*GCSE Biology (AQA)
1/491
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
492 Terms
microscope
an optical instrument used for viewing very small objects, such as mineral samples or animal or plant cells, typically magnified several hundred times.

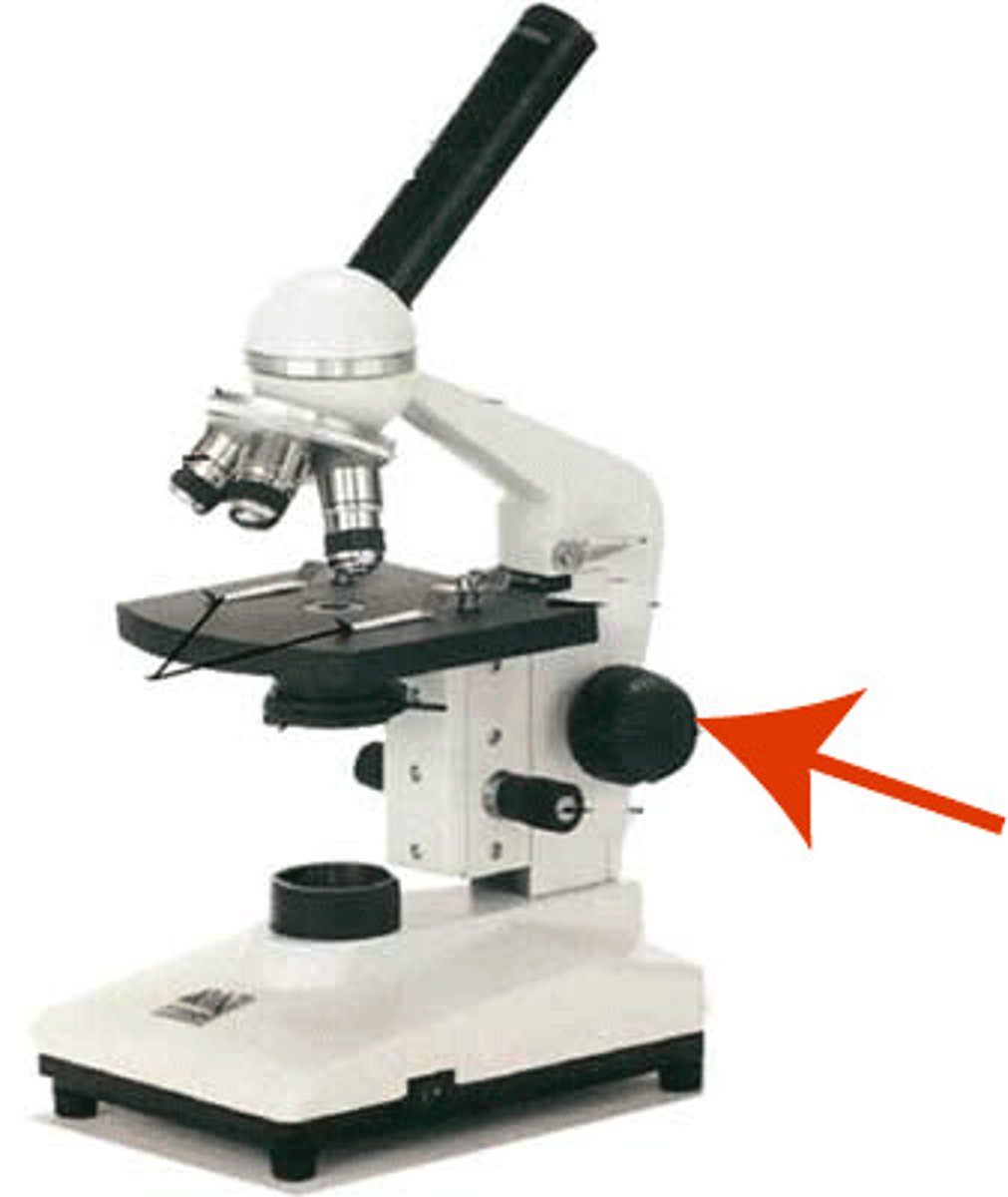
fine focus
Knob that allows you to make fine focusing adjustments. (small knob)
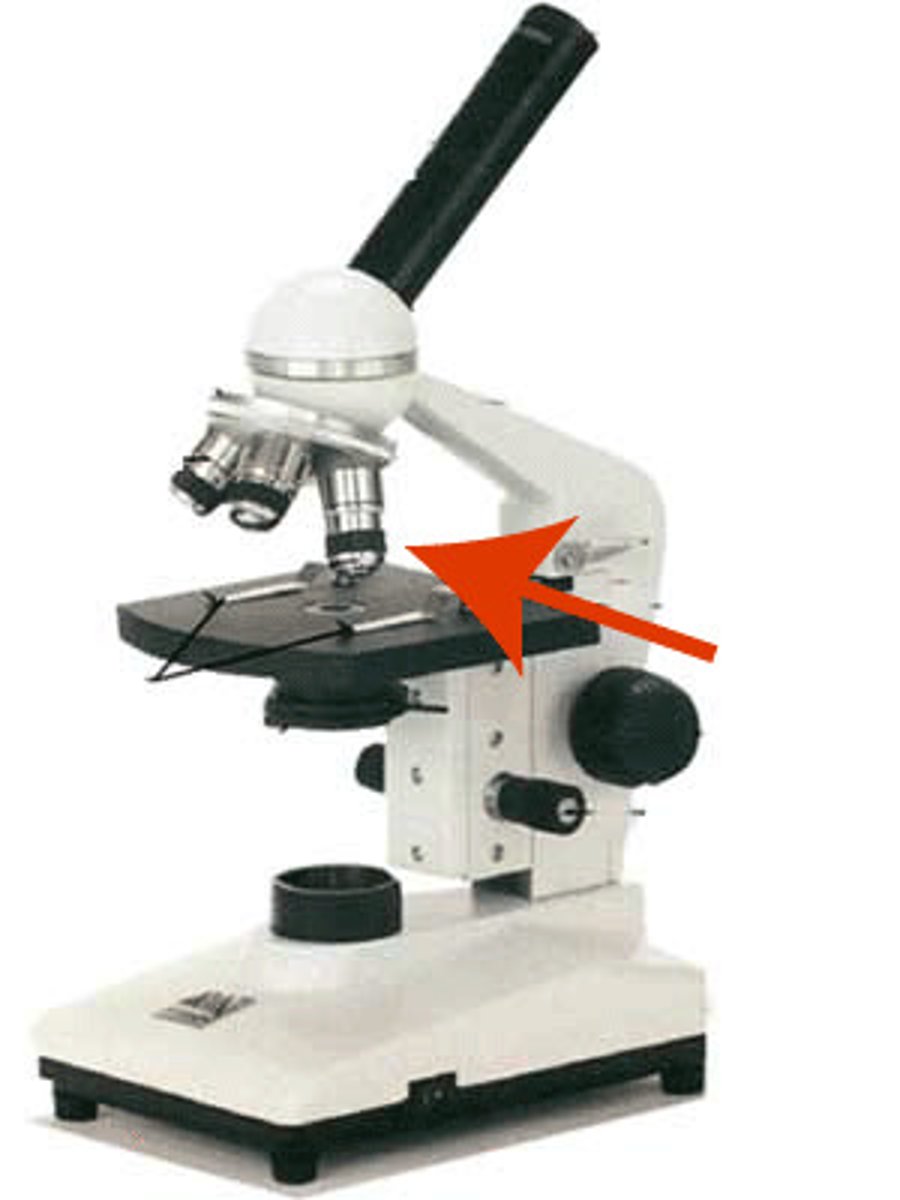
objective
the lens at the bottom near the sample
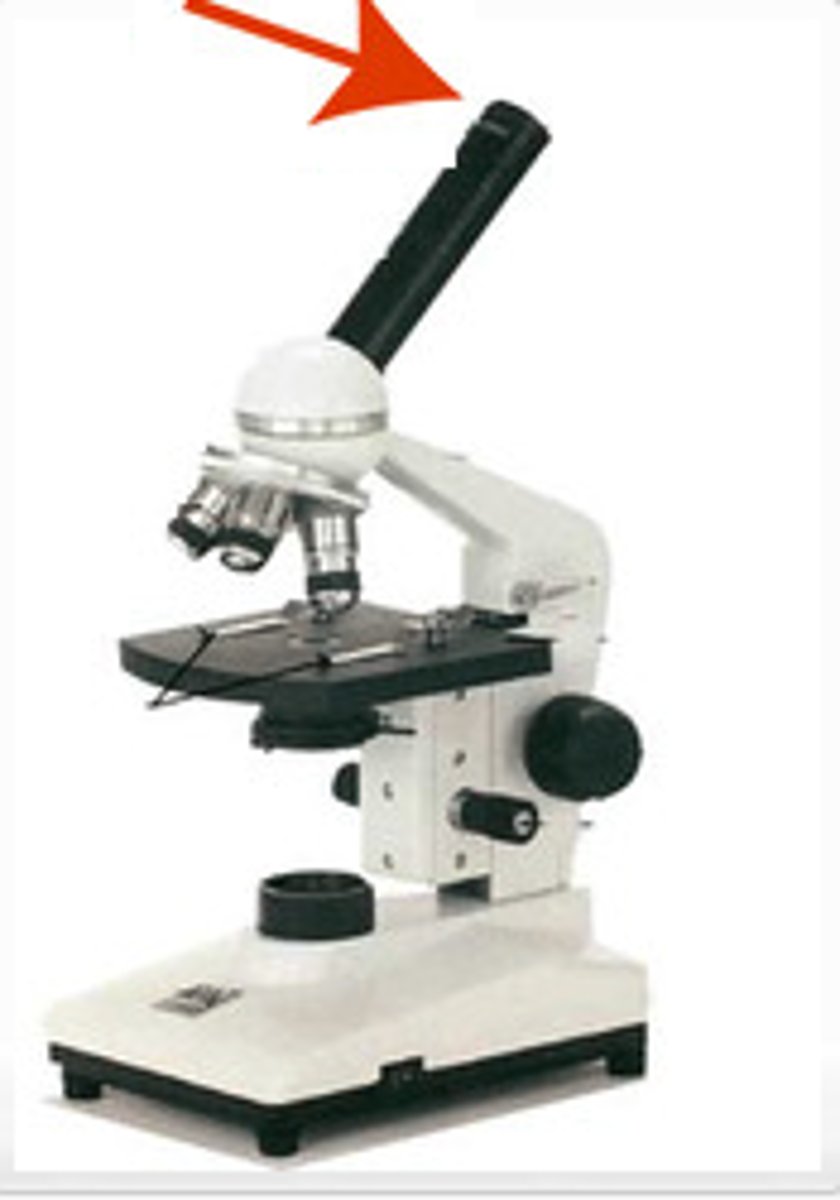
eyepiece
A lens that magnifies the image formed by the objective.
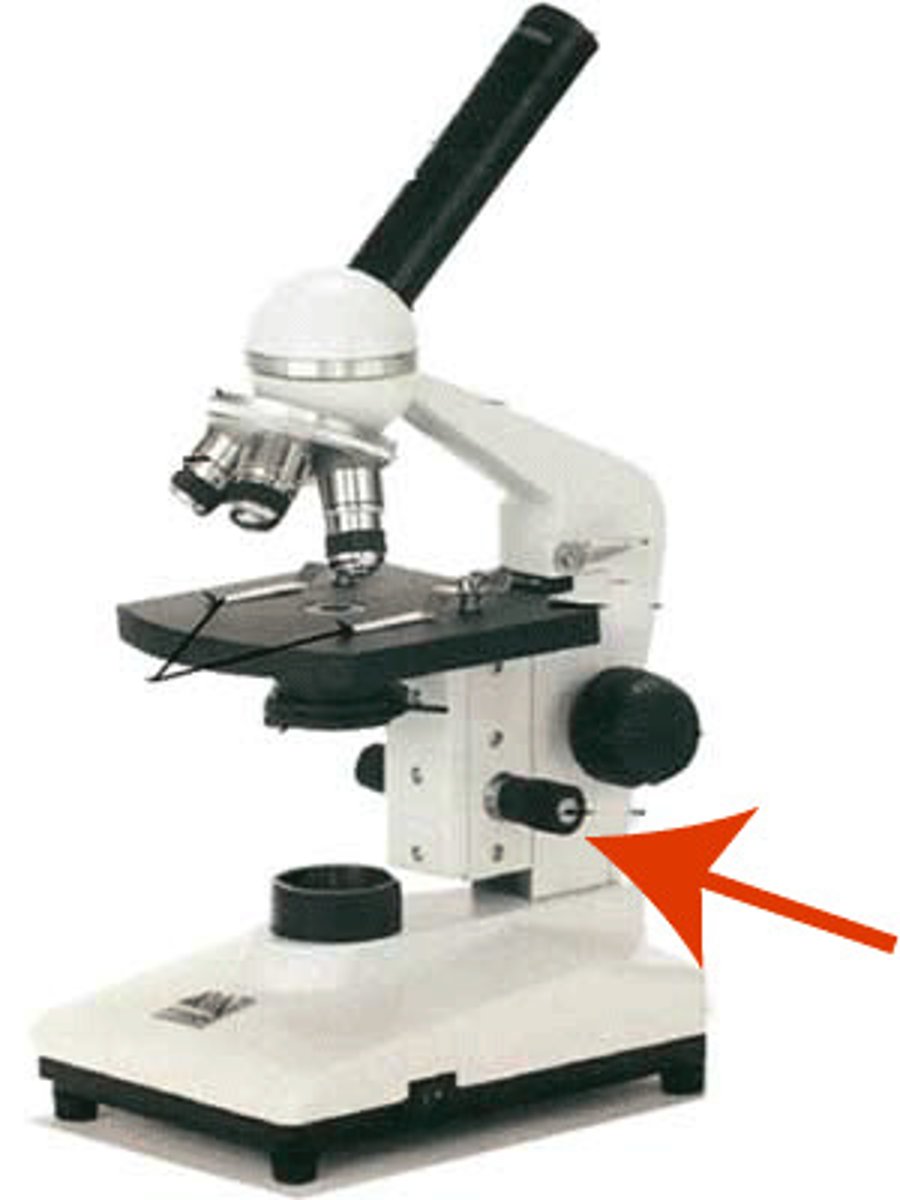
course focus
used to make big changes in focus (large knob)

magnification
= size of the image/size of real object
resolving power
A measure of the clarity of an image; the ability of an optical instrument to show two objects as separate.
cell
the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms
algae
Grow in soil, on trees and on the bodies of turtles and frogs; smallest of all green plants
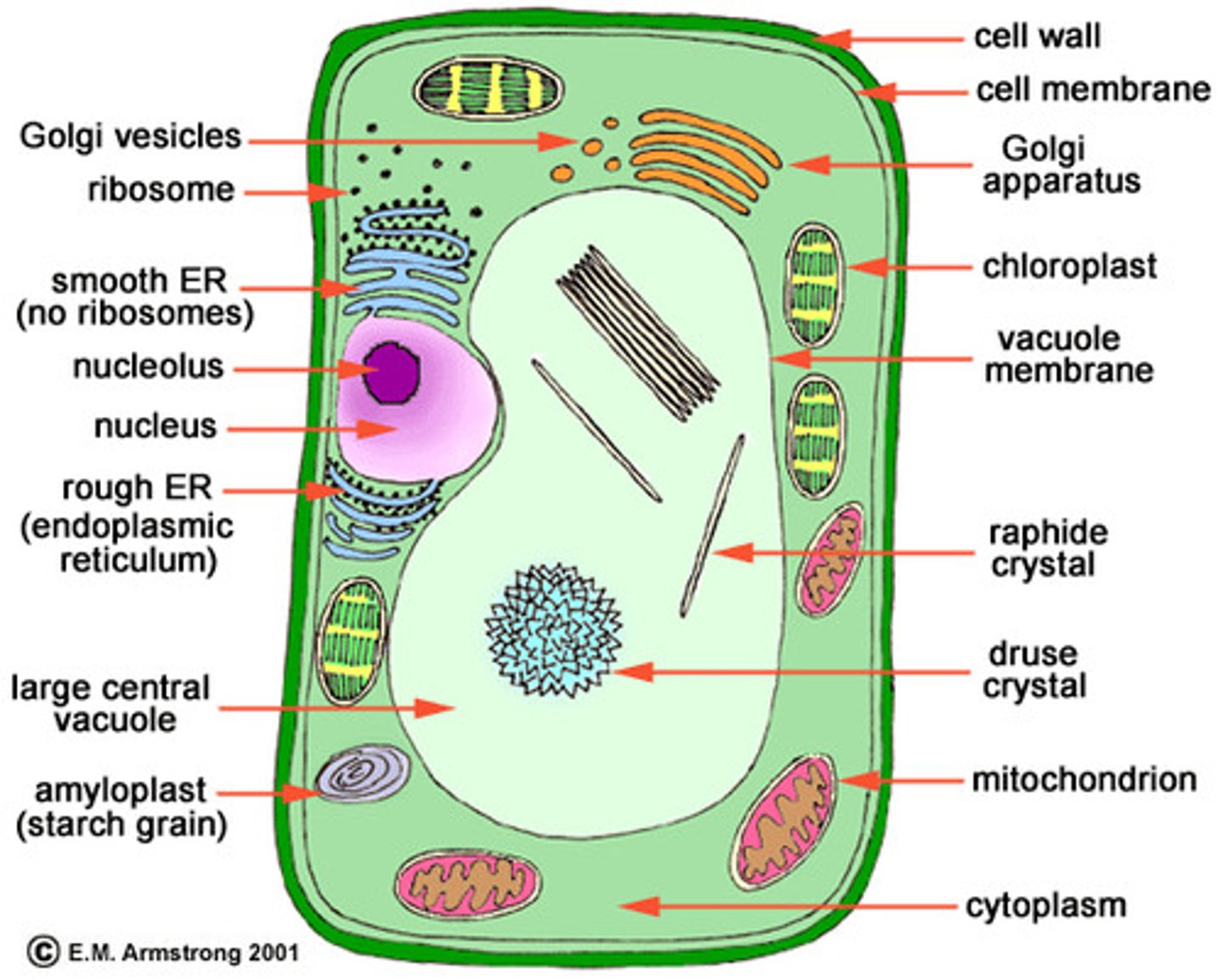
cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended, where many chemical reactions take place.
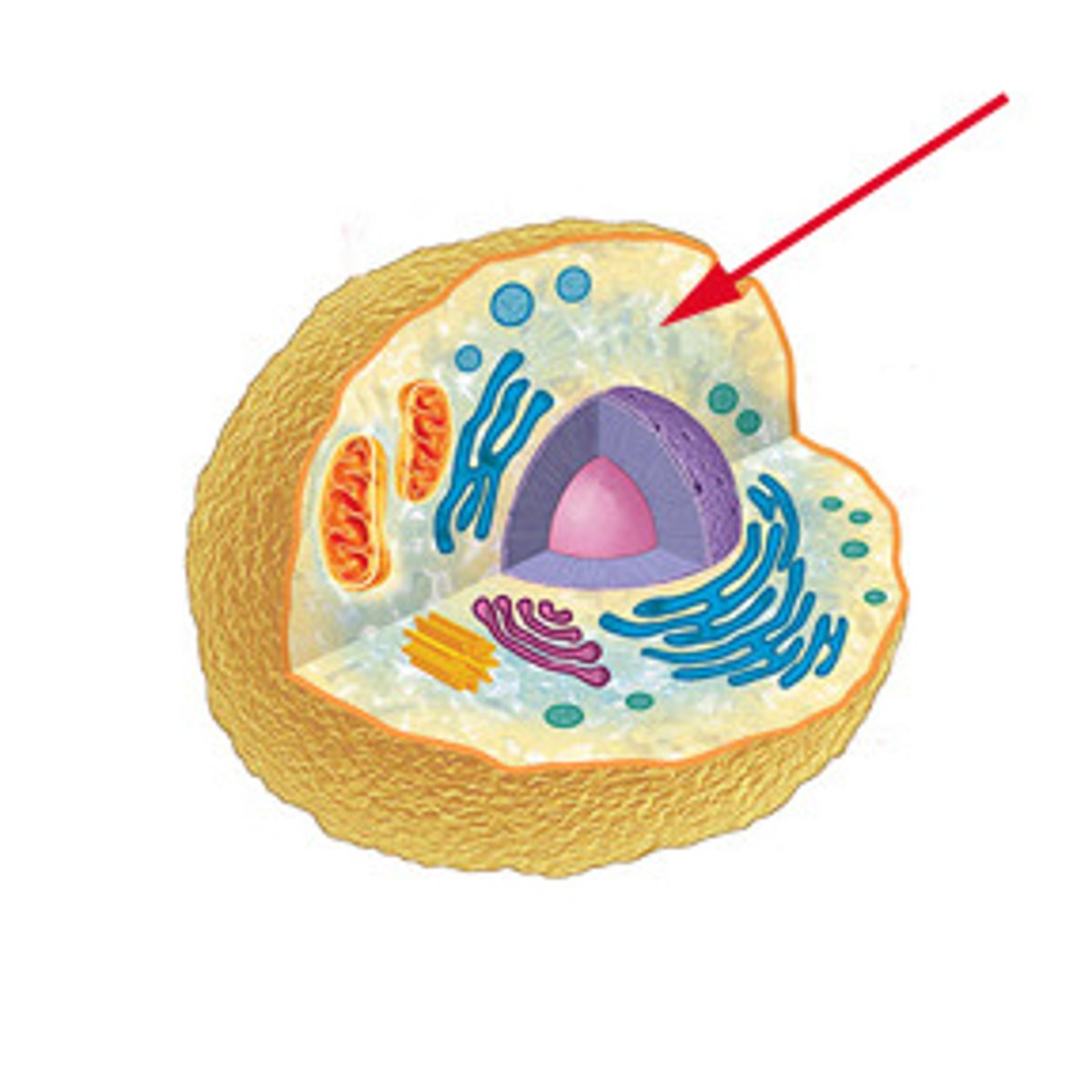
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
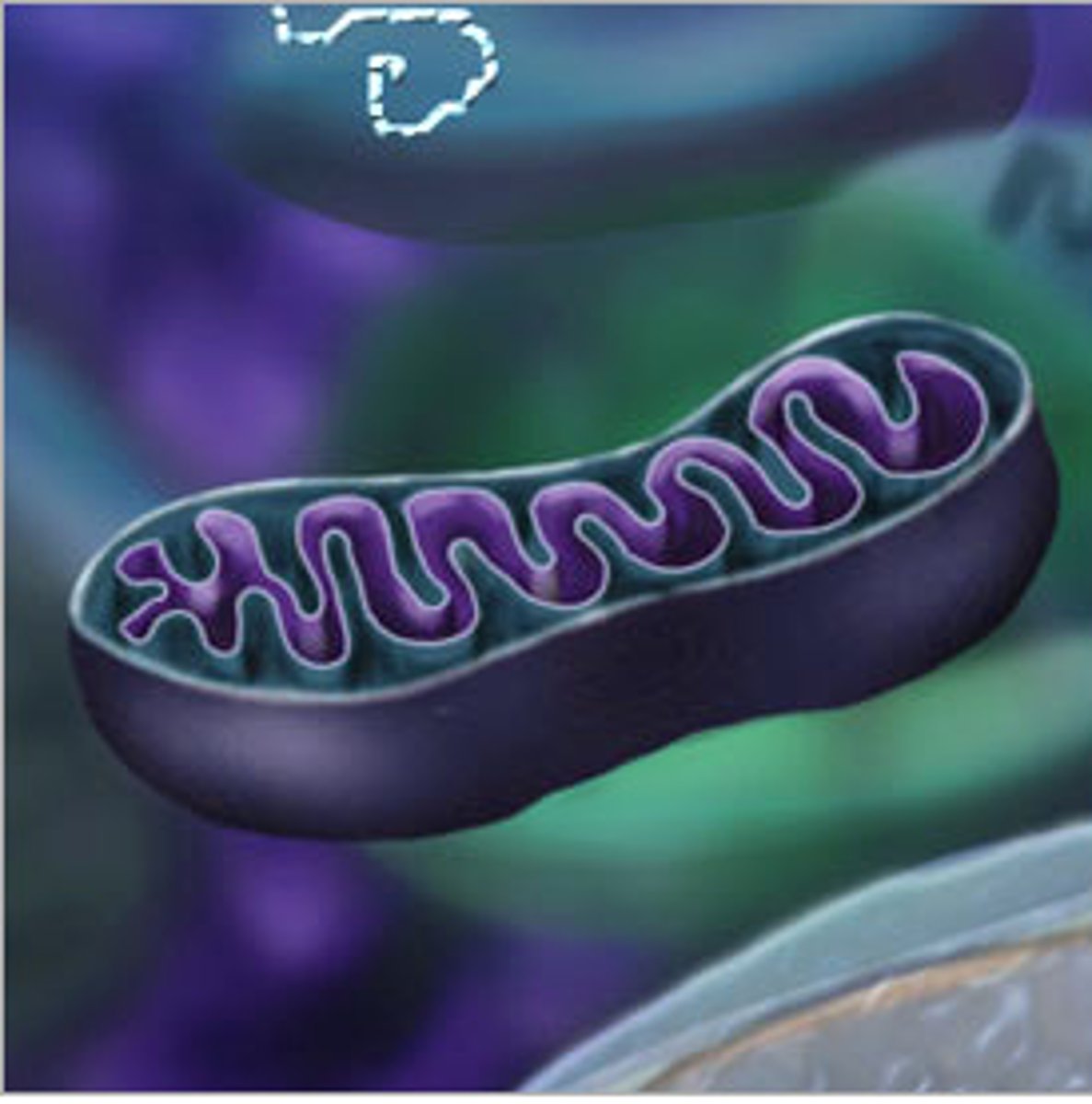
mitochondria
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
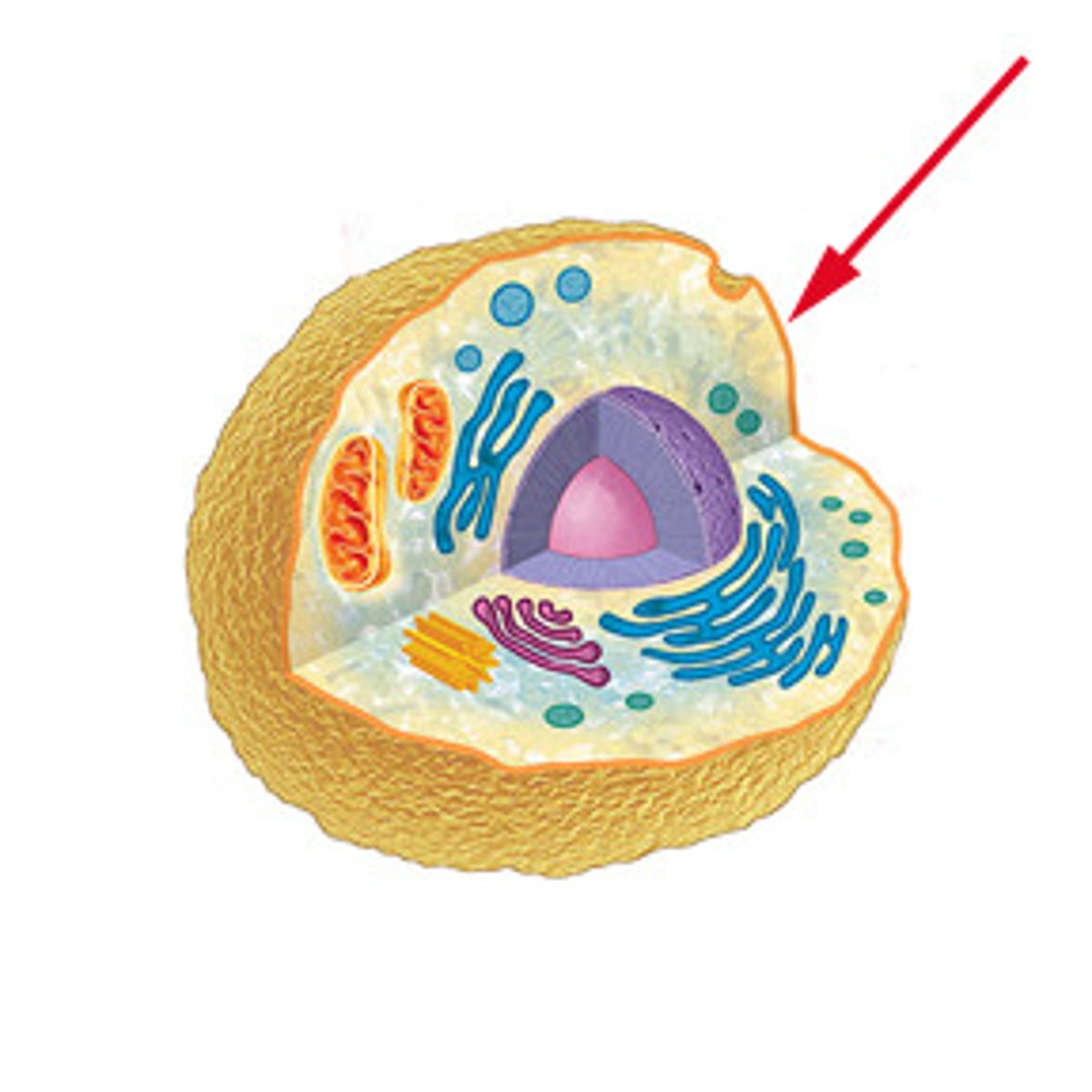
ribosome
Cytoplasmic organelles at which proteins are synthesised.
cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms

chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
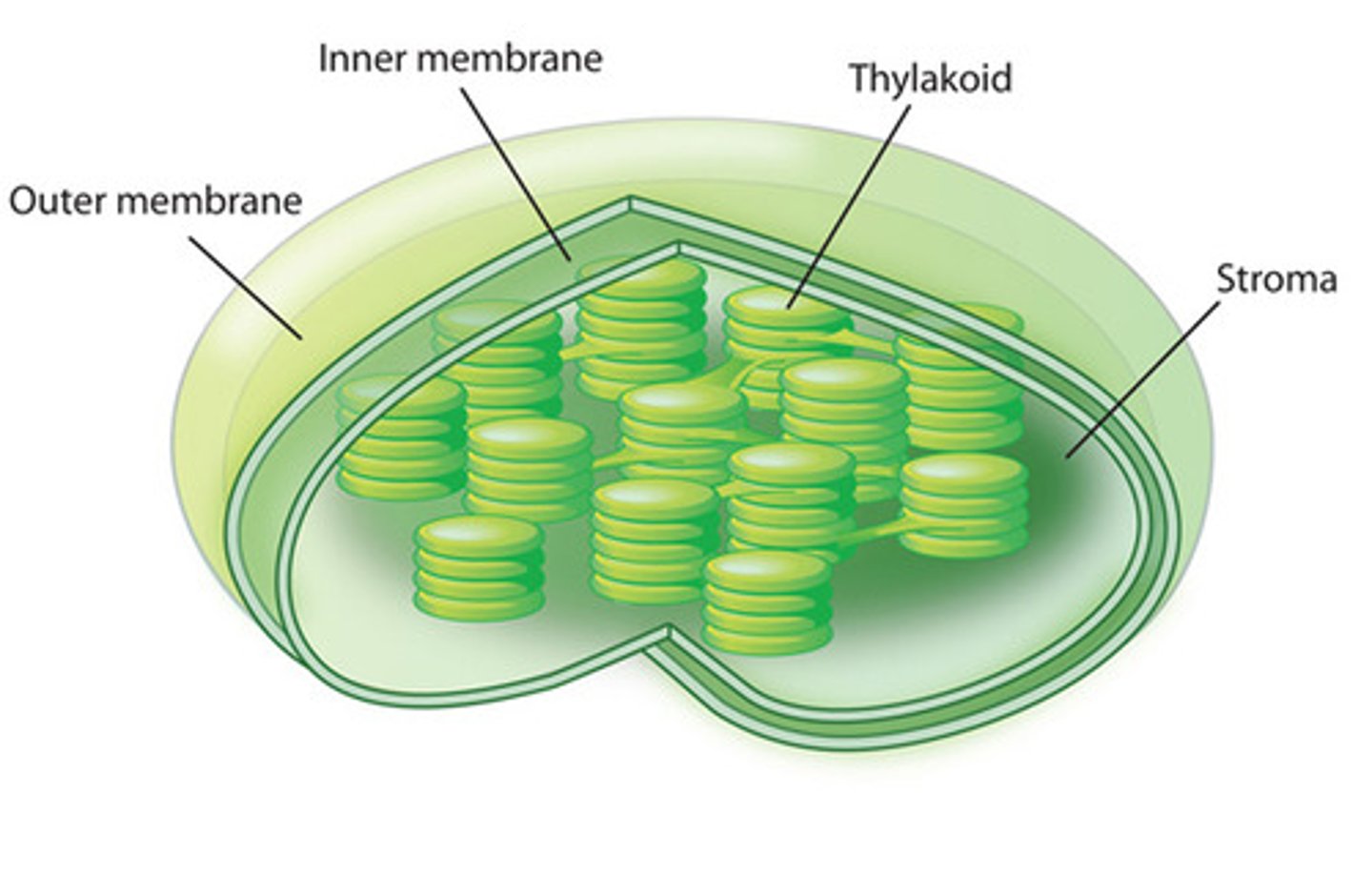
chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria

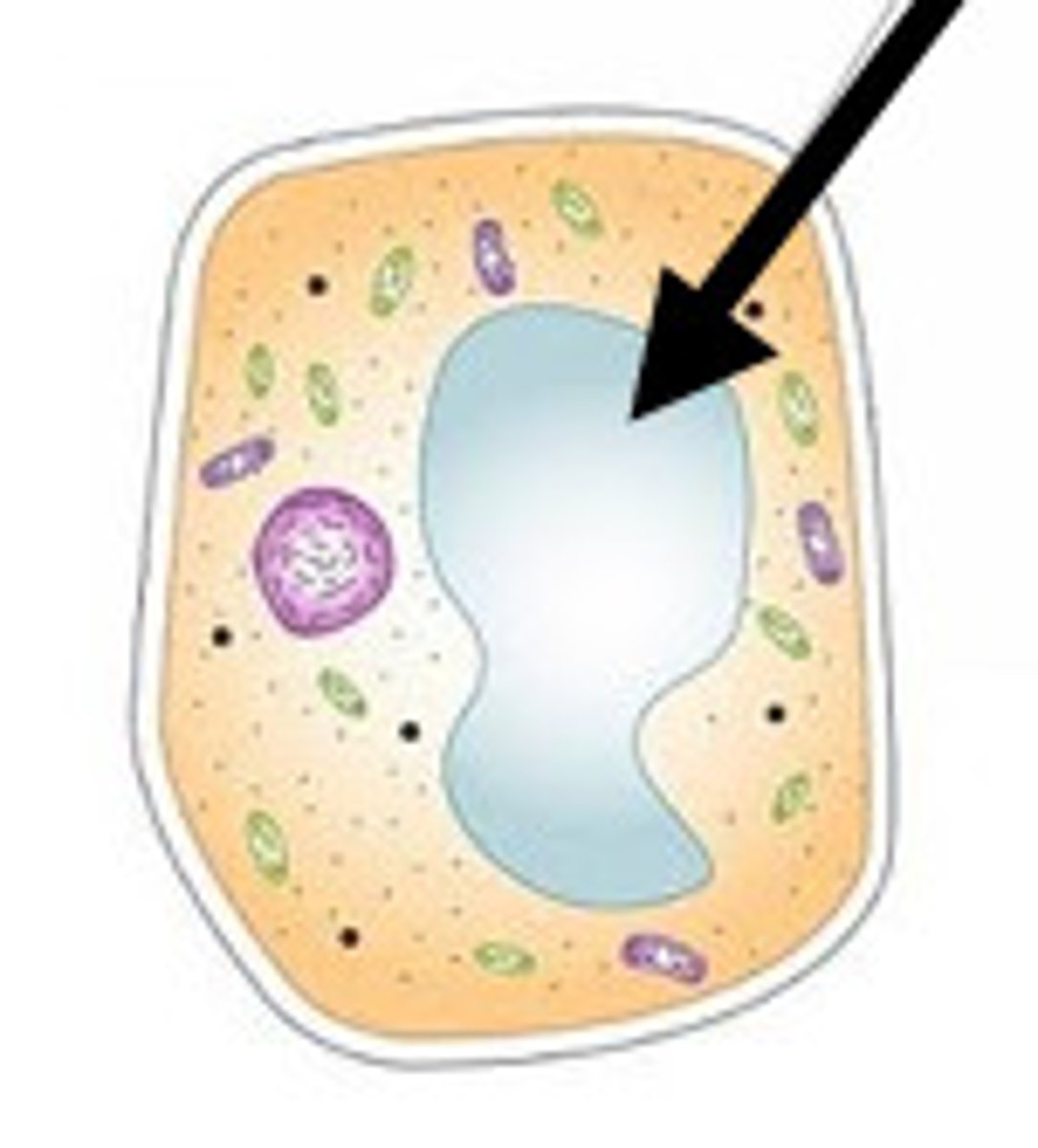
vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
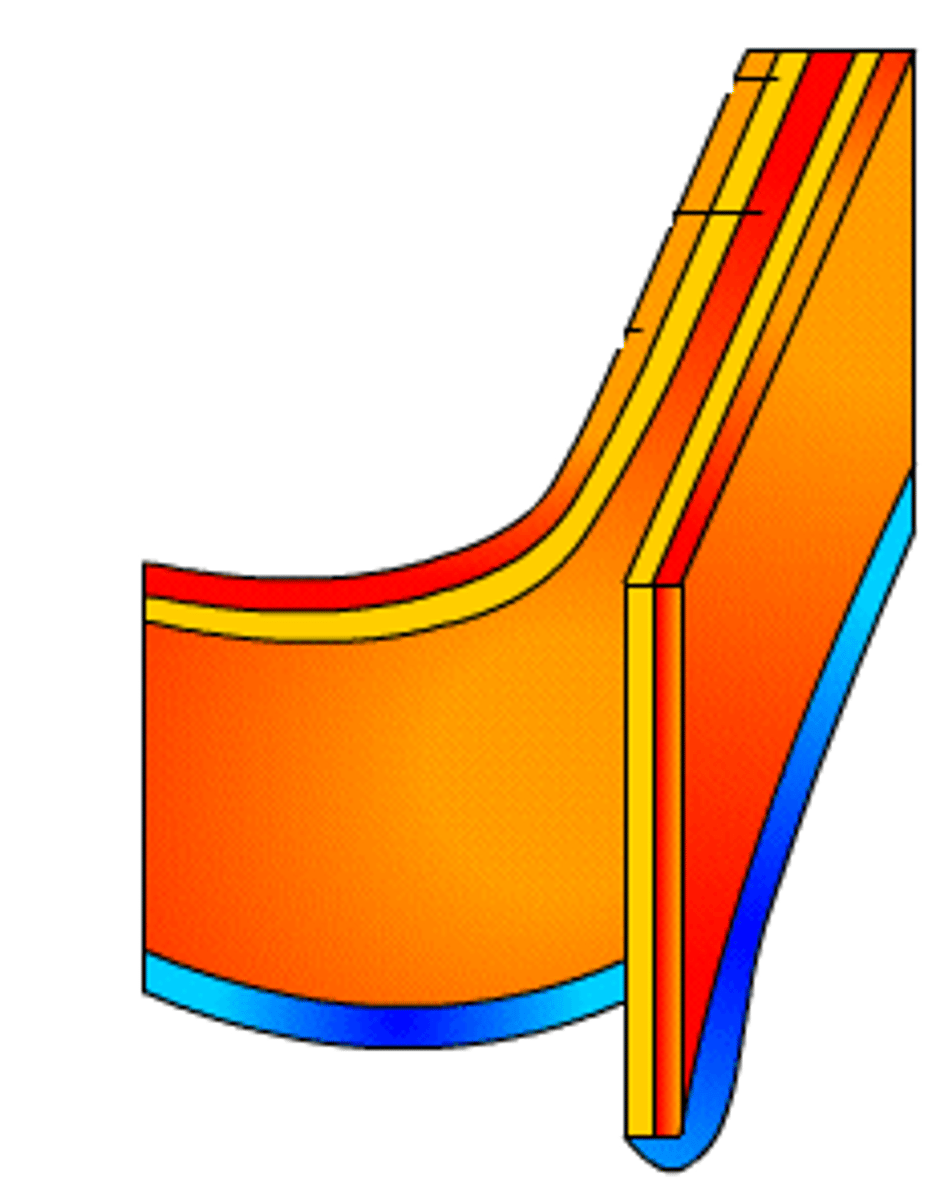
cytoskeleton
(A-Level)
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
Golgi apparatus
(A-Level)
An organelle found in eukaryotic cells responsible for the final stages of processing proteins for release by the cell.
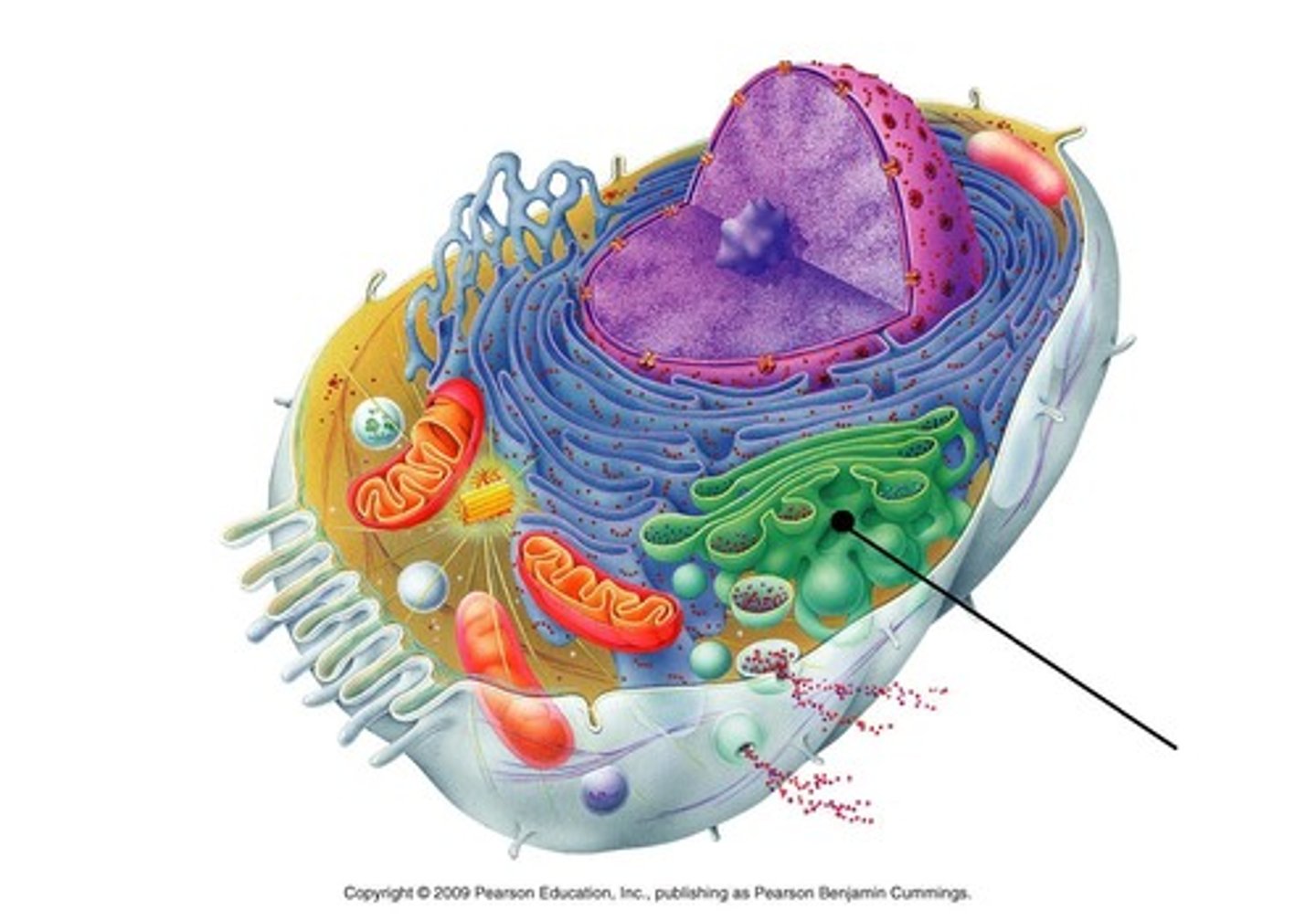
rough endoplasmic reticulum
(A-Level)
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasm. Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes. Functions in transport of substances such as proteins within the cytoplasm
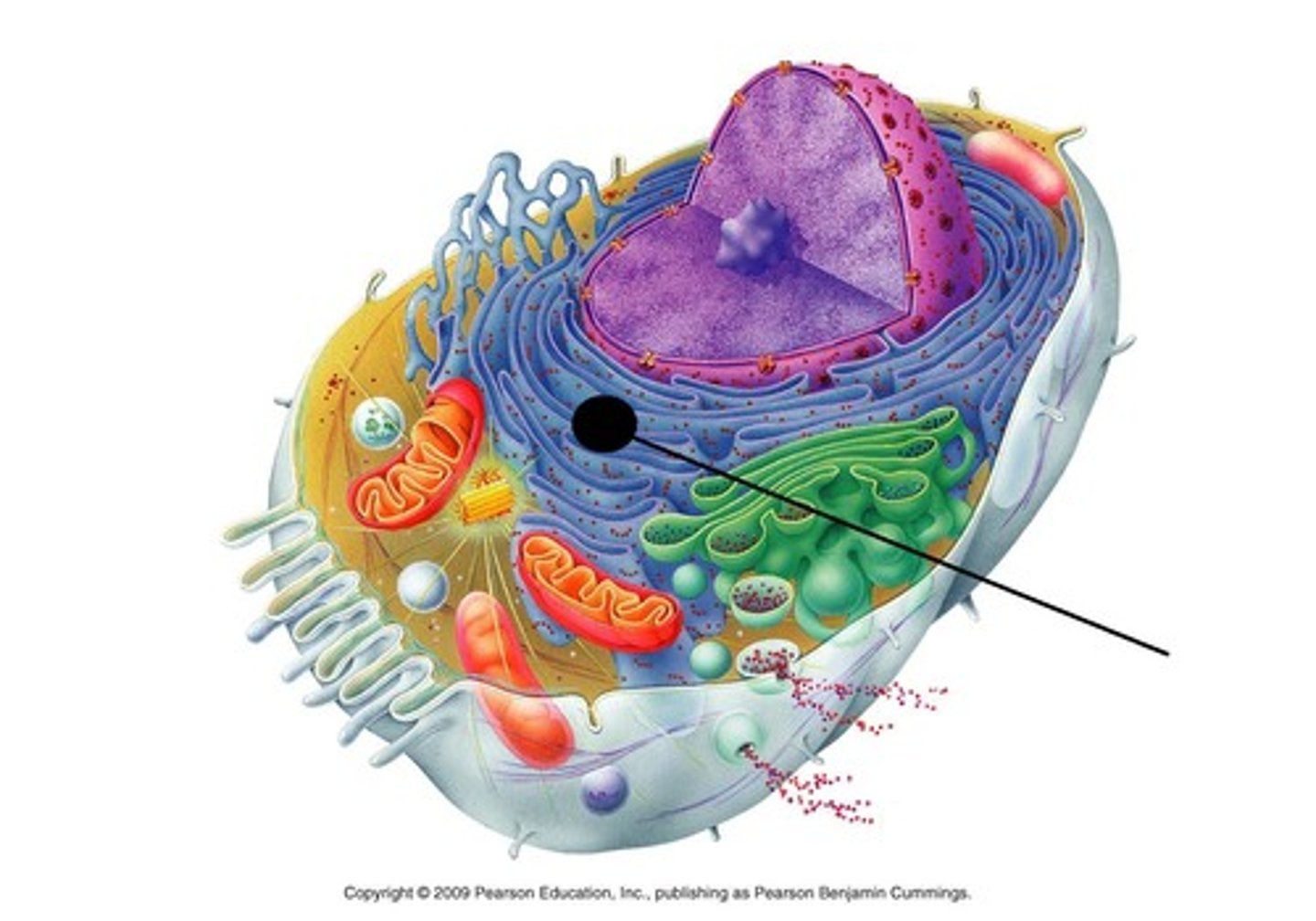
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(A-Level)
part of the endoplasmic reticulum that contains enzymes used for all sorts of processes
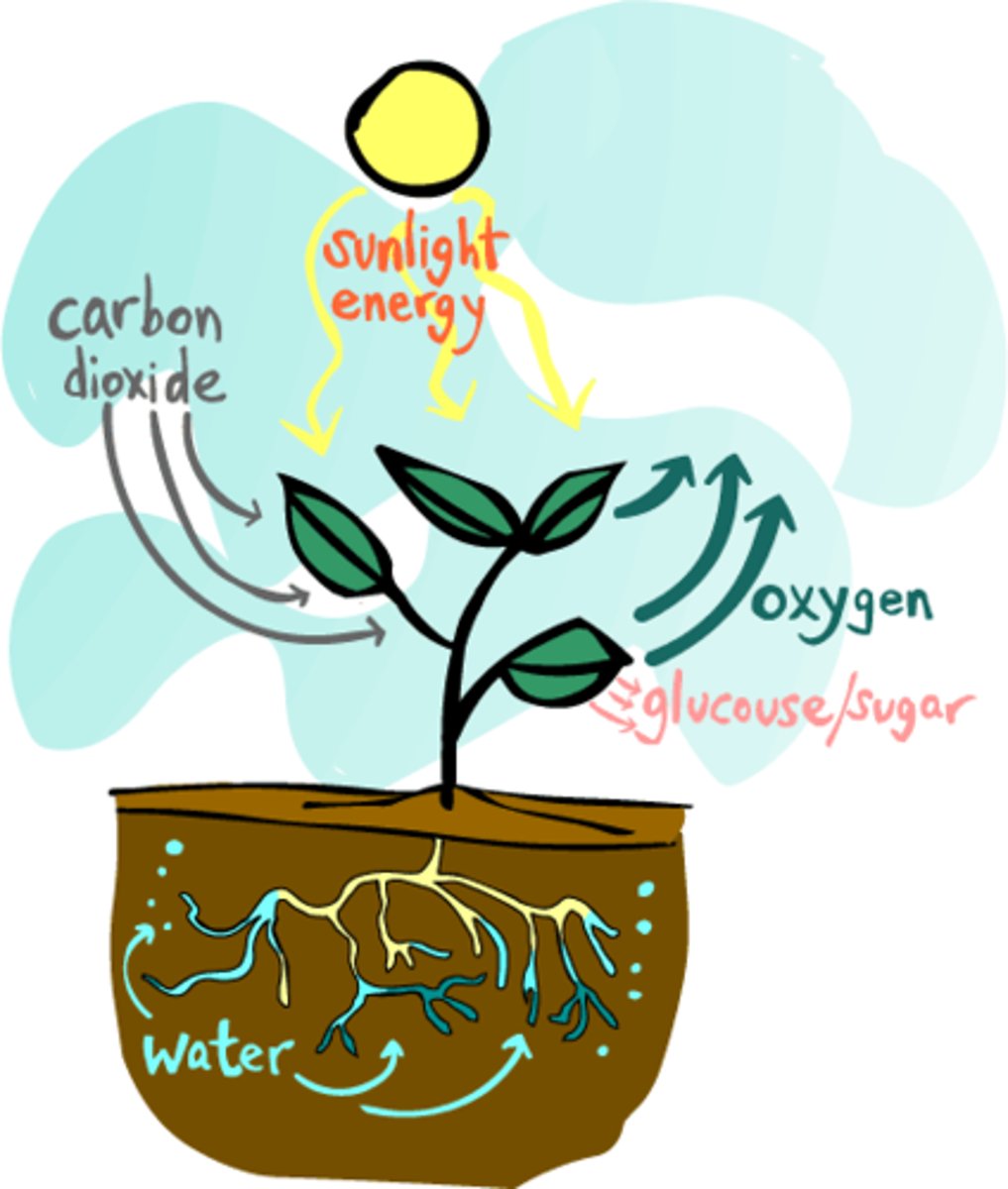
photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy.
6CO2 + 6H2O + light --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
glucose
A simple sugar that is an important source of energy.

