AQA GCSE Geography: Tropical Rainforests
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
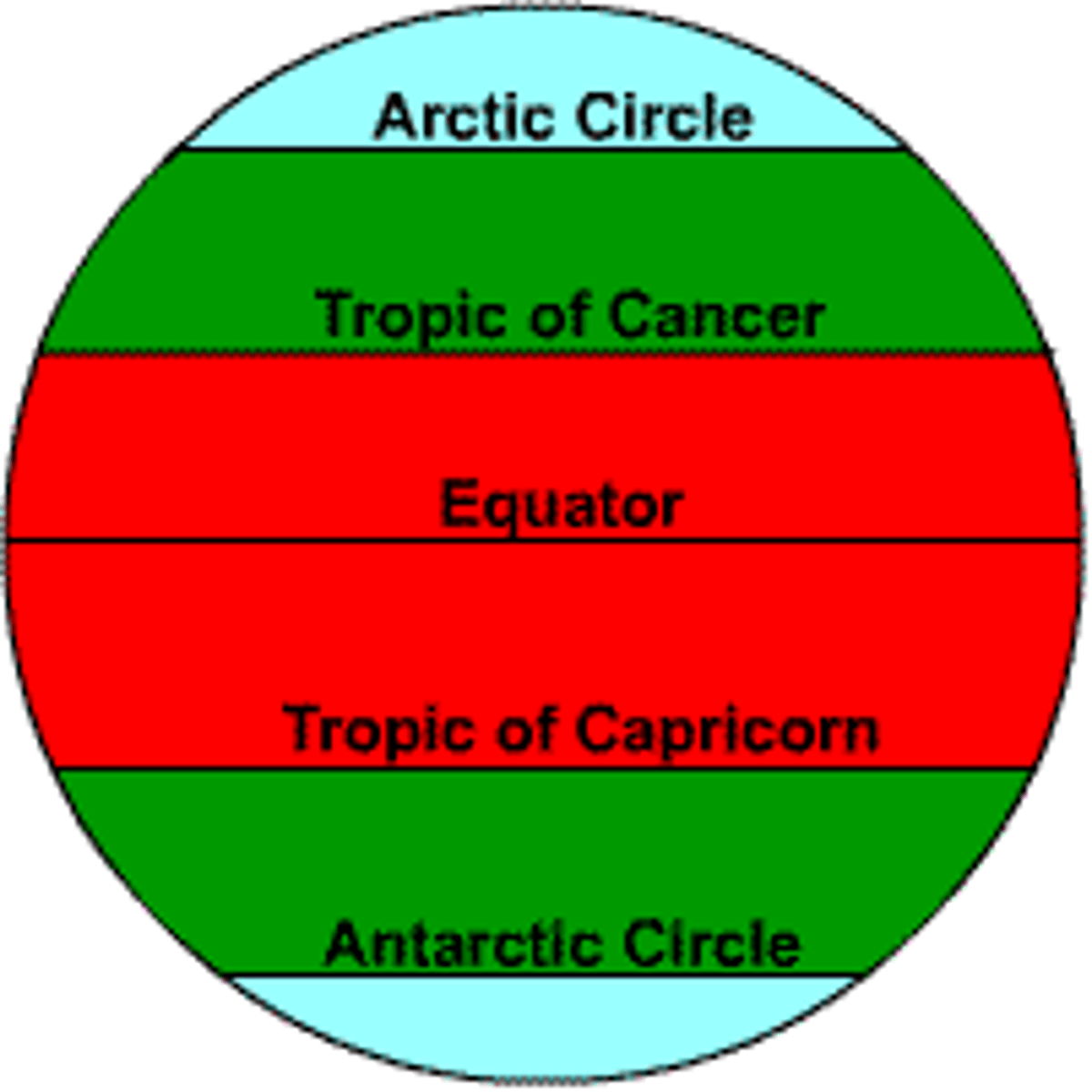
Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn
Imaginary lines either side of the equator bordering the area where the sun strikes directly, the area that receives the most heat.
