Module 4: Exposure Factors & Radiographic Quality
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Radiation Quantity
- Radiation intensity
- Amount of radiation produced
Radiation Quality
X-ray beam penetrability
___________ relates to the heating of the cathode filament
Milliamperage
Thermonic emission
Boiling off the electrons from their atomic orbits
What is the function of milliamperes in an x-ray unit?
Electrical current unit that heats filament
mA affects __________ of the beam and the _________ of radiation produced
intensity, quantity
What is exposure time?
Period during which the x-rays are permitted to leave the x-ray tube
Exposure time is measured in ________
Seconds
Kilovoltage determines _______ and ____ _____ of x-ray beam
quality, penetrating power
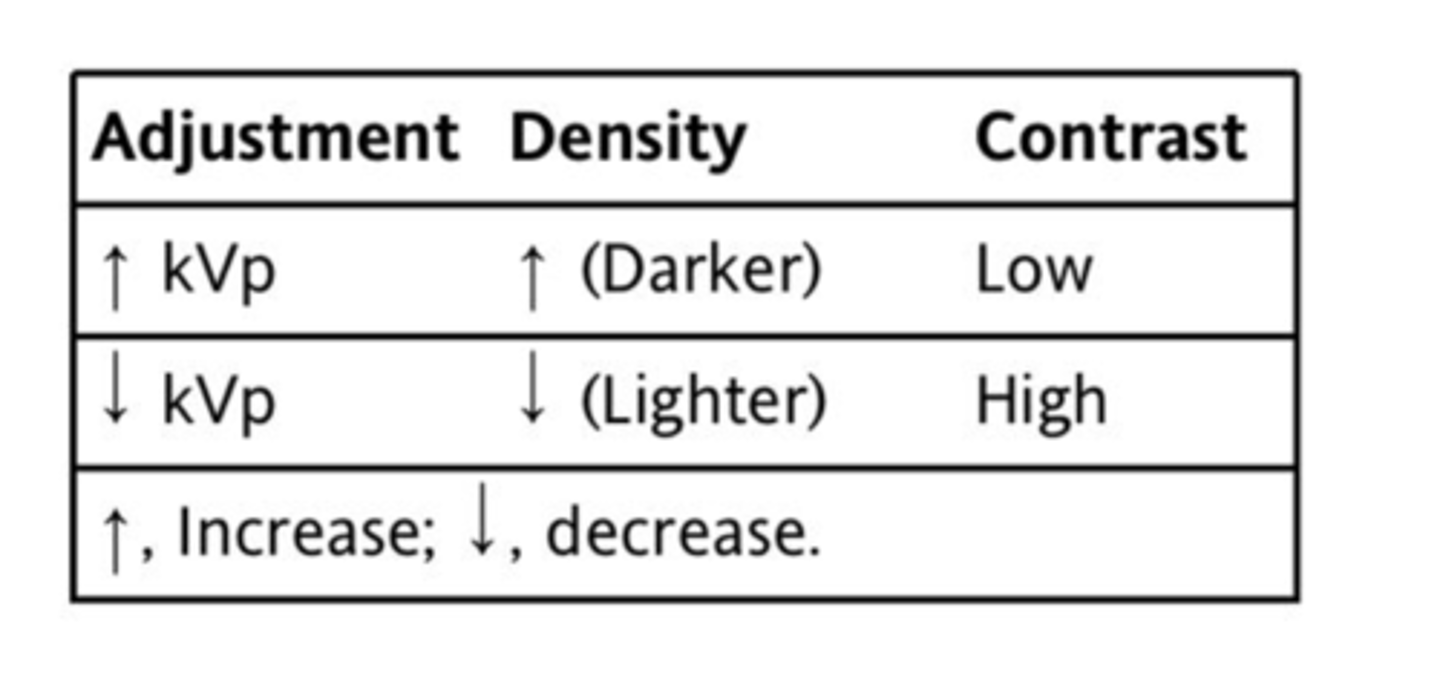
Higher kVp settings produce ________
more penetrating beams
Santes' rule
kVp = (2x thickness of body part in cm) + 40
kVp and mAs are __________________
inversely related
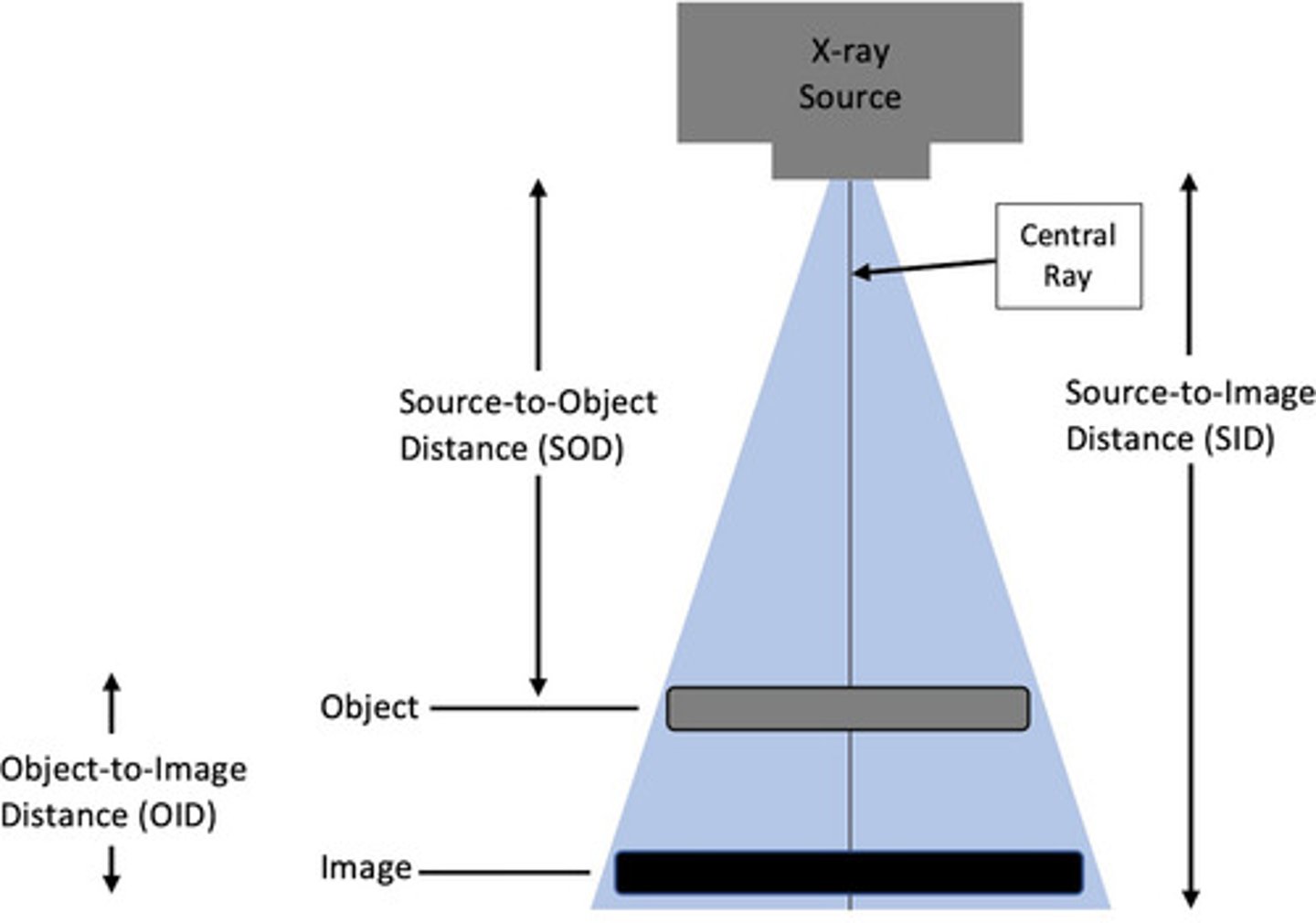
SID
SOURCE (x-ray tube) to IMAGE (cassette/IR) DISTANCE
As SID _______, intensity of x-ray beam _______
increases, decreases
Inverse square law
Intensity of beam inversely proportional to the square of the SID
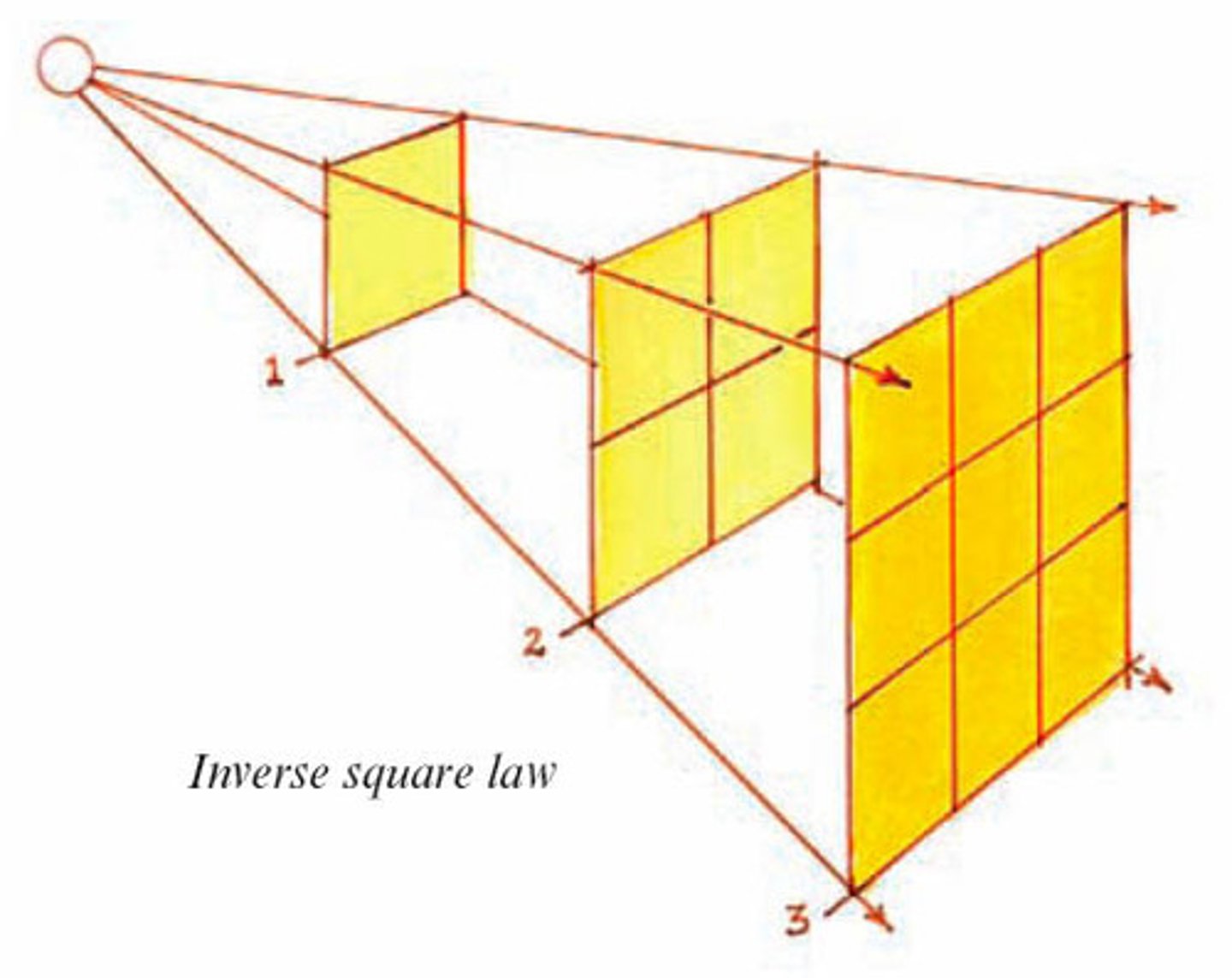
When SID changes, _______ needs to be changed to compensate
mAs
How is mAs setting calculated if SID is changed?
