Biochemistry Exam 1
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1-30 are quiz questions, the rest are things Dr. D stressed in class review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What is the net charge on the dipeptide lys-asp at a pH of 1.0?
A) +3
B) +1
C) +2
D) +4
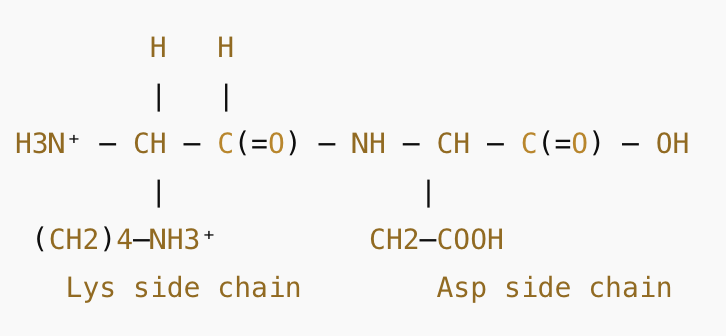
C) +2, because in acidic conditions the amine gains H and the carboxyl stays neutral
How many of the 20 common amino acids contain acidic side chains?
A) 2
B) 1
C) 3
D) 0
A) 2, aspartic acid and glutamic acid
How many of the 20 common amino acids contain sulfur?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 0
B) 2, methionine and cysteine
How many of the 20 common amino acids are achiral?
A) 0
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1
D) 1, glycine
The pKa’s of the -COOH groups of amino acids are usually between 2 and 3. Why are these so much lower than the pKa of acetic acid (4.7)
A) The amino group in amino acids can hydrogen bond with water.
B) The electron-withdrawing effect of the amino group increases the acidity of the acid group.
C) Amino acids are more soluble in water than acetic acid.
D) Amino acid are amphoteric
B) The electron-withdrawing effect of the amino group increases the acidity of the acid group. (NH3+ really positive)
How many of the 20 common amino acids are primary amines
A) 20
B) 18
C) 17
D) 19
D) 19, not proline
Which one of the following best defines the isoelectric point, pI?
A) The pH at which the charge on the amino acid is +1.
B) The pH at which the charge on the amino acid is 0.
C) The charge on the amino acid when the pH equals the pKa of the carboxylic acid group.
D) The charge on the amino acid when the pH is 7.0.
B) The pH at which the charge on the amino acid is 0
The amino groups in amino acids are
A) stronger bases than secondary amines.
B) same basicity of primary amines.
C) weaker bases than primary amines.
D) stronger bases than primary amines.
C) weaker bases than primary amines
Enantiomers are
A) Achiral
B) A pair of compounds that are not superimposable on their mirror images
C) Superimposable mirror images
D) Molecules with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic characteristics
B) A pair of compounds that are not superimposable on their mirror images
What is the name of the functional group at the end of the arginine side chain?
A) amidino group
B) imidazolium
C) guanidino group
D) amide
C) guanidino group
If the pI of amino acids with alkyl group side chains is 6.0, the pI of aspartic acid is ___________
A) larger than 6.0
B) equal to 6.0
C) less than 6.0
D) less than 0.0
C) less than 6.0
What is the relationship between the following two structures?

A) Diastereomers
B) Resonance forms
C) Keto-enol forms
D) Enantiomers
B) Resonance forms
Which one of the following amino acids has a side chain that is likely to be on the surface of a globular protein?
A) leucine
B) alanine
C) glutamic acid
D) phenylalanine
C) glutamic acid
Which of the following amino acids has its alpha carbon as part of a 5-membered ring?
A) proline
B) tryptophan
C) histidine
D) tyrosine
A) proline
What is the purpose of electrophoresis?
A) to neutralize amino acids
B) to synthesize amino acids or proteins
C) to separate amino acids or proteins
D) to analyze the amino acid sequence in a protein
C) to separate amino acids or proteins
What is the total number of tripeptides that can result from two L-alanines and one L-serine?
A) six
B) four
C) three
D) two
C) three, SAA, ASA, AAS
Nearly all naturally occurring amino acids _______?
A) have the (S) configuration at the alpha carbon.
B) have the (R) configuration at the alpha carbon.
C) are racemic mixtures.
D) have basic side chains.
A) have the (S) configuration at the alpha carbon.
Which of the following indicators is commonly used to visualize TLC bands of amino acids
A) Ninhydrin
B) Vanillin
C) potassium permanganate
D) bromocresol green
A) Ninhydrin
Which of the following arrangements is usually not found in the secondary structure of proteins
A) double helix
B) alpha helix
C) pleated sheet
D) random coil
A) double helix
Which amino acid has an imidazole ring in its side chain?
A) asparagine
B) tyrosine
C) tryptophan
D) histidine
D) histidine
Insulin is an example of a(an)
A) Storage protein
B) Transport protein
C) Hormone
D) Enzyme
C) Hormone
Myoglobin is a protein that contains oxygen in the muscles. To what class of protein does it belong?
