
LEFT: Radiolucent 1st phase
RIGHT: Mixed 2nd phase
Radiolucent rim
Which ones the 1st and 2nd phase?
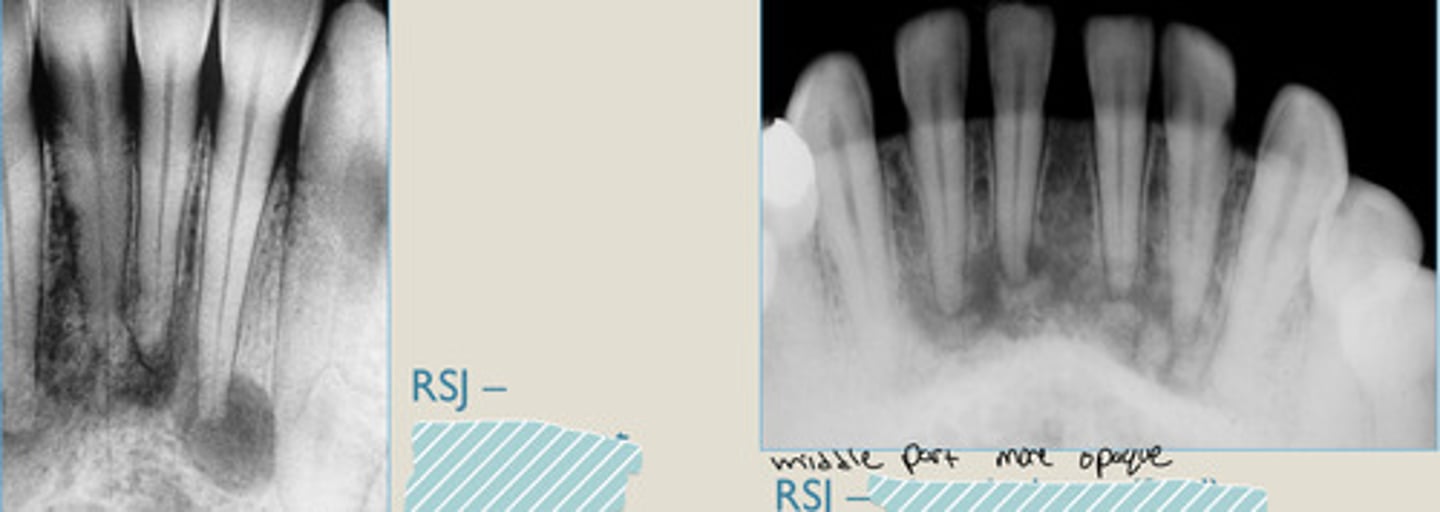
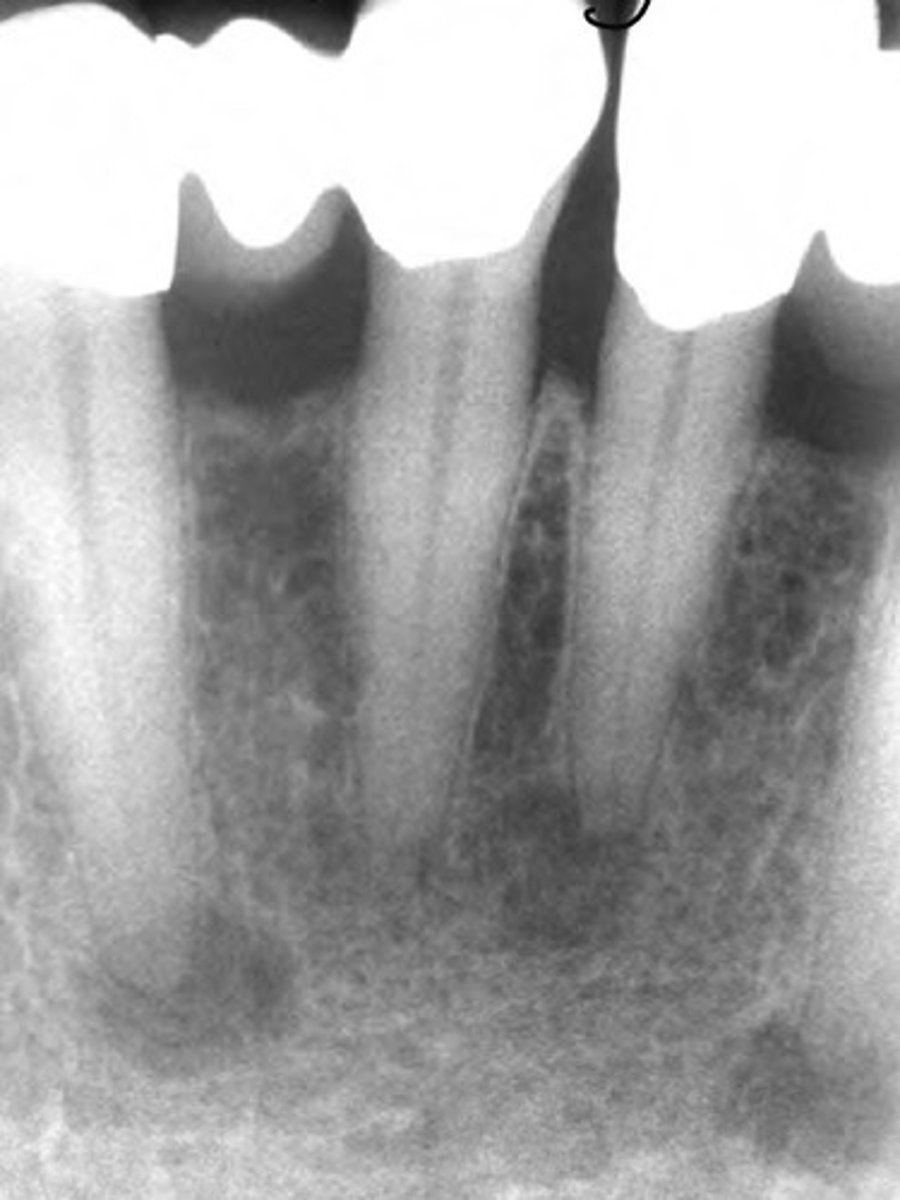
Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
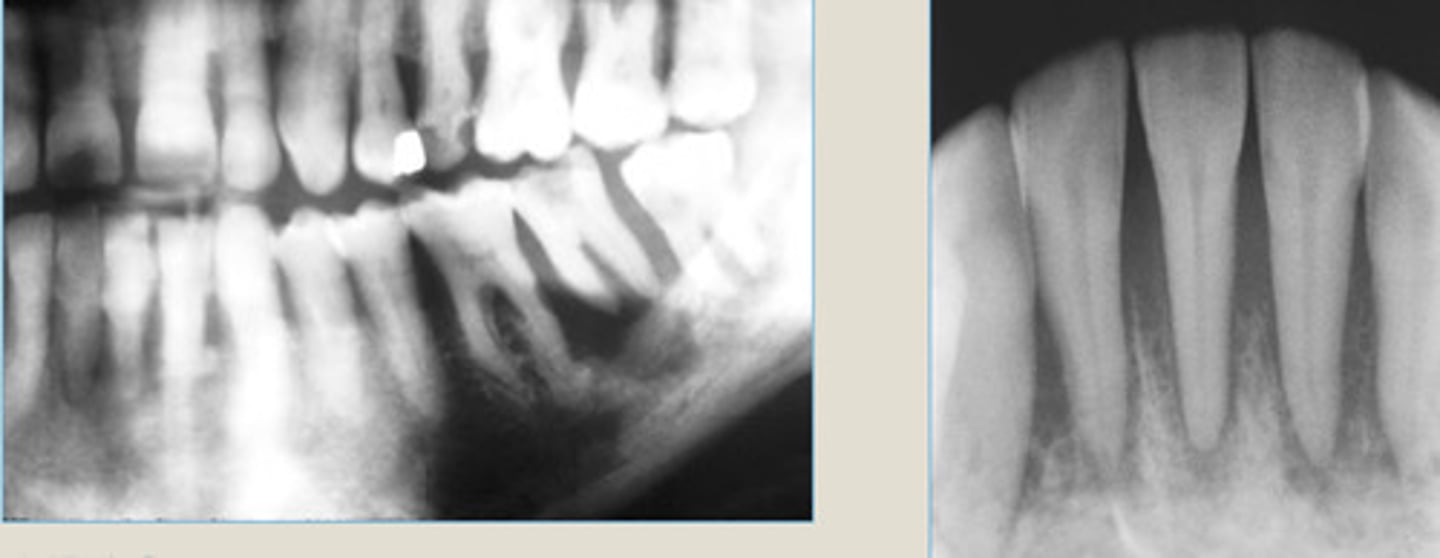
LEFT: mixed stage
RIGHT: mature stage
Which ones the mixed stage (2nd) vs the mature stage (3rd)?
Confined to anterior mandible, no symptoms, Lucent to opaque migration.

Florid Cemento-osseous Dysplasia
Middle-aged older adults
Black females
Vital teeth
Asymptomatic
Multiple lesions involving 3-4 quadrants
Common in: AGE, GENDER, RACE?
Associated with _____teeth
Symptomatic?
Florid Cemento-osseous Dysplasia
Implants + dentures contraindicated. DON'T extract immediately!
LEFT: radiolucent phase
RIGHT: Radiopaque phase
2 contraindications?