(new SID²/old SID²) = new mAs setting
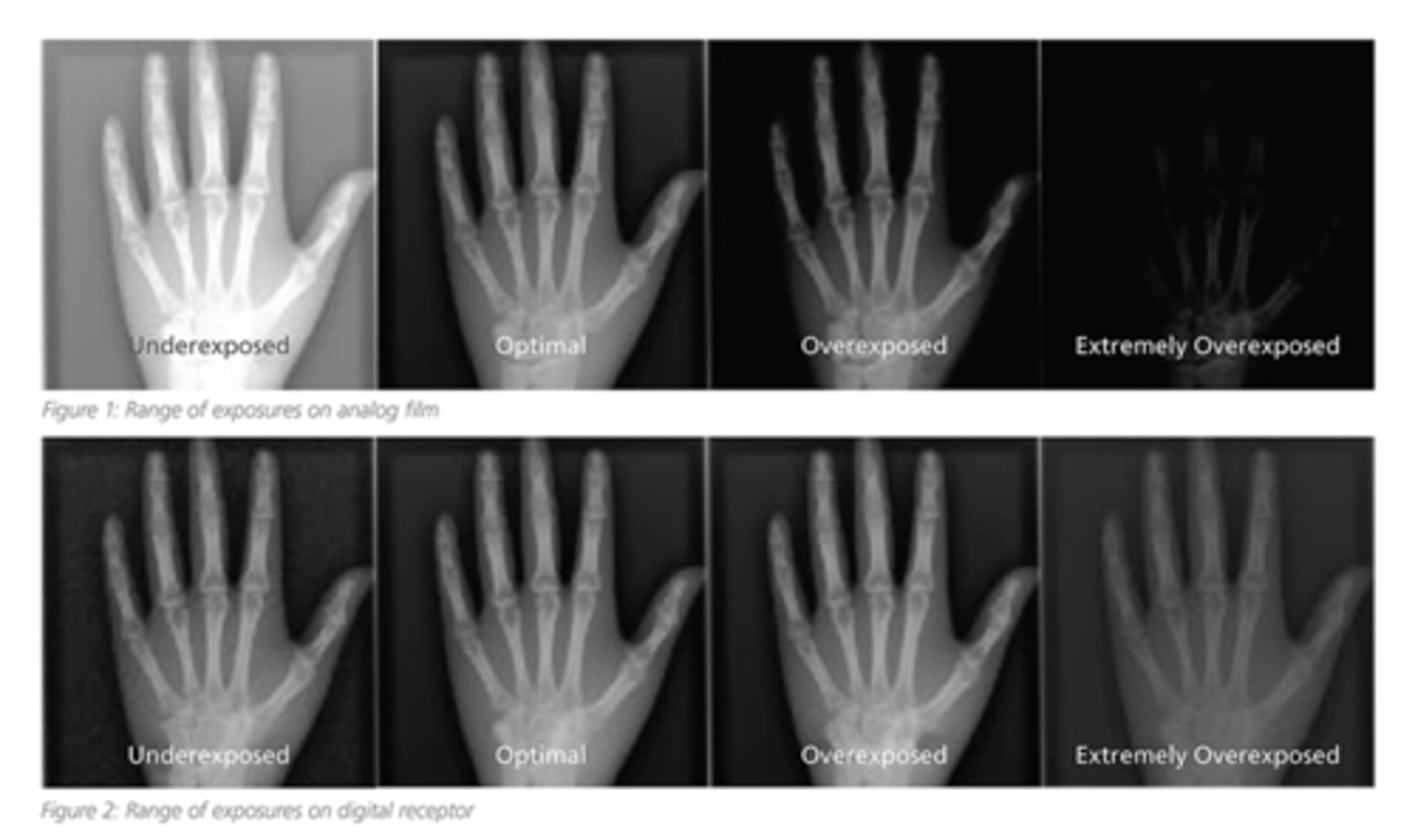
What is radiographic quality
Representation of the patients anatomy on image
What does radiographic quality depend on?
- Density
- Contrast
- Geometric factors
Radiographic density is the degree of _____ seen in an x-ray image
"blackness"
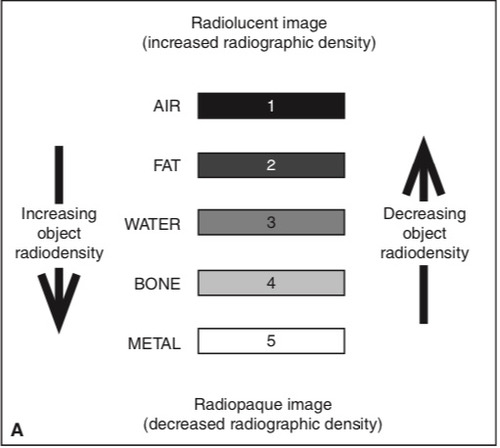
What is density affected by?
- Total number of x-rays that reach IR or film
- Penetrating power of x-rays
- Thickness of the body part
- Developing time (when using film)
- Temperature of developer (when using film)
What are the 2 types of contrast?
- Image receptor contrast
- Subject contrast
What is radiographic contrast
Density difference between two adjacent areas on a radiograph
(high contrast vs. low contrast)

What are the 2 forms of radiographic contrast that can be produced depending on kVp setting?
Short scale contrast (Low kVp)
Long scale contrast (High kVp)
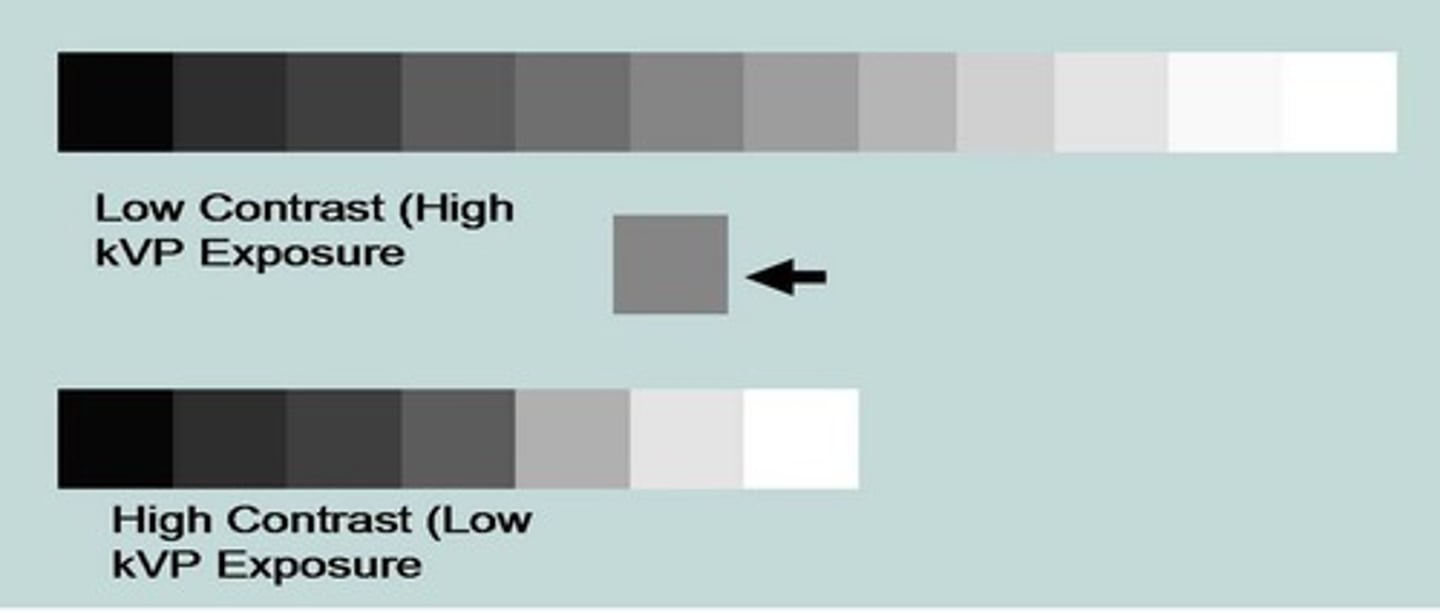
What is radiographic contrast influenced by?