A) Structural protein
B) Storage protein
C) Protective protein
D) Transport protein
B) Storage protein
All of the following are examples of fibrous proteins except.....
A) insulin
B) skin
C) wool
D) fingernails
A) insulin
All of the following are examples of denaturing proteins except.....
A) Souring of milk
B) Using a curling iron on your hair
C) Digestion of a cheeseburger
D) A mild sunburn
C) Digestion of a cheeseburger
Protein denaturation results in a disruption of the.....
A) Quaternary and Primary structure
B) Primary and Secondary structure
C) Secondary and Tertiary structure
D) Amino acid sequence
C) Secondary and Tertiary structure
Which protein is considered to be a globular protein?
A) collagen
B) albumin
C) keratin
D) myosin
B) albumin
The quaternary structure of hemoglobin contains......
A) 4 subunits
B) 2 subunits
C) 6 subunits
D) 8 subunits
A) 4 subunits
The protein configuration that is primarily the result of R group interactions is the…
A) tertiary structure
B) primary structure
C) secondary structure
D) quaternary structure
A) tertiary structure
All of the following are conjugated proteins except.....
A) hemoglobin
B) collagen
C) myoglobin
D) cytochrome P450
B) collagen
Proteins that consist of two or more chains assembled into a large 3-dimensional structure are said to display.....
A) secondary structure
B) primary structure
C) quaternary structure
D) tertiary structure
C) quaternary structure
What are the parts of an amino acid
carboxyl, amino, and side chain bonded to a C atom
Why are proteinogenic amino acids called alpha amino acids?
Because the amine group is on the alpha carbon
What determines the function of the amino acid in a protein
the side chain
How many proteinogenic amino acids are there
20
How many of the 20 amino acids are essential
10
What single amino acid has an R-configuration
cysteine
Are all amino acids L or R configurations
L
What are the neutral nonpolar aliphatic amino acids
Glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine
What are the neutral nonpolar amino acids
proline, methionine
What are the neutral nonpolar aromatic amino acids
phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan
What are the neutral polar amino acids
serine, cysteine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine
What are the basic amino acids
histidine, arginine, lysine
What are the acidic amino acids
glutamic acid, aspartic acid
Which two amino acids have two chiral centers
isoleucine and threonine
Which 2 amino acids have sulfur
methionine and cysteine
What does zwitterionic mean
the compound is overall neutral even though there are charged groups
Which amino acid is not chiral
glycine
In an integral protein where are nonpolar and polar amino acids located?
hydrophobic middle of the membrane and hydrophilic outside the membrane
Which amino acids serve as attachment and phosphorylation sites and why
serine, threonine, and tyrosine because of the hydroxyl group
How do disulfide bonds form
oxidation
Insulin storage
starts as an unreactive protein until it is needed, pancreas stores preproinsulin
Which amino acid is nonessential in desperate circumstances
arginine
What amino acids are essential?
His, Ile, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Thr, Trp, Val
How are peptide bonds formed?
dehydration
peptide bonds have slight double bond formation between N and C which causes what
rigid bond that cant rotate and bond is shorter than a single bond
The _____ C-----N bond is somewhat shorter than the _____ C----N bond
peptide; simple amine
Hydrolytic cleavage of the amide bond requires what kind of enzymes and what are two common ones and where do they cleave?
Hydrolytic enzymes
Trypsin: to the right of Arg and Lys groups
Chymotrypsin: to the right of Phe, Tyr, and Trp
How are amino acids named
start from N terminus and add -yl to group and final amino acid is normal name
structural proteins use what secondary structure
alpha helix
globular proteins use what secondary structure
beta sheets
What proteins reverse denaturation
chaperones
Prosthetic groups
non protein non amino acid groups like metals or organic materials
Ex: heme
Simple protein
no prosthetic groups, structural
Conjugated protein
have prosthetic groups
Heme structure
Iron II (ferrous) in middle of porphyrin ring
Iron binging in heme
bound to 4 nitrogens and hemoglobin by histidine, one site for oxygen
How does hemoglobin transport CO2
as carbamate
T Form (Taut) of Hemoglobin
deoxygenated, low O2 affinity
R Form (relaxed) of hemoglobin
oxygenated, high O2 affinity
Allosteric interactions
when specific molecules bind to a protein and modulates its activity
biphosphoglycerate
allosteric moderator, influence affinity of O2 for hemoglobin
Carbon monoxide poisoning
CO finds to Fe++ so hemoglobin cant bring O2 to tissues
Methemoglobin
Fe++ turns to Fe+++ > cant bind to oxygen, use antioxidants to prevent oxidation
Cyanide poisoning
messes with ETC, take methemoglobin to bind with cyanide