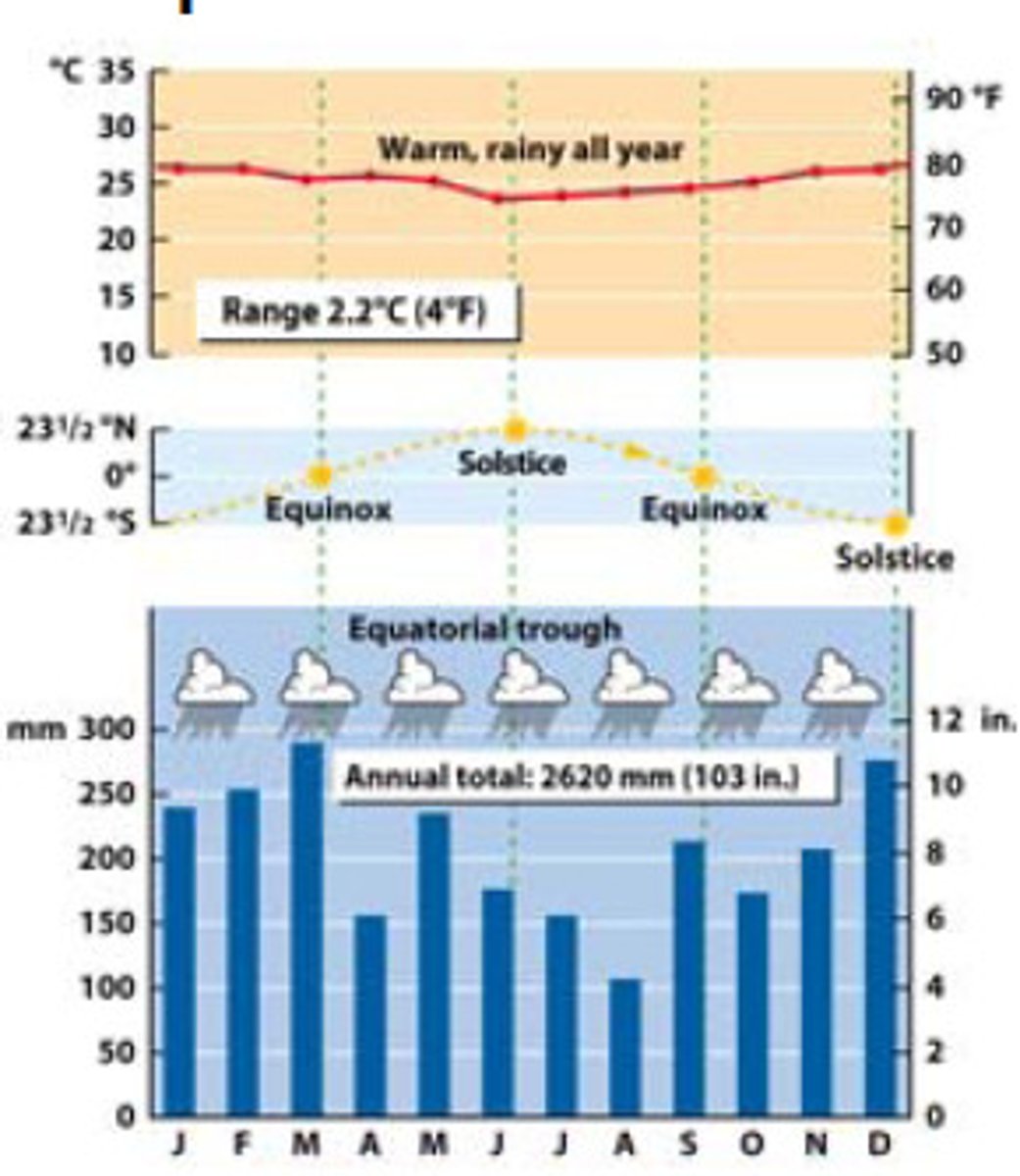
Equatorial climate
The constantly hot and wet climate of regions near the Equator.