- Subject contrast
- Exposure factors
- Scatter
- Film/screen type
- Film fog
What are the 2 factors of subject contrast?
Patient thickness & shape
Tissue density
Contrast exposure factors: mAs
Affects contrast with either excessive or insufficient mAs
When mAs is ________, contrast is ___________ because overall density of radiograph is reduced, creating a ____ image
insufficient, reduced, lighter
When mAs is ___________, overall density will ___________ and contrast reduced, creating a _____ image
excessive, increase, darker
- If mAs is set correctly, _____ affects contrast
kVp
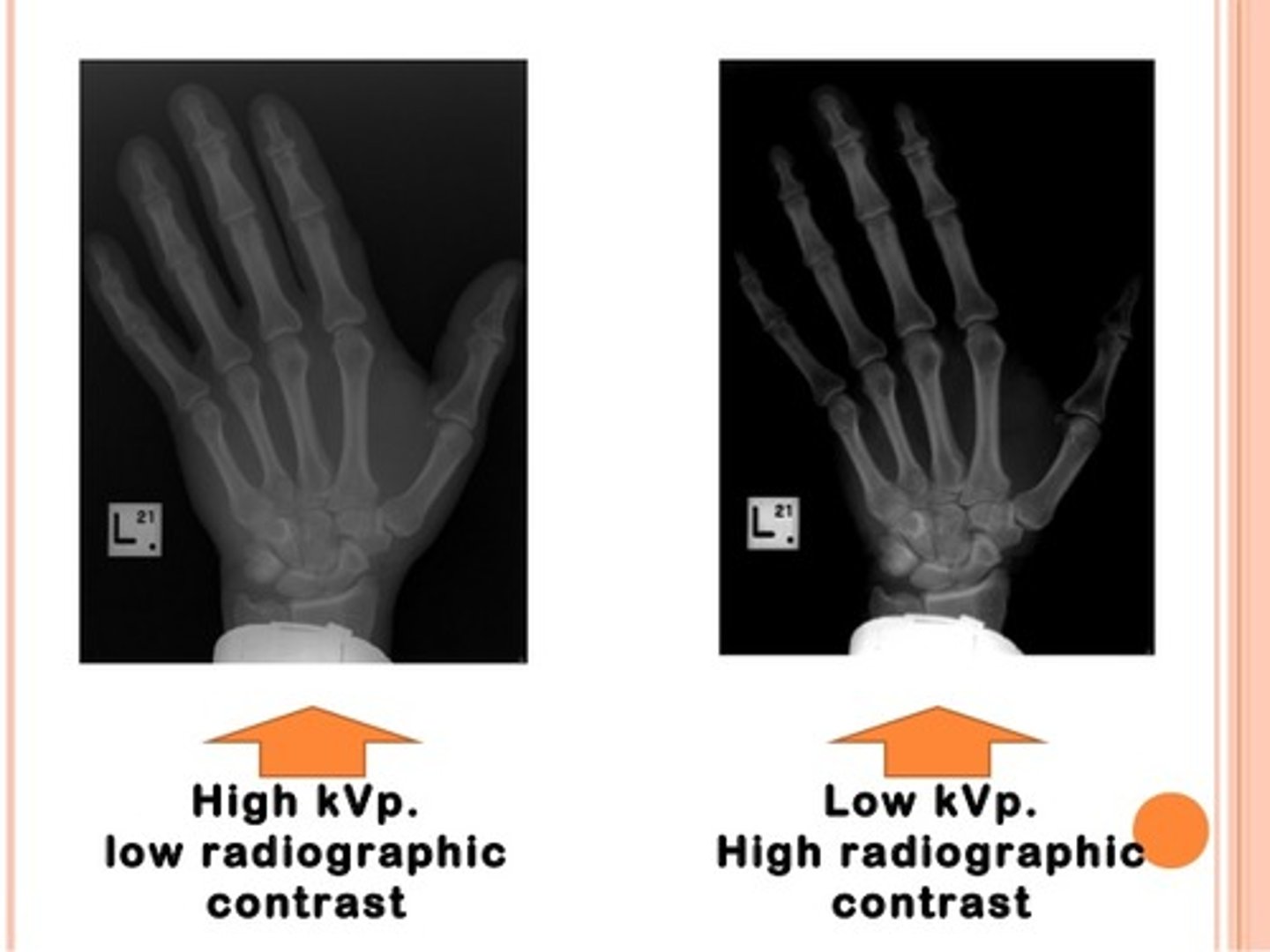
Increasing kVp
- Increases penetrating power of the beam
- Increases amount of scatter radiation produced
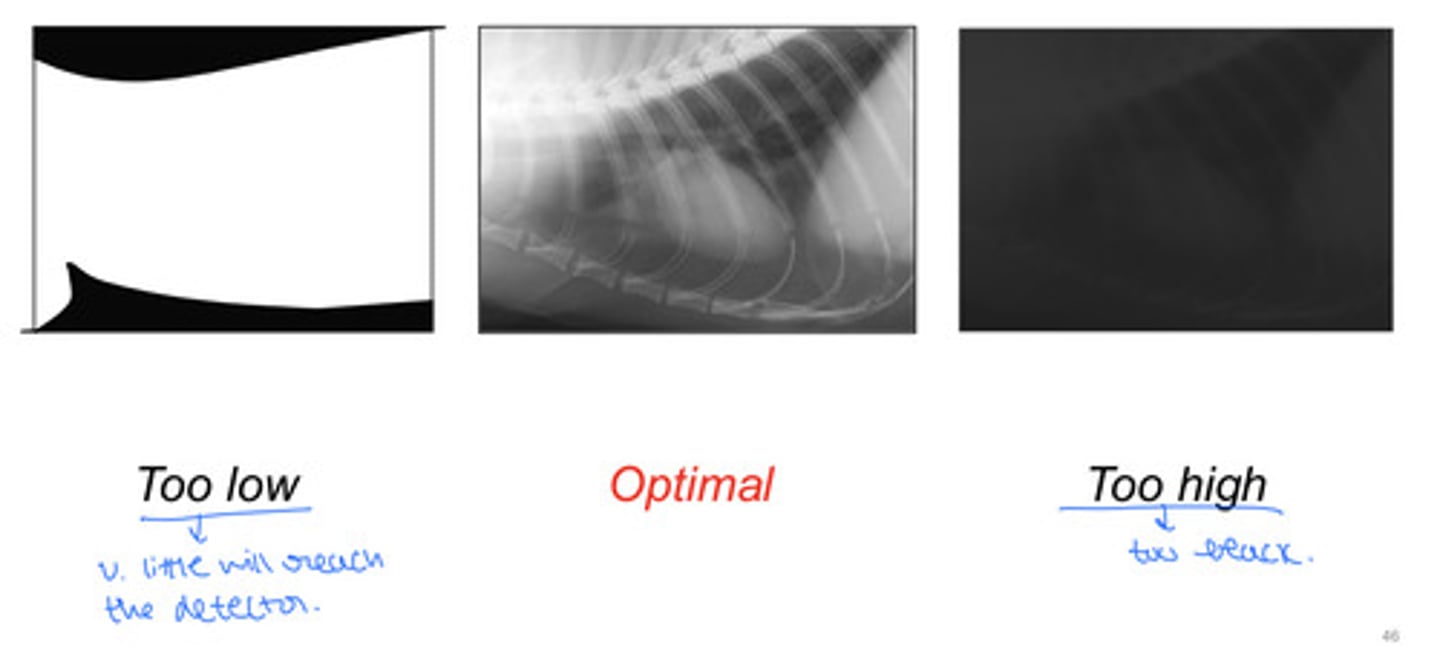
Decreasing kVp
- Decreases penetrating power of the beam
- May cause insufficient number if x-rays to reach film/IR
What 2 questions should you ask of contrast is poor?
Is radiograph too light or dark?
How well is the tissue penetrated?