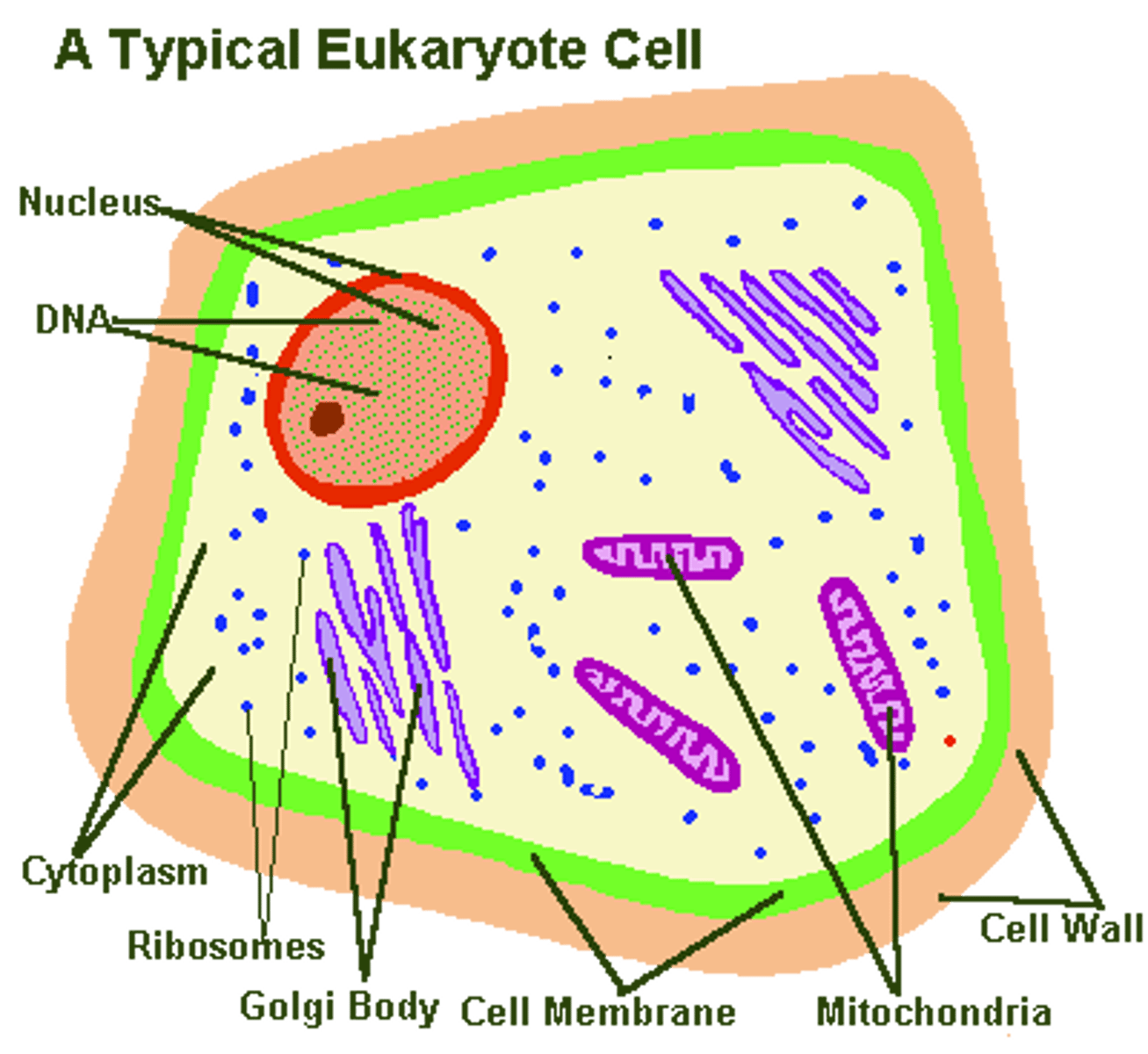
eukaryotes
Organisms whose cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles
prokaryotes
Cells that have no internal membranes or internal organelles, like nuclei or mitochondria.
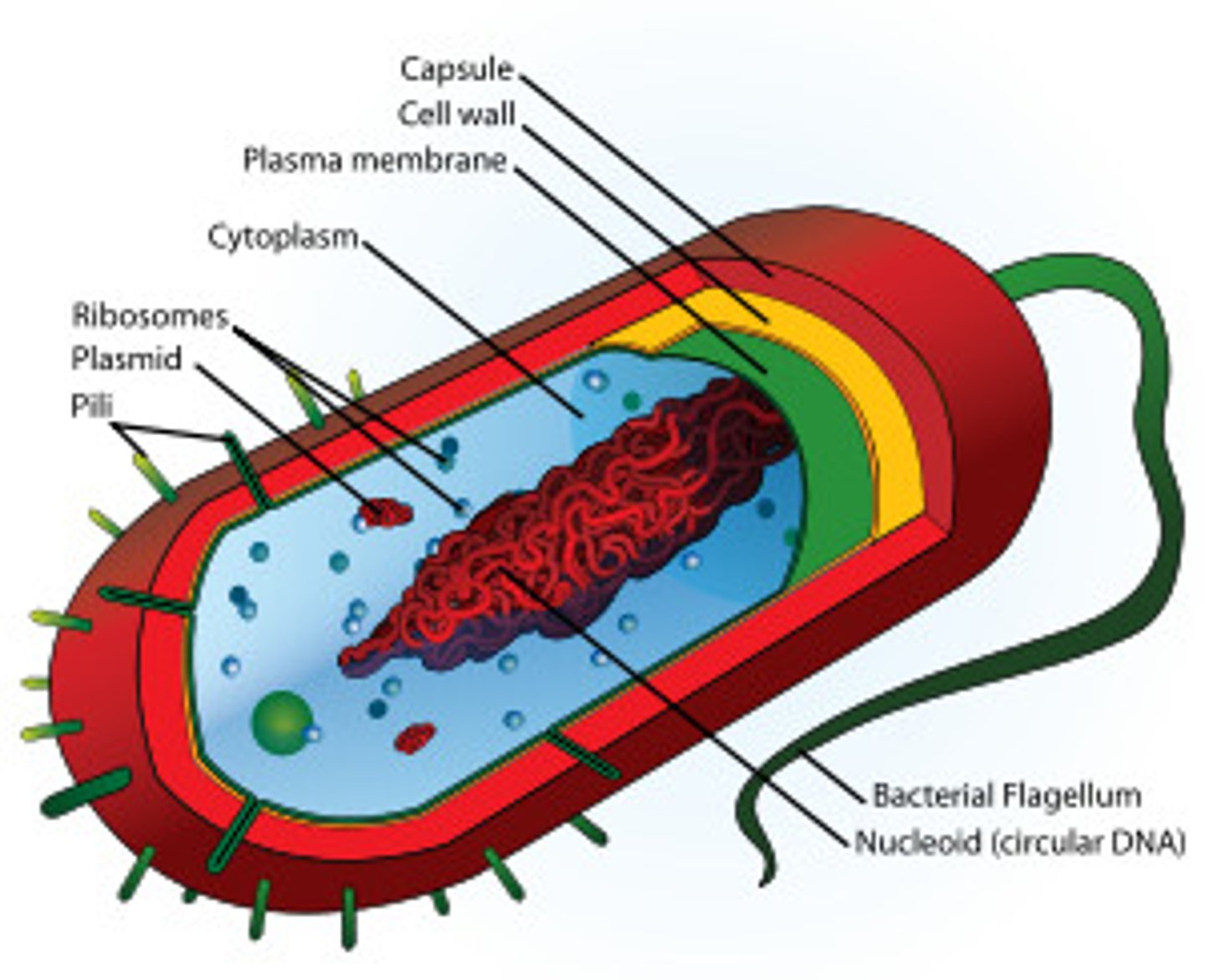
bacteria
Constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, they have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals.
plasmids
Small rings of DNA found naturally in some bacterial cells in addition to the main bacterial chromosome. Can contain genes for antibiotic resistance or other "contingency" functions.
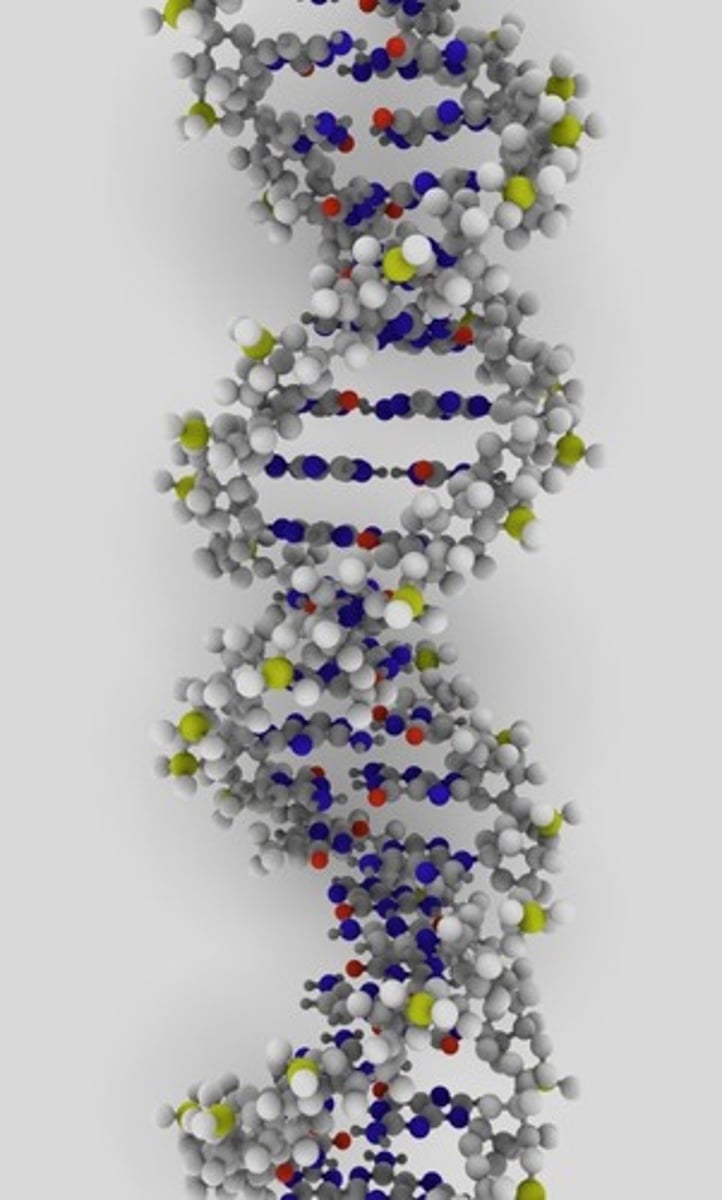
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
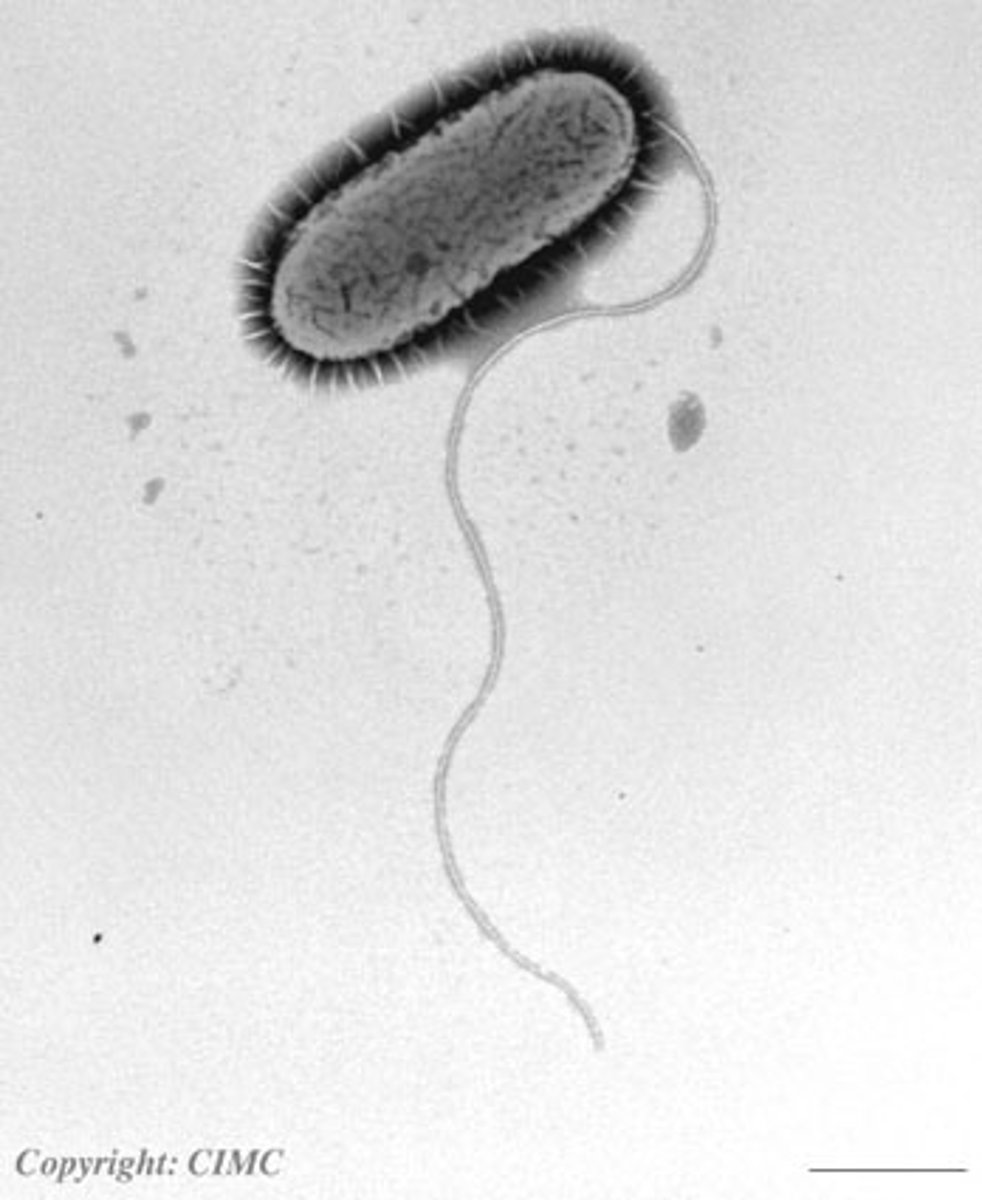
flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell movement. Many bacteria are flagellated, and sperm are flagellated.
neuron
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
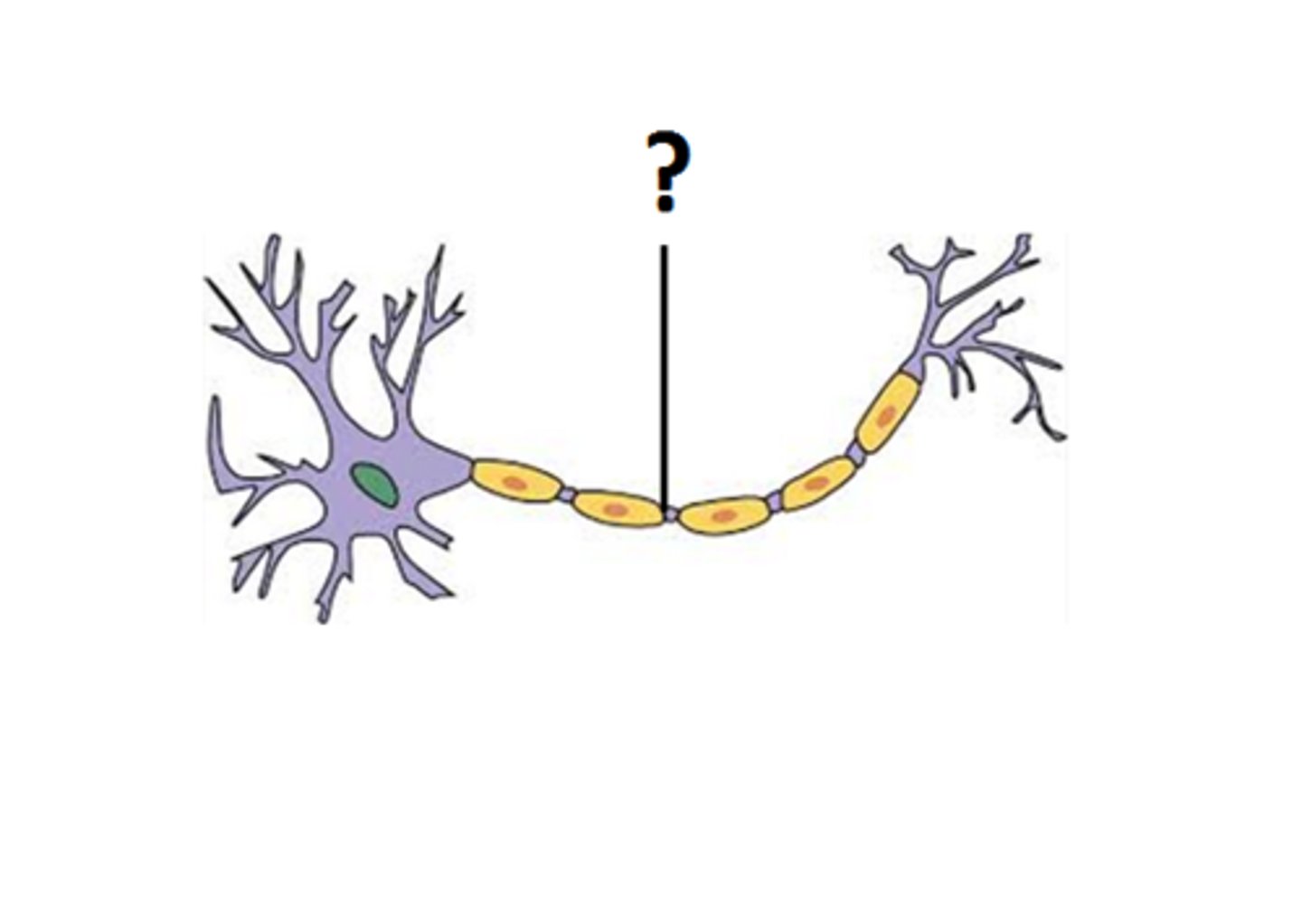
dendrites
A neuron's bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body.

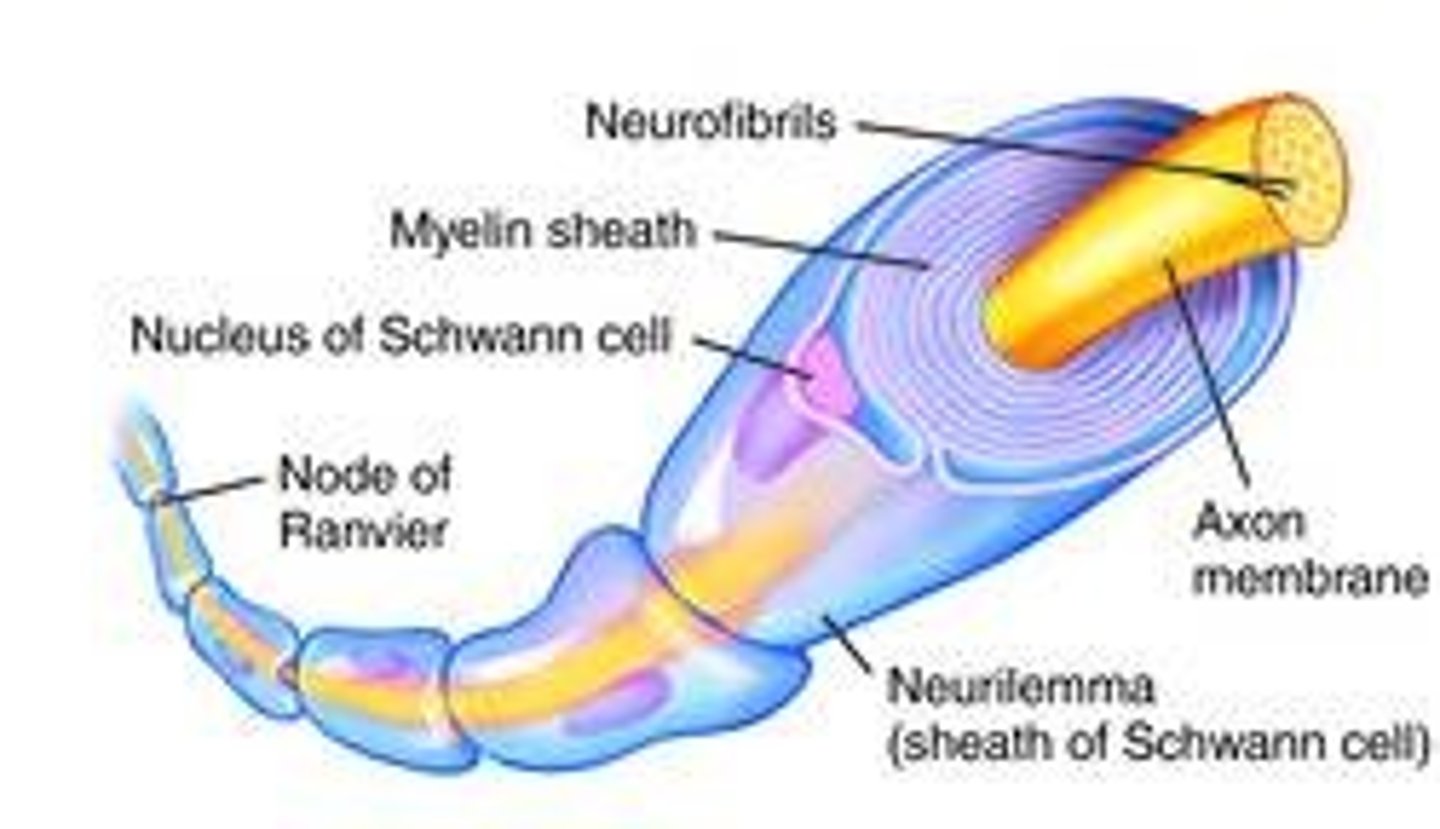
myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; insulates the cell and enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
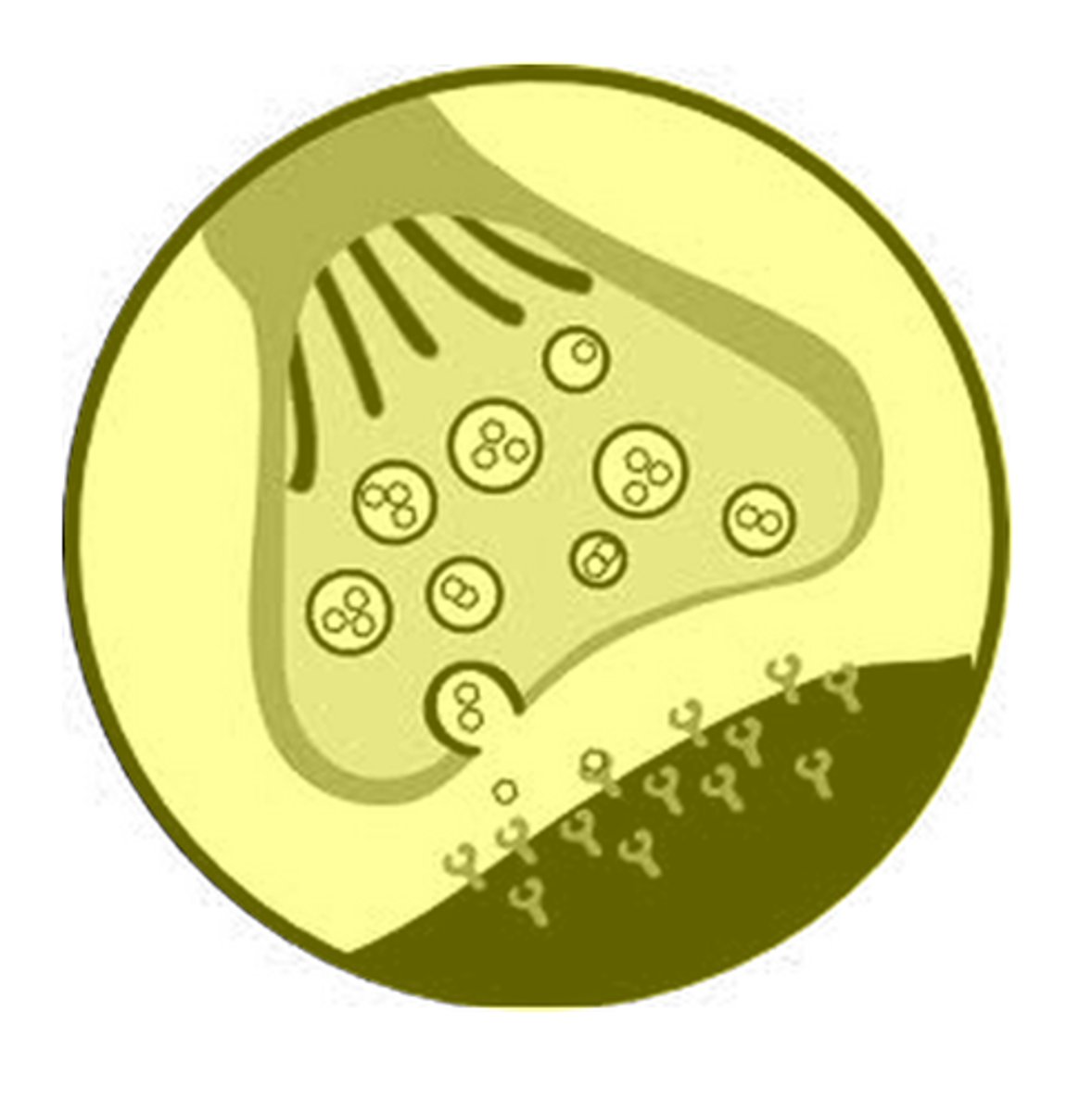
synapse
A junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to the next.
striated muscle cells
These cells are made up of fibres and can be much larger than normal animal cells, with lengths up to 300mm; they can also be multi-nucleated. Combine to make muscle tissue.
