Lecture 10: Predation and Herbivory
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
How does predation work?
predators obtain energy and nutrients by killing and eating prey
What do herbivores consume?
producers, such as plants and/or algae
Generalists
select and eat a wide variety of food items
specialists
feeding upon a single species or a restricted range of closely related species
predators and herbivores can limit what?
the abundance of species
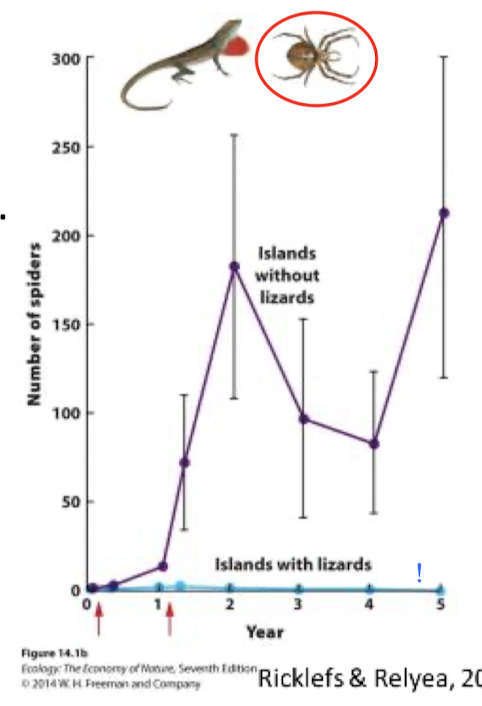
Explain this graph: spider densities on the Caribbean islands with and without lizards
The islands with lizards seem to have less number of spiders than the islands without lizards
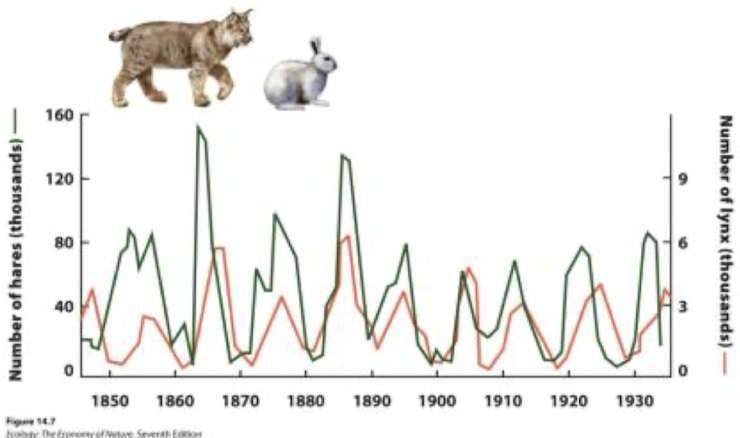
Explain what this chart mean
snowshoe hares and Canada lynx predators exhibit population cycles of 9-10 years, with lynx cycles lagging about 2 years behind the hare cycles
the synchrony of population cycles between predators and prey suggests that?
oscillations are the result of interactions between them
Predator-prey cycles: Decline of predators
—> increase of prey
Predator-prey cycles: Increase of prey
—> more food for predators —> increase of predators
Predator-prey cycles: more predators
—> decline of prey
Predator-prey cycles: decline of prey
—> lower survival and reproduction of the predator
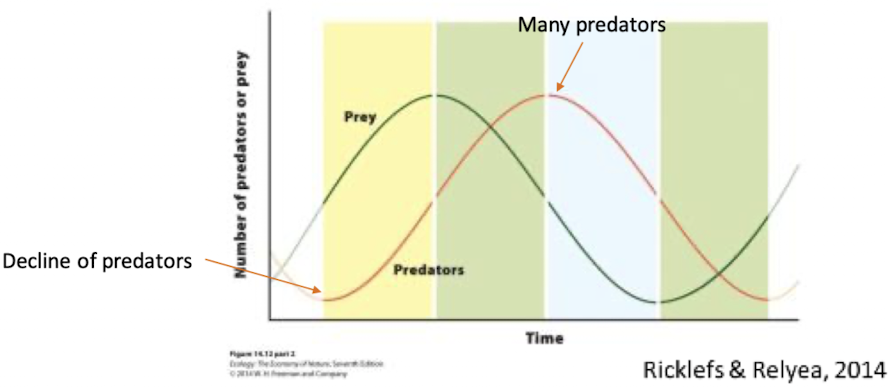
what does this figure illustrate
predator population size lagging behind prey abundance
What are some predator hunting strategies
Active hunting strategies and Ambush hunting strategies
Active hunting strategies
predators spend most of the time moving around looking for prey
Ambush (sit-and-wait) hunting strategies
wait for a potential prey to pass by
What are some behavioral defenses?
