Circulation: Hearts and Circulatory Plans
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
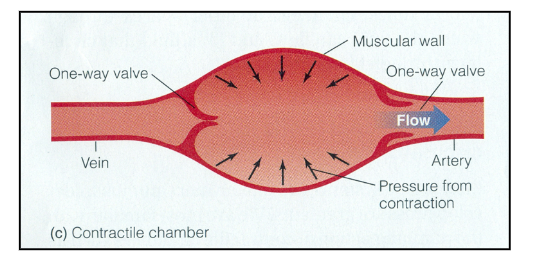
Vertebrate hearts
Acts as reservoir and pump
1-way valves to prevent backflow
What is the order of complexity of vertebrate circulatory systems?
Fish → Amphibian → Reptiles (non-crocodilian) → Mammals/Birds
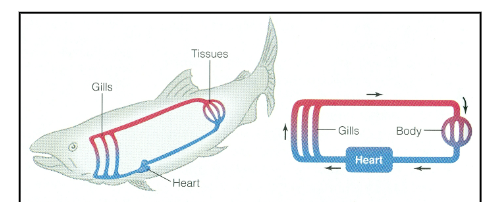
Single-circuit circulatory system
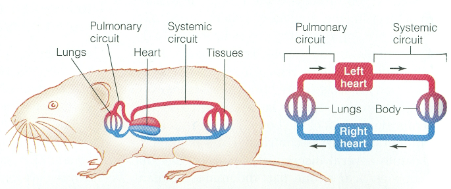
Double-circuit circulatory system
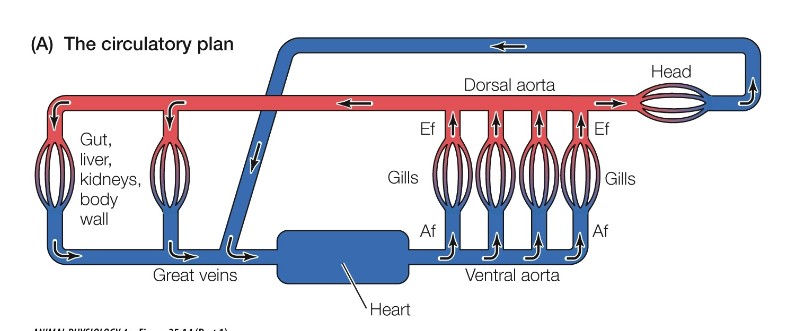
Teleost circulatory plan
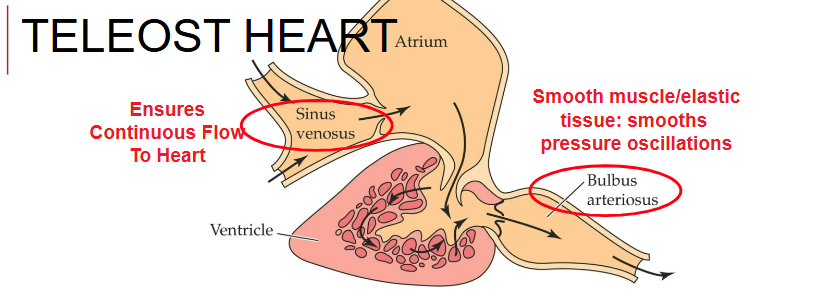
Teleost heart
2 contractile elements
Ventricle: larger pump, sends blood to gills
Atrium: collects blood and pumps, rapidly forces blood into ventricle
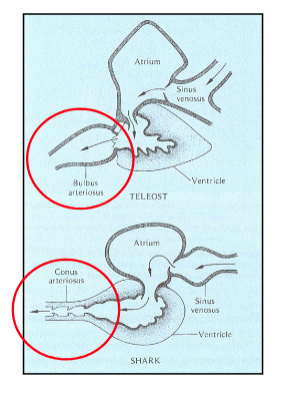
Teleost vs. Elasmobranch
Difference in arteriosus shape bulbus and conus
Air breathing fish
EX. Bowfin, lungfish, electric eel
Aire breathing organs include mouthparts, gut, and swim bladder