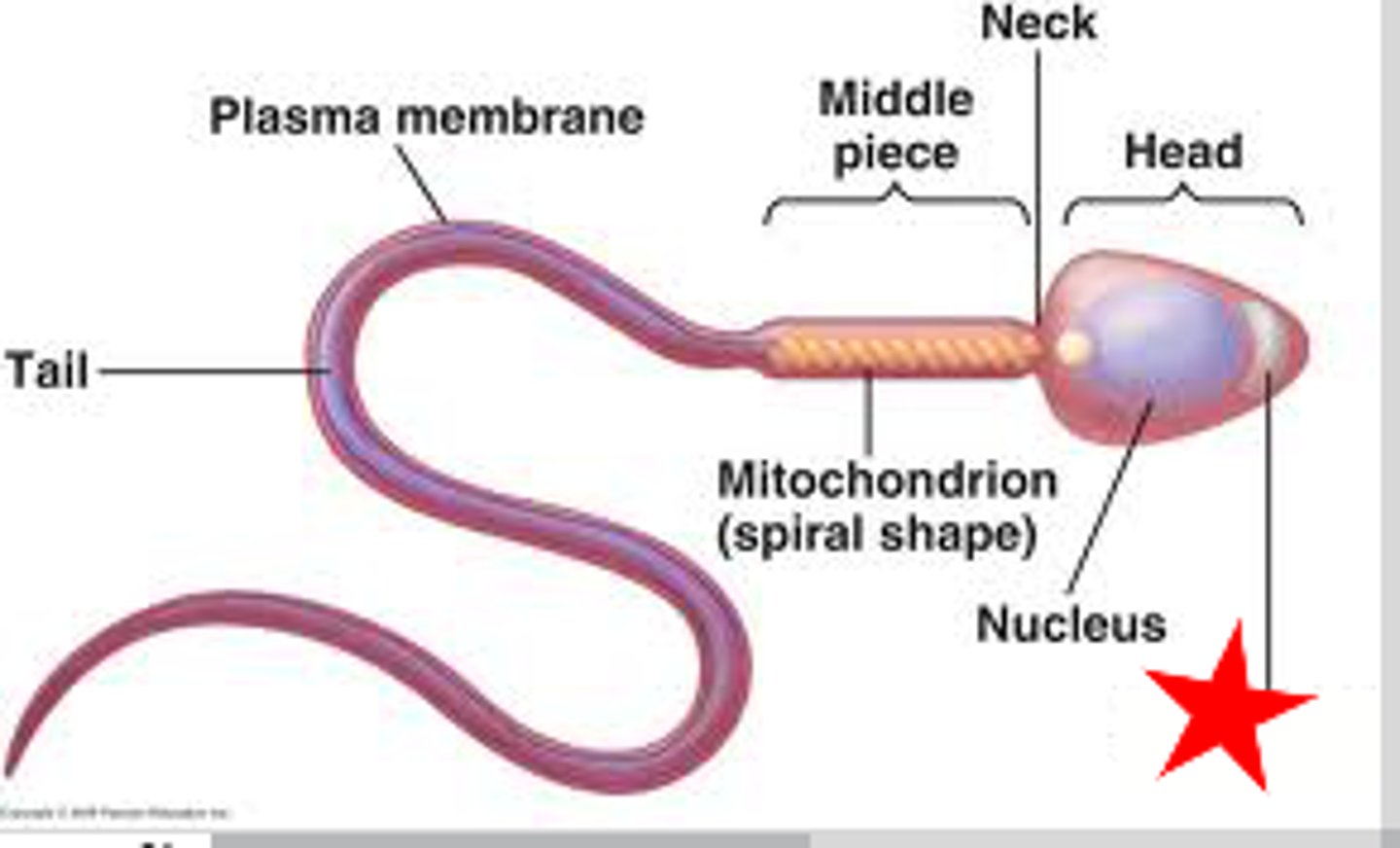
sperm
Male sex cell or gamete.

acrosome
A vesicle at the tip of a sperm cell that contains digestive enzymes to help the sperm penetrate the egg
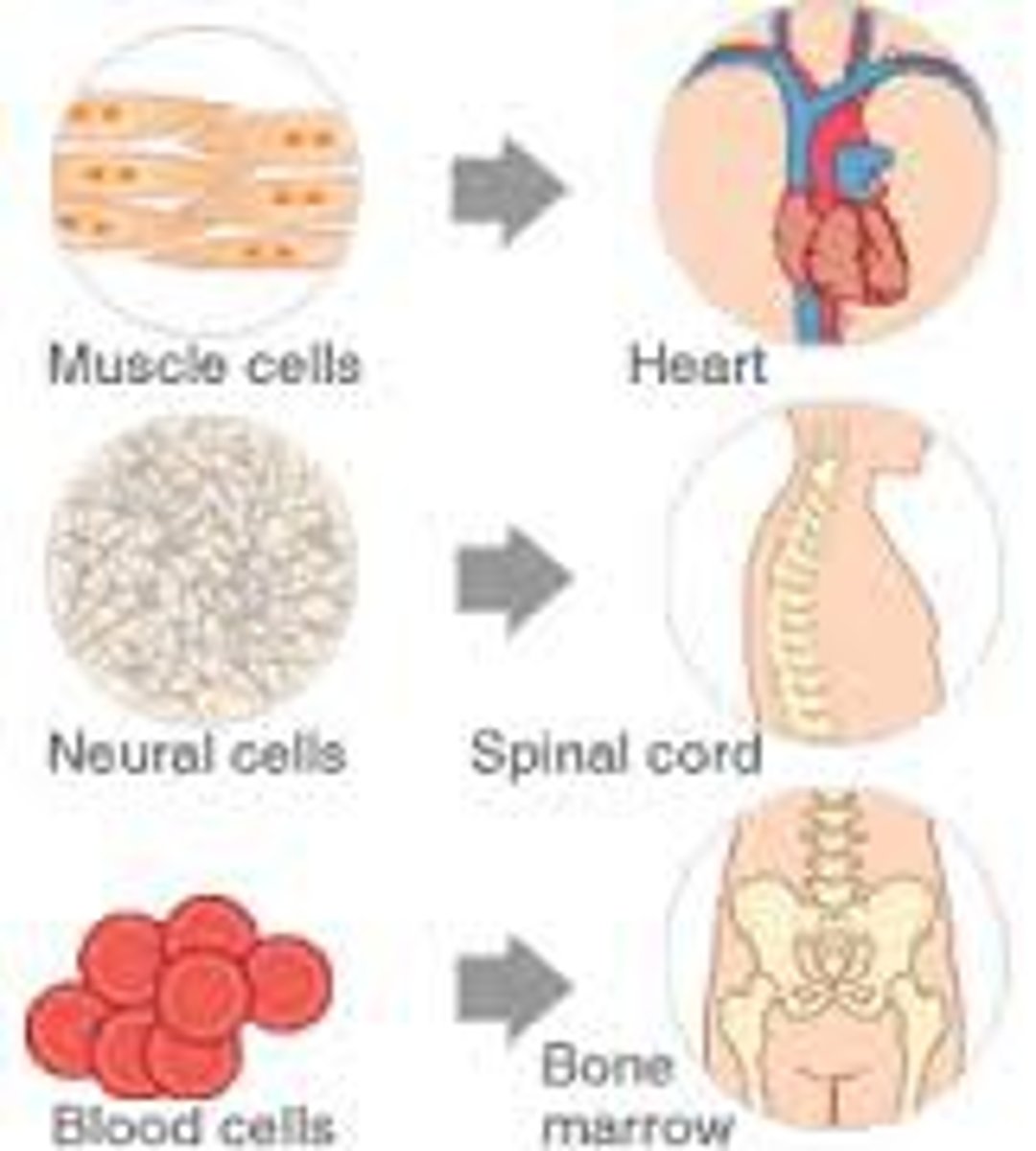
specialisation
The structural adaption of a cell to suit a particular function (Eg: Red blood cells have no nucleus to make room for space to carry oxygen).
tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
organ
A collection of tissues that carry out a specialized function of the body
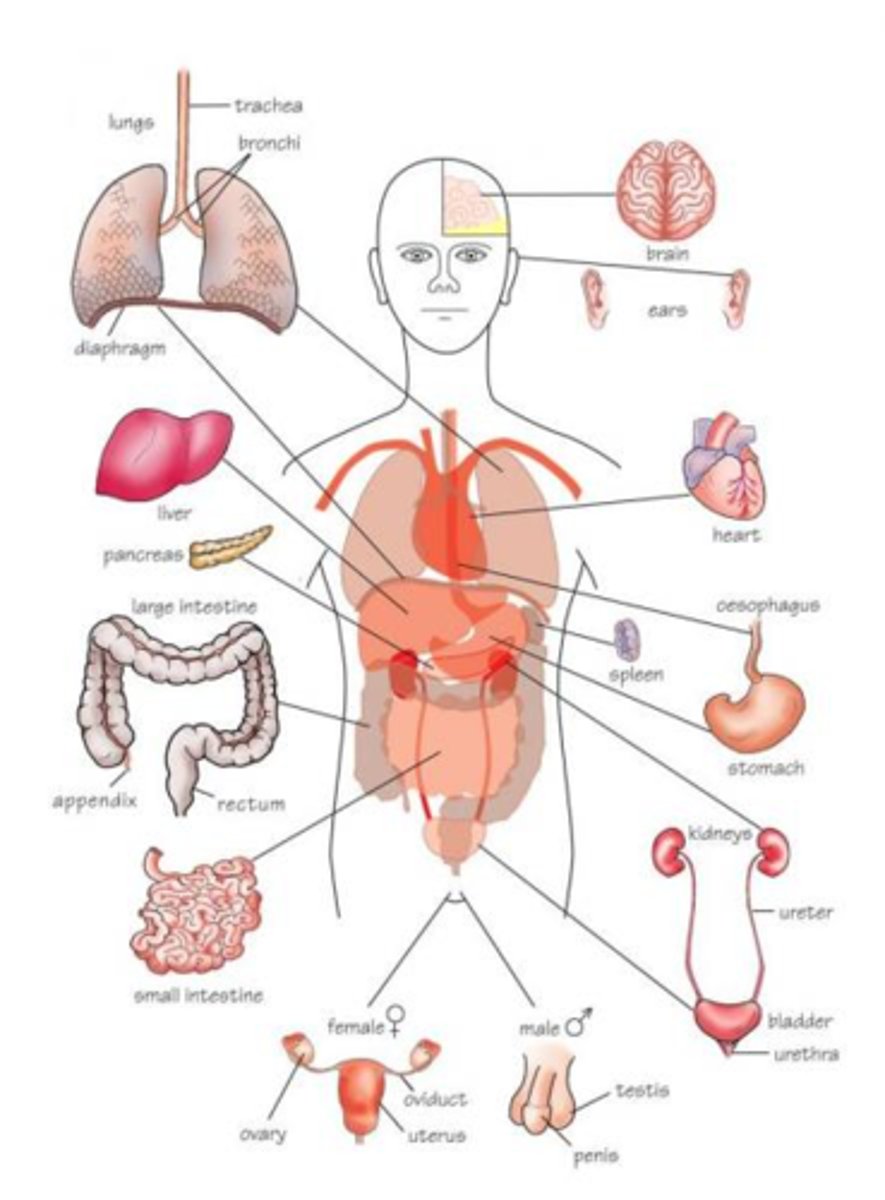
organ system
A group of organs that work together in performing vital body functions.
organism
A living thing

root hair cell
Cell found in roots. It has a large surface area to help the cell absorb water quickly.
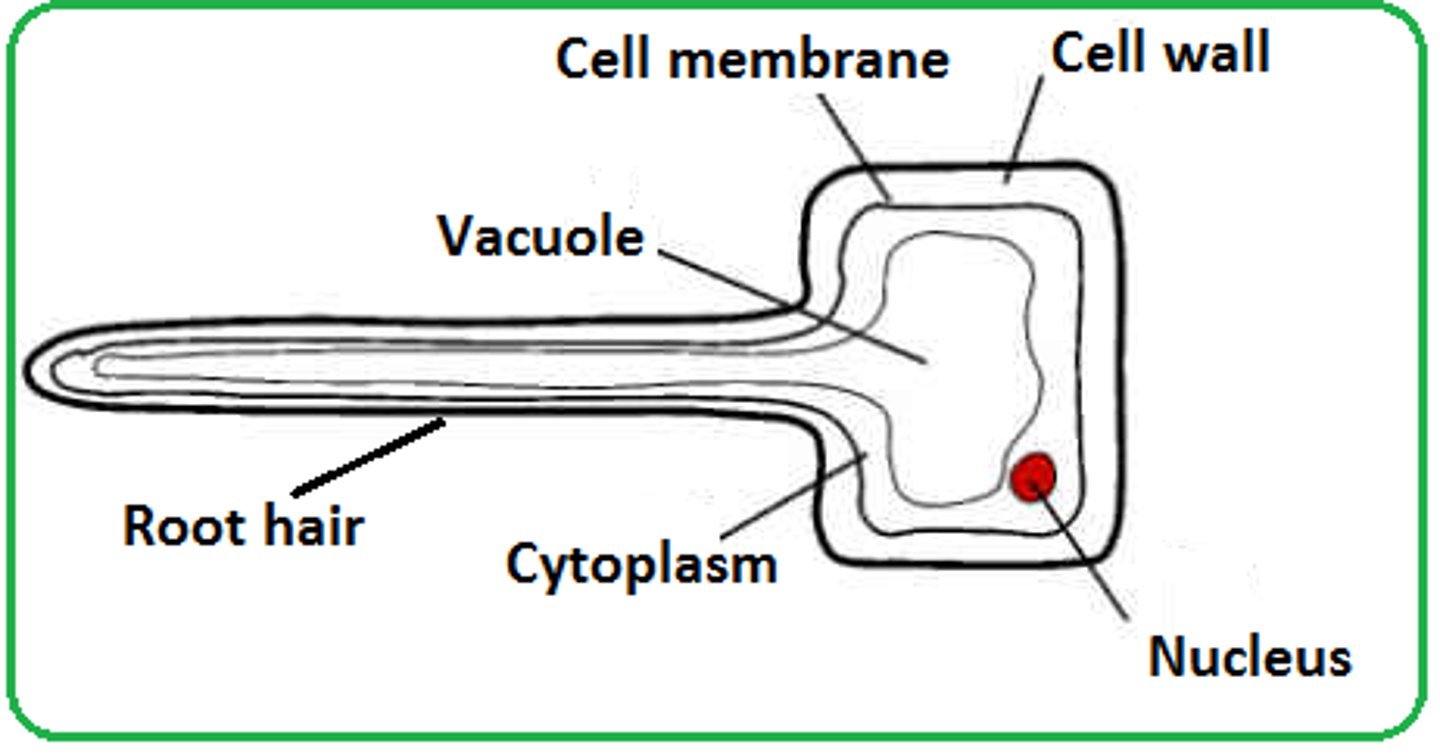
photosynthetic cell
Contains many chloroplasts for photosynthesis
phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant
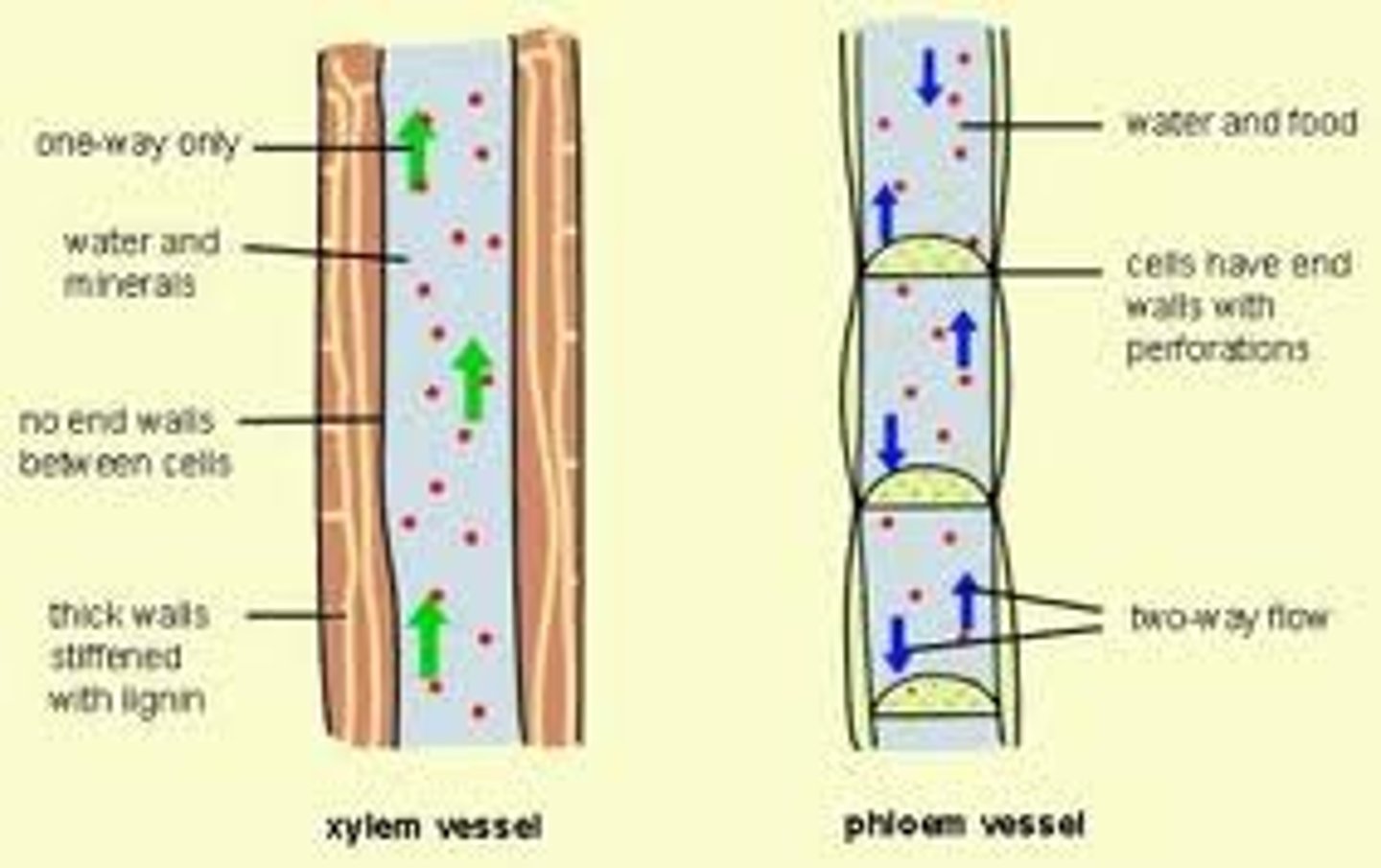
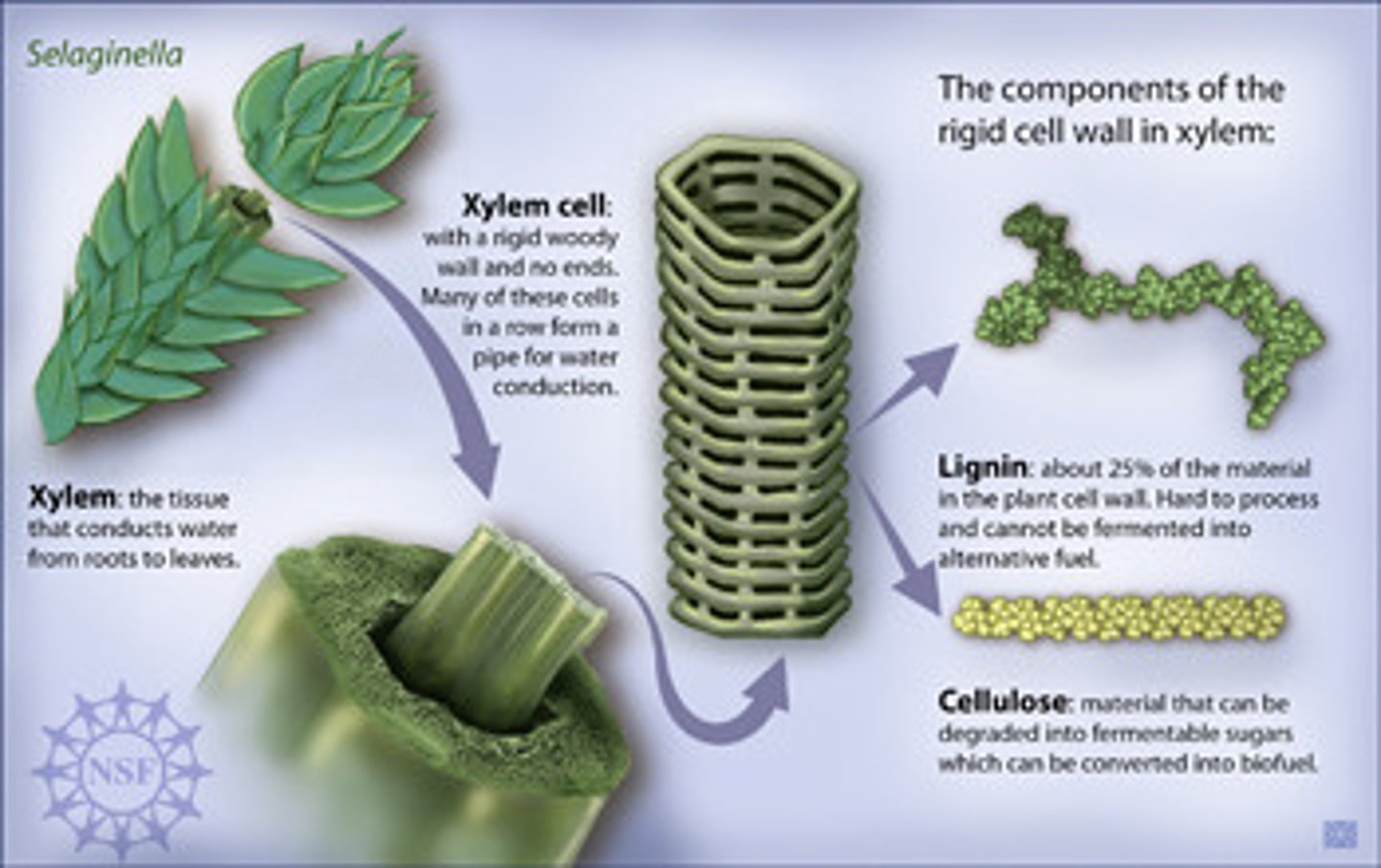
xylem
Nonliving vascular tissue that carries water and dissolved minerals from the roots of a plant to its leaves
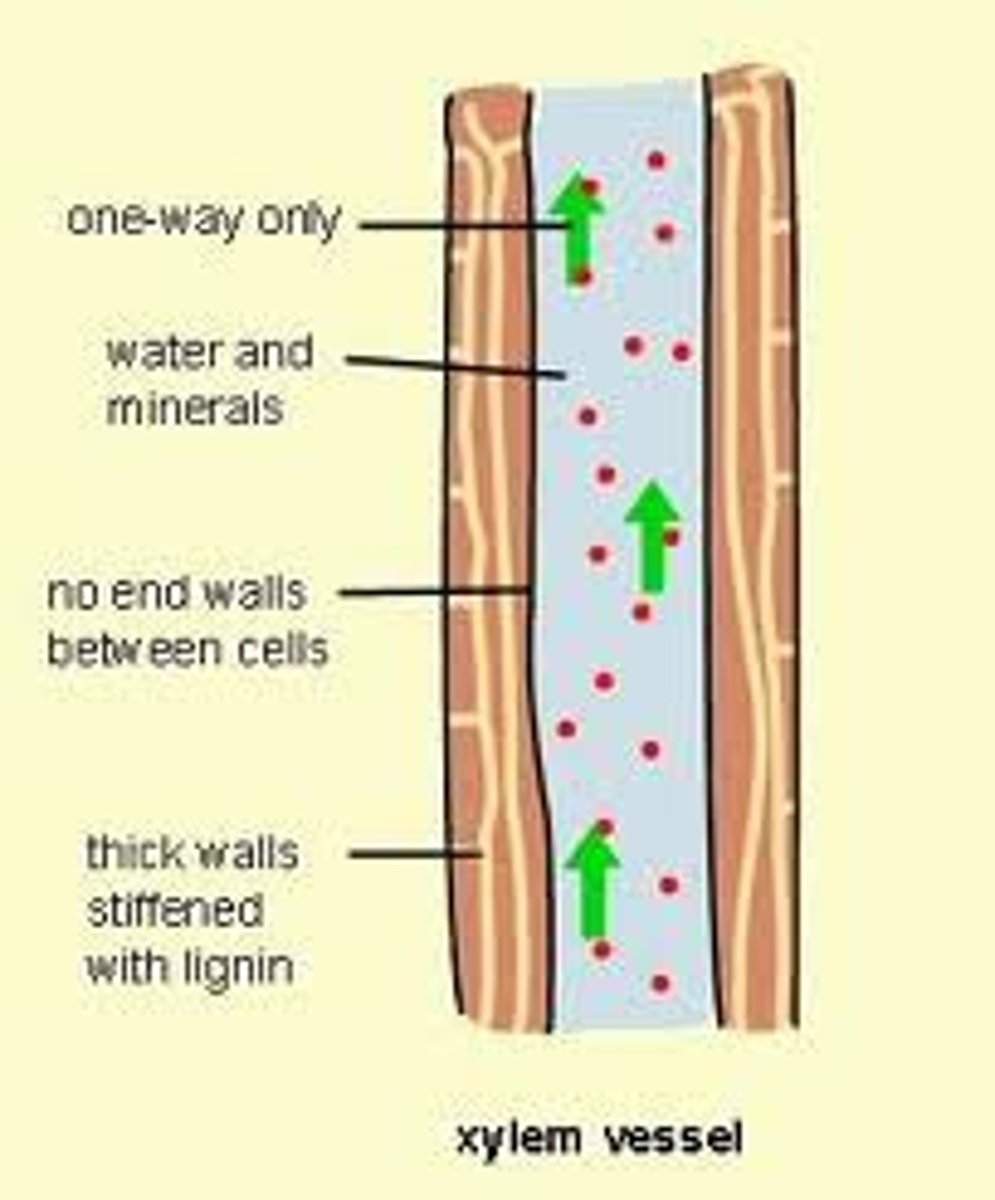
lignin
substance in vascular plants that makes cell walls rigid
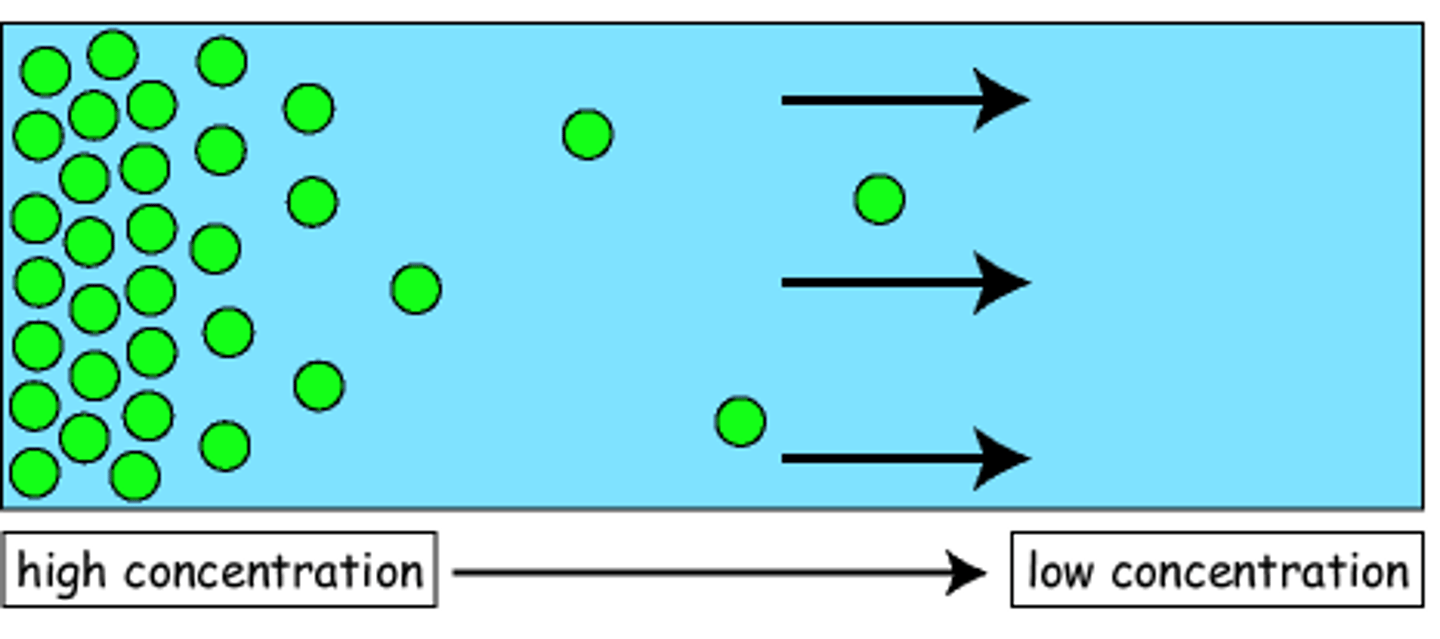
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
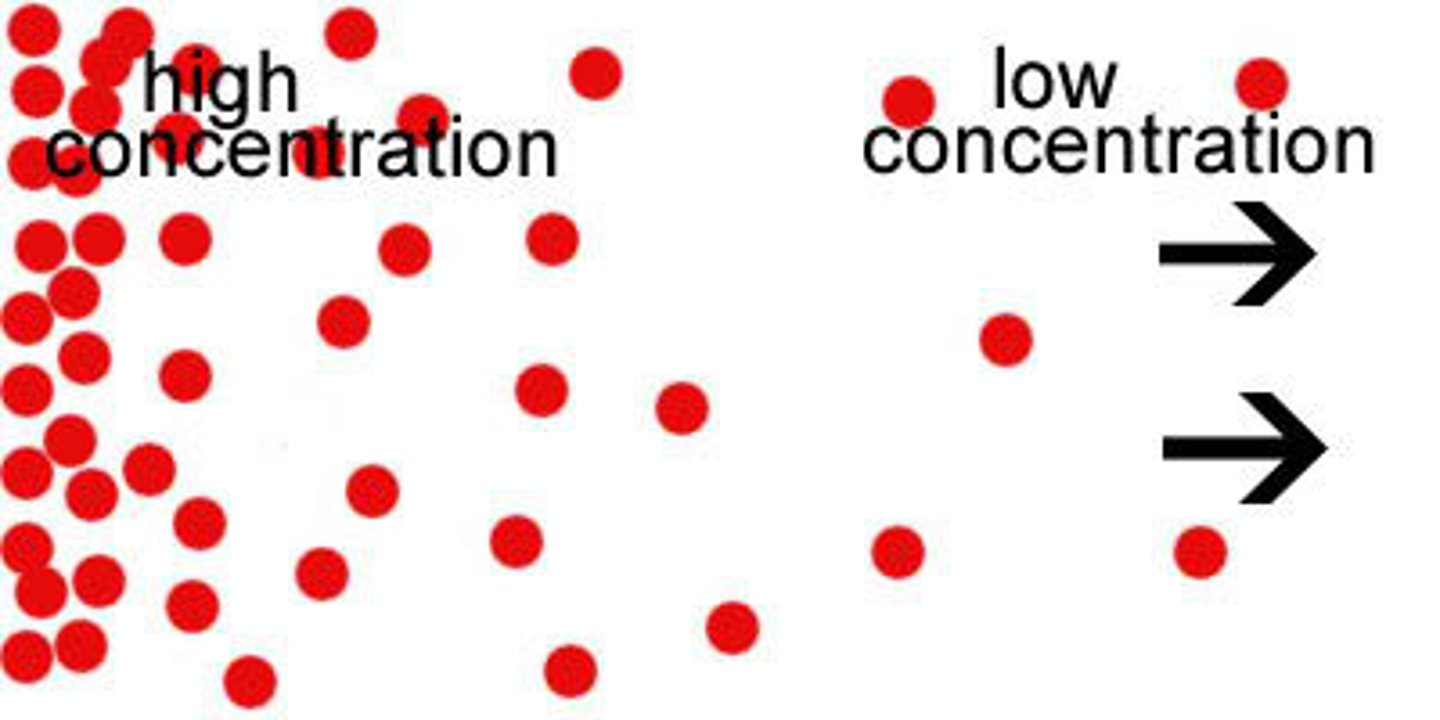
concentration gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a distance.