alarm calling
spatial avoidance
reduction of activity
mobbing
Alarm calling
warning relatives: predators are approaching
spatial avoidance
potential prey moves away from predator
reduction of activity
to avoid being detected by a predator
Mobbing
surround and attack predator
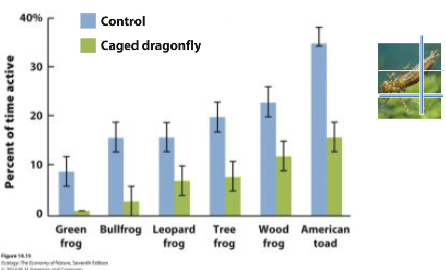
Explain this graph.
the tadpoles and activity levels
What is crypsis? (behavioral defense)
camouflage that either allows an individual to match its environment or breaks up the outline of an individual to blend in better with the background
Chemical defenses can what?
deter a predator
Explain how bombadier beetles use chemical defenses.
bombadier beetle mixes two chemicals from separate glands to make a boiling-hot liquid that it sprays to either kill or injure predators
Chemical defenses are often more effective at deterring predators if??
the prey can convey the dense before an attack occurs
what is warning coloration (aposematism)?
distastefulness evolves in association with very conspicuous colors and patterns
What is batesian mimicry?
mimicry of chemical defenses
palatable species evolve warning coloration that resembles unpalatable species
what is Müllerian mimicry?
mimicry of chemical defenses
several unpalatable species evolve a similar pattern of warning coloration
What is an example of Müllerian mimicry?
several species of poison dart frogs have evolved similar warning coloration
Herbivores can have substantial effects on what?
the species they consume
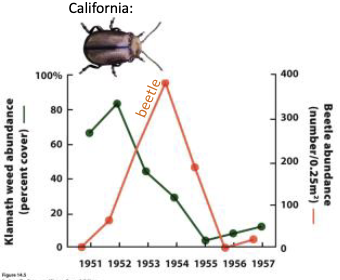
Explain this graph.
The klamath weed abundance in comparison to the beetle abundance. More beetles= less weeds
What is an example of herbivores having a substantial effect on the species they consume?
a beetle has eliminated 99% of the Klamath weed population in North America
what is one example of herbivores regulating populations (deers and plants)?
long term fencing to prevent deer herbivory, resulted in much greater amount of plant growth in Canadian National Park
what is one example of herbivores regulating populations (sea urchins and algae)?
removal of sea urchin from a rocky shore habitat, resulted in biomass of different algae increase
Pressures from herbivores equals what?
evolution of plant defenses
What is an example of structural defenses?
sharp spines, “hairs”
What is an example of chemical defenses?
sticky resin and latex compounds and alkaloids (e.g., caffeine, nicotine, morphine) with a wide range of toxins
Are parasitoids predators or parasites?
they have characteristics of both
What does a parasitoid do?
parasitoids larva lives on or in the host (usually another insect) slowly consuming or killing it
unique type of predation, can limit what?
abundance of prey
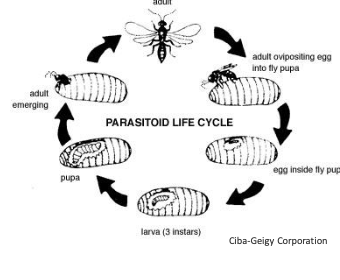
explain this illustration
parasitoid uses host (caterpillar) to inject eggs and larva begins to eat host