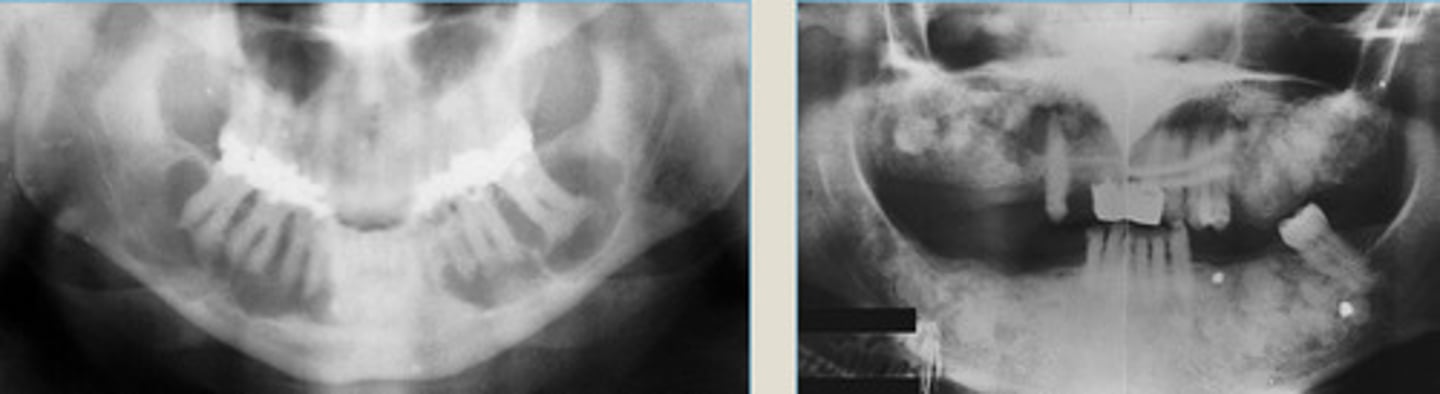
Florid Cemento-osseous Dysplasia
it indicates NO infection present
LEFT: multiple mixed radiolucent/radipaque lesions involving ant/post mandible
RIGHT: multifocal radiopaque lesions of post jaw
What does opacity in the middle indicate?
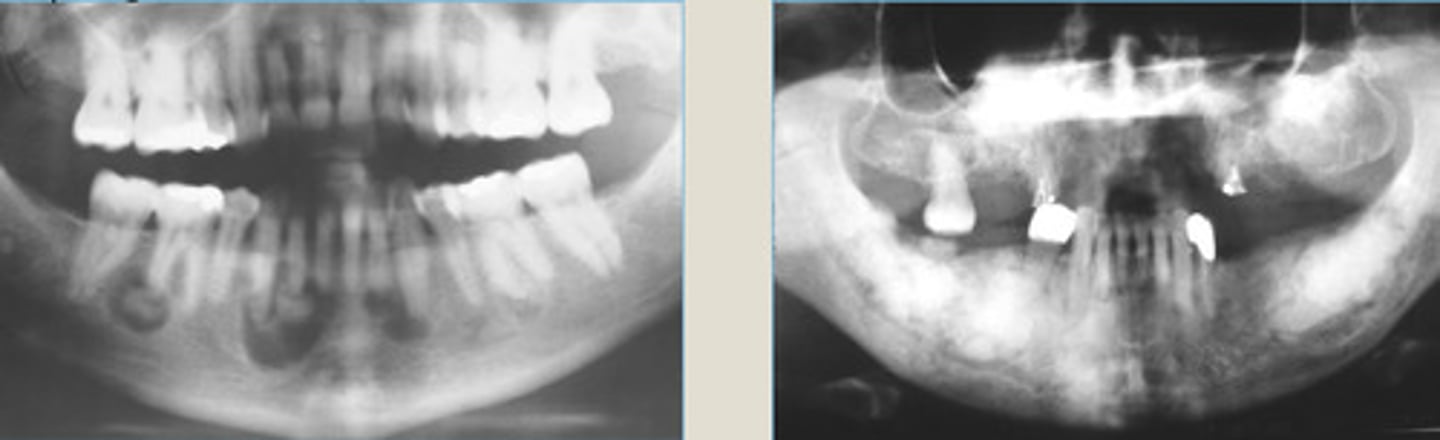
1. none for bony lesions
2. Periodical radiographic evalv recommended
Florid form has a risk for:
Secondary infection
Simple bone cysts
Cemento-osseous Dysplasia TX
Florid form has a risk for (2)?
Fibrous Dysplasia
Developmental disorder characterized by disordered maturation of bone and expansion.
Characteristics include:
Sm irregular trabecular of woven bone
Loose fibrous CT stroma
Age: early teens
Monostotic: adolescence
Polystotic: childhood
Symptoms: Painless gradual bony enlargement
RAD features: ground glass bone
Fibrous Dysplasia Clinical Features
AGE?
Monostotic/Polystotic prevalent in what age?