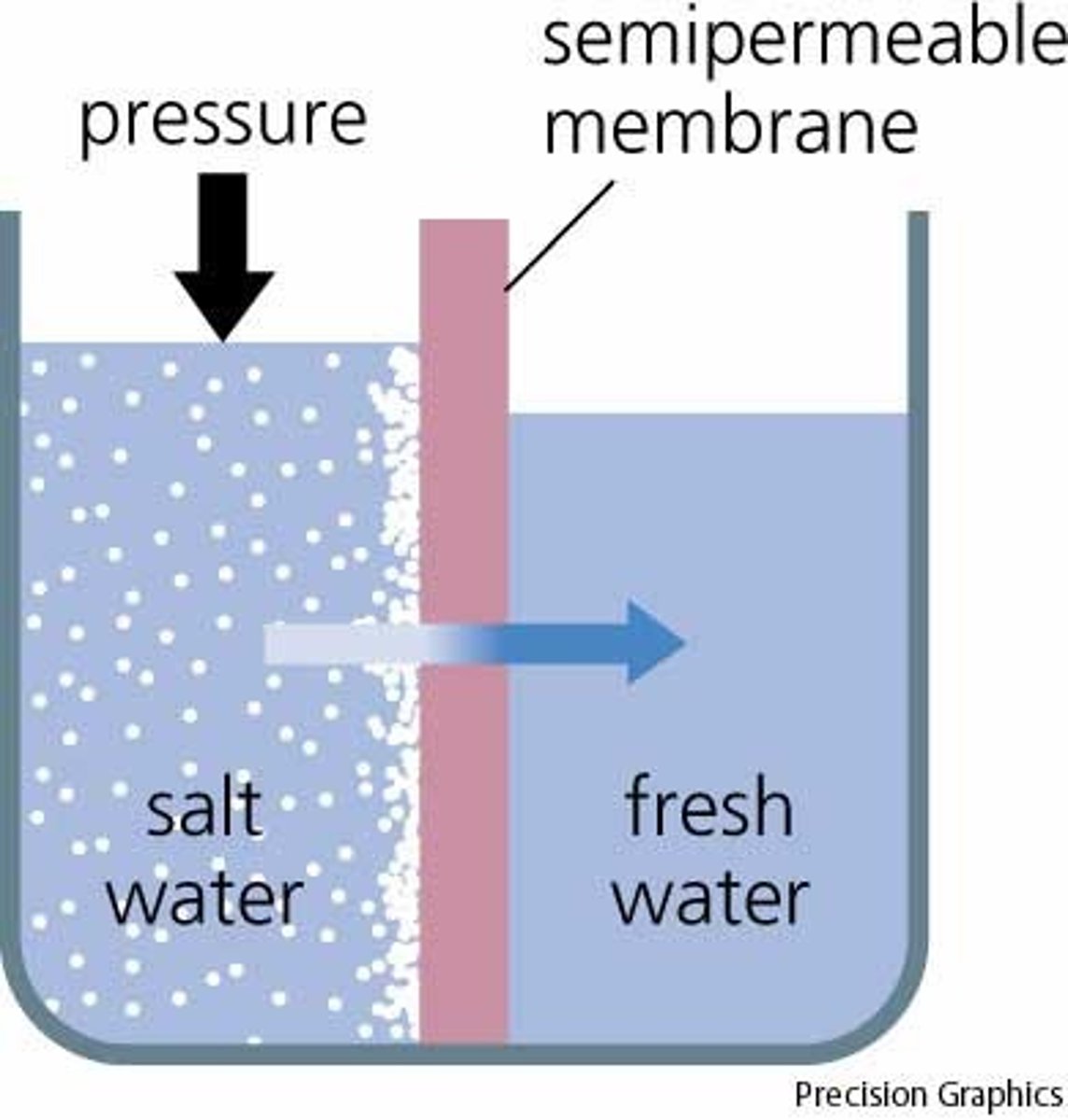
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
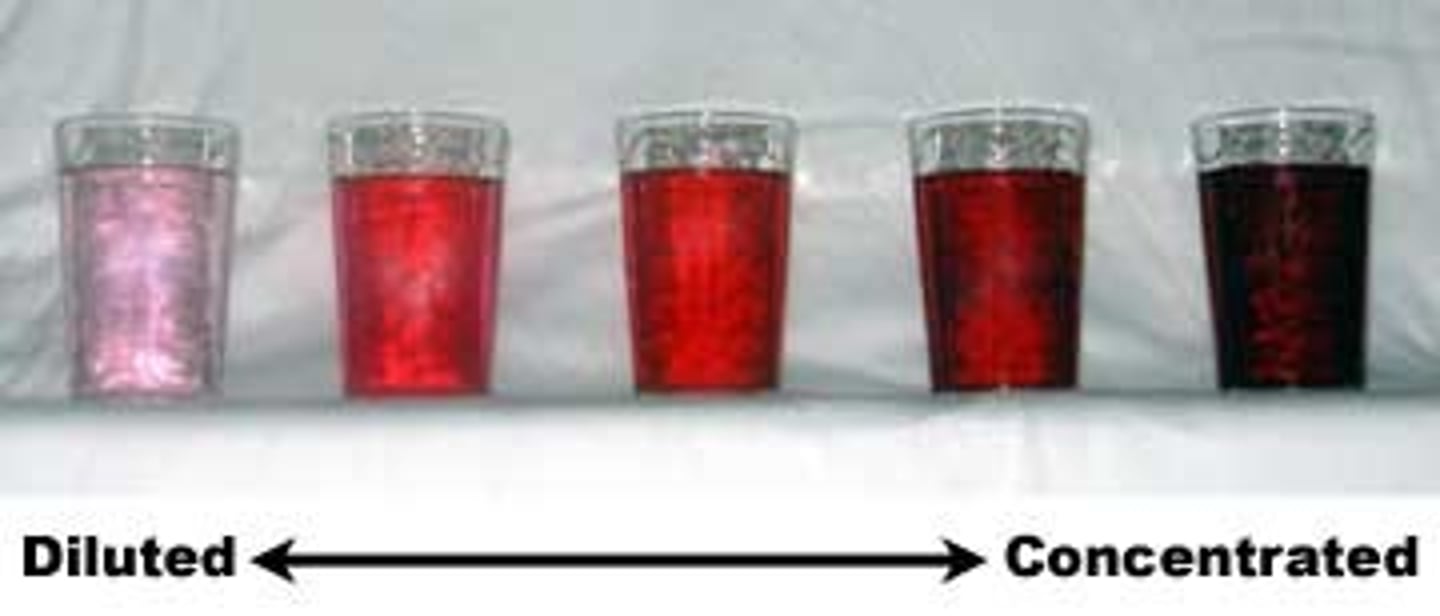
dilute solution
a solution that contains a small amount of solute
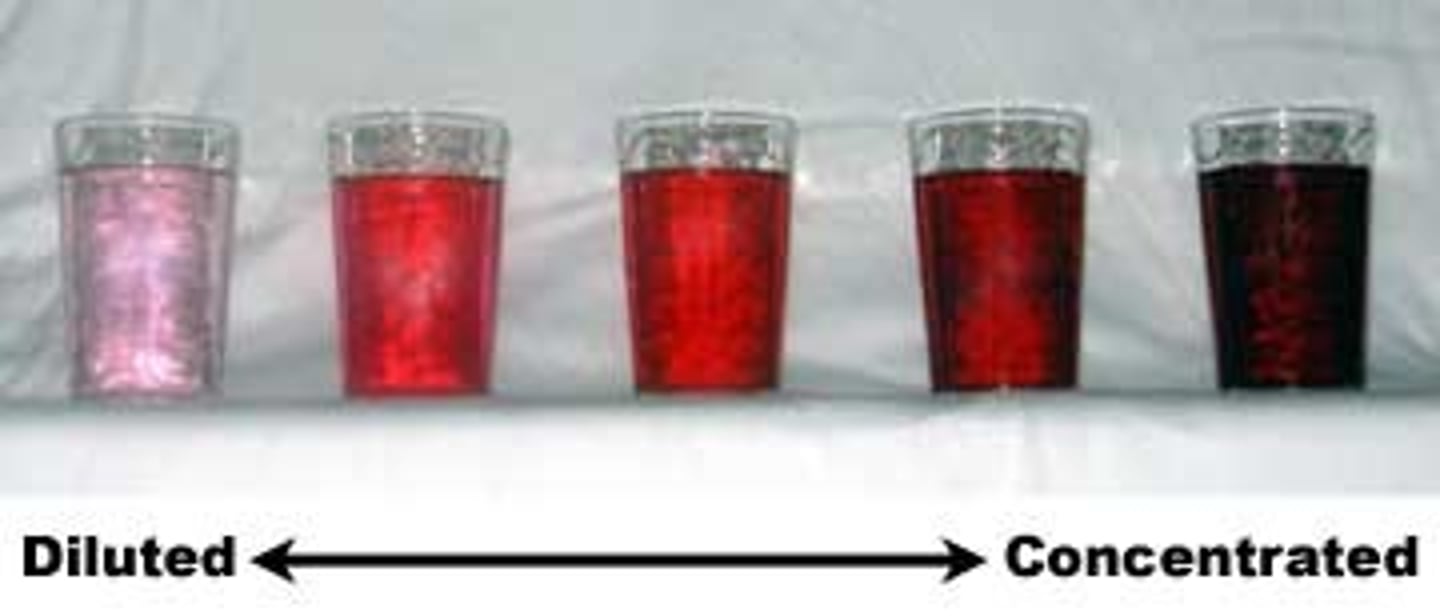
concentrated solution
a solution containing a large amount of solute
partially permeable membrane
A membrane that is permeable to certain substances, such as water, but is not permeable to other substances.
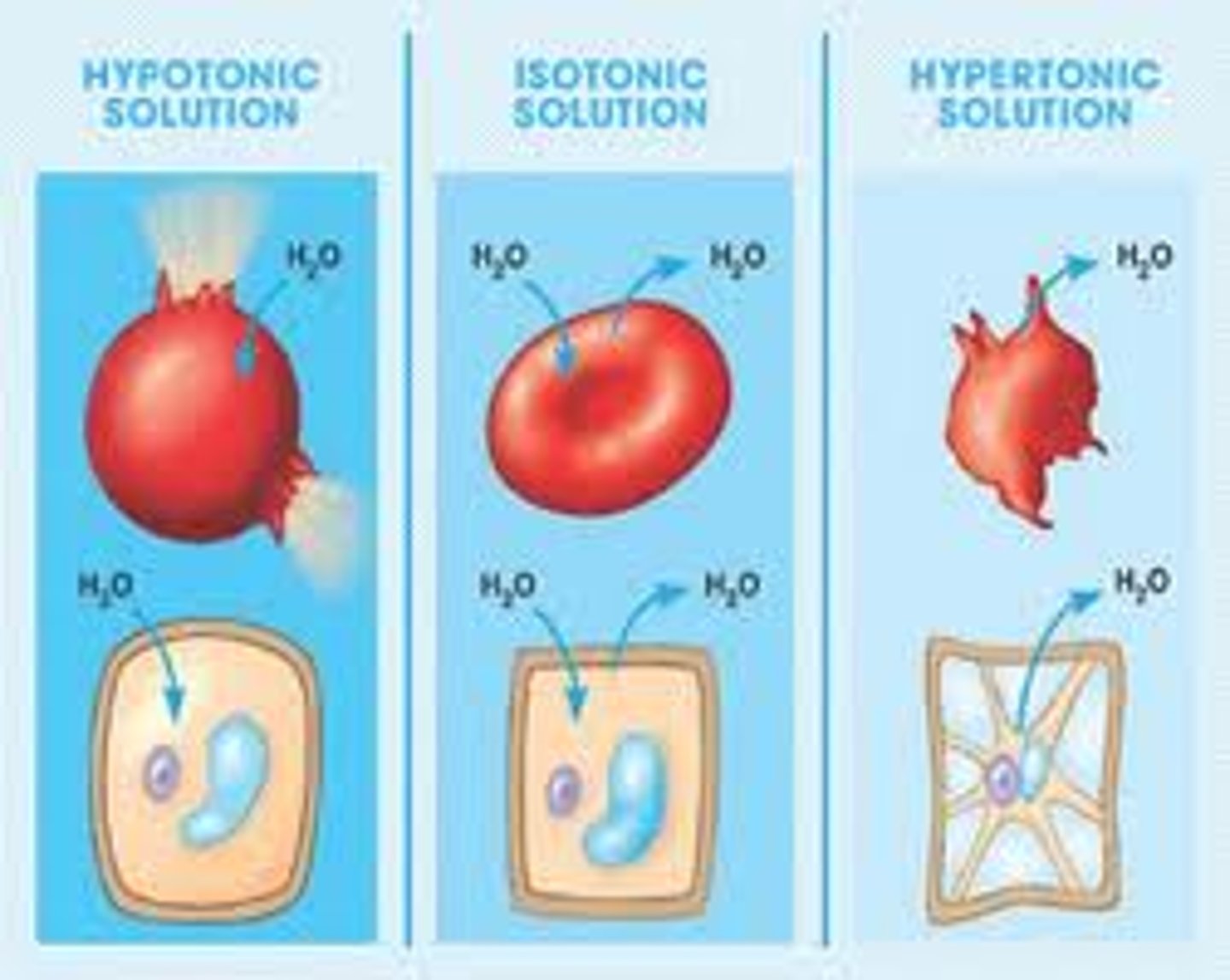
isotonic
Having the same solute concentration as another solution.
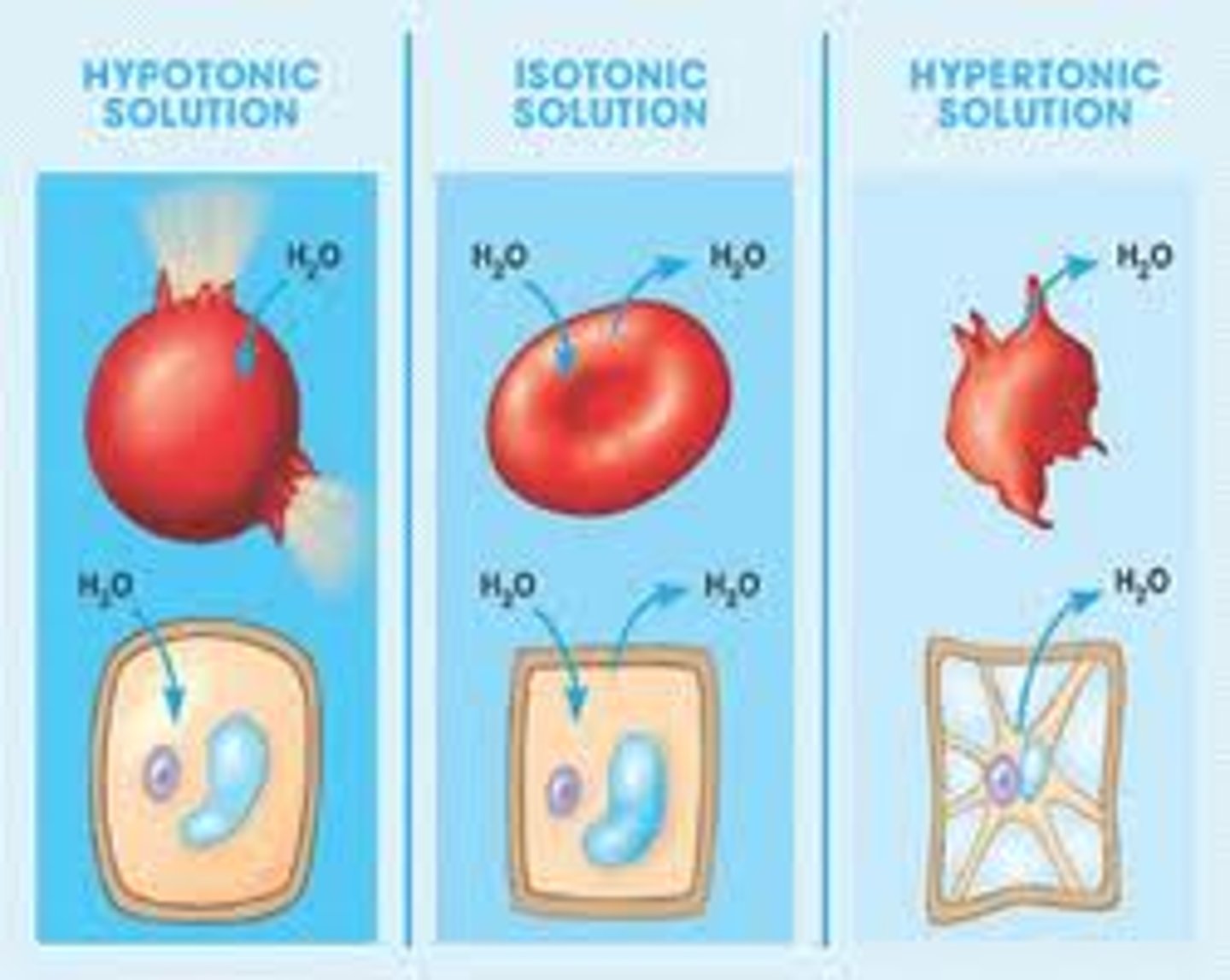
hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
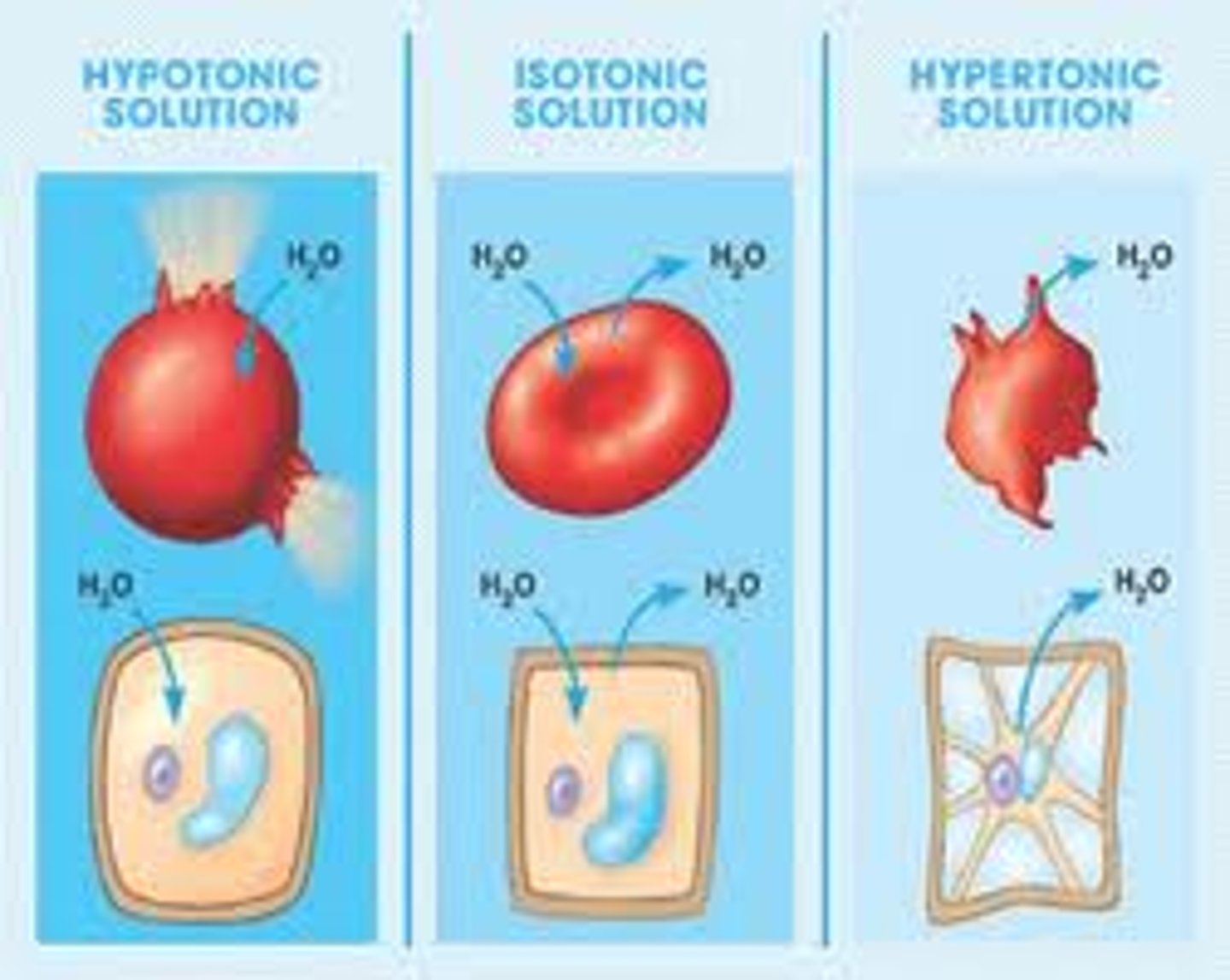
hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
soluble
Capable of being dissolved

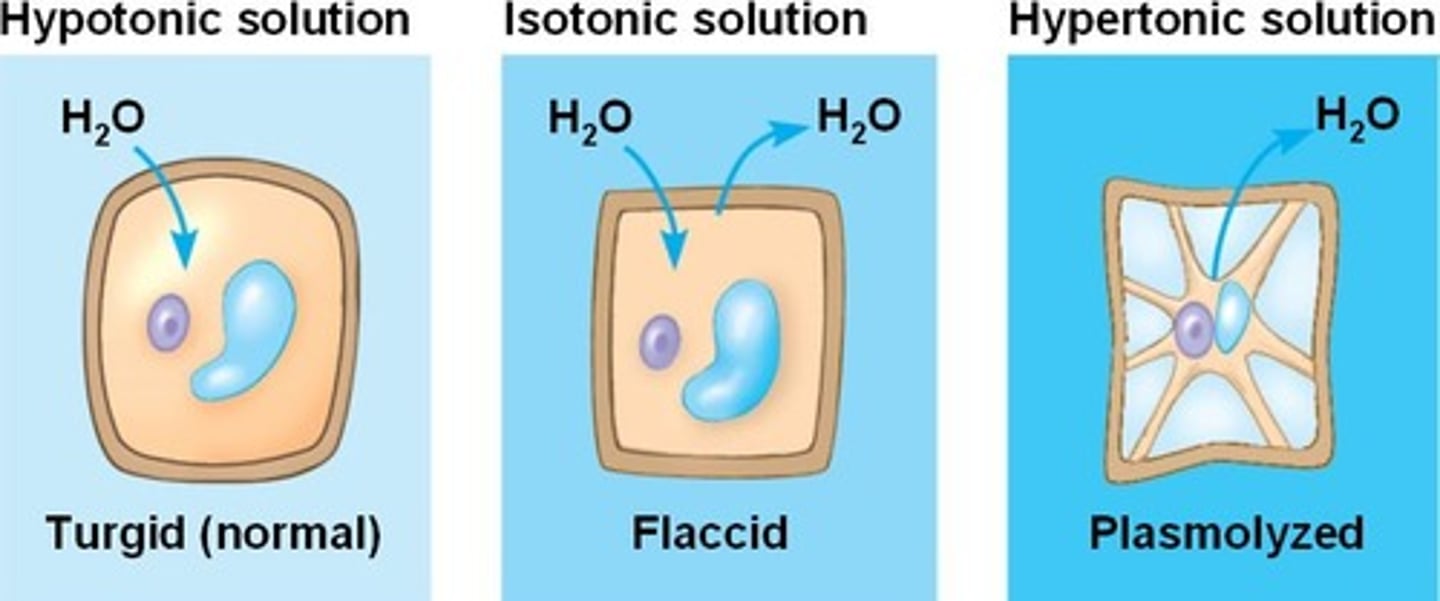
turgor
Condition of being distended or swollen; normal fullness

plasmolysis
A phenomenon in walled cells in which the cytoplasm shrivels and the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall; occurs when the cell loses water to a hypertonic environment.