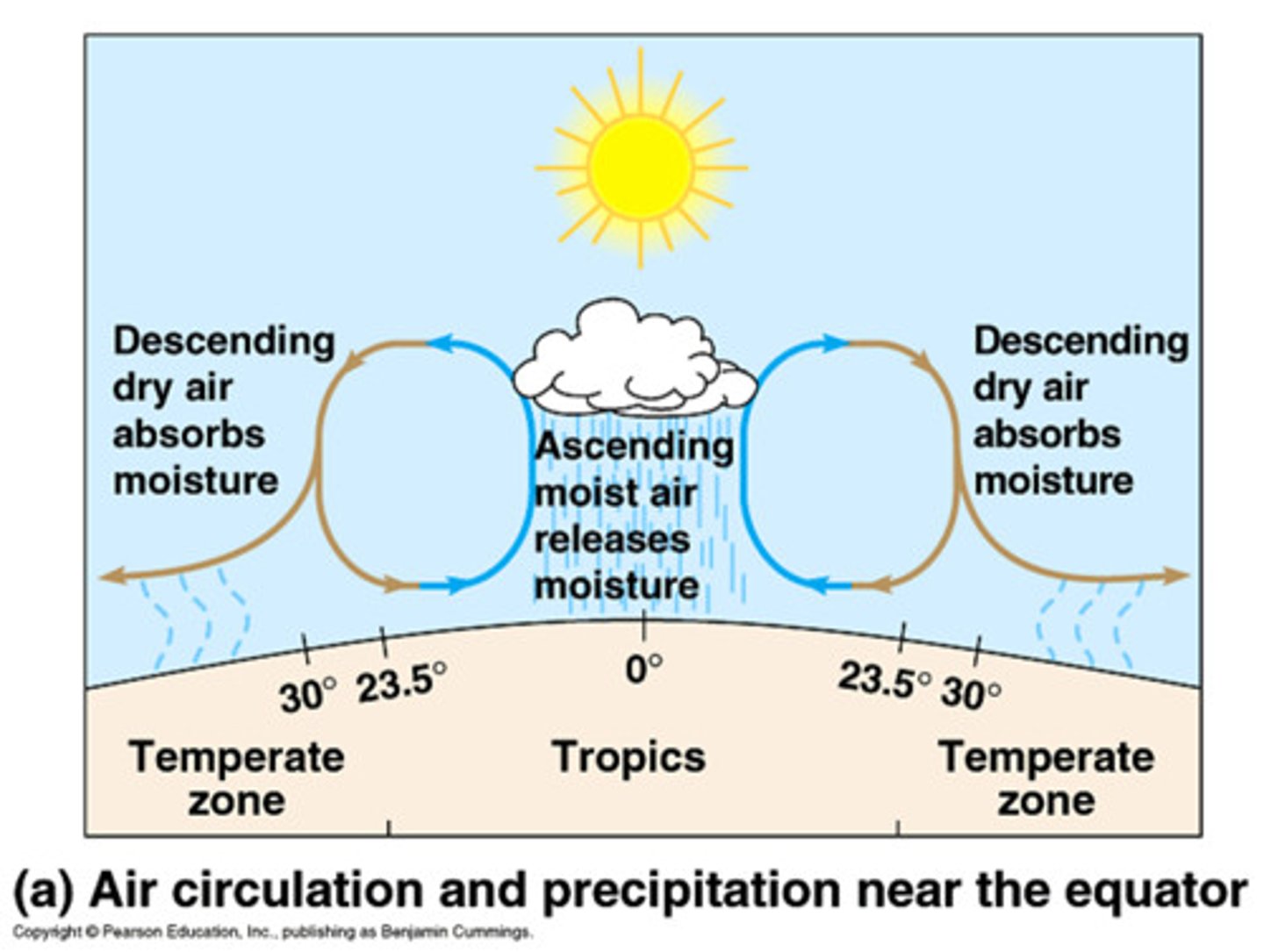
Hadley Cell
A large-scale atmospheric convection cell in which air rises at the equator and sinks at medium latitudes, typically about 30° north or south.