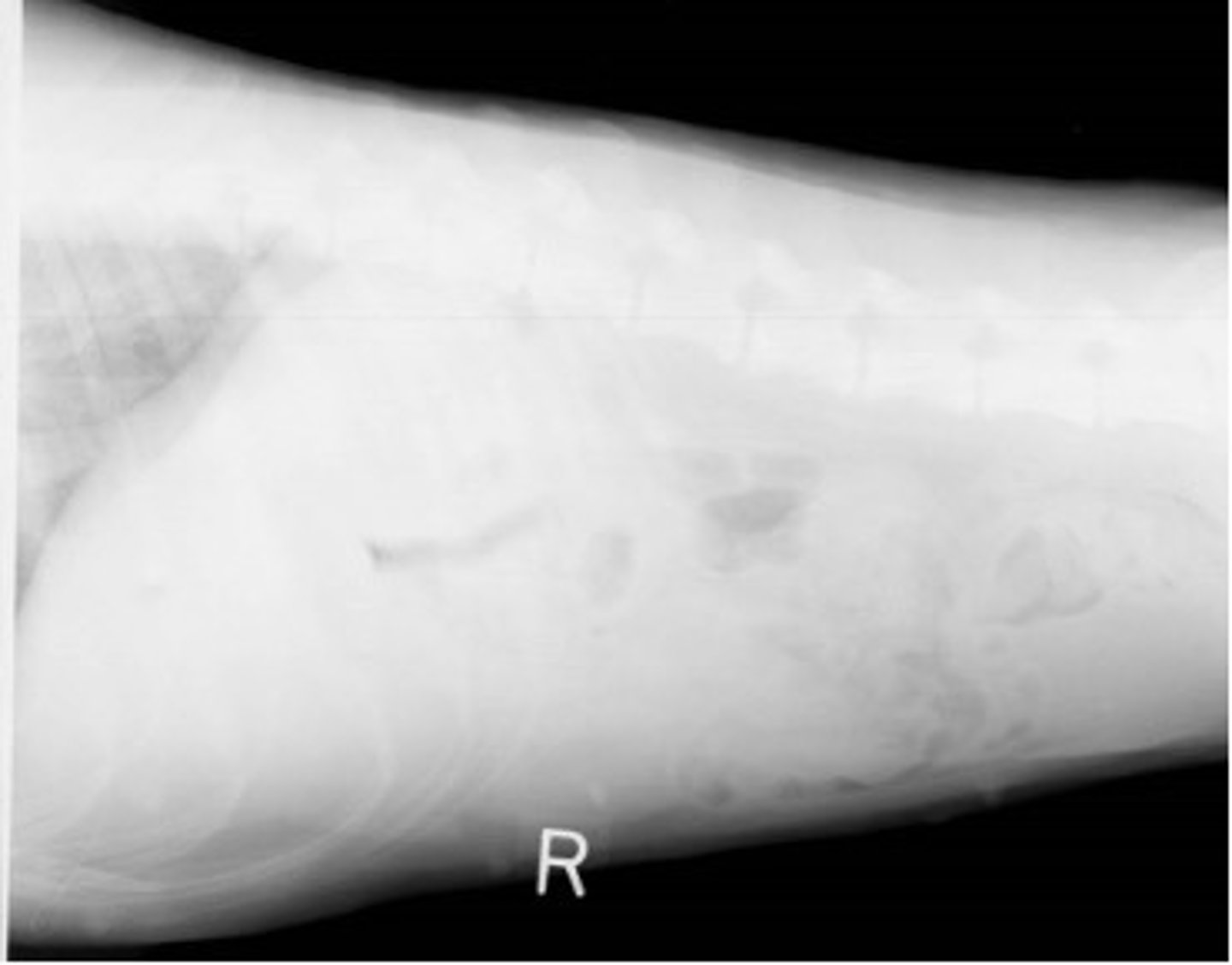
What should you do if a radiograph is too light?
Need to increase either kVp or mAs
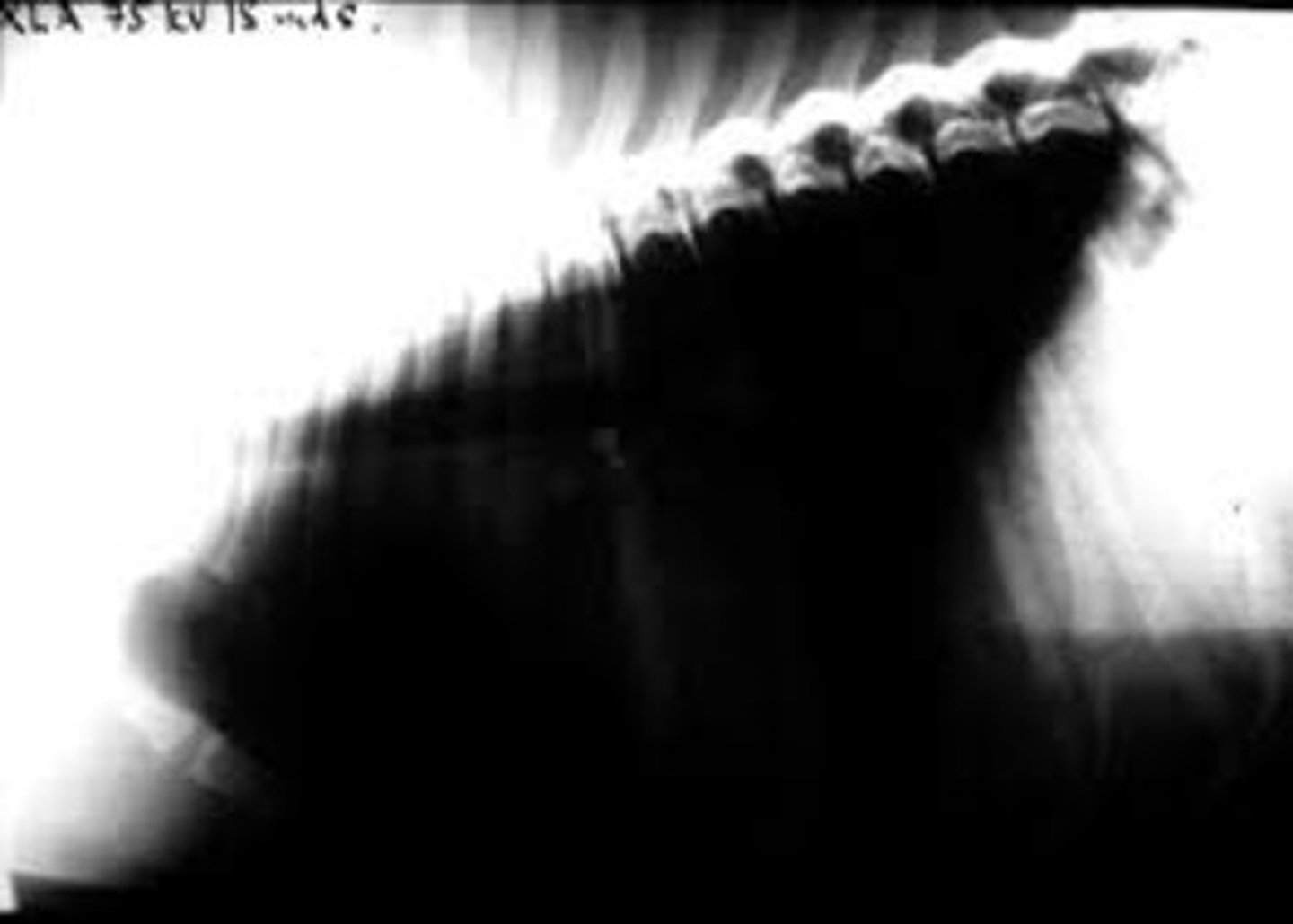
What should you do if a radiograph is too dark?
Need to decrease either kVp or mAs
What should you do if a radiograph is too light but anatomical structures are still identifiable?
Increase mAs by 30-50%
What should you do if a radiograph is too light and anatomical structures are not identifiable?
Increase kVp by 10-15%
If a radiograph is too dark, and bone is not distinguishable from tissue, what should you do?
Decrease kVp 10-15%
If a radiograph is too dark, but bone is distinguishable from tissue, what should you do?
Decrease mAs by 30-50%
What is scatter radiation?
