Chemistry Exam 5 Flashcards
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Ionic compound
Combination of cations and anions
Octet rule
Rule that states that atoms will form covalent bonds as to be surrounded by eight valence electrons
Bond length
Distance between adjacent nuclei in a molecule
Covalent bond
Two electrons shared by two atoms
Polar covalent bond
Electrons are shared by two atoms, but the electrons spend more time around one atom
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract an electron in a chemical bond to itself
up, right
Electronegativity increases as you go ____ (up/down) and ____ (right/left) on the periodic table
Non-polar covalent bond
A difference in electronegativity of 0.0-0.4 indicates a(n) _______
Polar covalent bond
A difference in electronegativity of 0.5-1.9 indicates a(n) _______
Ionic bond
A difference in electronegativity of 2.0+ indicates a(n) _______
Resonance
Two or more structures needed to represent a particular molecule
Formal charge (F.C.)
The difference between the number of valence electrons the atom originally has, and the number of electrons assigned to it in the Lewis structure
Bond enthalpy (bond dissociation energy)
The enthalpy change required to break a particular bond in one mole of gaseous molecules
Lattice energy
The energy change occurring when one mole of a solid ionic compound forms from its gaseous ions, or the energy required to completely separate one mole of a solid compound
increase, decreases
Lattice energy increases as charges ______ (increase/decrease) and as ionic radius (increases/decreases)
stronger, smaller
Lone pairs exert a _____ (stronger/weaker) repulsive force and need more space, resulting in a _____ (larger/smaller) bond angle
Linear
Arrangement of electron pairs for a molecule with 2 electron pairs
Trigonal planar
Arrangement of electron pairs for a molecule with 3 electron pairs
Tetrahedral
Arrangement of electron pairs for a molecule with 4 electron pairs
Trigonal bipyramidal
Arrangement of electron pairs for a molecule with 5 electron pairs
Octahedral
Arrangement of electron pairs for a molecule with 6 electron pairs
the same as
For molecules with no unshared pairs, the arrangement of electron pairs is ____ (the same as/different from) the molecular geometry
Bent
Molecular geometry of AB2E class of molecule
Trigonal pyramidal
Molecular geometry of AB3E class of molecule
Bent
Molecular geometry of AB2E2 class of molecule
Seesaw
Molecular geometry of AB4E class of molecule
T-shaped
Molecular geometry of AB3E2 class of molecule
Linear
Molecular geometry of AB2E3 class of molecule
Square pyramidal
Molecular geometry of AB5E class of molecule
Square planar
Molecular geometry of AB4E2 class of molecule
ABm
These types of molecules have polar bonds, but are all nonpolar
polar
Most ABmEn molecules are _____ (polar/nonpolar) (Two exceptions: linear and square planar)
Valence Bond Theory
Theory that explains how covalent bonds are formed through the overlap of atomic orbitals from two atoms, each contributing one electron to form a shared pair
sigma
A single bond will always be a _____ (sigma/pi) bond
1
A double bond counts as _ electron domain(s)
sp
2 electrons domains around the central atom creates an __ orbital
sp2
3 electrons domains around the central atom creates an __ orbital
sp3
4 electrons domains around the central atom creates an __ orbital
dsp3
5 electrons domains around the central atom creates a __ orbital
d2sp3
6 electrons domains around the central atom creates a __ orbital
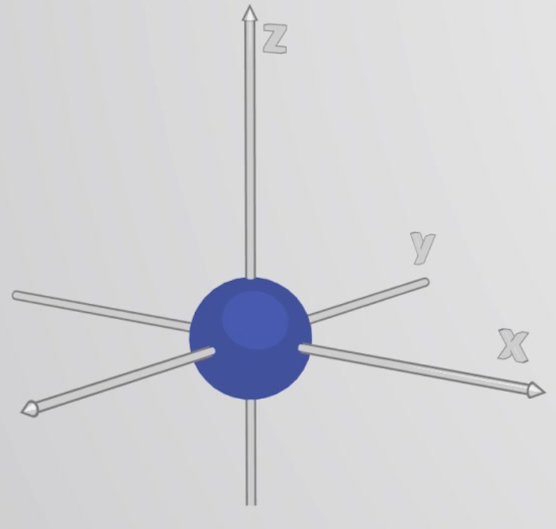
s orbital
What orbital is this?
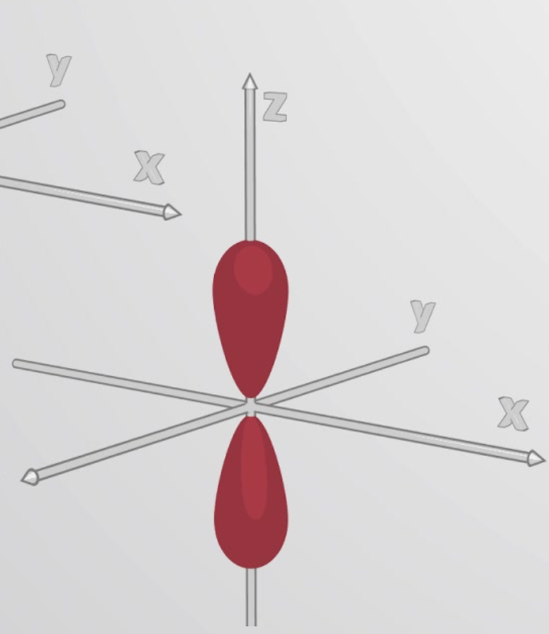
p orbital
What orbital is this?
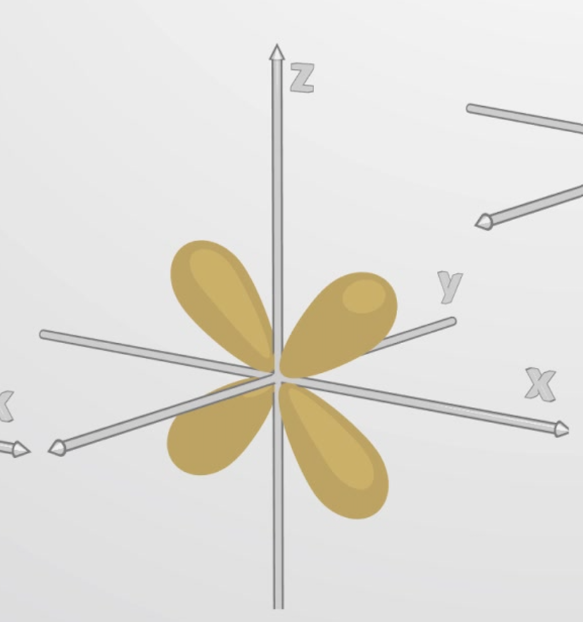
d orbital
What orbital is this?
Sigma bond
A covalent bond formed by orbitals overlapping end-to-end, with its electron density concentrated between the nuclei of the bonding atoms
Pi bond
A covalent bond formed by sideways overlapping orbitals, with its electron density concentrated above and below the plane of the nuclei of the bonding atoms
longer
A single bond is _____ (shorter/longer) than a triple bond
Coordinate covalent bond
Covalent bond in which one atom donates both electrons in a shared pair