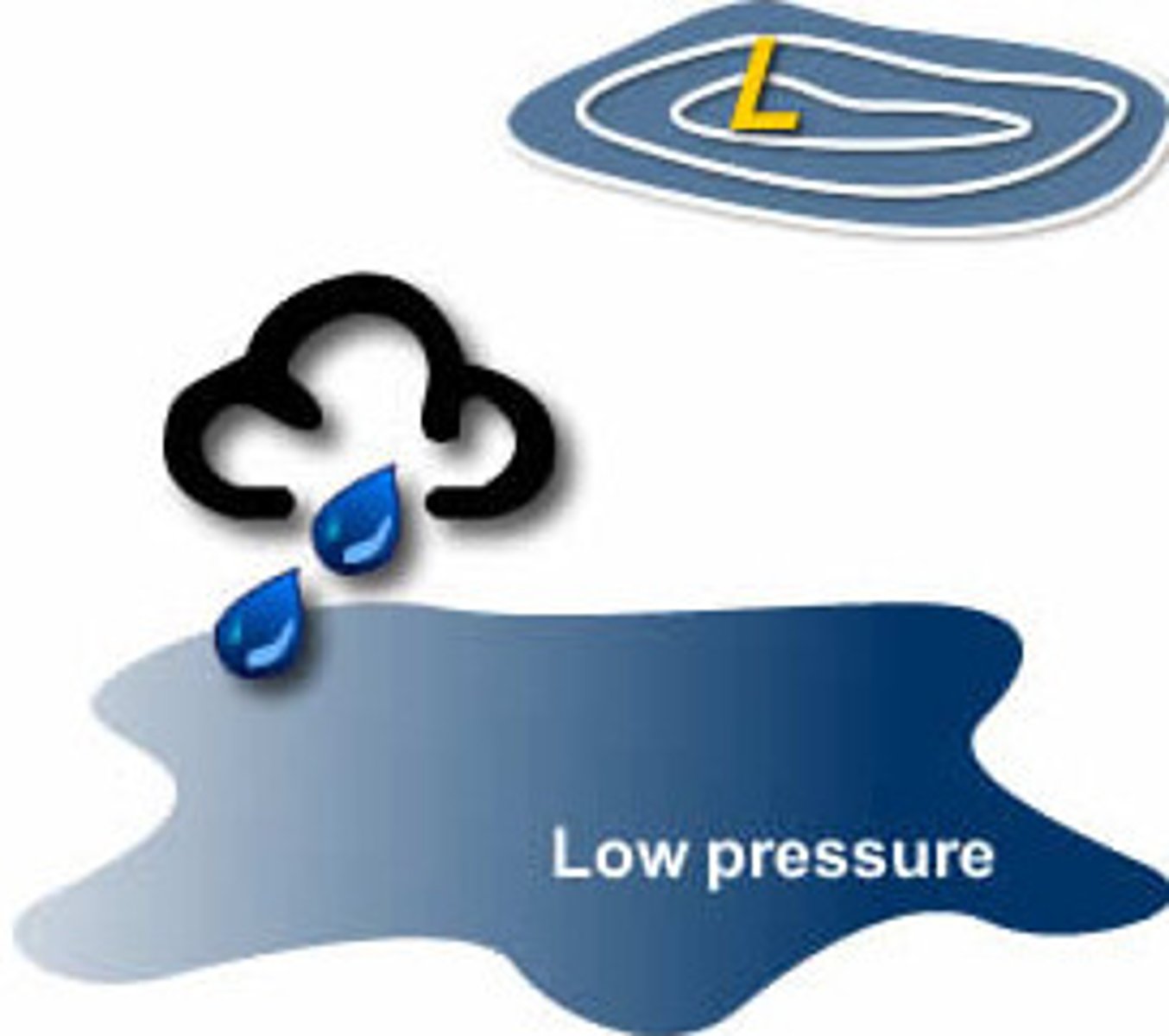
Low air pressure conditions
A mass of rising warm air that usually bring wet, stormy weather.