Non-image forming radiation that is scattered in all directions as a result of object in path of the beam
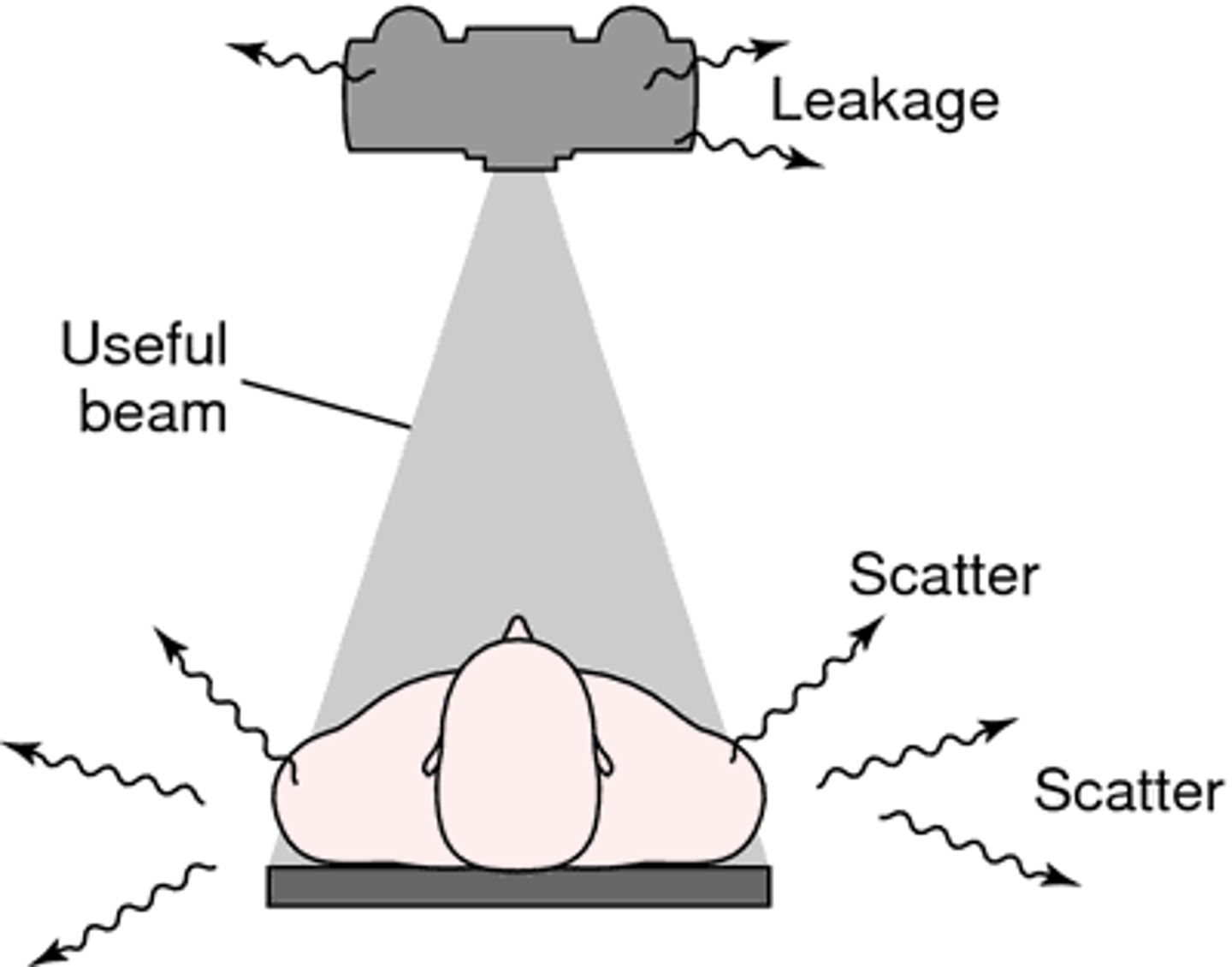
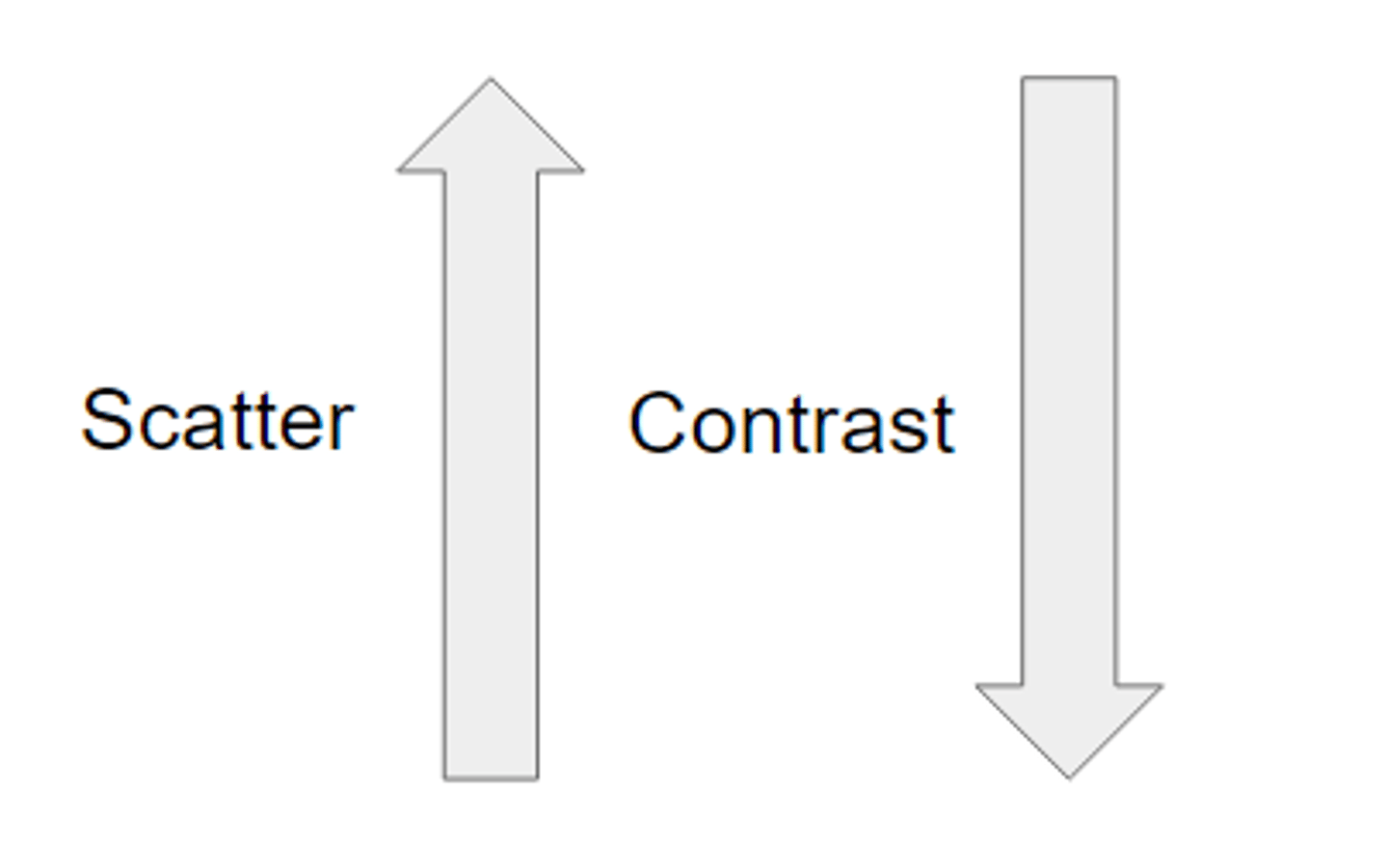
Scatter radiation _______ contrast
decreases
How can you "clean up" scatter radiation?
Use of grid
What are grids?
Thin plate containing lead strips placed between patient and IR
What is the placement of a grid?
- On top of IR
- Inside IR
- Directly within tabletop
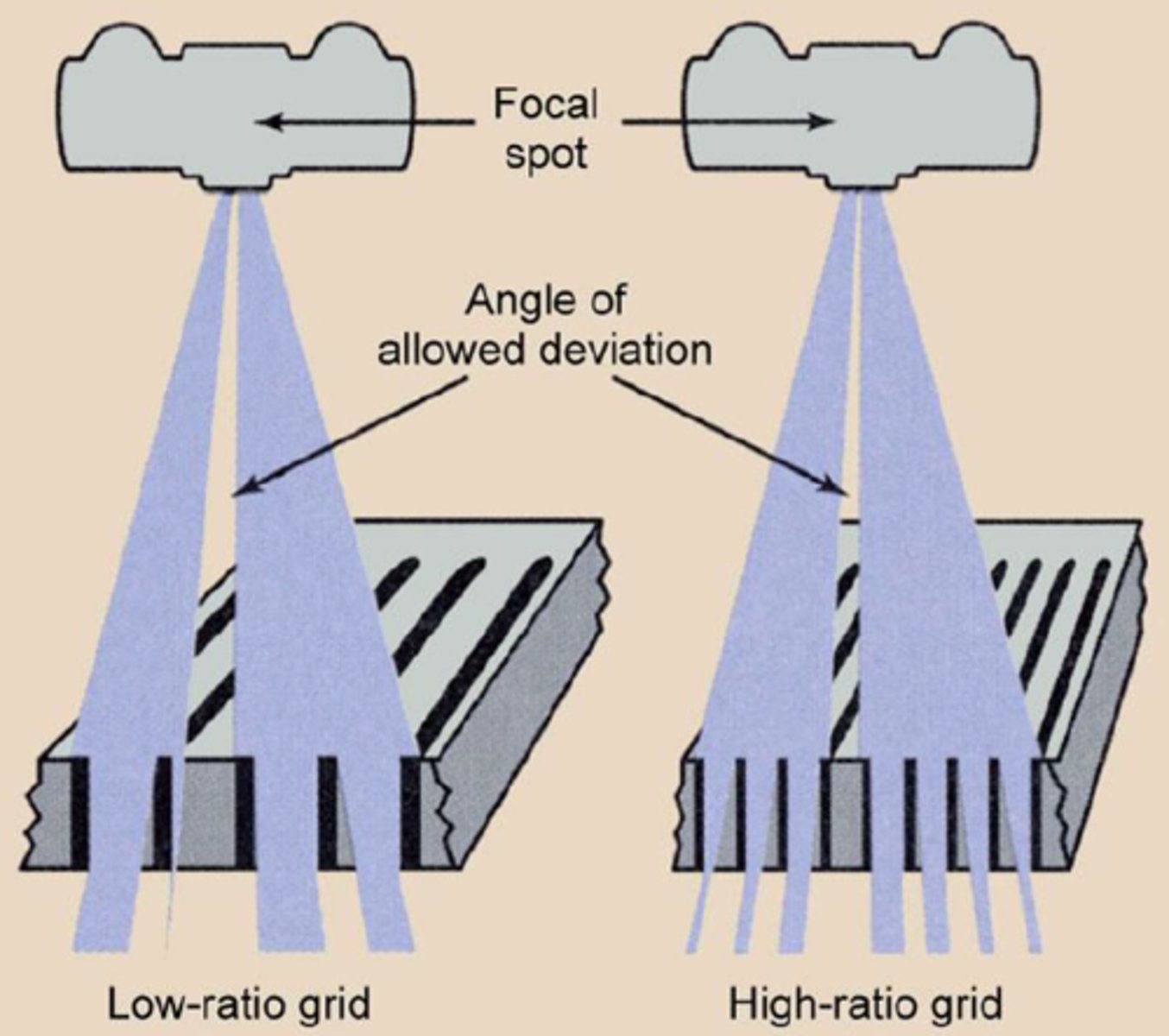
Why are high-ratio grids more effective than low-ratio grids?