Symptoms?
RAD features?
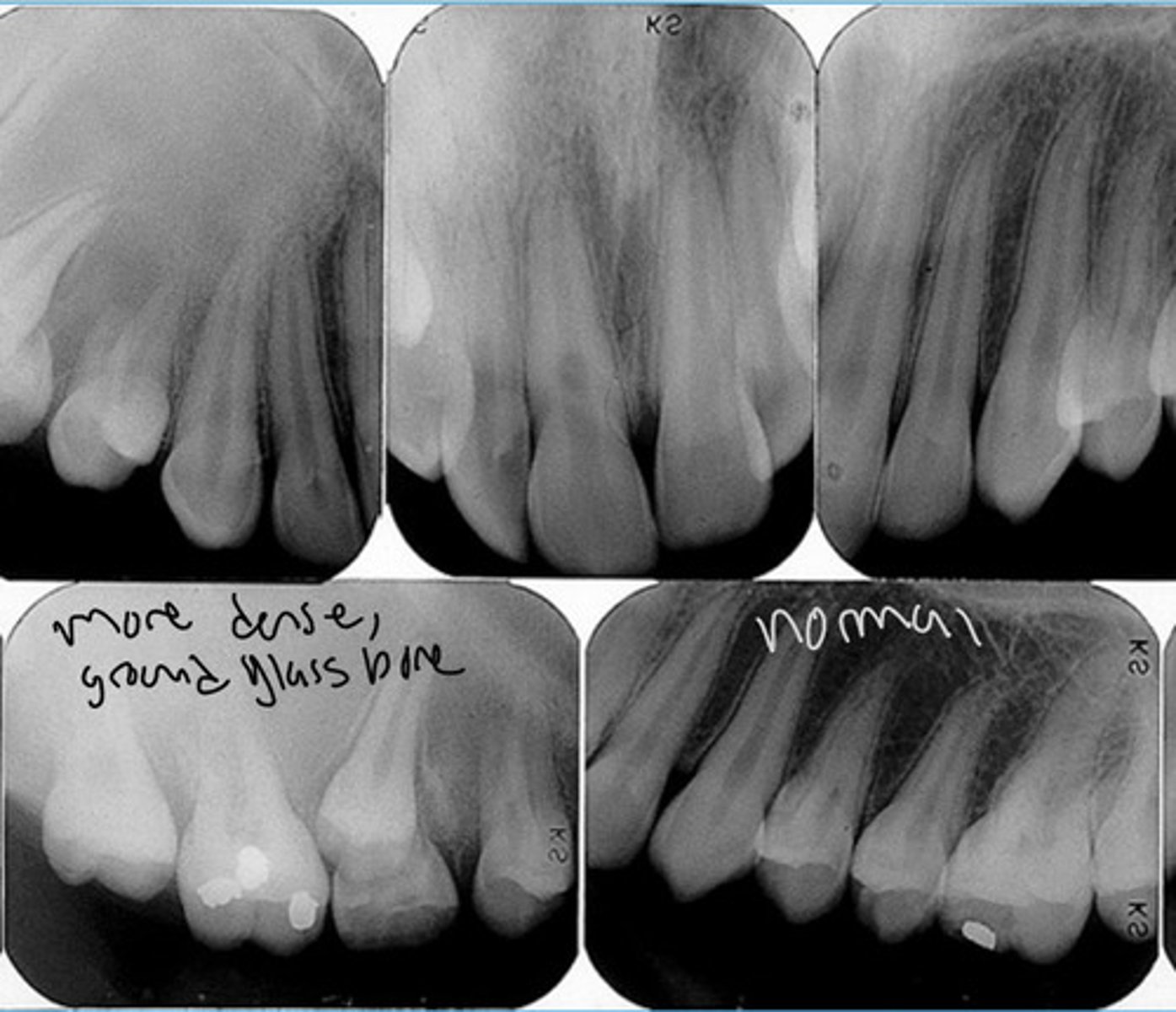
Fibrous Dysplasia
asymmetric expansion
gradual taper to normal
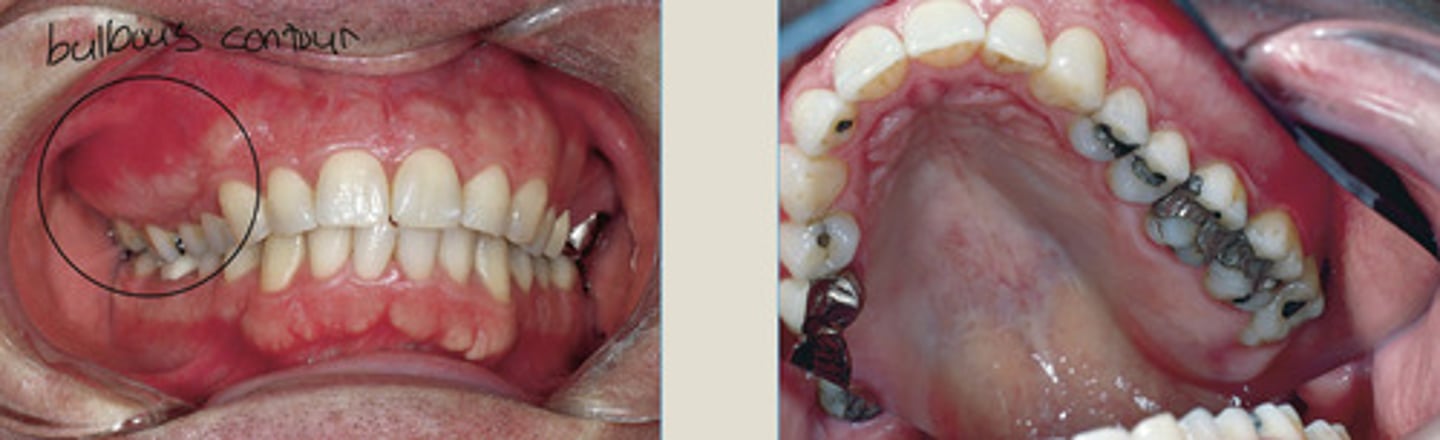
Fibrous Dysplasia Monostotic
diffuse ground glass effect
blending borders, no sharp edges
Fibrous Dysplasia Monostotic
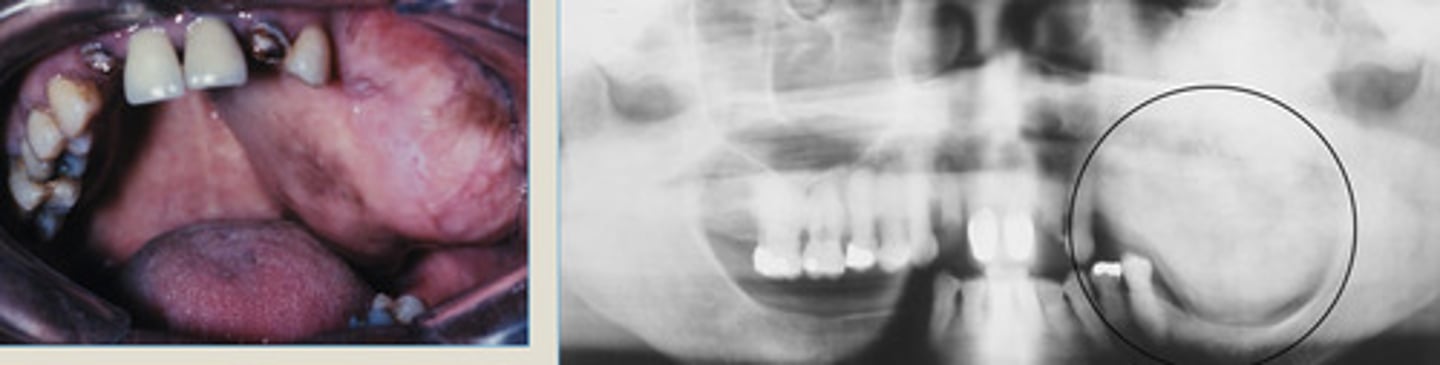
Expansile mass of the left maxilla in a 45 yr old
Lesion known to be present for 20 yrs
Diffuse ground glass radiopacity
Fibrous Dysplasia Monostotic
Diffuse "ground glass" radiographic appearance
Takes over lamina dura + alveolar crests
Margins ill-defined + blend into bone
surgical recontouring for cosmetics after growth spurt
asymptomatic and self limiting
OCCURS: between 10-20, stabilizes at puberty and very slow growth afterward.
Fibrous Dysplasia TX?
OCCURS WHEN?
Ossifying Fibroma
Benign fibro-osseous lesion
True neoplasm
Age: 20-40 yrs
Site: Mandibular Molar or PM