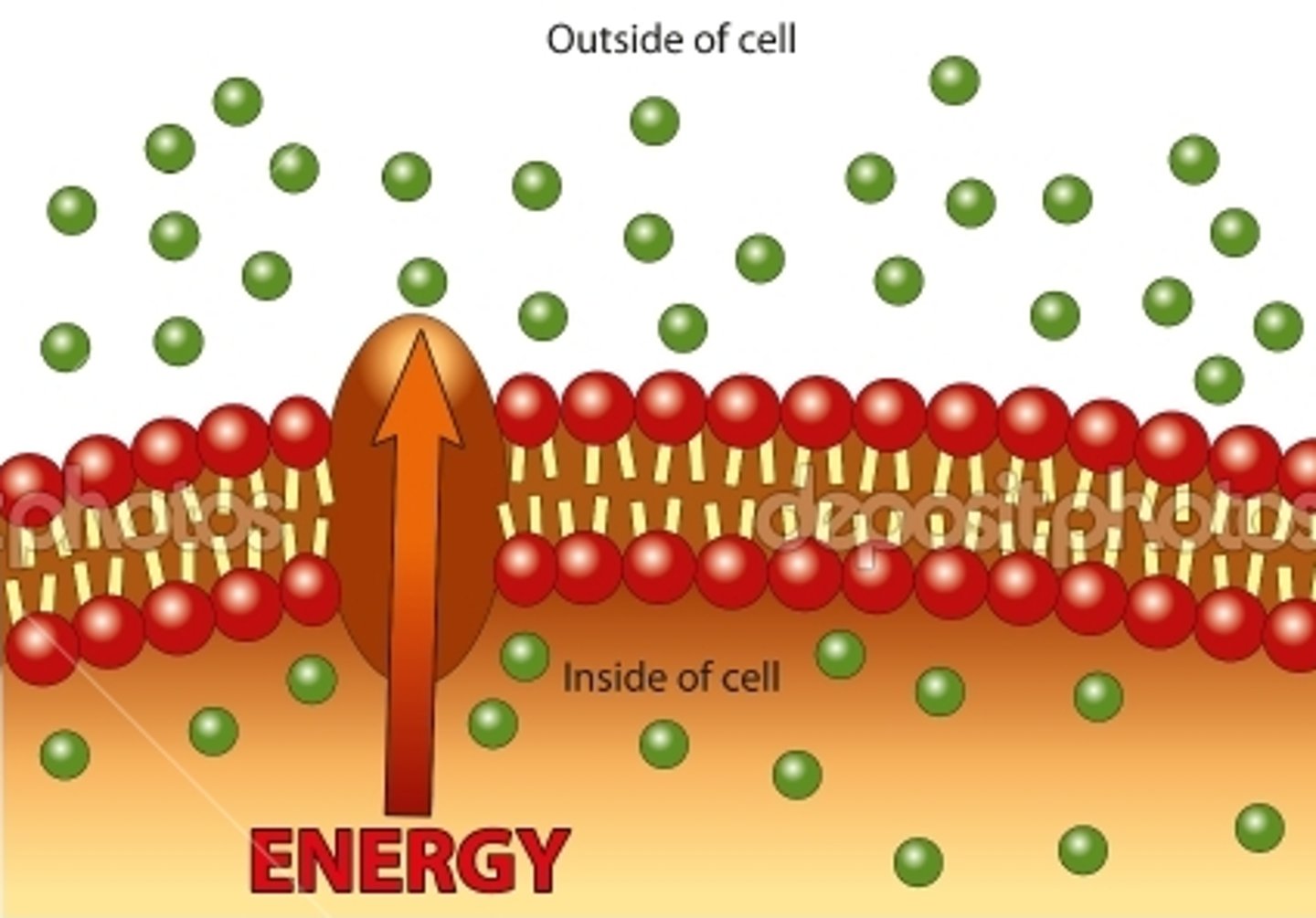
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
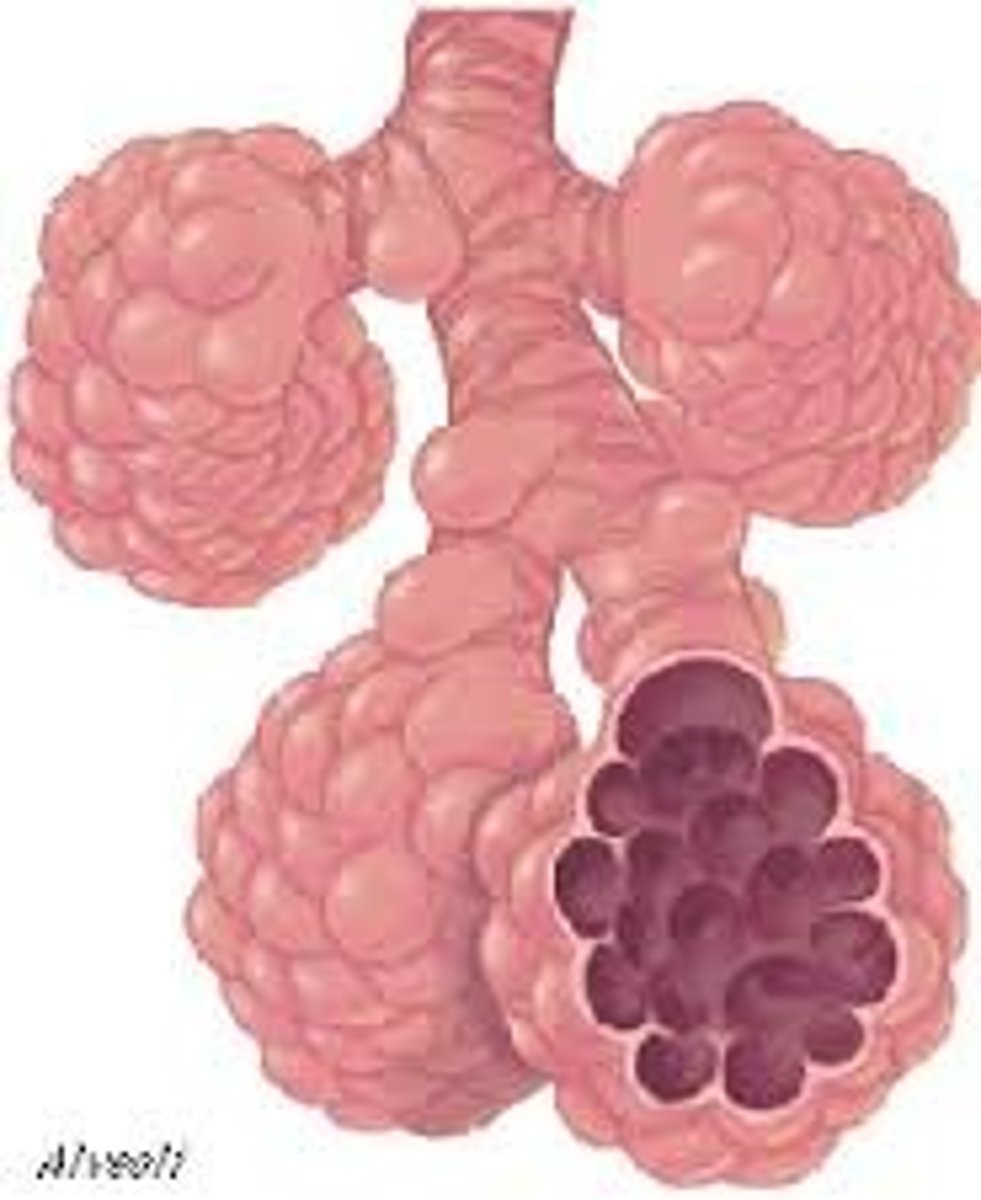
alveoli
(singular alveolus) Tiny sacs, with walls only a single cell layer thick, found at the end of the respiratory bronchiole tree. They are the site of gas exchange in the respiratory system.
stomata
A microscopic pore surrounded by guard cells in the epidermis of leaves and stems that allows gas exchange between the environment and the interior of the plant.
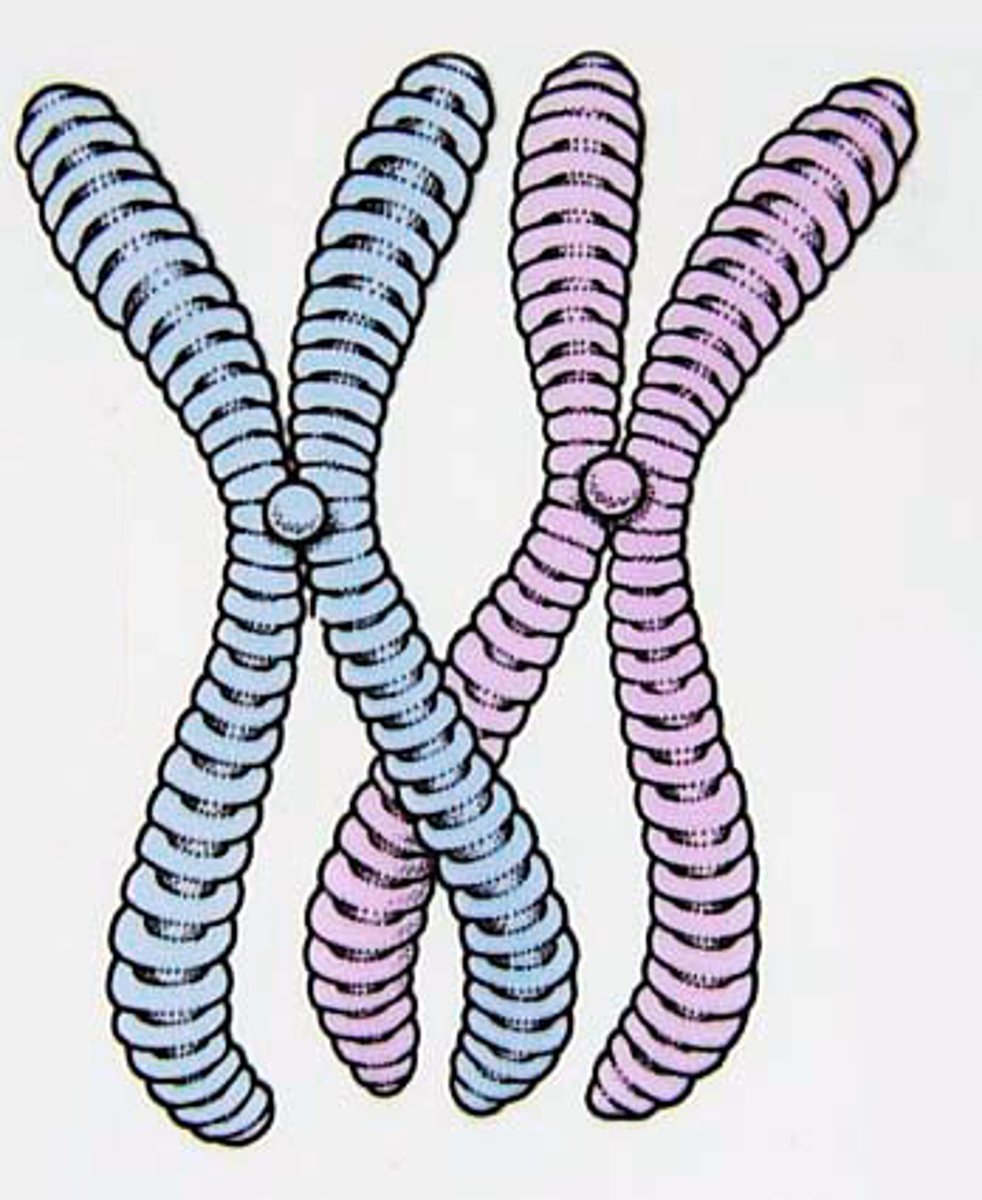
chromosomes
A cellular structure carrying genetic material, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Each consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins
cell cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
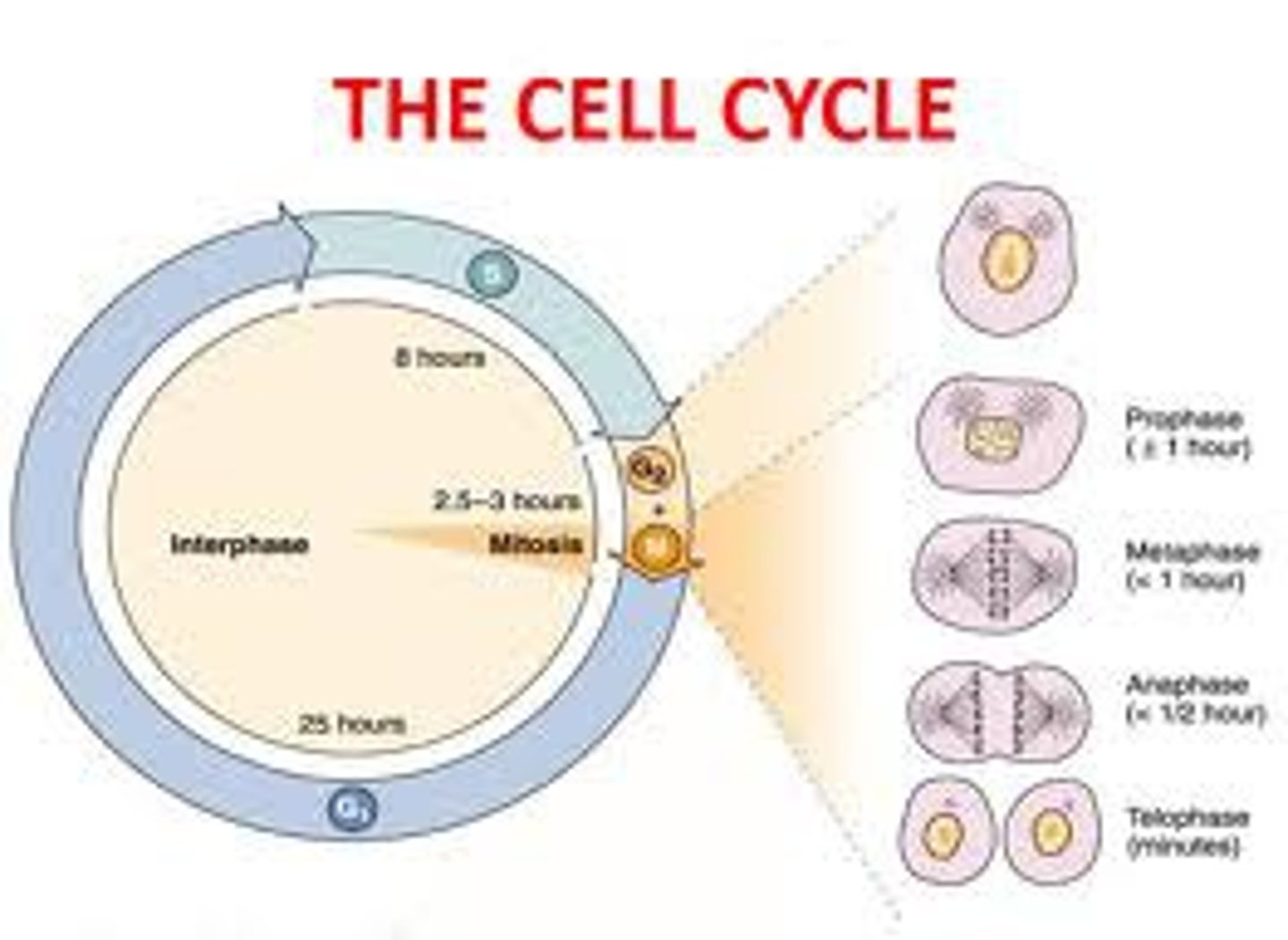
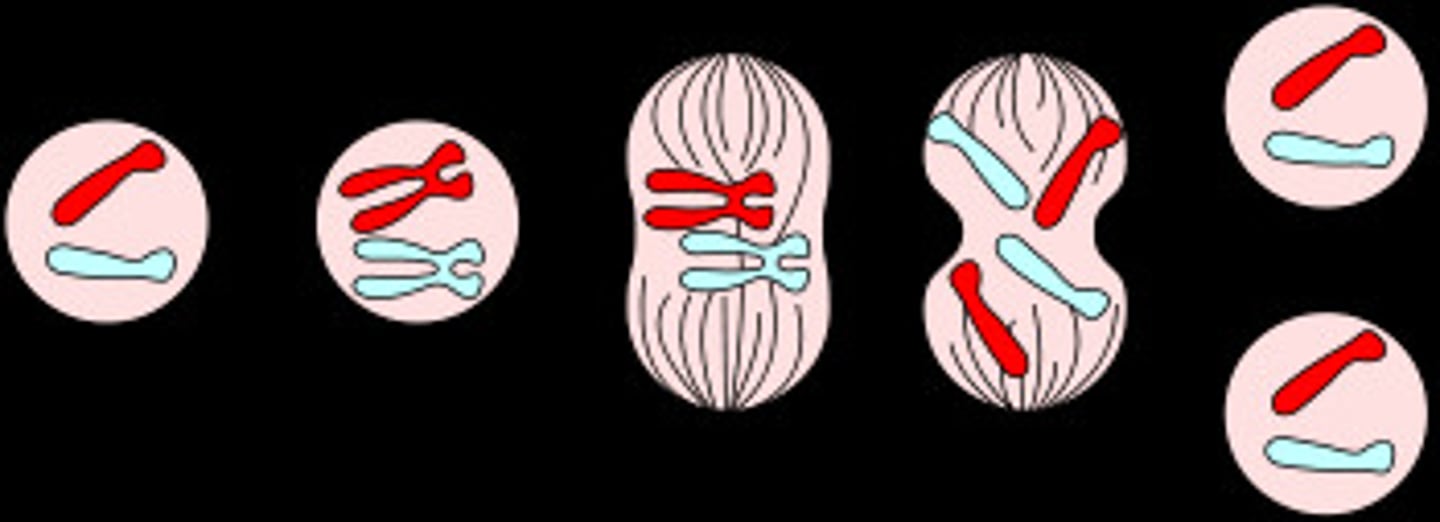
mitosis
A process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells. Conserves chromosome number by equally allocating replicated chromosomes to each of the daughter nuclei.
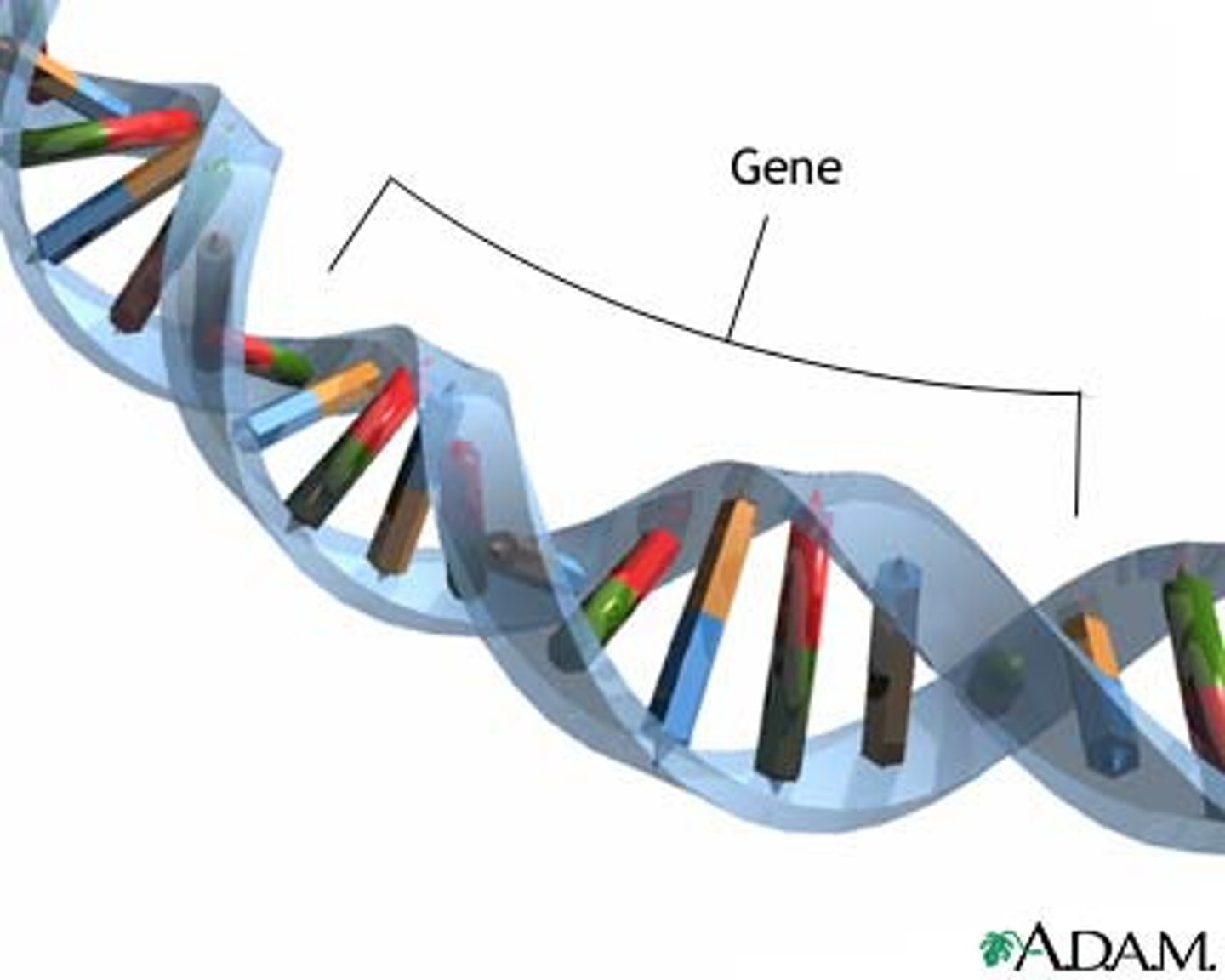
gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific protein, which determines a specific trait.
multicellular
Made up of more than one cell.
differentiation
Process in which cells become specialized in structure and function

gametes
A haploid sex cell such as an egg or sperm. Gametes unite during sexual reproduction to produce a diploid zygote.