Angle of deviation is smaller
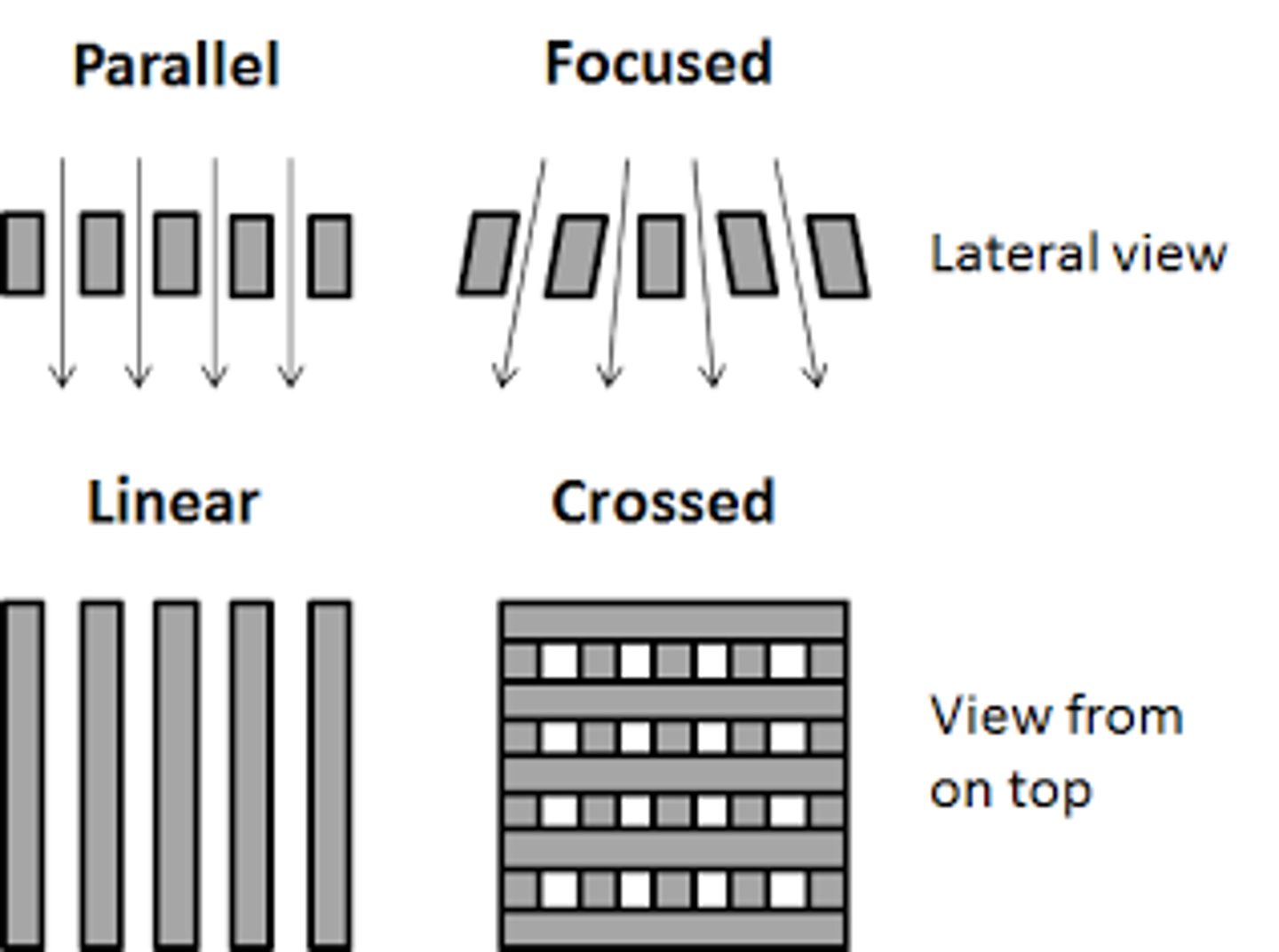
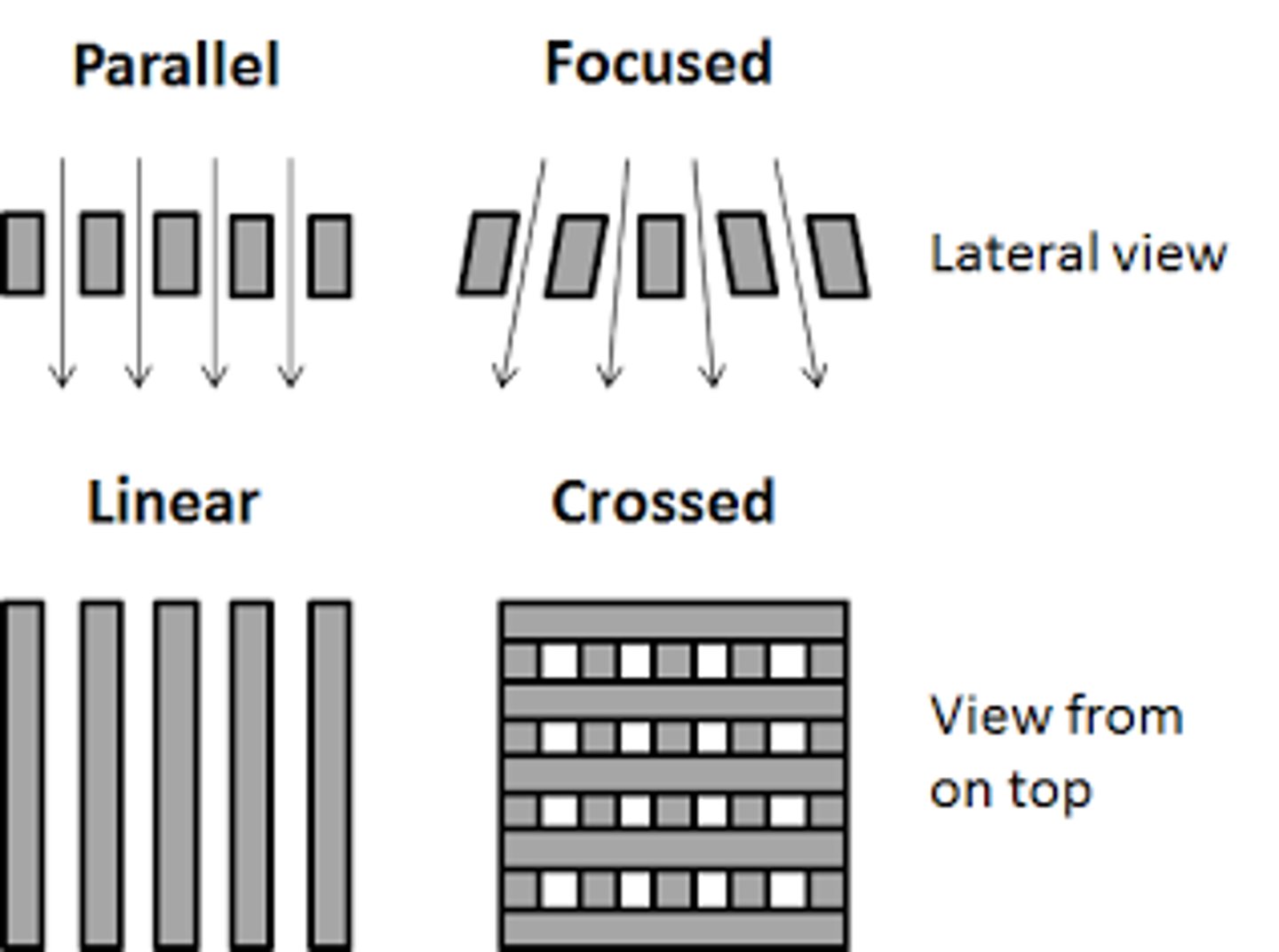
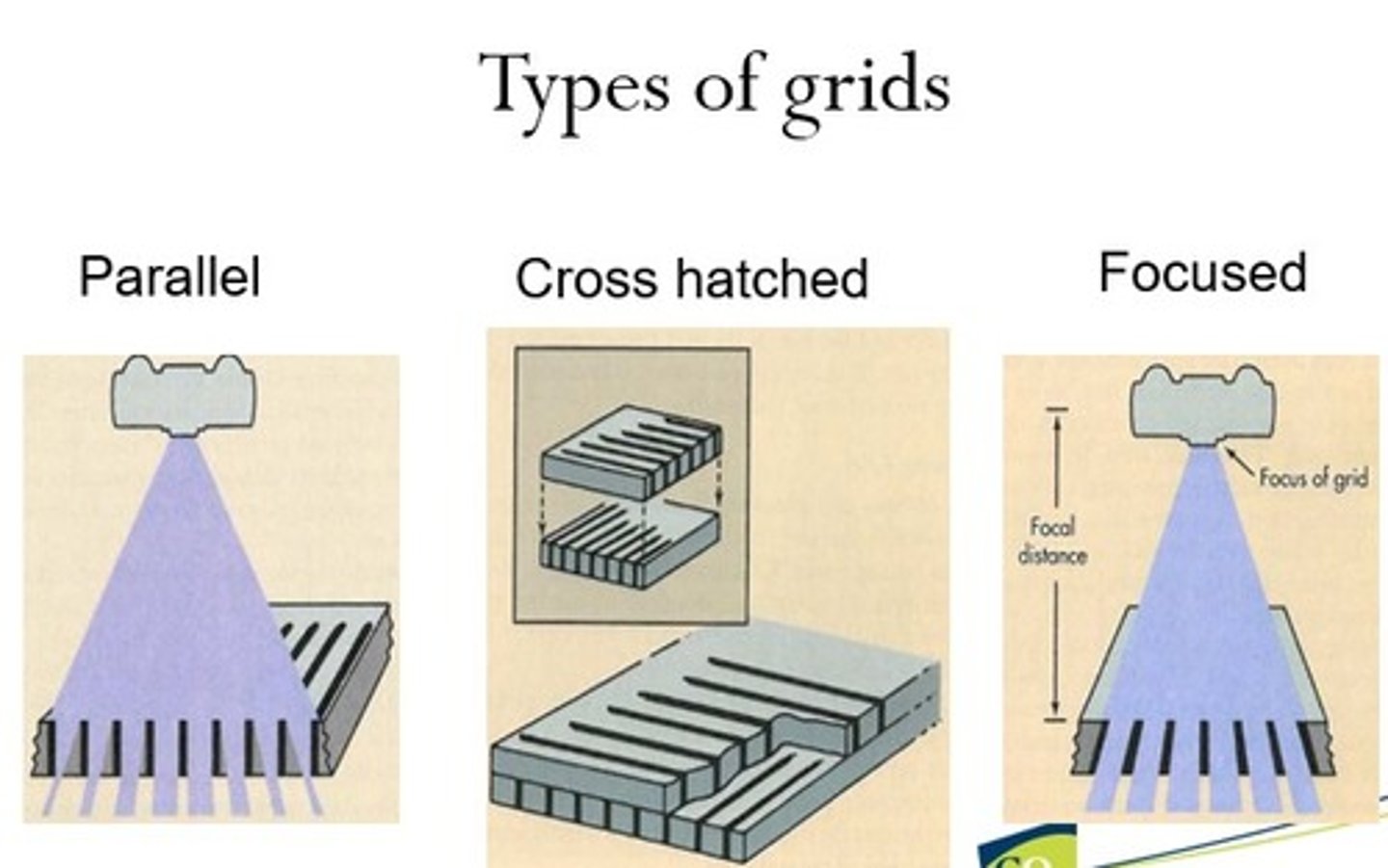
Grid types
- Unfocused grin
- Focused grid
- Cross hatch grid
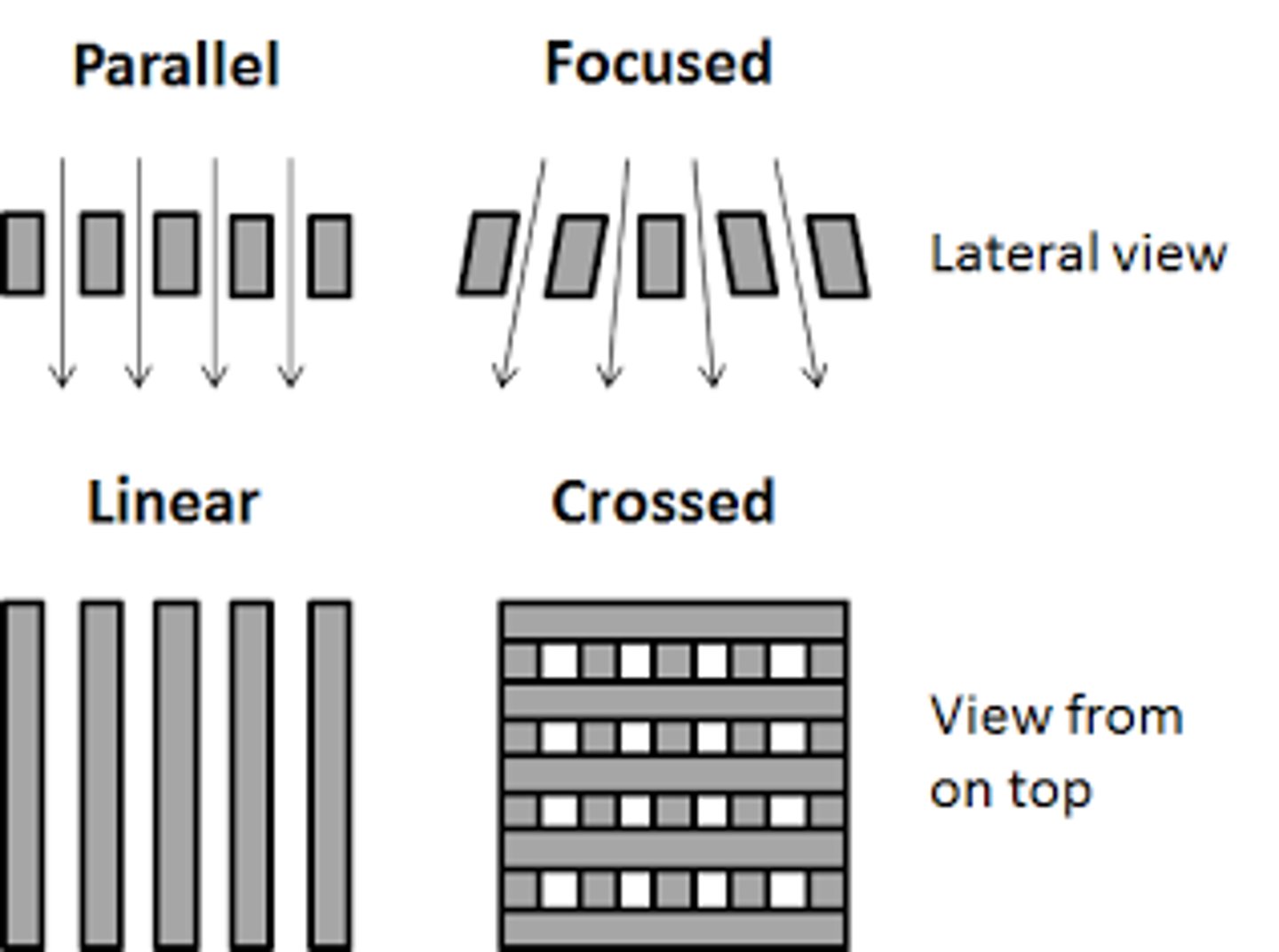
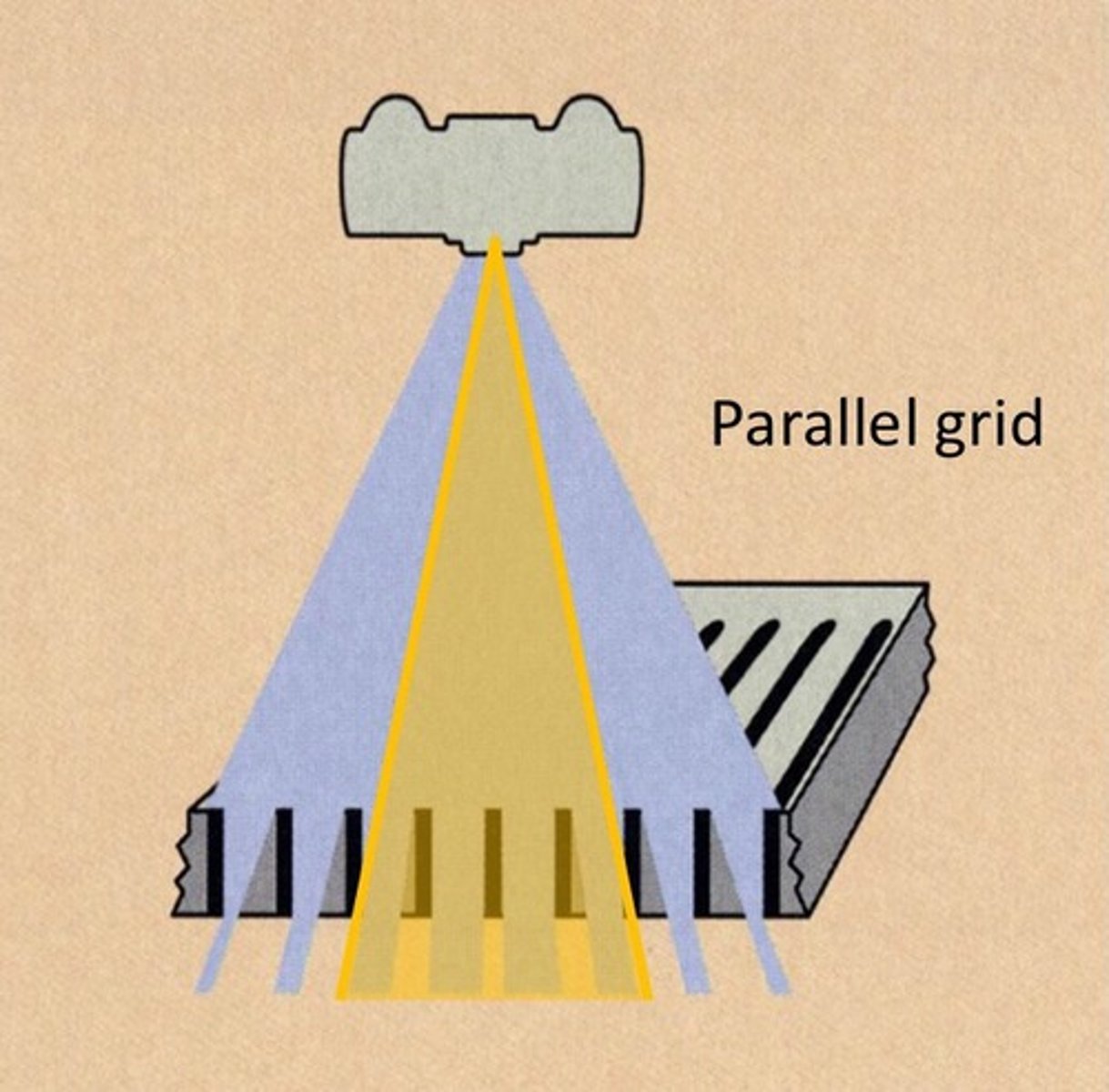
Unfocused grid
All lead strips are parallel
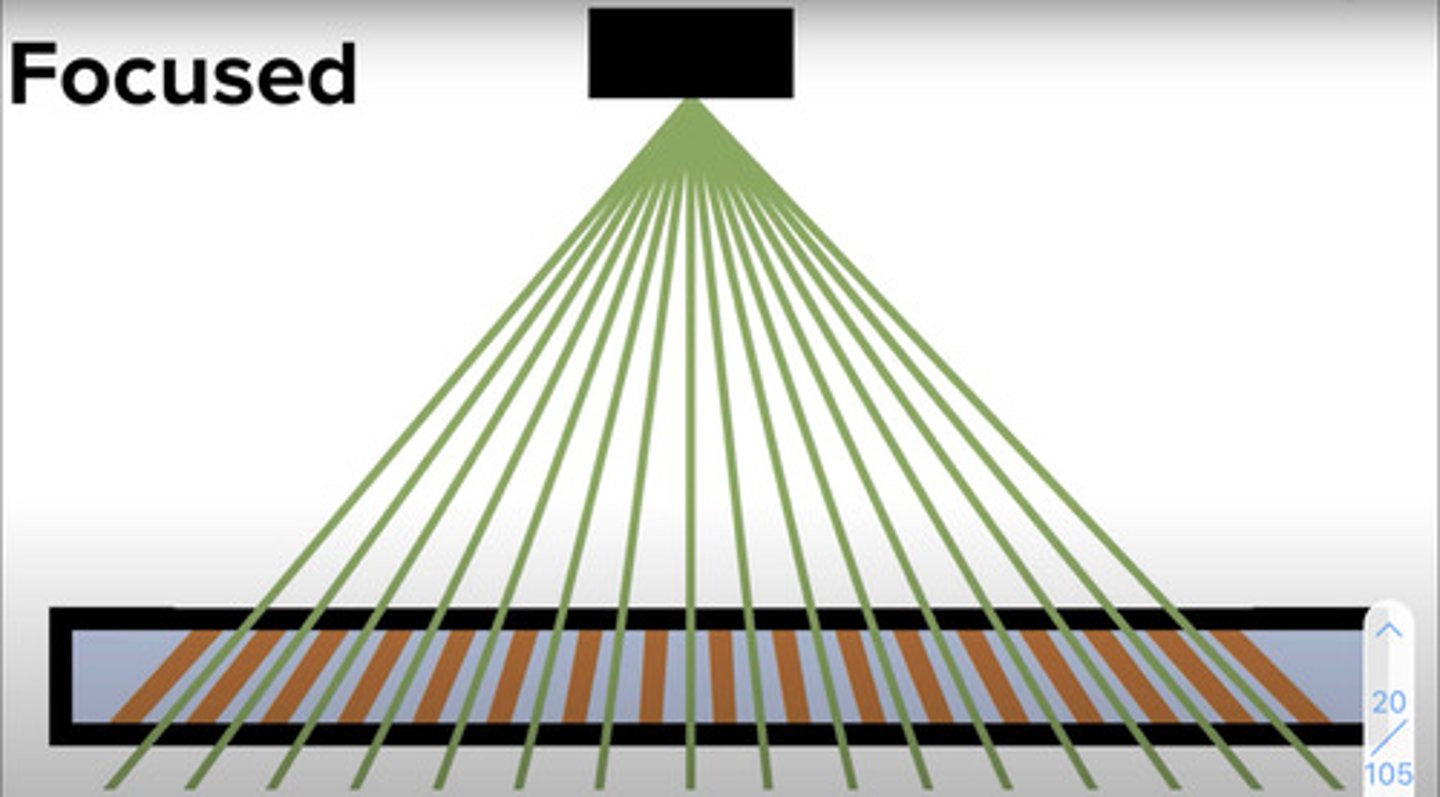
Focused grid
Lead strips angled to match angle of x-ray beam
What type of grid cannot be placed upside down?