Oxygenated venous blood flows into systemic venous circulation, not arterial circulation
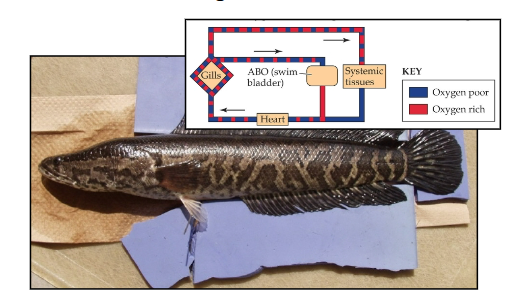
Circulatory plan of the air breathing Snakehead
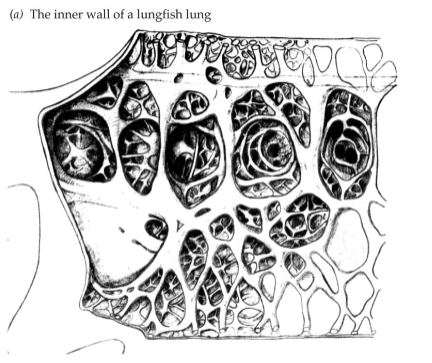
Air breathing African lungfish
Atrium and ventricle partly divided
Conus arteriosus in partly divided
Shares similarities with both fish and amphibians
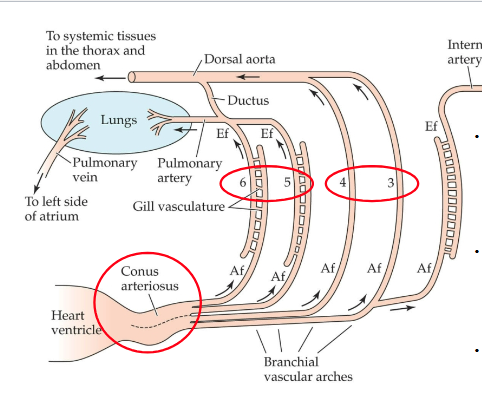
Internal carotid artery goes to the brain
Inner wall of lungfish lung
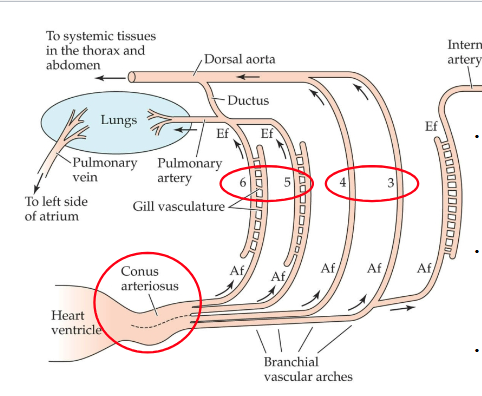
Flow of oxygenated blood in lungfish lung?
Oxygenated blood from lungs flows to left part of atrium and then into left part of ventricle, and then through ventral part of conus arteriosus into gill arches 3 and 4 (w/ no gills)
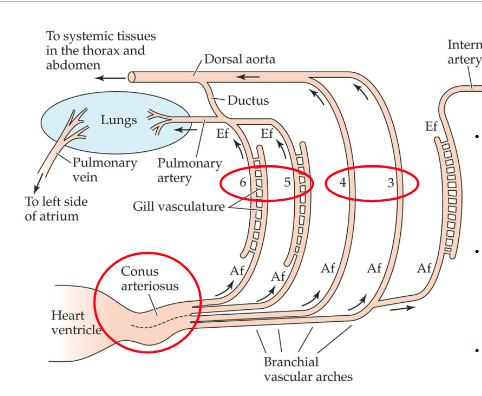
Flow of deoxygenated blood in lungfish lung?
Deoxygenated blood from tissues to right portions of heart chambers and then into gill arches 5 and 6 (w/ residual gills) and then to the lungs where it can oxygenate.
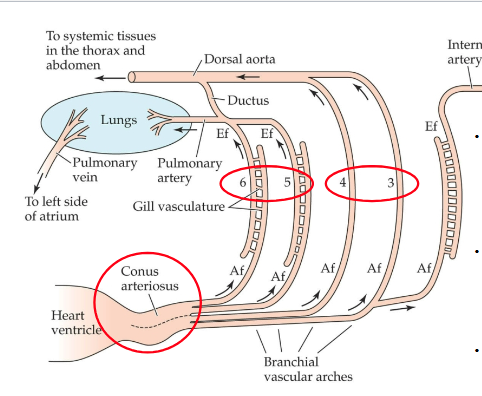
What does the ductus do?