Twice as common in females
Well-defined lesion
Round
Lucent to mixed
Clinical Features + Radiographic features of Ossifying Fibroma
Age?
Site?
Twice as common in?
Well/Ill defined?
Shape?
Opacity?
Ossifying Fibroma
Well-defined capsule w/ radiolucent border.
Very round + mixed lesion.
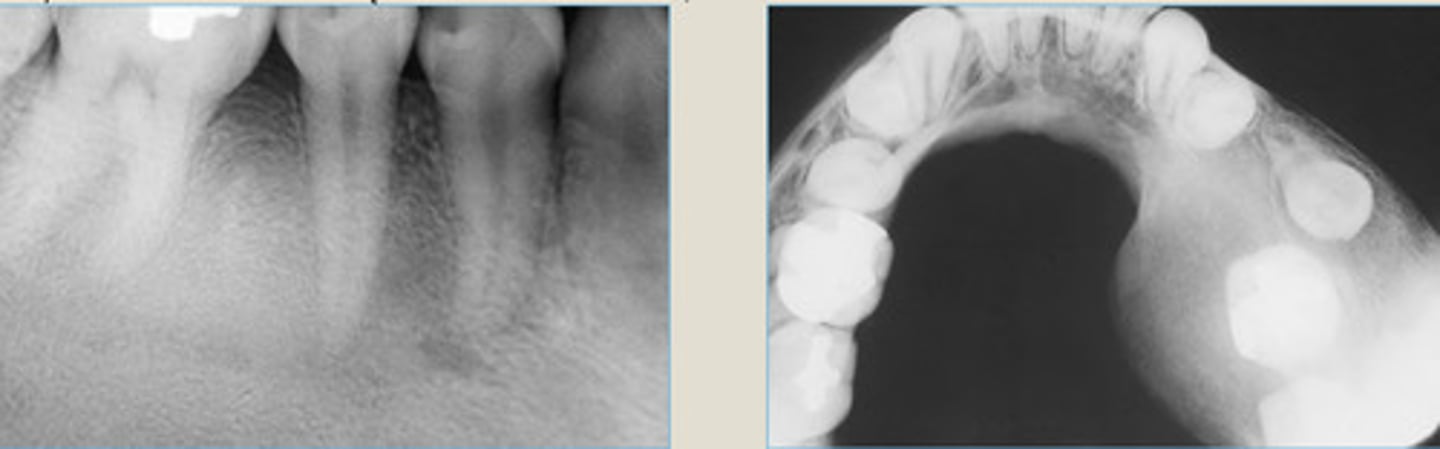
LEFT: cortical expansion in Ant. MN
RIGHT: Lesion radiolucent at apices of MN PM
Ossifying Fibroma
Very round cortical expansion of maxilla
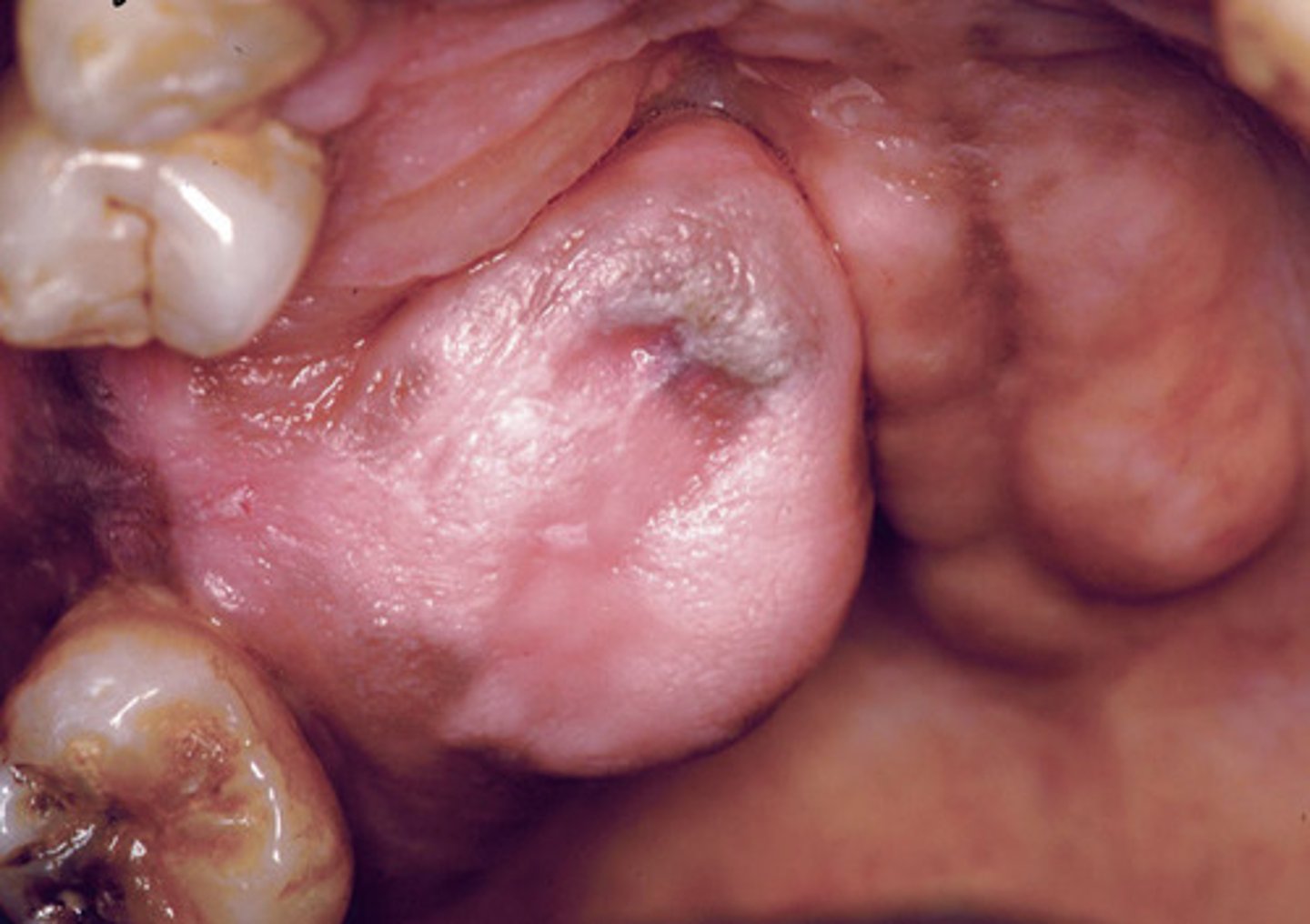
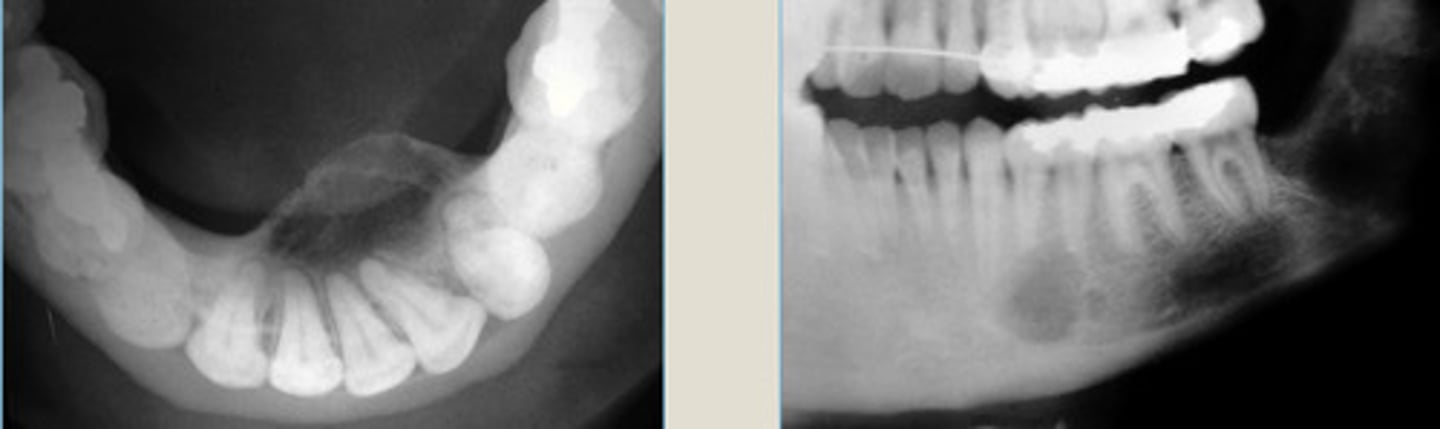
Ossifying Fibroma
Enlargement of post. maxilla
More discrete edges
RIGHT: mixed radiolucent and radiopaque lesion expanding into post MX
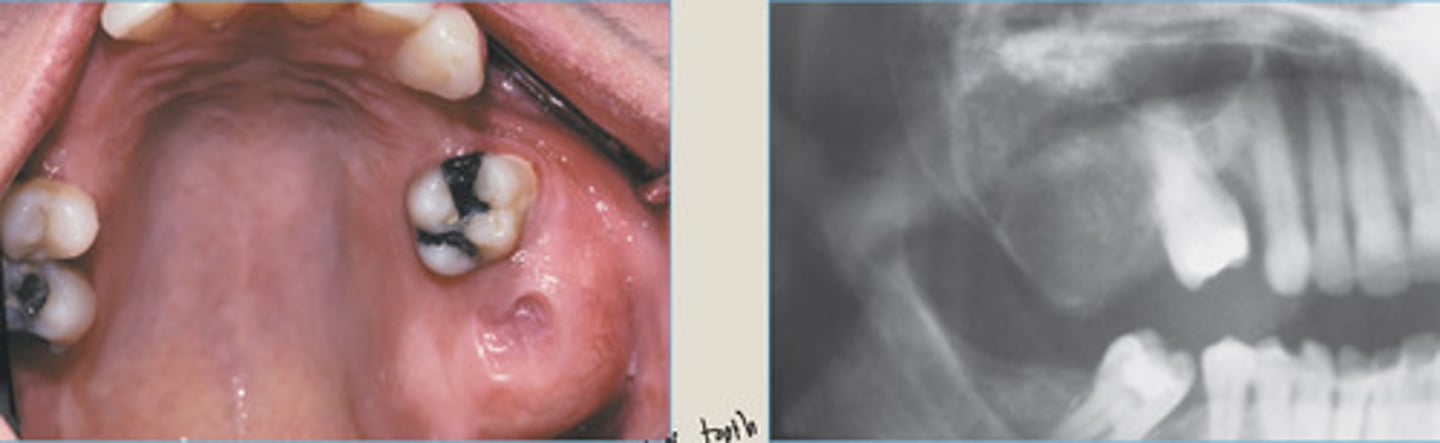
Fibrous Dysplasia:
Age: 10-20
Site: Maxilla
Appearance: Diffuse opacity
Growth: Self-limited
Stabilizes at: Puberty
Ossifying Fibroma:
Age: 30-40
Site: Mandible
Appearance: Circumscribed
Growth: Continuous
