TOPIC 4: OBEY THE LAW!
ISAAC NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION
LAW #1: THE LAW OF INERTIA
LAW #2: FORCE =MASS x ACCELERATION (F=ma)
LAW #3: FOR EVERY ACTION, THERE IS AN EQUAL AND OPPOSITE REACTION
OUTCOME 1: FORCE, MASS, AND ACCELERATION
A force pushes or pulls. It influences the velocity of an object and is measured in Newtons (N).
Mass is a measurement of the amount of matter in a object. It is measured in kilograms (kg). Other units include grams, tonnes, milligrams, stone, and pounds.
Acceleration is a change in velocity. Velocity can change by speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction. It is measured in m/s². Acceleration is the rate in which this change occurs at. This is calculated by the equation below:
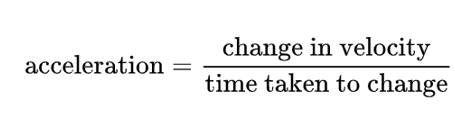
The relation between the three is summarised in Newton’s 2nd law, F=ma.
OUTCOME 2: DISTANCE, SPEED, AND TIME
Speed is the distance travelled by an object in a unit of time. For example, if the distance is measured in kilometers and the unit of time is hours, then the speed is kilometers per hour, or km/h.
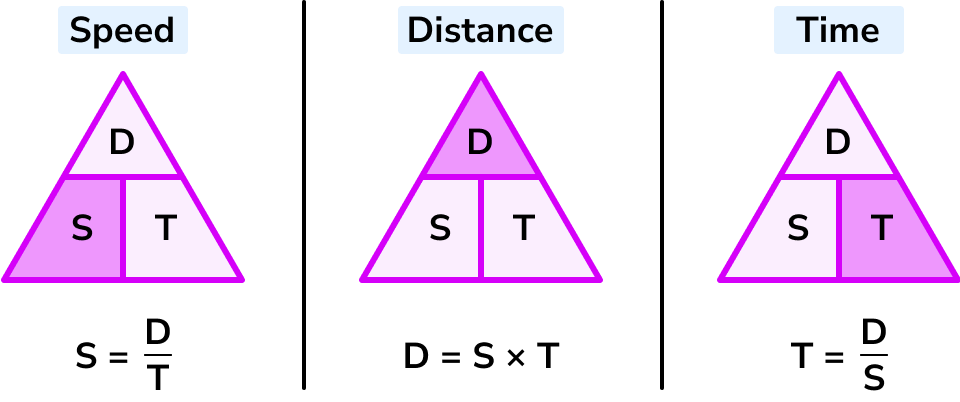
Speed, distance, and time can all be calculated by following the pyramid.
Speed = distance/time
Time = distance/speed
Distance = time x speed
OUTCOME 3: MOTION OF OBJECTS
Net force is the sum of forces acting on something. The equation for acceleration is v-u/t, meaning the final velocity minus the initial velocity divided by the time taken.
The longer the acceleration, the greater the change in velocity.
When acceleration is constant, the change in velocity is directly proportional to time.