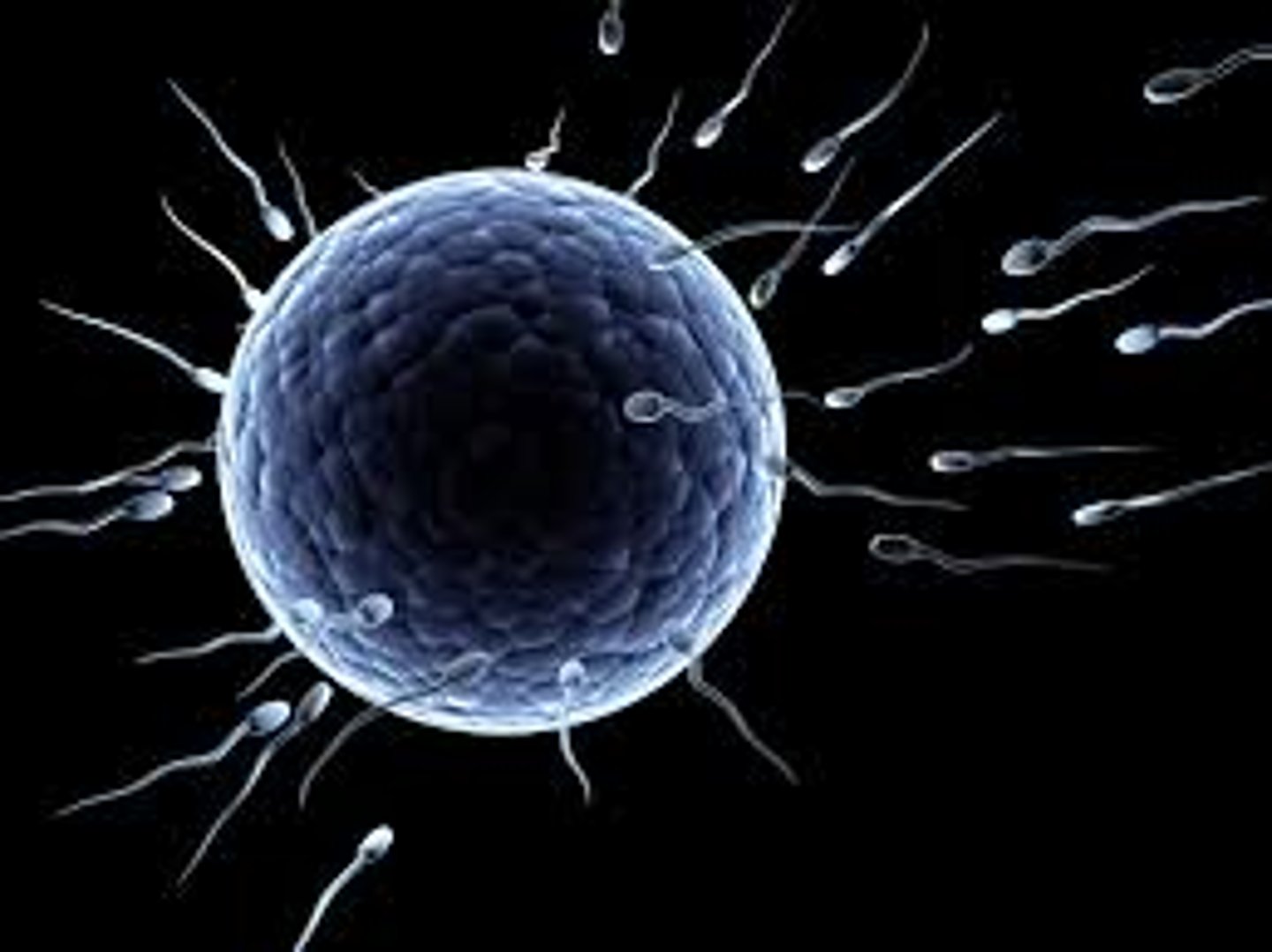
egg cell
the female reproductive cell
embroyonic stem cell
undifferentiated cells that are unlike any specific adult cell however they have the important ability to form any adult cell
adult stem cell
Cells present in adult tissues that generate replacements for nondividing differentiated cells that can be of great therapeutic potential.
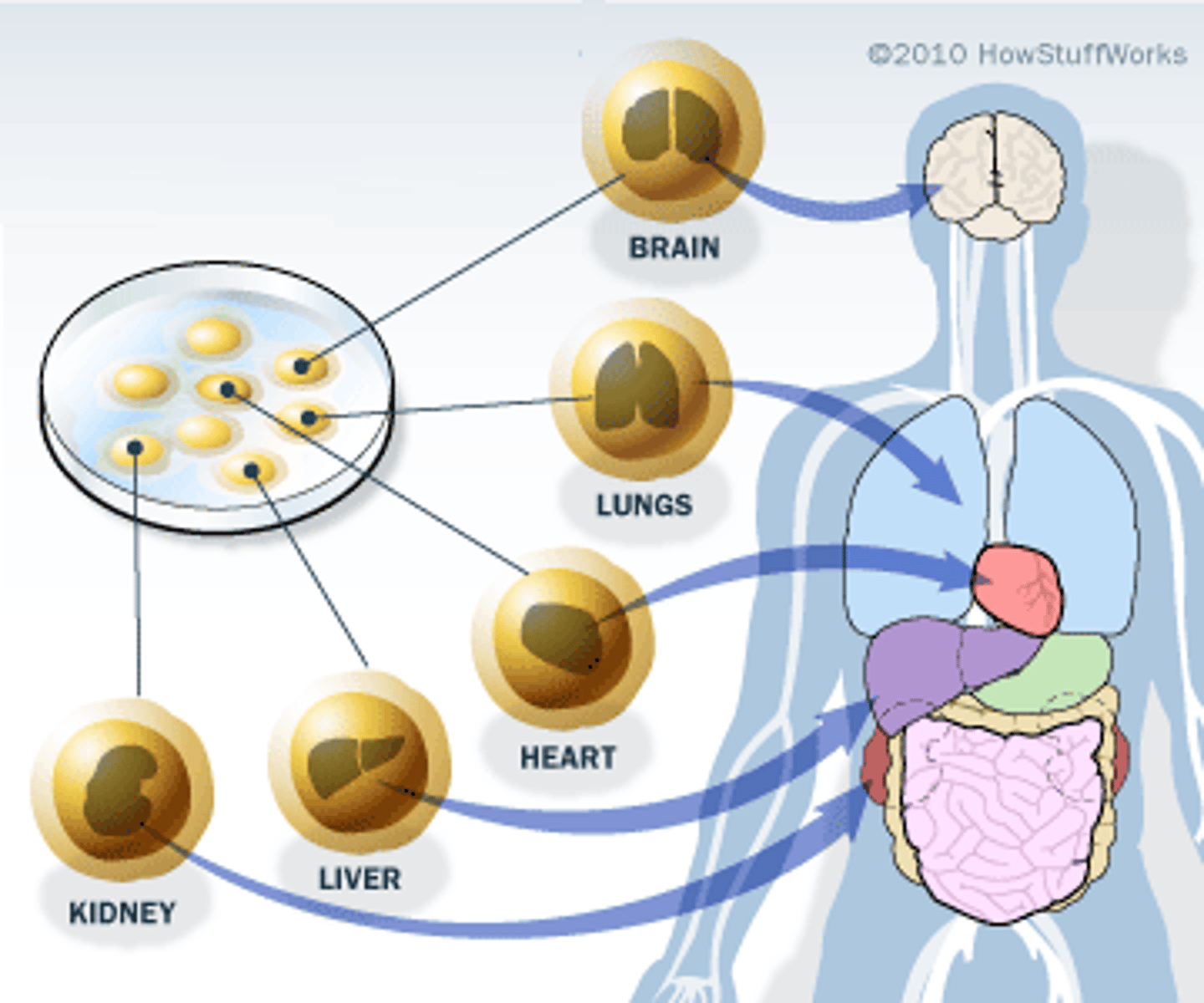
cloning
A process in which a cell, cell product, or organism is copied from an original source.

ovum
A mature egg cell.
epidermis
The outer layer of cells covering an organism
meristem
an undifferentiated, growing region of a plant that is constantly undergoing cell division and differentiation
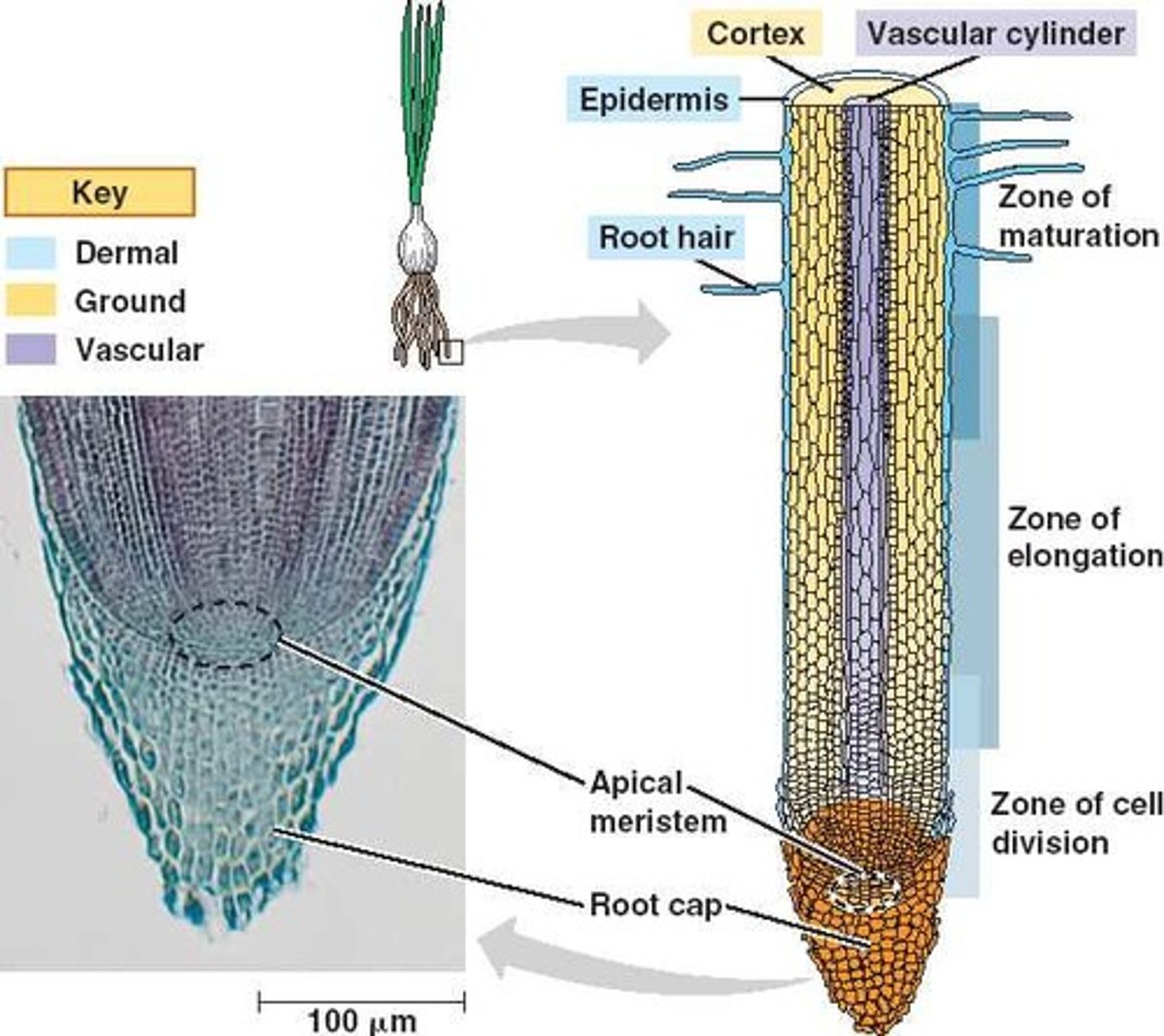
elongation
The fractional increase in a material's length due to stress in tension or expansion.
vascular
Of or relating to blood or fluid vessels

zygote
Fertilized egg

therapeutic cloning
The cloning of human cells by nuclear transplantation for therapeutic purposes, such as the generation of embryonic stem cells to treat disease.
small intestine
Digestive organ where most chemical digestion and absorption of food takes place
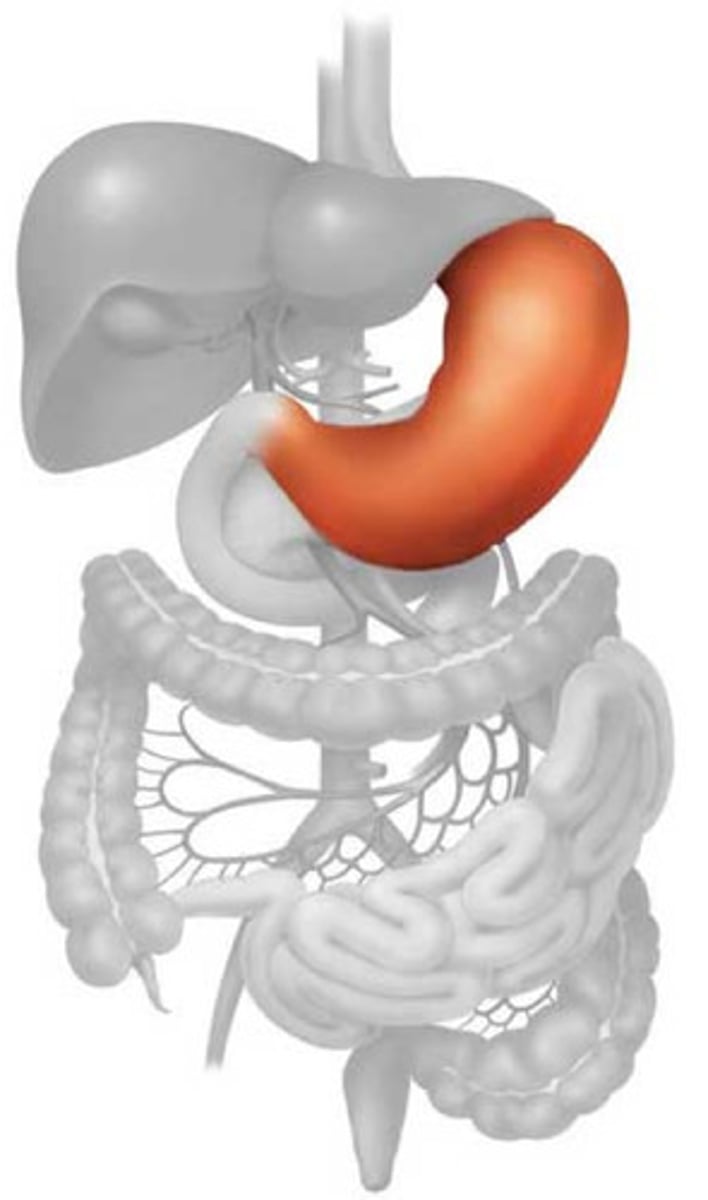
stomach
A muscular and elastic sac that serves mainly to store food, break it up mechanically, and begin chemical digestion of proteins and fat.
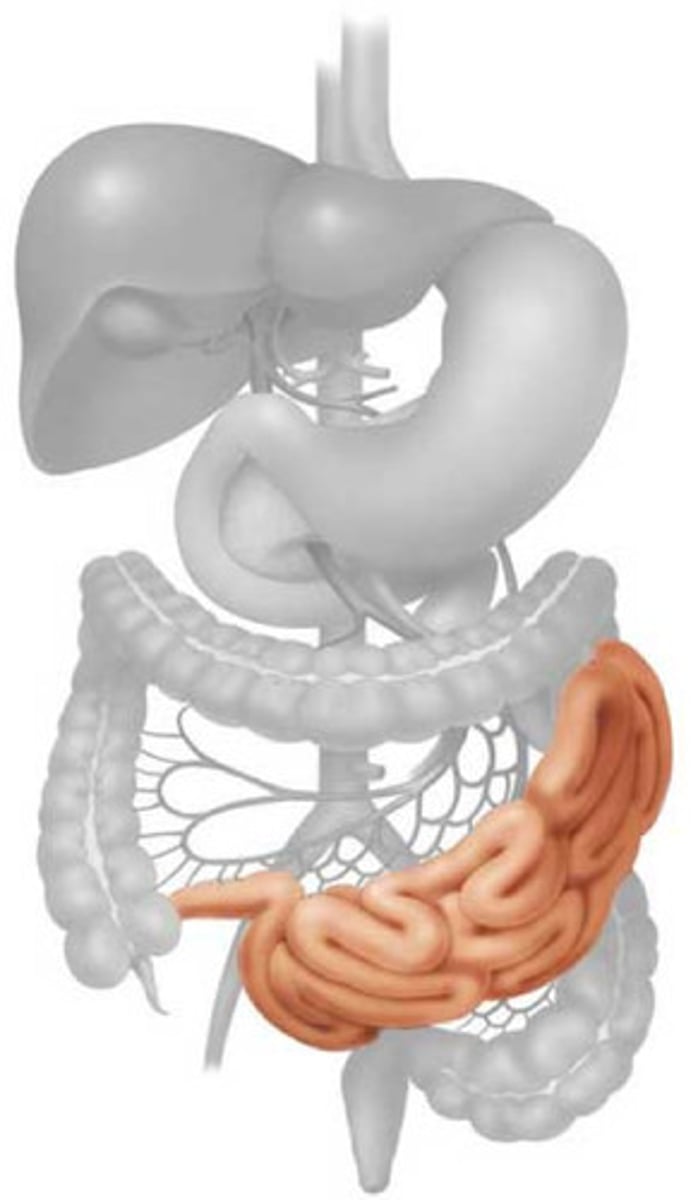
large intestine
The last section of the digestive system, where water is absorbed from food and the remaining material is eliminated from the body
digestive system
Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells.
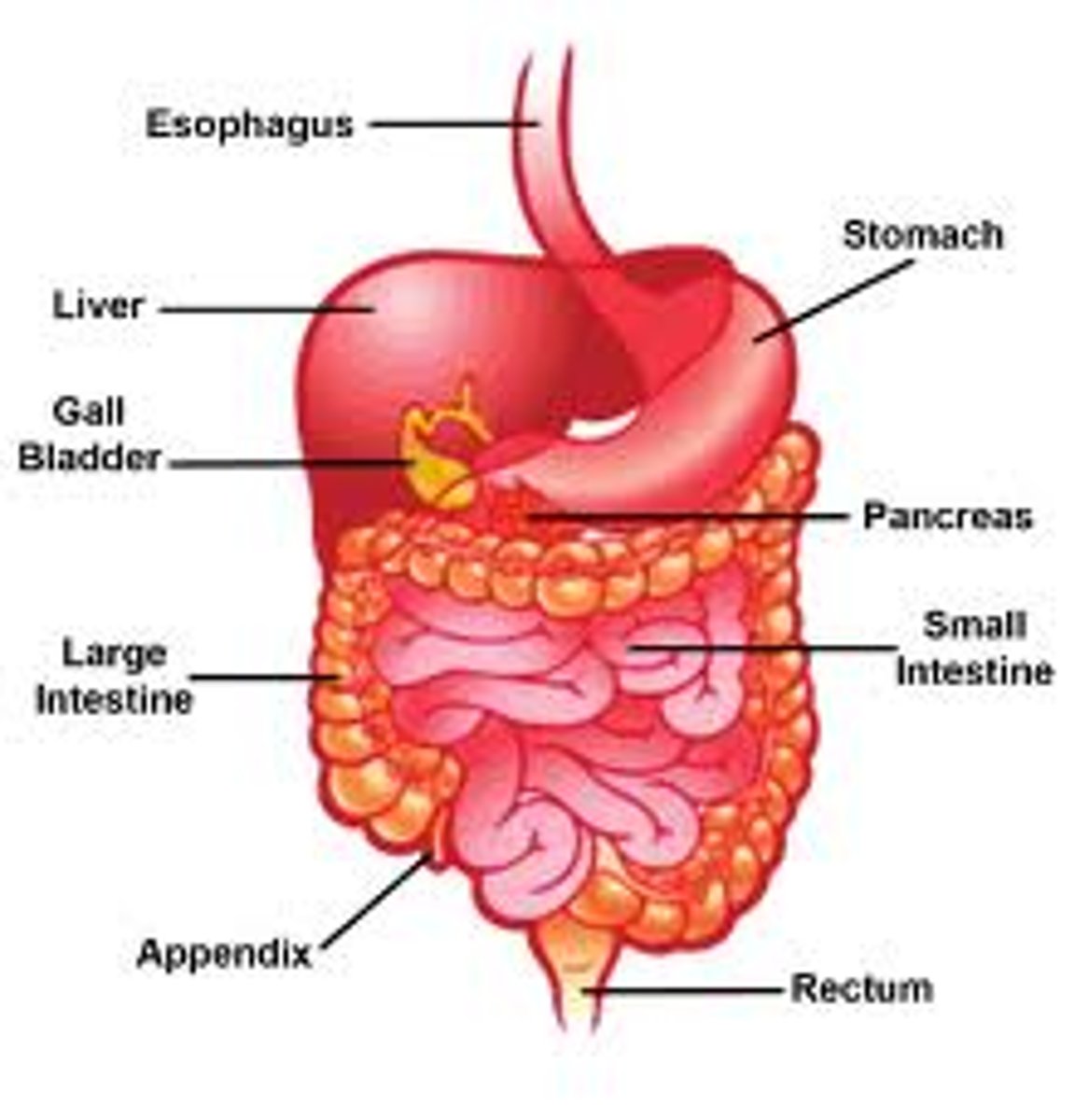
diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
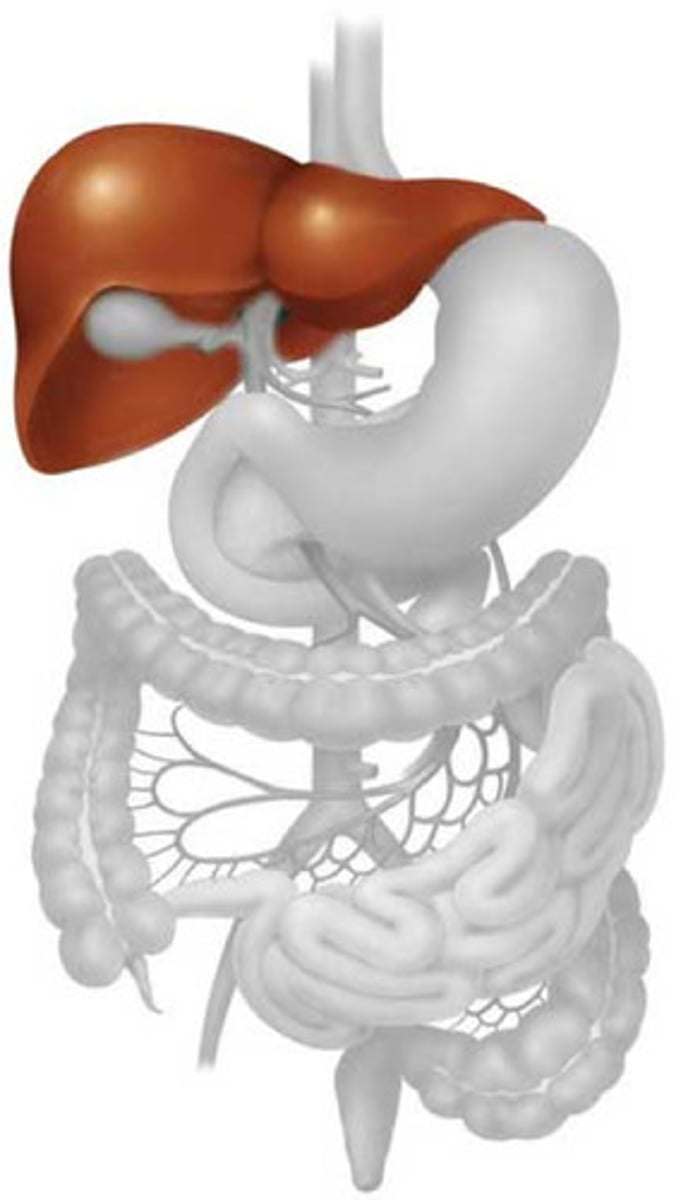
liver
A large solid organ that lies in the right upper quadrant immediately below the diaphragm; it produces bile, stores glucose for immediate use by the body, and produces many substances that help regulate immune responses.
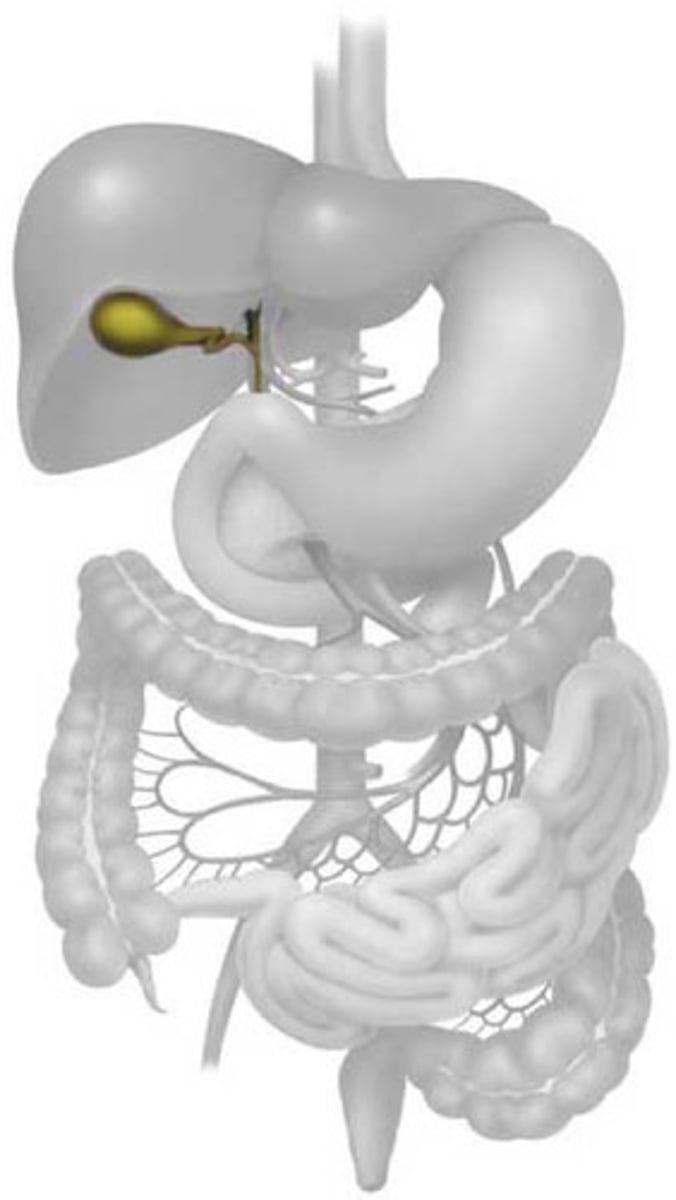
gall bladder
An organ that stores bile and releases it as needed into the small intestine
duodenum
First part of the small intestine
mouth
Oral cavity; opening to the digestive tract or alimentary canal; Begins preparation of food for digestion
salivary gland
Glands of the mouth that produce saliva, a digestive secretion and lubricant
gullet
the passage by which food passes from the mouth to the stomach; the esophagus.