Stabilizes: NOT hormone related
Fibrous Dysplasia vs. Ossifying Fibroma
Central Giant Cell Granuloma
This jaw lesion has both reactive and neoplastic features
The equivalent lesion in the skeleton is considered to be a neoplasm
Age: <30 (can be under 10 yrs old)
Site: Mandible
Symptoms: Asymptomatic jaw swelling (can have pain/paresthesia)
Clinical Features of Central Giant Cell Granuloma
Age?
Site?
Symptoms?
Pure lucency
No border reaction
Unilocular/Multilocular
Radiographic features of Central Giant Cell Granuloma
Opacity?
Border reaction?
Unilocular or Multilocular or both?
Central Giant Cell Granuloma
Dentigerous cyst
Odontomas
Ameloblastic fibroma
What 4 diseases can occur in kids <10?
Central Giant Cell Granuloma
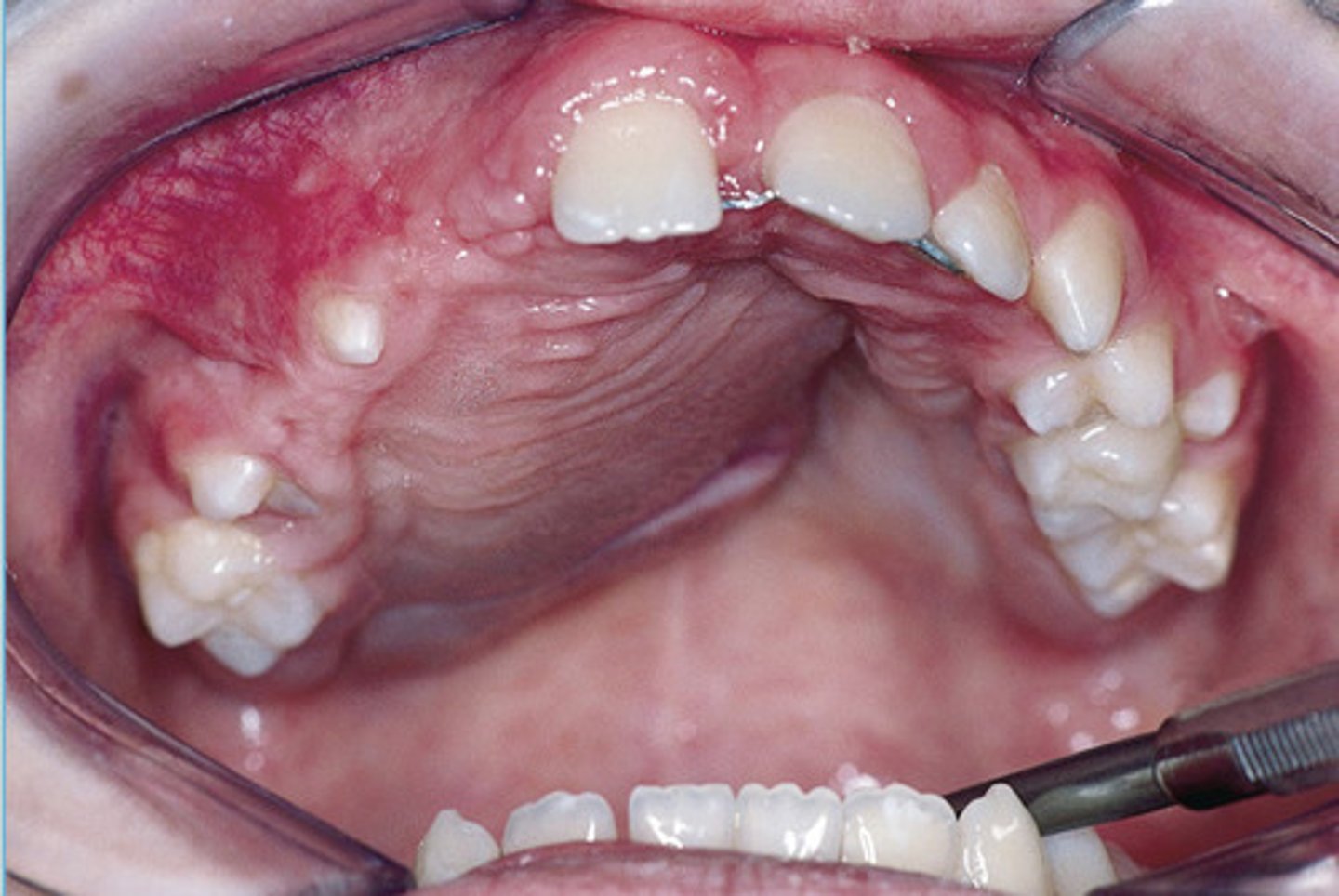
Central Giant Cell Granuloma
Well defined lucency with no cortication
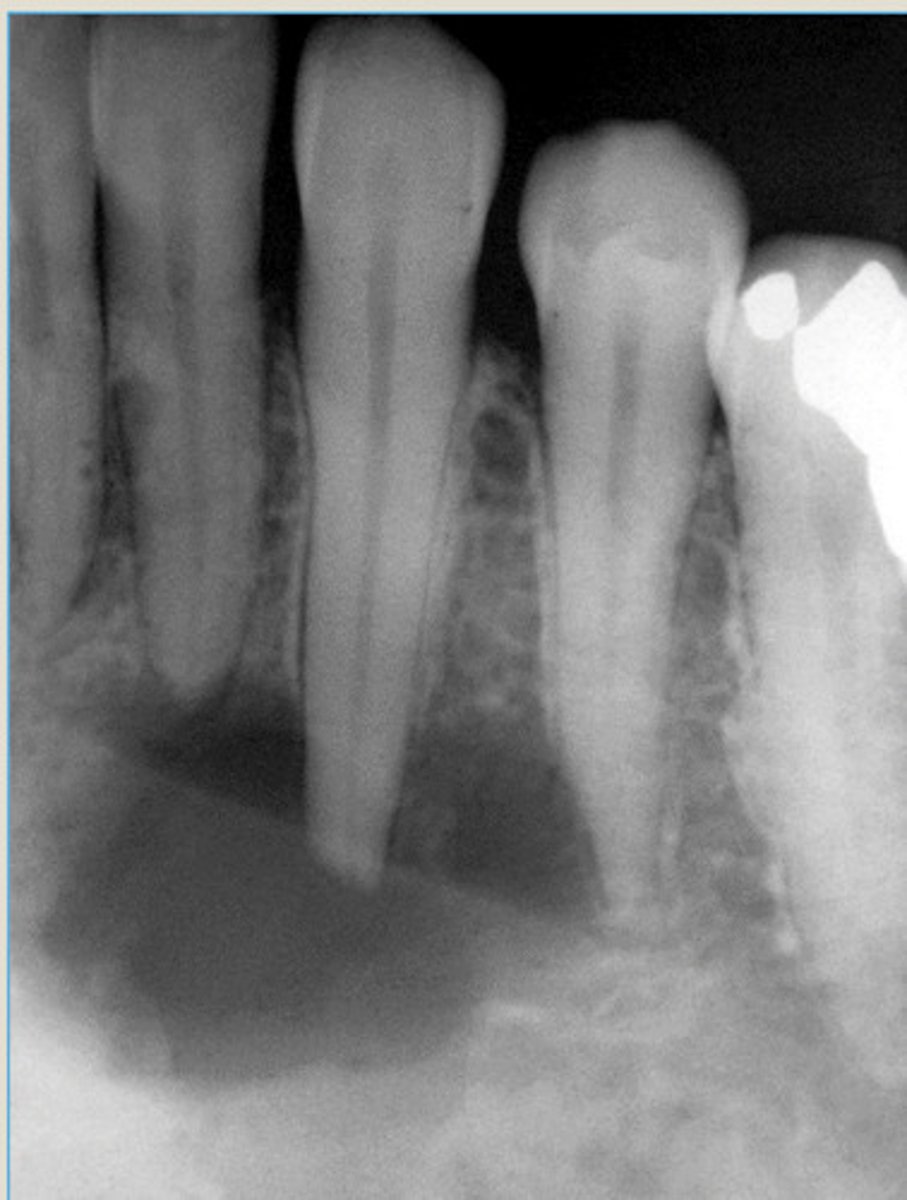
Central Giant Cell Granuloma