Ductus provides a shunt to bypass lungs when the fish is not air breathing
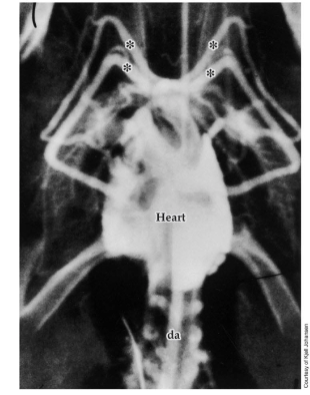
Lungfish Heart X-ray
Opaque fluid injected into pulmonary vein
White areas show location of opaque fluid
Only arches 3 and 4 leading to dorsal aorta, carry oxygenated blood
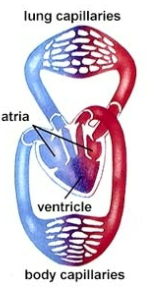
Amphibian Heart
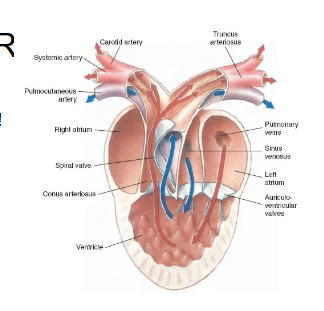
Amphibian heart anatomy
2 atria and 1 ventricle
Left atrium collects oxygenated blood from pulmonary circuit
Right atrium: collects deoxygenated blood from systemic circuit
Undivided ventricle: receives blood from both atria, little mixing due to spiral fold (valve)
Pulmonary Artery: sends blood to lungs and skin
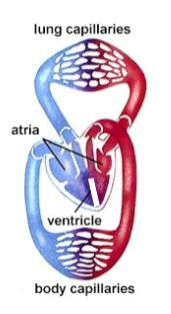
Reptile Heart
Non-crocodilian heart
Ventricle partially divided
Blood flow similar to amphibians, except less to skin
During apnea (intermittent breathing), reduce blood flow to lungs
Crocodilian heart
4 chambers
Structurally different from birds and mammals
Two systemic aortas
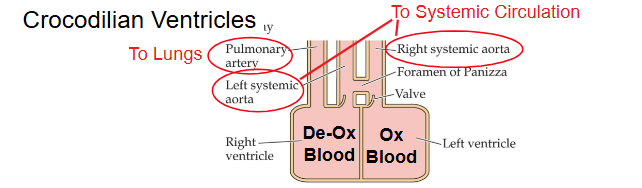
Crocodilian ventricles
Delivers oxygenated blood to tissues and deoxygenated to lungs
Reduces pulmonary blood flow to lungs when lung air is oxygen depleted
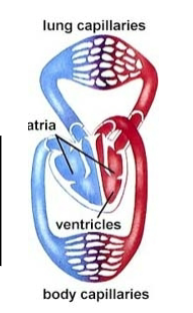
Bird and Mammal Heart
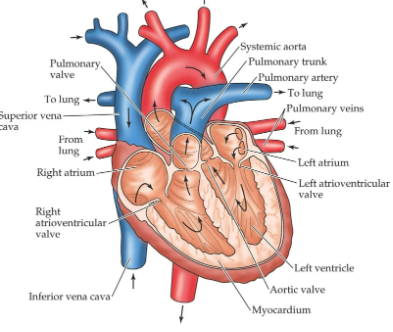
Hearts of mammals and birds
Multichambered
Muscle tissue is formed from cardiac muscle, called myocardium
Left side has two chambers that receive and pump freshly oxygenated blood from the lungs to the rest of the body
Right side has two chambers that receive deoxygenated blood from the body and pump it to the lungs
What are the two distinct pumps of the avian/mammal heart?
Pulmonary pump = right
Systemic pump = left
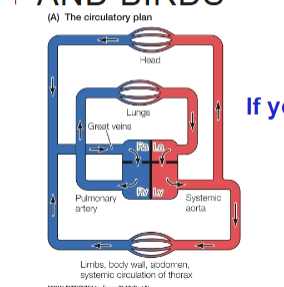
Circulatory plan of mammals and birds
What are the advantages of a divided heart?
Can maintain 2 circuits at different pressures
Why have a divided heart?