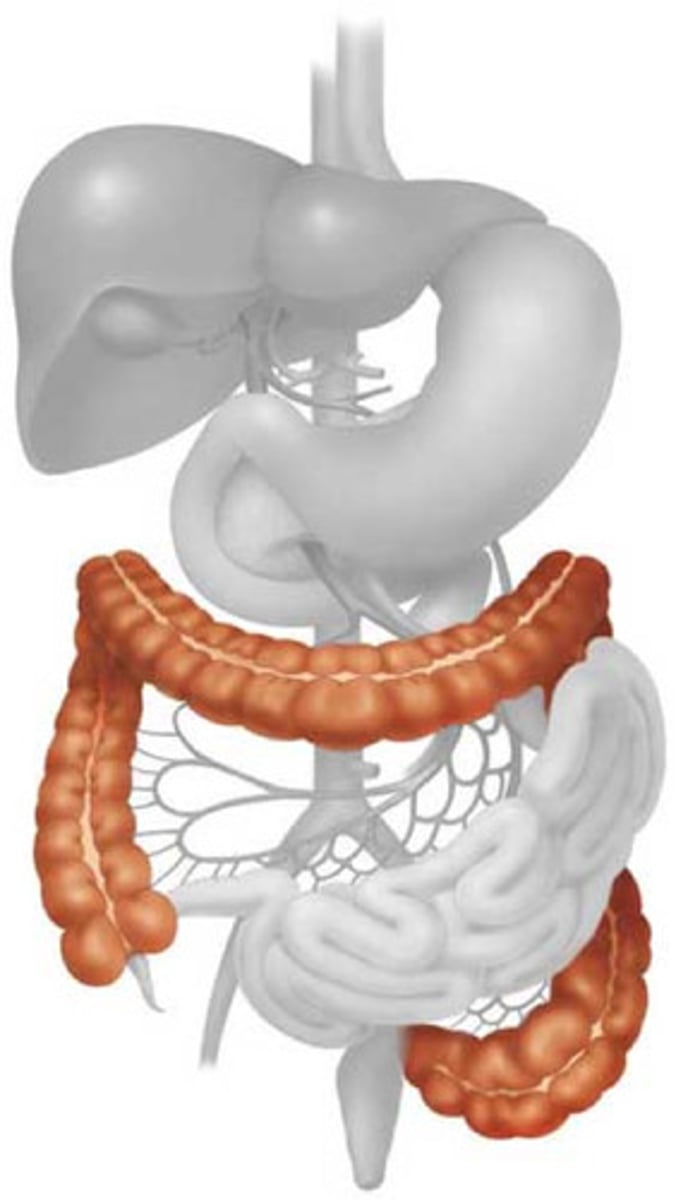
pancreas
An organ in the abdominal cavity with two roles. The first is an exocrine role: to produce digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, which are delivered to the small intestine via the pancreatic duct. The second is an endocrine role: to secrete insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to help regulate blood glucose levels.
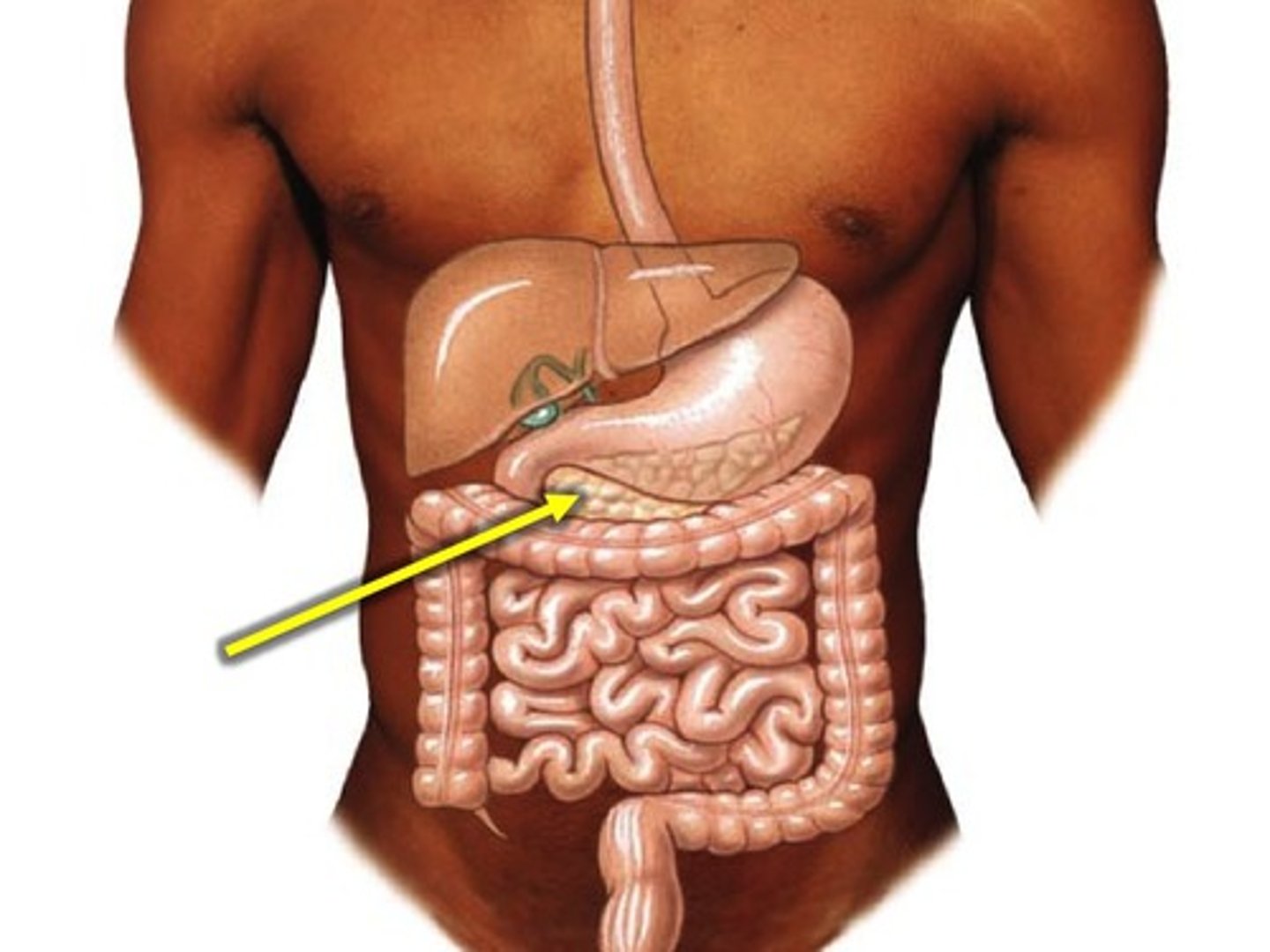
bile duct
A tube that carries bile from the liver and gallbladder to the intestine
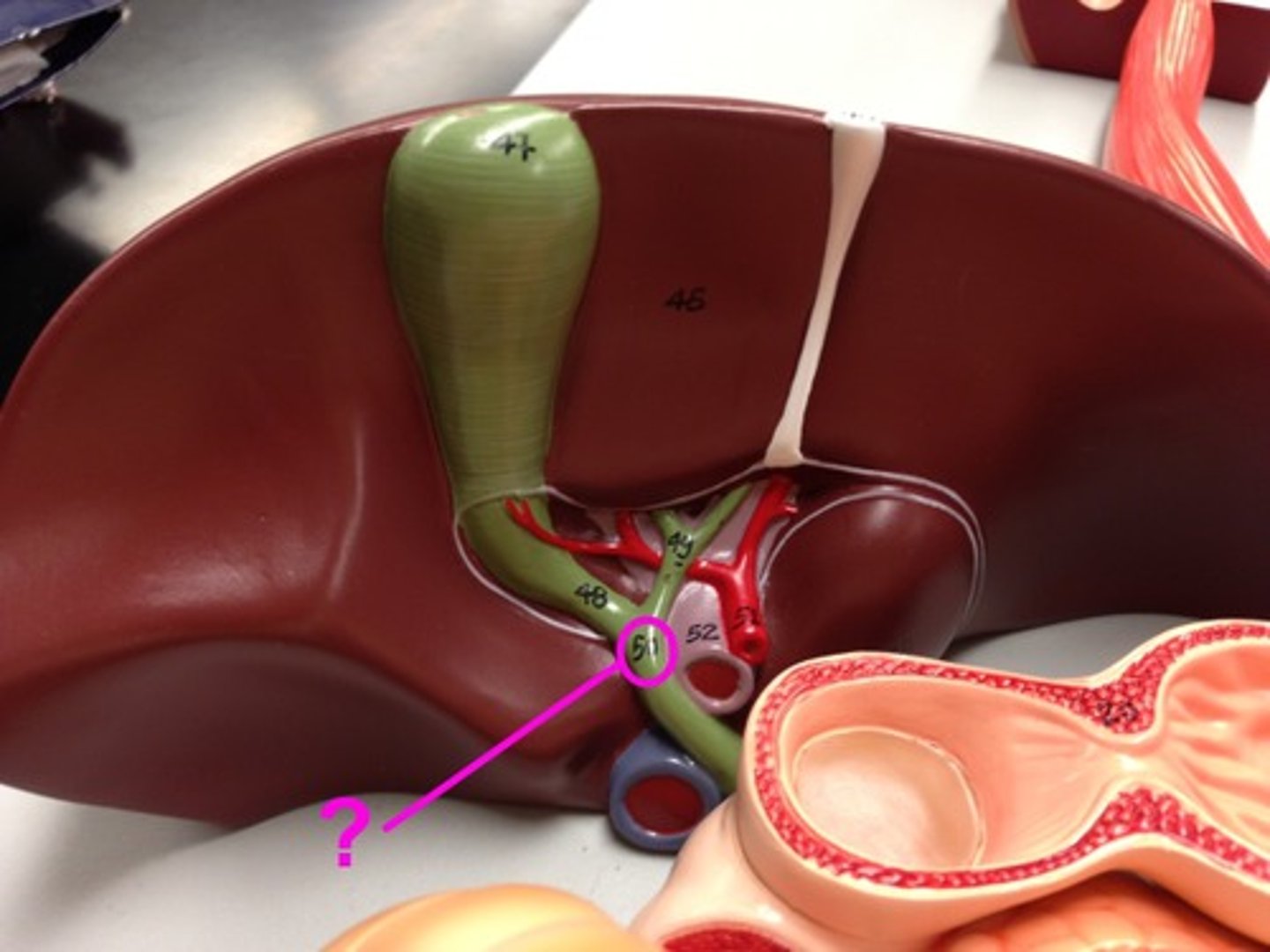
appendix
A mass of lymphatic tissue at the beginning of the large intestine that helps trap ingested pathogens.
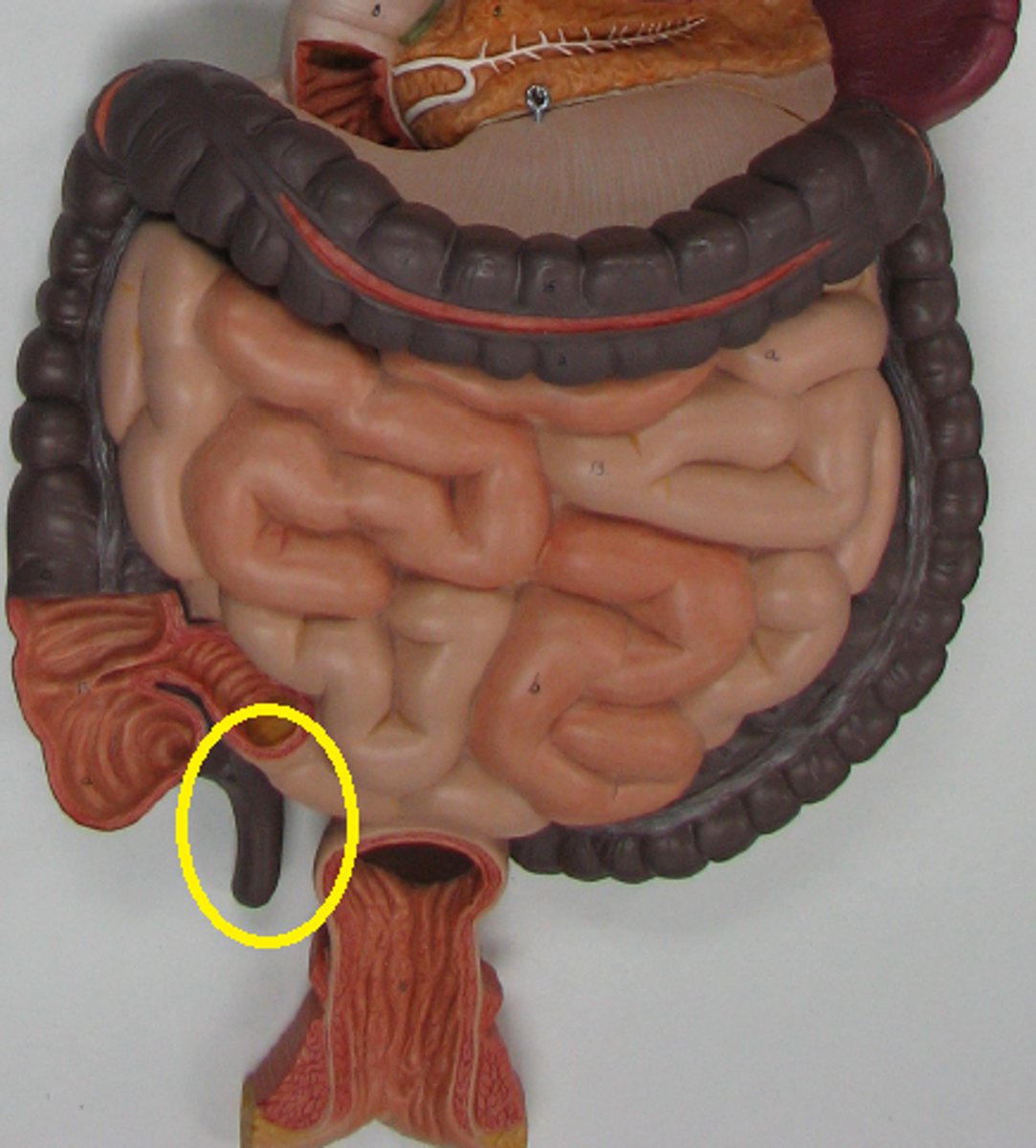
rectum
A short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated
anus
A muscular opening at the end of the rectum through which waste material is eliminated from the body
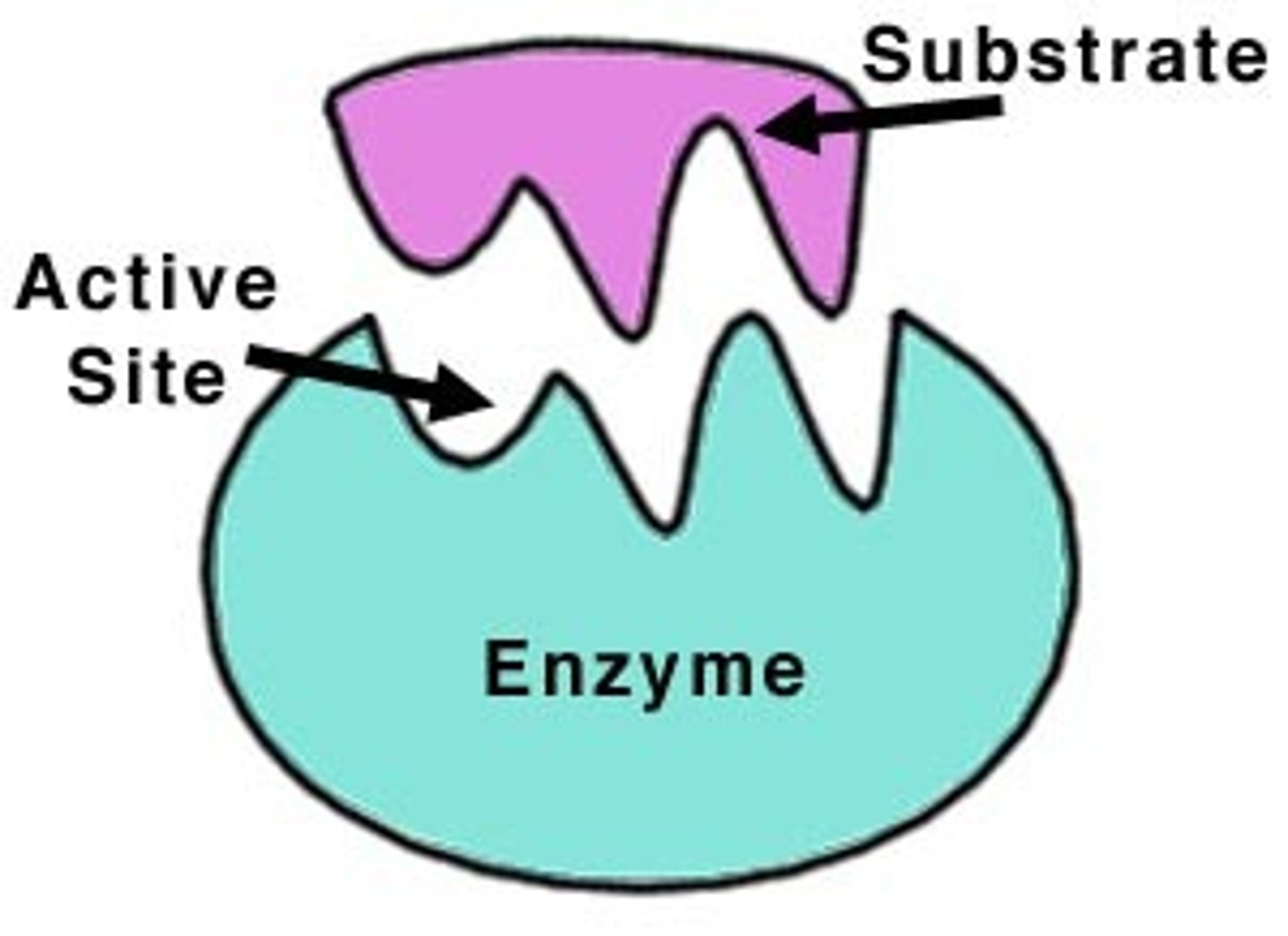
enzymes
Proteins that act as catalysts for biological chemical reactions
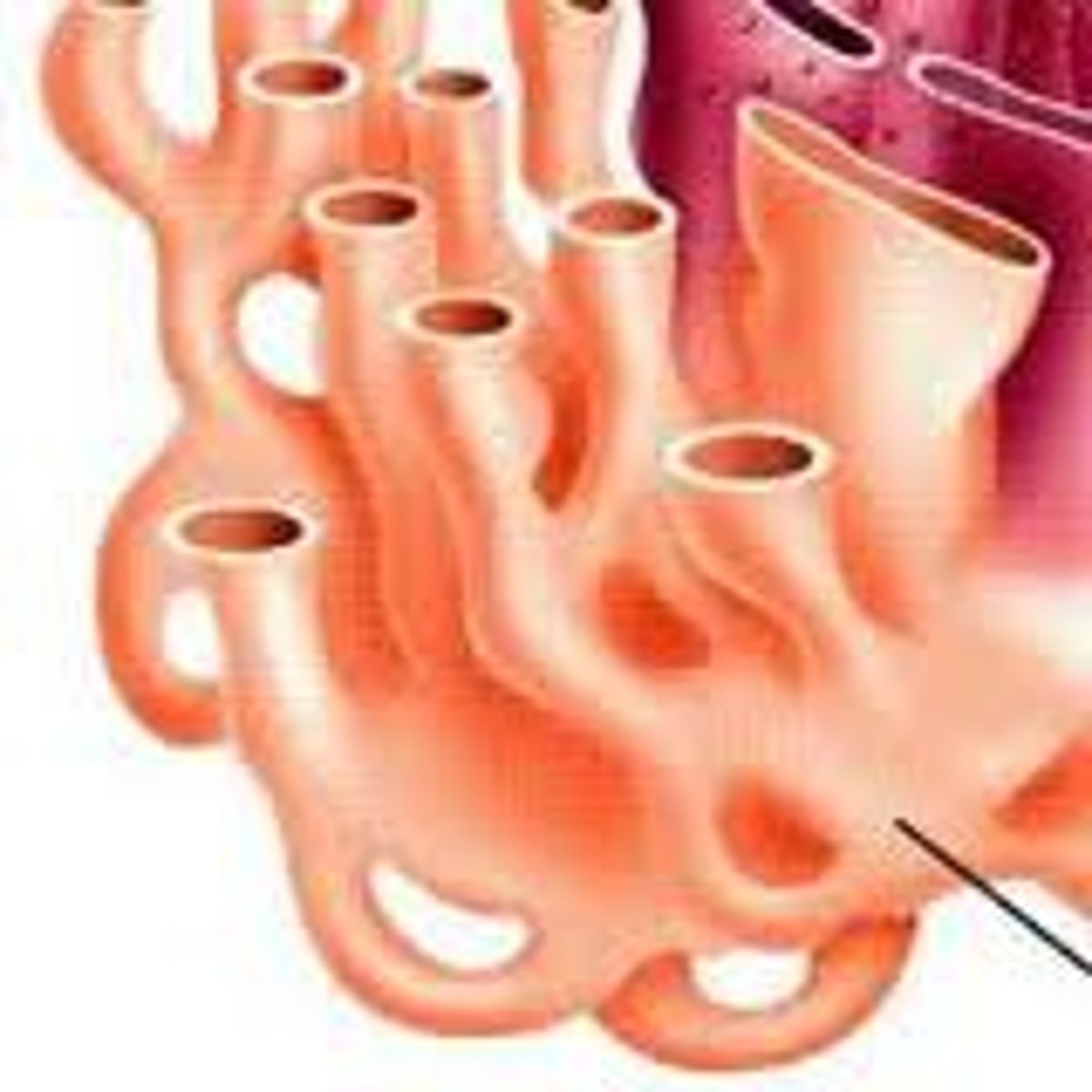
villi
Tiny finger-shaped structures that cover the inner surface of the small intestine and provide a large surface area through which digested food is absorbed
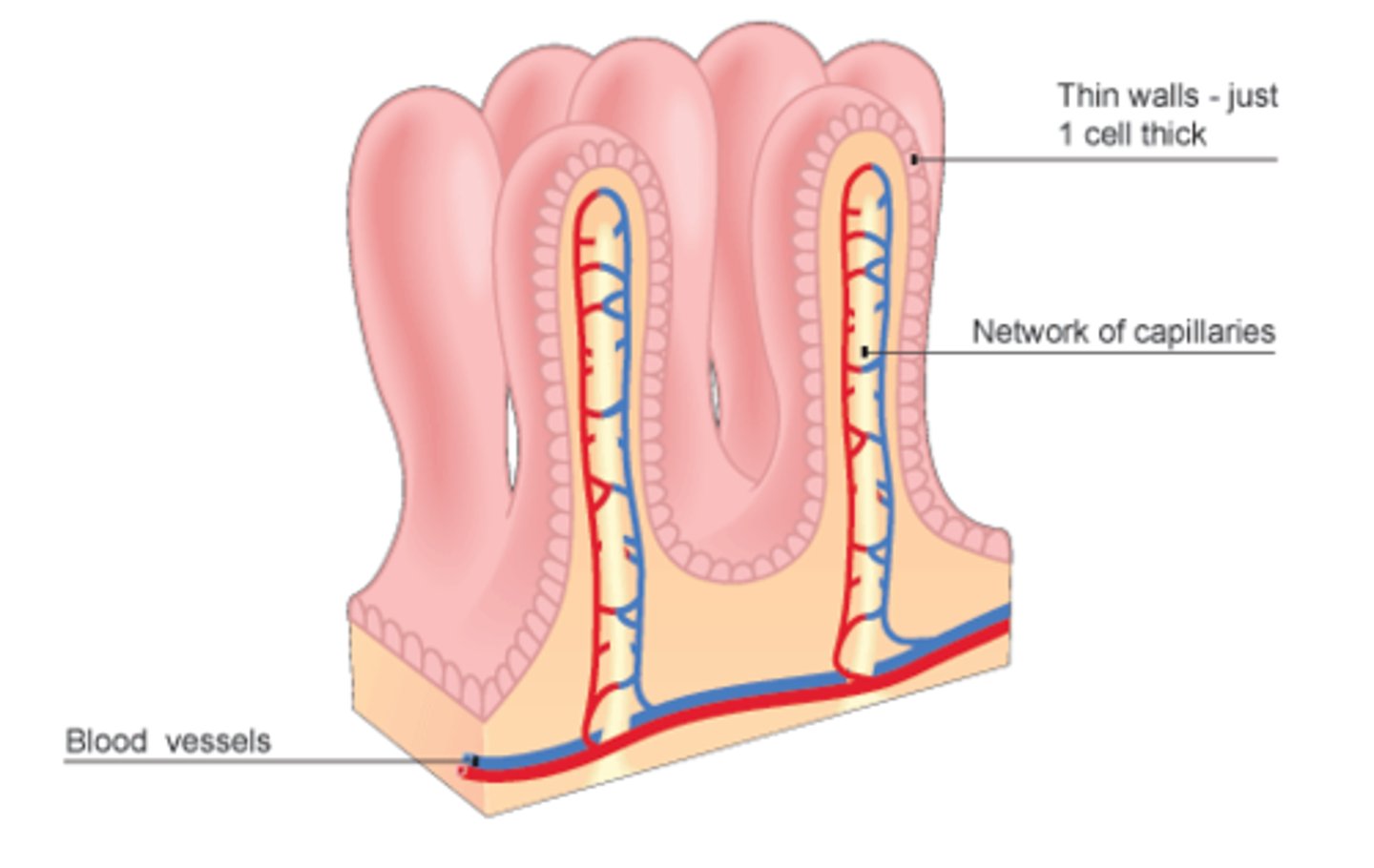
carbohydrates
Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; ready source of energy (glucose and glycogen can be stored in tissues); can be simple sugars (glucose), simple polymers (starch), or very complex polymers (cellulose)