loculations and cortical expansion
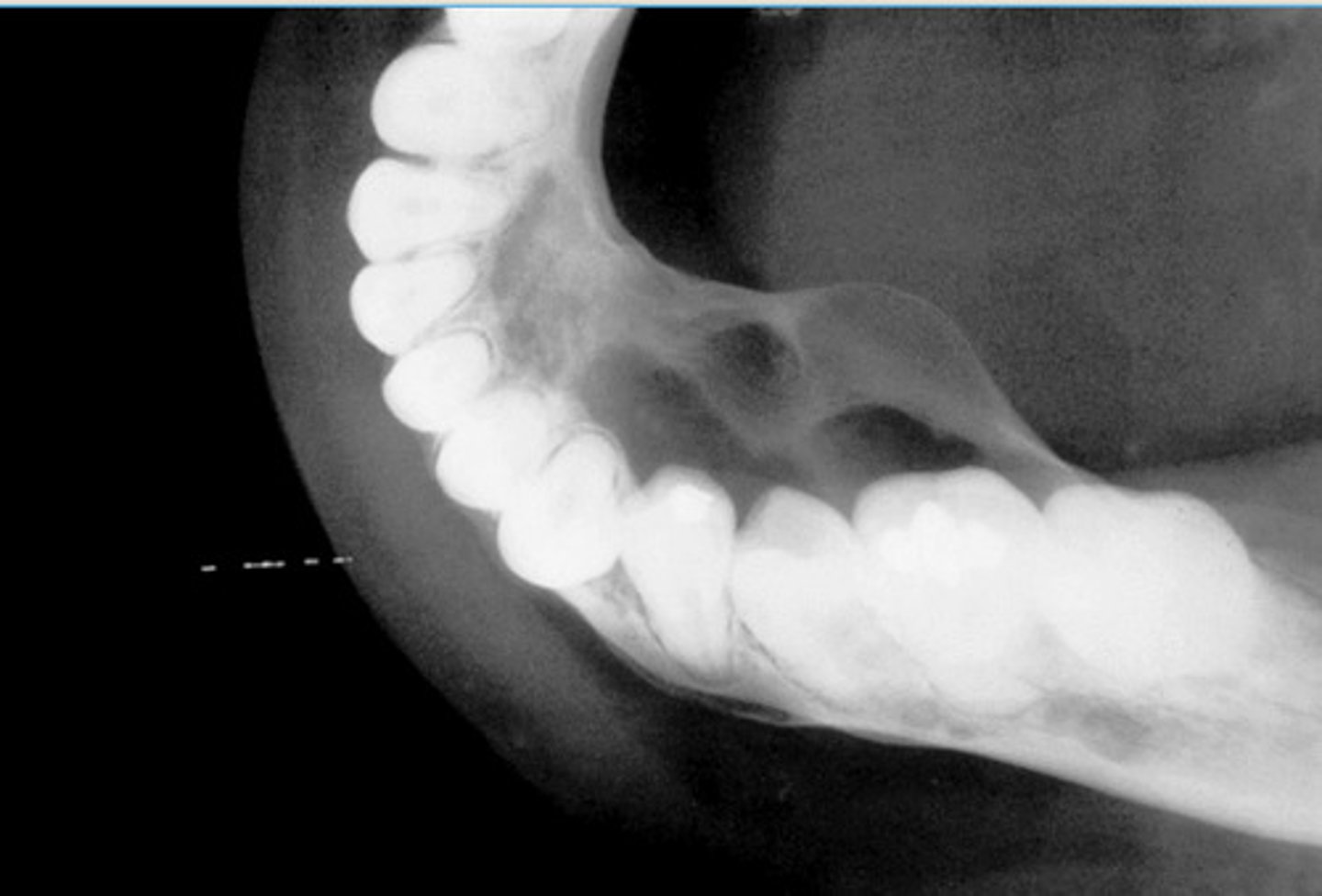
Central Giant Cell Granuloma
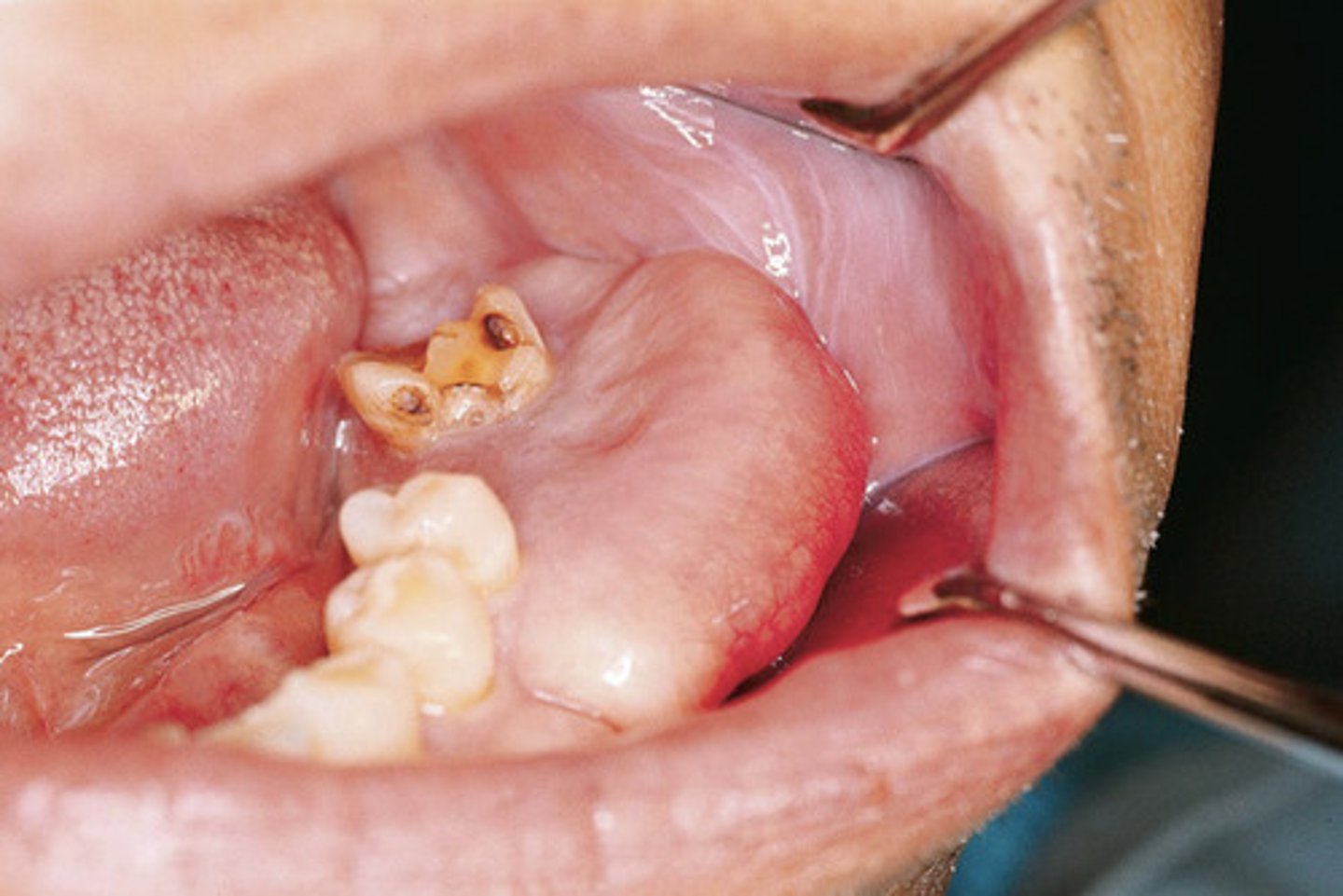
Blue-purple mass present on the anterior alveolar ridge of a 4 yr old boy
*cortical expansion
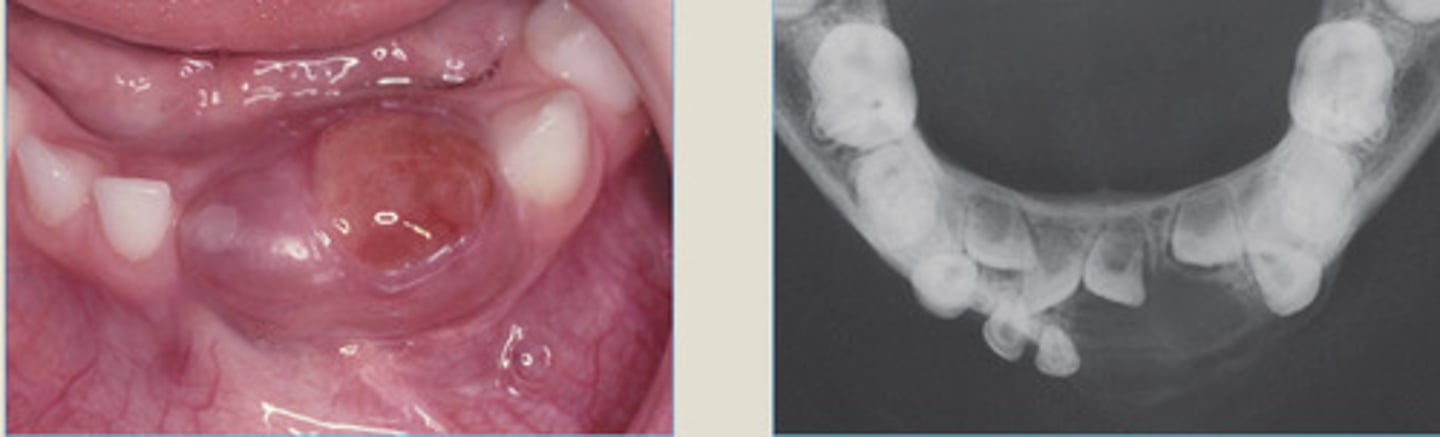
Central Giant Cell Granuloma
what lesions can present as perfectly round corticated expansion?
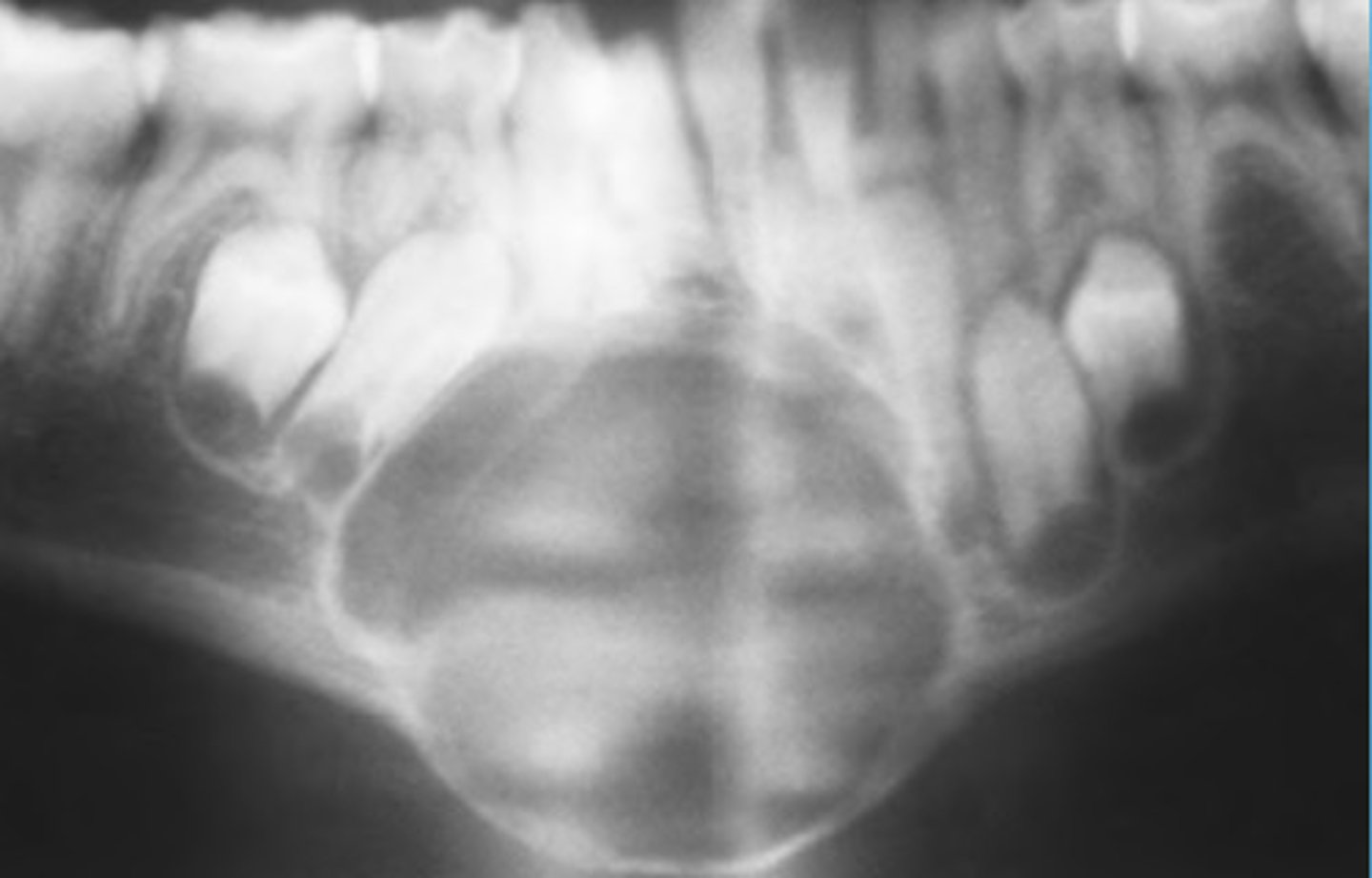
conservative excision by curettage
Central Giant Cell Granuloma TX
1. Paresthesia (numbness)
2. Pain
3. Mobility
4. Tooth resorption
5. Rapid growth
6. Ill-defined lesion
6 Malignancies in the Jaws: Signs and Symptoms
Osteosarcoma
Pagets disease
Prior irradiation in area
Malignant neoplasm of osteoblasts.
Most common primary bone malignancy of the jaws.
2 predisposing factors?
Age: 20-40 yrs old
Symptoms: bone swelling + pain (loose teeth or paresthesia)
Osteosarcoma Clinical Features?
Age?
Symptoms?
