M1L1 - Radio Messages, Spin, Resonance, NMR
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
RADTH 305 - MRI Physics. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Describe the basic idea of how MRI works
An MRI machine sends an Rf signal to the protons in body tissue, which causes them to resonate and emit a response signal which is picked up by an NMR receiver
Are protons (aka spins & hydrogen atoms) magnetic?
Yes, protons are magnetic due to their spin.
what is the name of the signal protons send out after they are affected by an Rf pulse?
Nuclear Magenetic Resonance signal
Charge + angular momentum =
magnetic moemnt
Do protons have direction, and what is this direction in the absence of an external magnetic field?
Yes, protons do have a direction, which is random in the absence of an external magnetic field.
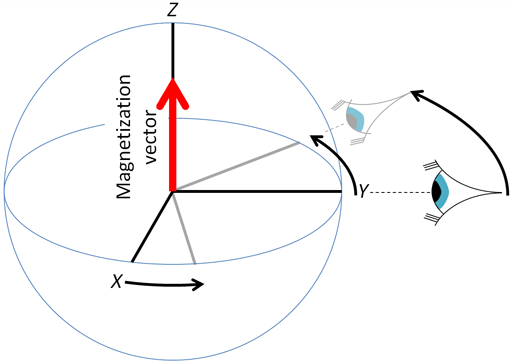
What is the B0 Magnet?
The main static uniform and STRONG magnetic field produced by the superconducting magnet in an NMR system.
What direction is B0 coventially drawn along
The Z-axis, also know as the longitudinal direction
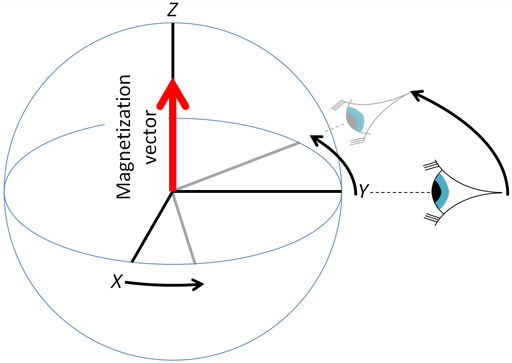
What is the XY plane called?
The transverse plane
Three rules for a single spin (proton) in a B0 field
Each proton has a magnetic direction (in ANY 3D Direction) represented by a vector
The transverse component (xy plane) of a spin precesses about the Z-axis at the Larmour frequency
The Z component of a spin dies not spin
if a spin is pointing along ± Z, it will remain pointing in the same direction with no rotation
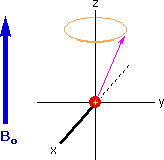
What is the Larmor frequency
The frequency at which a magnetic moment precesses around the direction of an external magnetic field, related to the strength of the field and the specific properties of the nucleus.
what is the formula for Larmor frequency
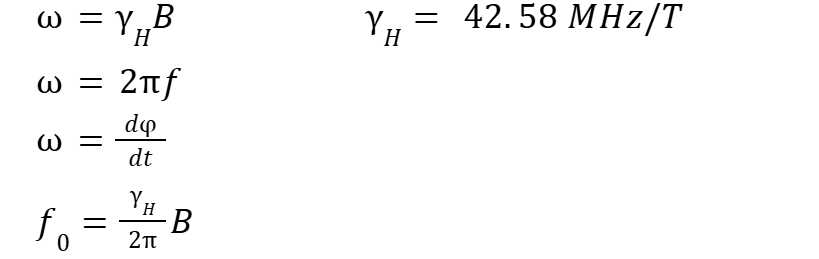
How is frequency impacted by magnetic field
The frequency of the Larmor precession increases linearly with the strength of the magnetic field; as the magnetic field strength increases, the precession frequency also increases.
When is spin precession detectable? When is it not detectable?
Spin precession is detectable when the transverse component of the spin vector is non-zero, typically during resonance with an external radiofrequency field. It is not detectable when the spin is aligned along the Z-axis, as in this case, there is no transverse component to observe.
Spin is affected by it’s ….
environment
electrons, other spins, fields we apply, etc.
Excited spins precess within which plane?
the transverse (xy) plane away from the equilibrium state
what is phase?
Phase refers to the position of a spin system in its precession cycle, represented as an angle in radians or degrees. It describes the timing of spin behavior relative to an external reference point.
phase = rotation angle
Formula for phase
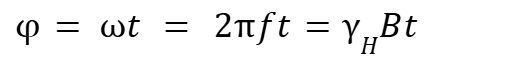
Does an exicted spin have phase?
Yes, an excited spin has phase, indicating its position in the precession cycle.
What does the saying “spin phase accumulates over time, like a memory” mean in MRI physics?
It means that the phase of spins in an MRI system builds up over time, affecting the overall signal strength and coherence, which reflects previous interactions and influences the imaging results.
Phase reflects the history of a spin’s precession. Differences in local magnetic fields or applied gradients cause spins to gradually drift apart in phase. This accumulated phase shift is not lost — it “remembers” the effects of the magnetic environment and can be manipulated (e.g., refocused in spin echo, used in phase encoding) to generate MRI signal and spatial information.
Spin phase in MRI
Phase refers to the instantaneous direction that the precessing spins are pointing in. If many spins point in the same direction (‘in -phase’ with eachother), then the fields they produce add, and we can detect the signal
What happens to the MRI signal if the spins are in phase
if many spins point in the same direction (in phase), the fields they produce have an additive effect, and we can detect a signal
what happens to the MRI signal if the spins are out of phase
if the spins are pointing in many different directions, we get a weak signal or none.