Focused grid
Cross hatch grid
Two parallel grids together so that their grids are perpendicular
What type of grid absorbs the most scatter radiation?
Cross-hatch grid
What type of grid cannot be used for oblique images?
Cross-hatch grid
Grid placement concerns
- Off center: Partial cut off across entire image
- Off level: Partial cutoff occurs over entire image receptor
- Upside down: Can be problematic depending on type of grid used
What can cause diminished/decreased radiographic detail?
- Increased focal spot size
- Motion
- Screen/Film contact
- Geometric distortion
Geometric distortion
- Image foreshortening
- Image elongation
- Image magnification
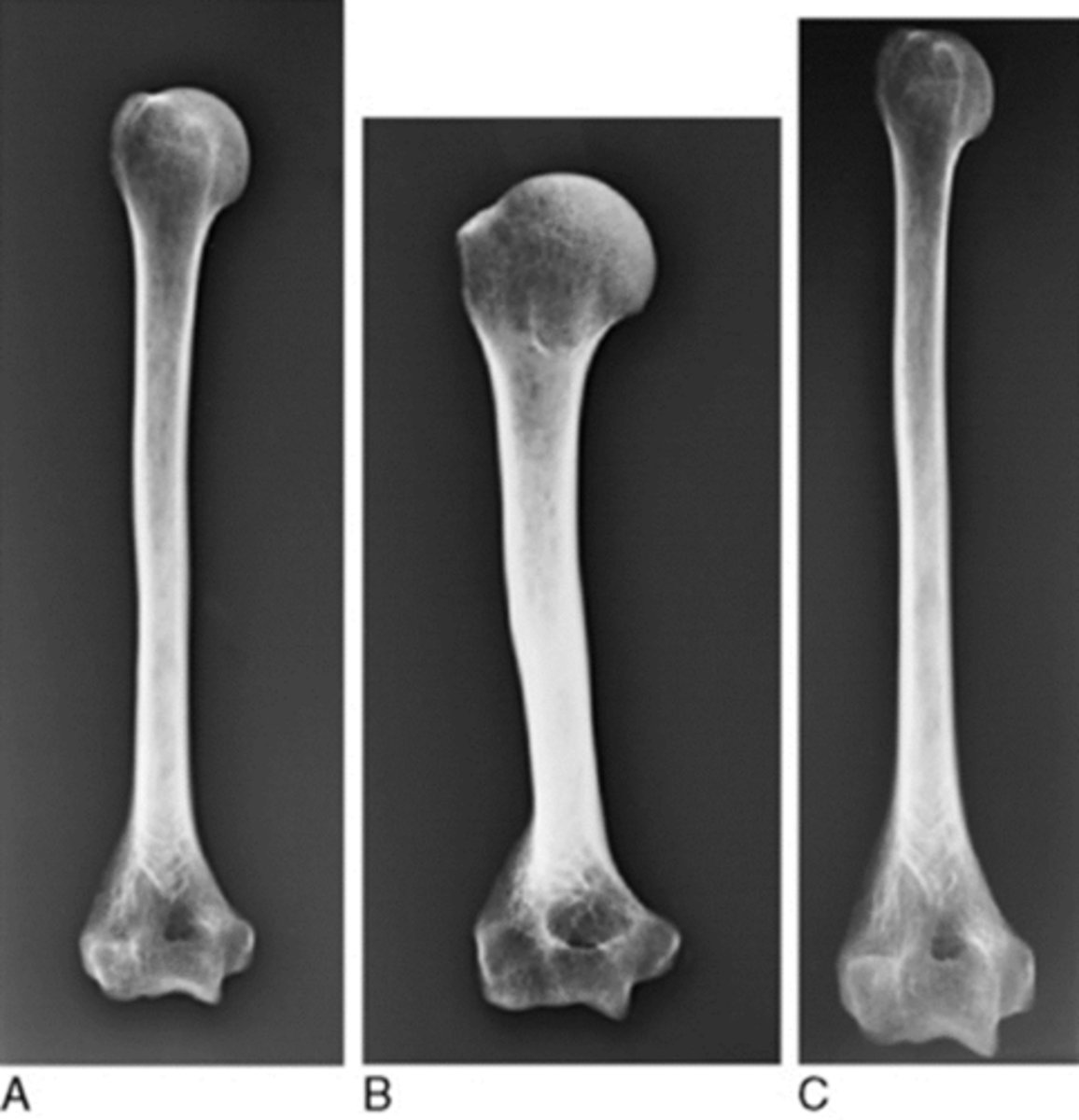
How do you reduce magnification?
Keep patient anatomy as close to image receptor as possible
How do you prevent foreshortening or elongation?
Patient anatomy parallel to image receptor
Image receptor perpendicular to anatomy