1. Expansile mixed lesion
2. May have widened PDL around entire root
3. Classic osteosarcoma of skeleton showing sunburst pattern (sunburst pattern uncommon in jaw lesions)
Radiographic Features of Osteosarcoma
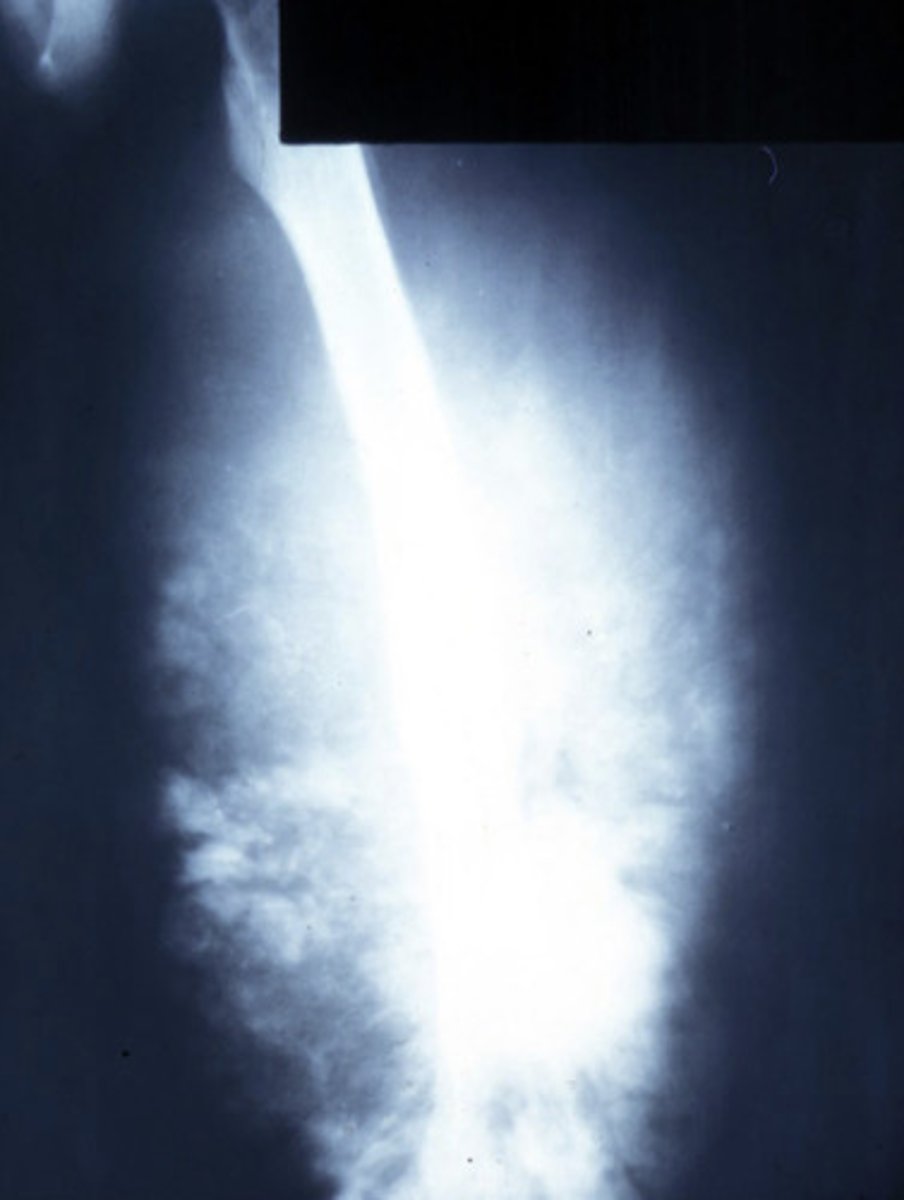
Osteosarcoma
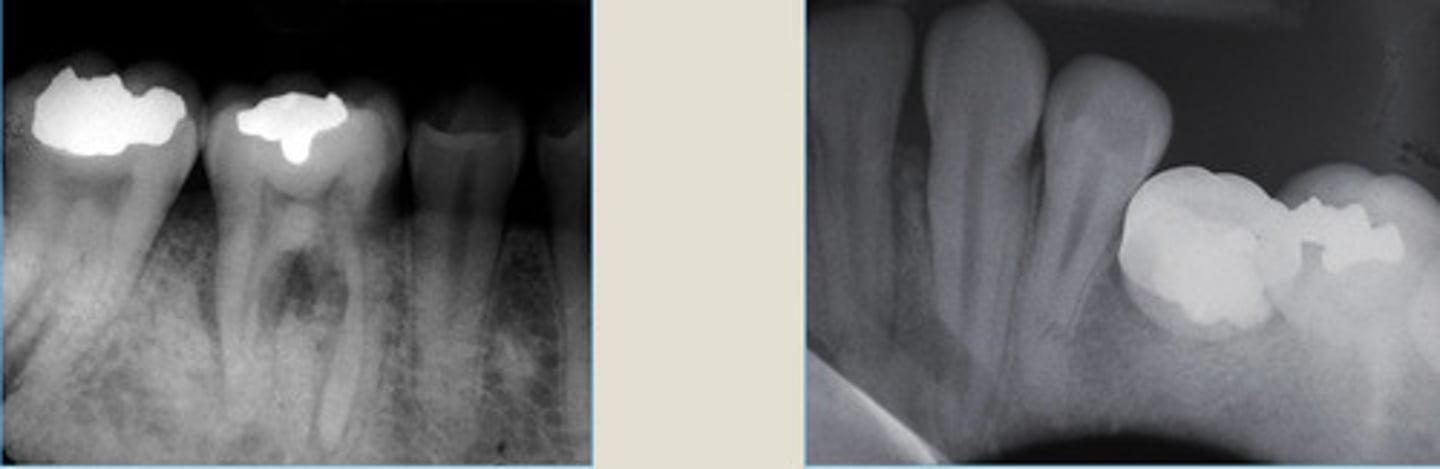
LEFT: surrounding roots of the first molar tooth (widened PDL ligament)
RIGHT: lesion between a MN lateral incisor + canine (widening of PDL)
widened PDL, increased density, no corticated edge
Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma of MN showing sunburst pattern of tumor radiating from alveolar ridge (on left) + mandible (on right)
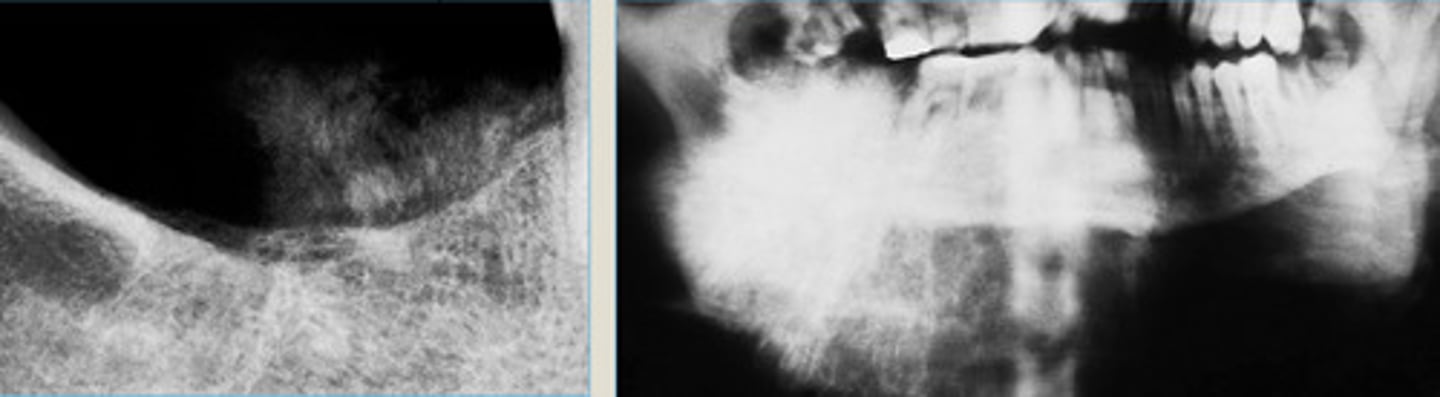
Osteosarcoma
on the mandible
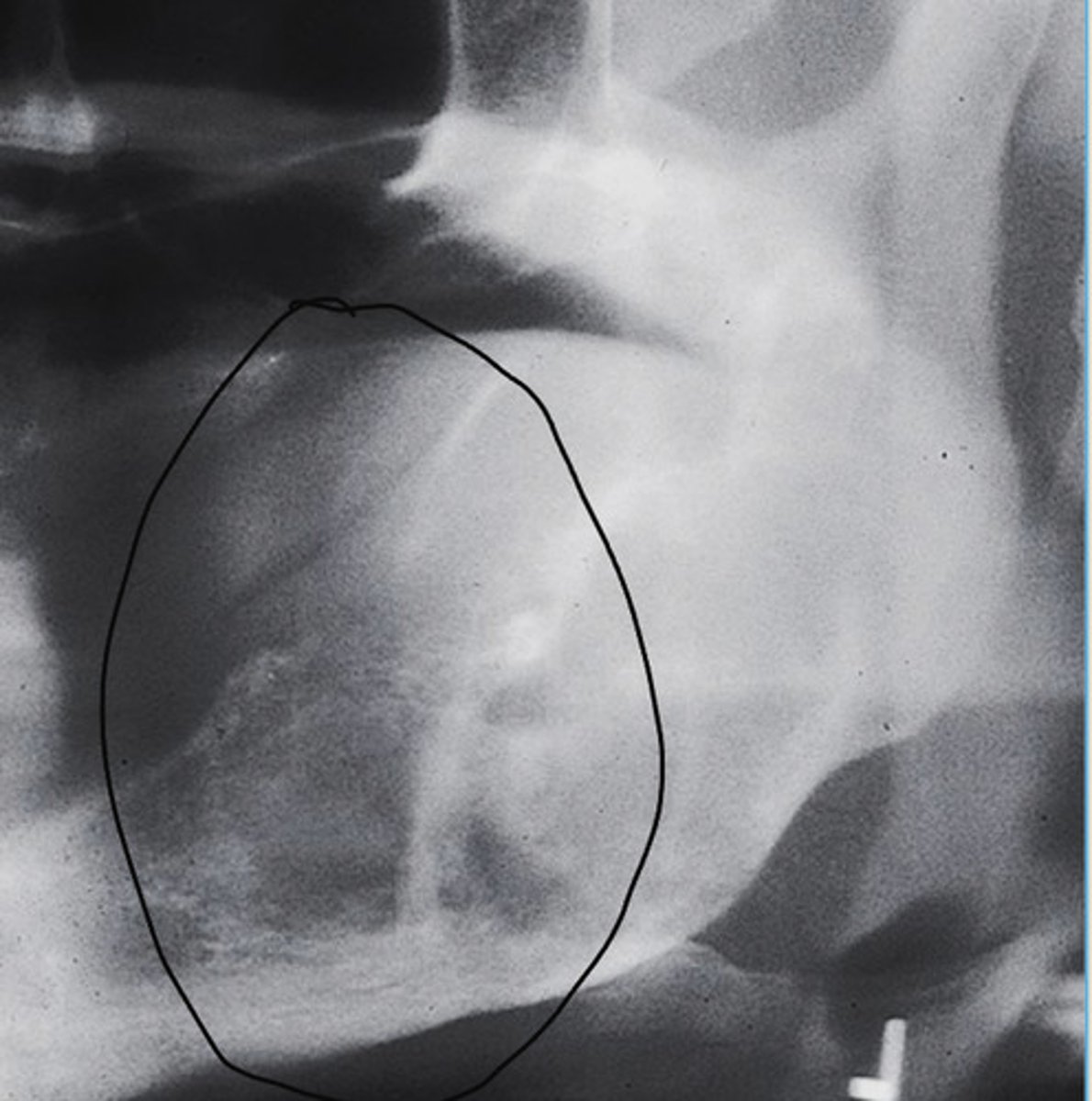
Osteosarcoma
Gradual > more opaque bone pattern
Widened PDL
Firm painful swelling of the left maxilla
Osteosarcoma
sunburst pattern
advanced due to ______ pattern
Osteosarcoma
Ill defined, increased density, mobile teeth.