What is resonance
Resonance is the phenomenon that occurs when the frequency of the applied radiofrequency pulse matches the natural frequency of the precessing protons, allowing for maximum energy absorption and enhanced MRI signal.
will a resonant system accept energy at a different frequency?
No, a resonant system will not efficiently accept energy at a different frequency.
four factors of a resonant system
has it’s own natural frequency
accepts energy at a resonant frequency
vibrates/oscillates at it’s resonant frequency
radiates energy at the resonant frequency
What is the resonant frequency range in NMR
radiofrequency = Rf = B1 , is in the MHz range
spins accept energy at at specific …
frequency, the resonant frequency
once the system is excited, it emits energy at what frequency?
its resonant frequency (the same resonant frequency)
resonant frequency depends on what two factors
type of nucleus
magnetic field strength
Calculate the linear resonant frequency for a 1.5 T magnet

What conditions must be met for resonance in an MRI machine
The frequency of the RF (B1 field) is set to match the B0 field strength
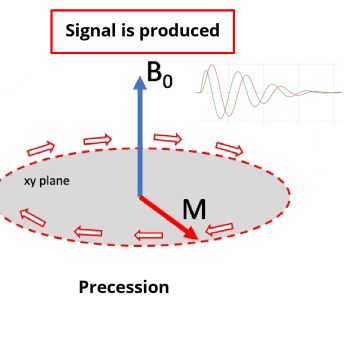
which component precesses about the Z-axis at the larmor frequency?
the transverse component
spin frequency is proportional to …
the applied magnetic field
spins have to be excited in the ____ plane
XY plane
M__ precesses, M__ does not
Mxy precesses, Mz does not
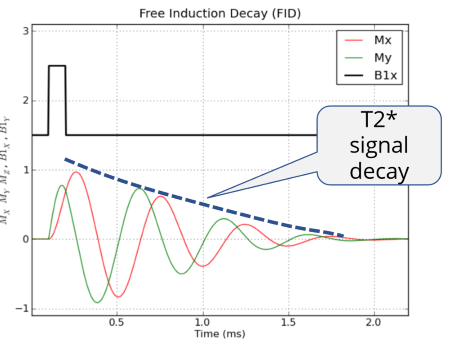
What is FID
Free induction decay
the decaying signal detected by the RF coil after a single RF excitation pulse
why is it called free induction decay
it’s called “free” because no further RF or gradient pulses are applied; the spins are just left to evolve on their own.
It’s called “induction” because the changing transverse magnetization induces a current in the receiver coil (Faraday’s law).
It’s called “decay” because the signal strength decreases over time due to relaxation.
Step-by-step process of FID
RF pulse applied
tips magnetization (usually 90 into the xy plane)
Spins in phase
net transverse magnetization is at maximum —> strong signal
As time passes
spins dephase due to T2 effects, transverse magnetization decreases
The decaying oscillation is recorded by the coil —> this is the FID
the decay constant of FID decay is
T2*
what are the two mechanisms of T2* decay
B0 inhomogeneities
T2 decay
short T2 means …
rapid decay
describe T2 decay
T2 decay refers to the time it takes for the transverse magnetization to decrease to 37% of its original value due to interactions between spin states and dephasing caused by local magnetic field inhomogeneities.
What is TR
TR stands for Time of Repetition, which is the time interval between successive RF pulsations in MRI. It is crucial for determining image contrast and influences the signal received during imaging.
What does T1 relaxation govern
the return of Mz back to equilibrium
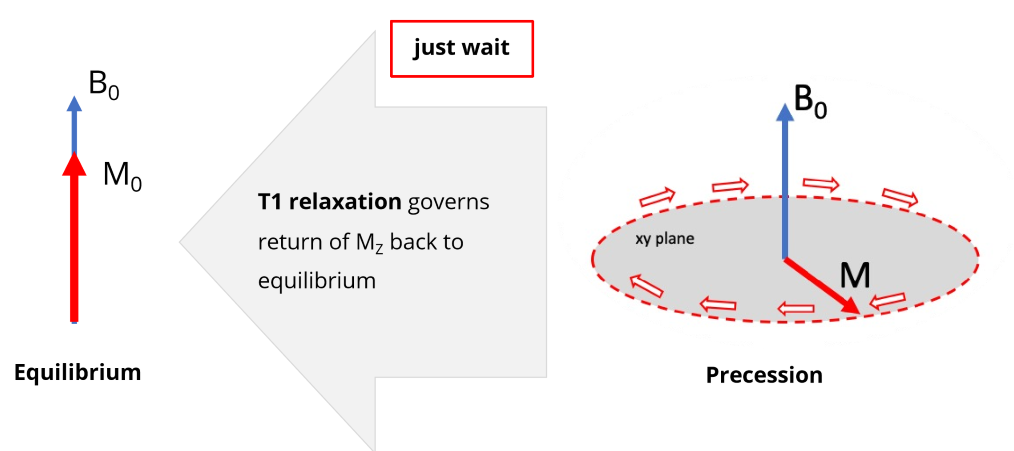
T1 recovery is 95% completed after ____ T1 times
three T1 times
T1 relaxation vs T2 relaxation
T1 (longitudinal) relaxation
Protons give energy back to the surrounding lattice → recover along z-axis.
Fat (short T1) recovers fast, water (long T1) recovers slow.
b) T2 (transverse) relaxation
Spins lose phase coherence in the xy-plane due to spin–spin interactions.
Signal decays as they dephase.
Fat (short T2) dephases fast, water (long T2) dephases slow.