Often harder to pump blood to the periphery than to the lungs
Endotherms need lots of blood delivery to support the high metabolism of tissues
Disadvantages of a divided heart
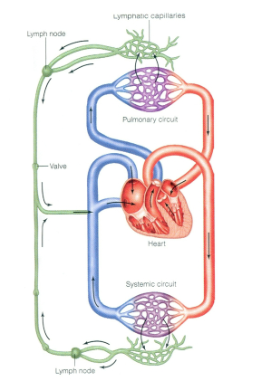
Need for a lymphatic system
Must coordinate
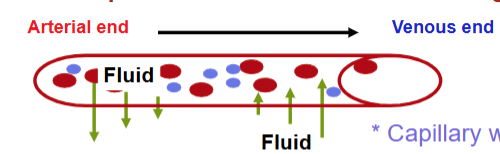
Capillaries
Pressure and fluid exchange
Capillary walls are semipermeable
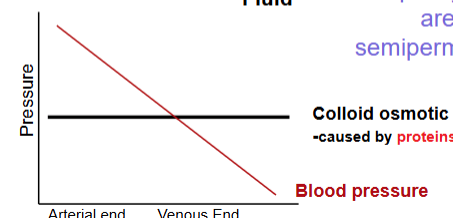
Colloid osmotic pressure
Caused by protiens in blood
What is the net effect of ultrafiltration at capillaries? Where is excess fluid captured?
Loss of fluid
Excess fluid is captured by the lymphatic system
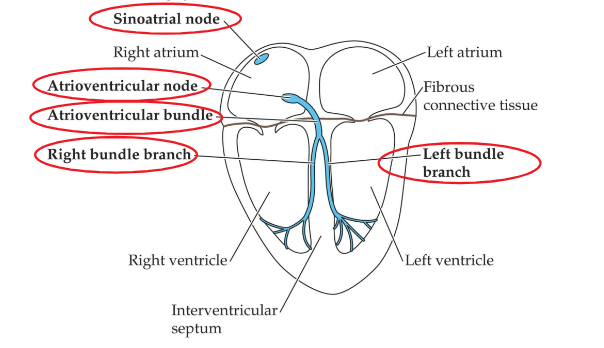
The conducting system and sinoatrial node
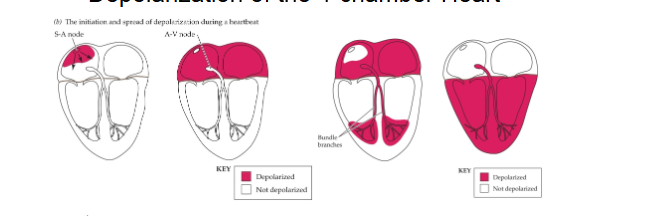
Depolarization of the 4-chamber heart
Contraction originates in SA node
Spreads through muscle of atria to AV node
Delay occurs
Atrioventricular bundle conducts contraction to ventricles
Cardiac output
Volume pumped per unit time
CO = HR * SV
What influences cardiac output?
Nervous system
Endocrine system
Autoregulation
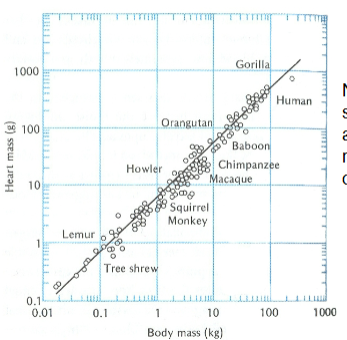
Heart size vs. body size
Neither heart size nor stroke volume accommodate high metabolic demands of small endotherms
Elephant weights 3000kg, its heart weights 18kg and beats at a rate of 25bpm
Shrew weights 3g, its heart weights 0.18g and beats at a rate of 600bpm
Distribution of blood flow
Not equivalent throughout body: kidneys, liver, heart and brain make up 5% of body mass but get over 50% of cardiac output
Changes due to physiological condition: e.g., arousal (penis erection)
Changes due to environmental circumstances: e.g., temperature (vasodilation vs. vasoconstriction)
Changes during exercise
Effects of exercise on circulation
Changes distribution of blood flow
Increase oxygen extraction efficiency
Increase cardiac output
Increase ventilation (water loss)
Example: exercise in humans
At rest: muscles receive 1L blood/min, oxygen extraction 25%, cardiac output 5L/minute (avg: 70bpm, SV=70ml)
During exercise: muscles receive 20L blood/min, oxygen extraction 80-90%, cardiac output 25L/min (avg:200bpm, SV=100ml)
Example: pronghorn antelope
Top speed 100km/h
Can travel 11km in 10min w an avg speed of 65km/h
Fastest sustained runners on earth
Sustain running aerobically
Capable of using 3-5x as much oxygen as similarly sized mammals
How does a Pronghorn do it?
Oversized trachea, lungs, and heart
High cardiac output
Blood completely saturated with O2
High hematocrit (concentration of RBCs)