Exophytic tumor bone production resulting in a "sunburst" pattern.
RIGHT: tumor of the anterior mandible, widening of PDL and mottled radiopacity superimposed on teeth.
Wide to radical surgical resection
Osteosarcoma TX
Metastatic Tumors to the Jaws
Most common malignancy in jaws is metastasis from some other site in a middle-aged person! (STILL not as common as SCC)
AGE: older adult
Symptoms: Pain, swelling, paresthesia or pathologic fracture
Rad Features: Ill-defined, moth-eaten radiolucency
Clinical features of Metastatic Tumors to the Jaws
age?
symptoms?
rad features?
1. Breast
2. Lung
3. Thyroid
4. Prostate
4 MOST COMMON metastatic tumors to the jaws
Metastatic Carcinomas to the Jaws
irregular, pure lucency
"moth-eaten" bone destruction
Metastatic Carcinomas to the Jaws
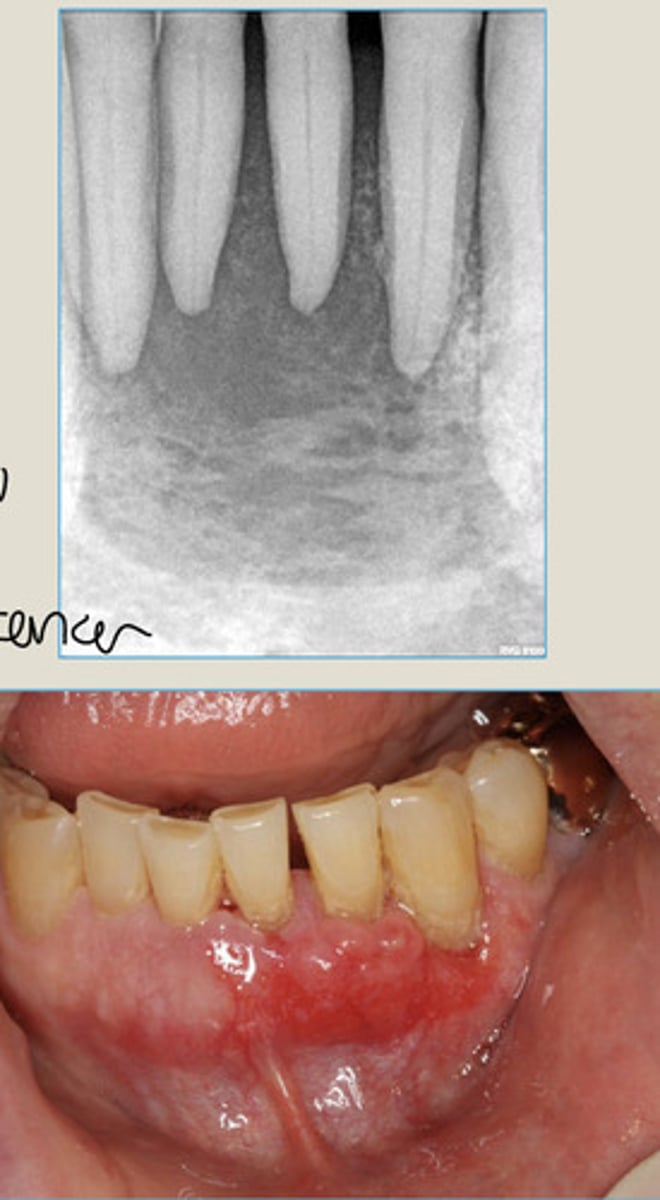
LEFT: destruction of alveolar bone surrounding roots of MN 2nd M
RIGHT: carcinoma metastatic to jaws, widening of PDL
Metastatic Carcinomas to the Jaws
irregular jaw path with history of cancer
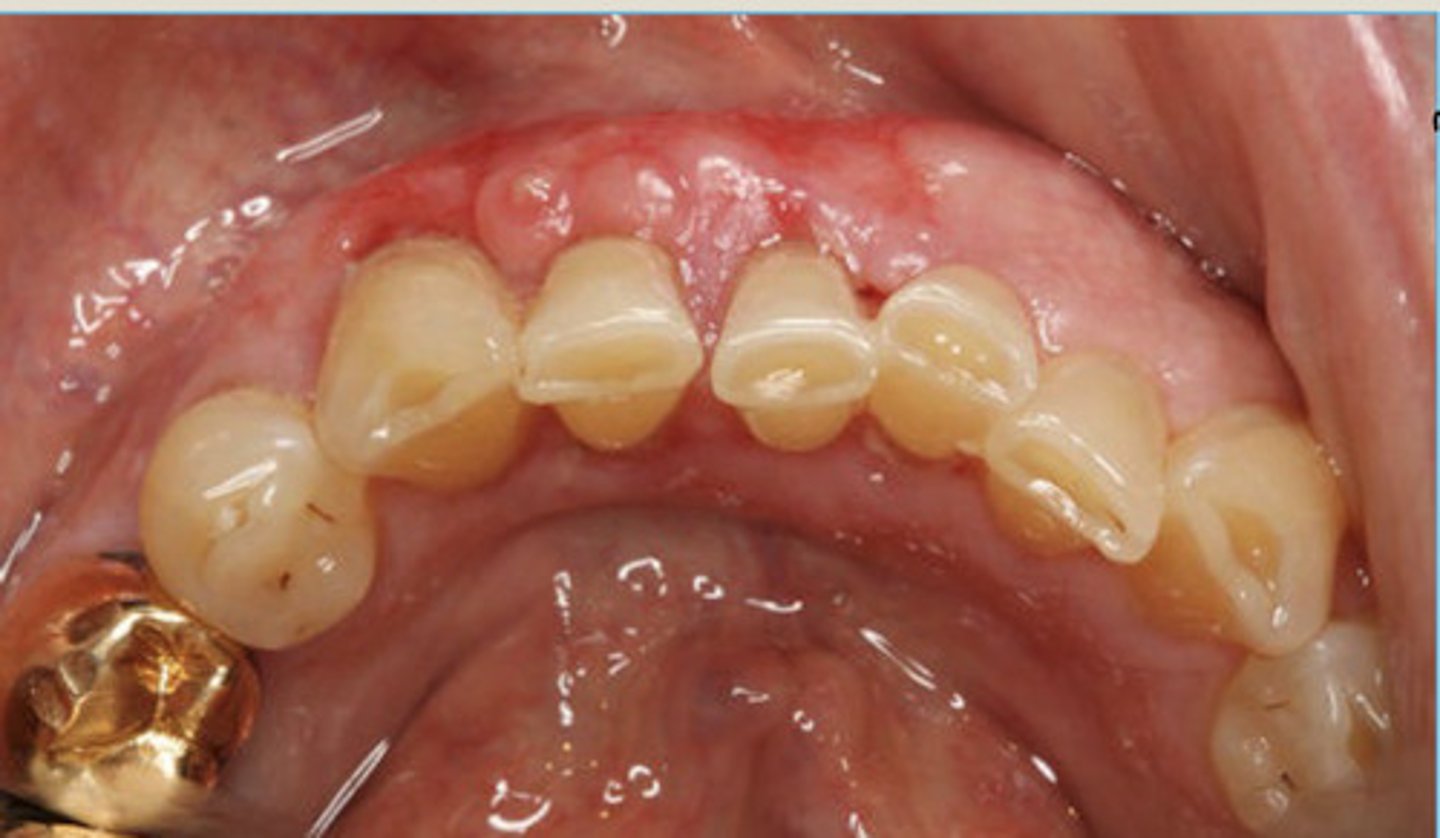
Metastatic Carcinomas to the Jaws
1. Metastatic cancers (more common)
2. Multiple Myeloma (more common)
3. Osteosarcoma (in younger pts)
PRIMARY:
1. Osteosarcoma
2. Chondrosarcoma
Most common malignant tumors occurring in jaws + most common PRIMARY malignant tumors in jaws?
1. Cemento-osseous dysplasia
2. Central giant cell granuloma
3. Ossifying fibroma
3 Unilocular Radiolucent Radiographic Presentations
1. CGCG
2. Cherubism
Multilocular Radiolucent Radiographic Presentations
1. Tori and exostoses (most common)
2. Idiopathic osteosclerosis
3. Condensing osteitis
4. Osteosarcoma
4 Radiopaque Radiographic Presentations
1. Osteomyelitis
2. Mets to jaws
2 Moth-eaten Radiographic Presentations
1. Cemento-osseous dysplasia
2. Ossifying fibroma
3. Osteosarcoma
3 Mixed Radiographic Presentations
Fibrous dysplasia
1 Ground Glass Radiographic Presentations