Leaching
Removal of dissolved materials from soil by water moving downwards.
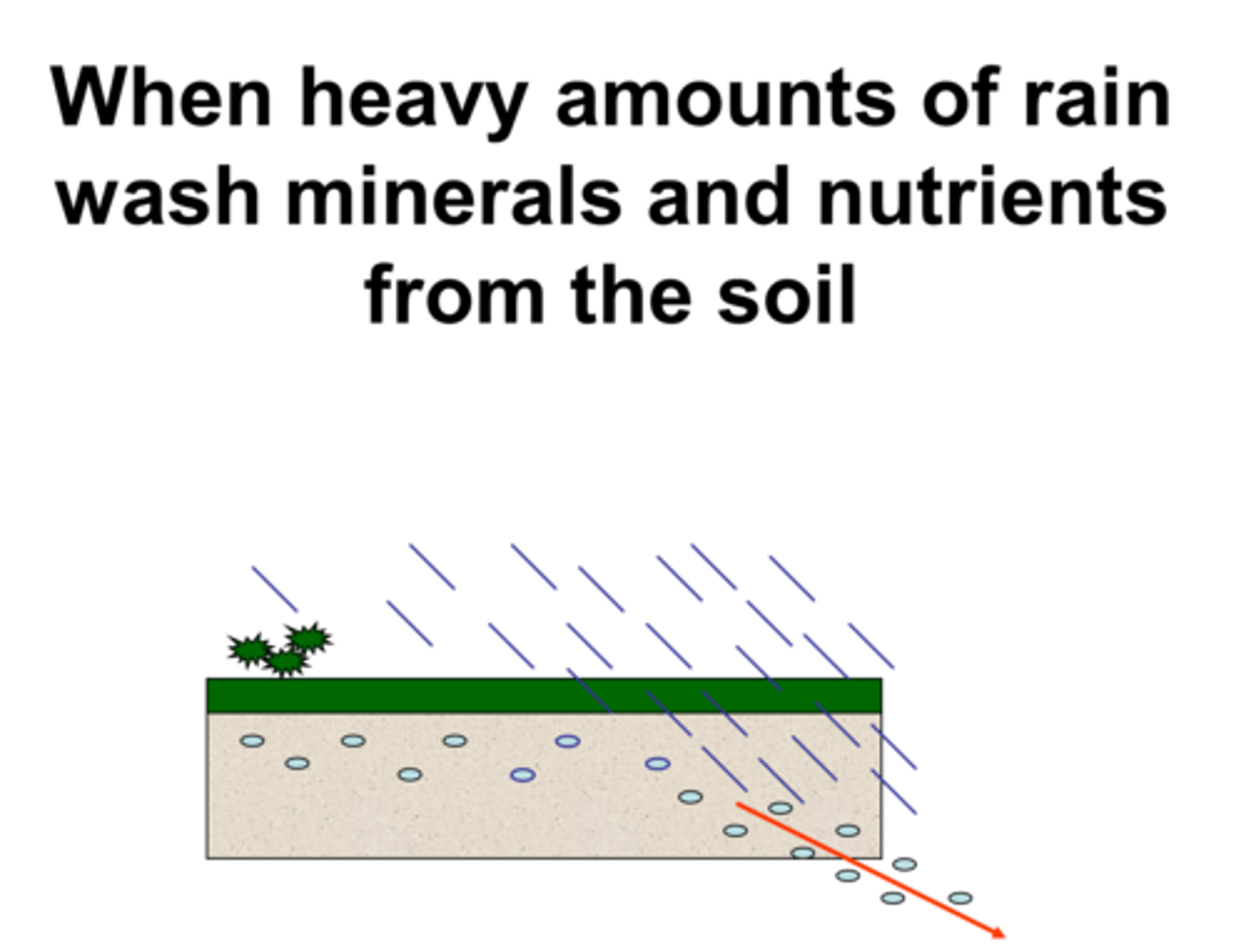
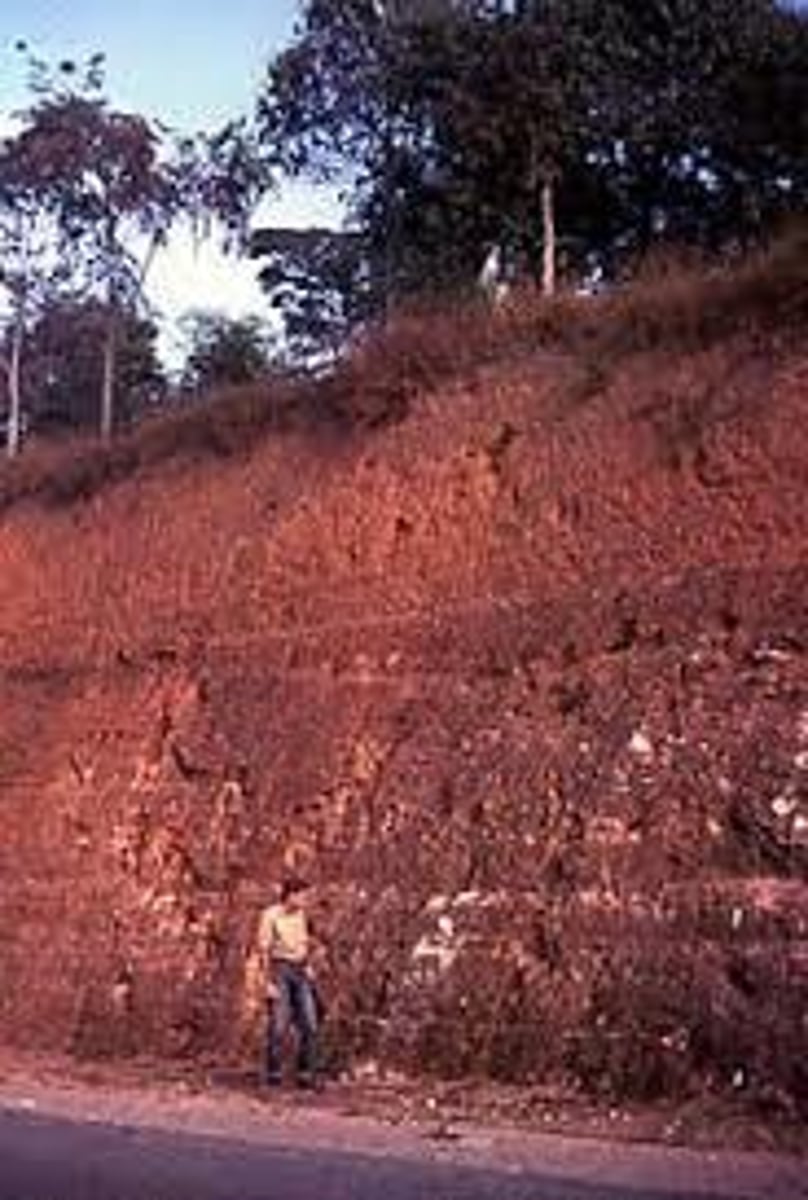
Latosol
An iron-rich, infertile soil found in tropical rainforests

Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem. Tropical forests are biodiversity 'hotspots'.

Adaptation
A characteristic that improves an individual's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment.
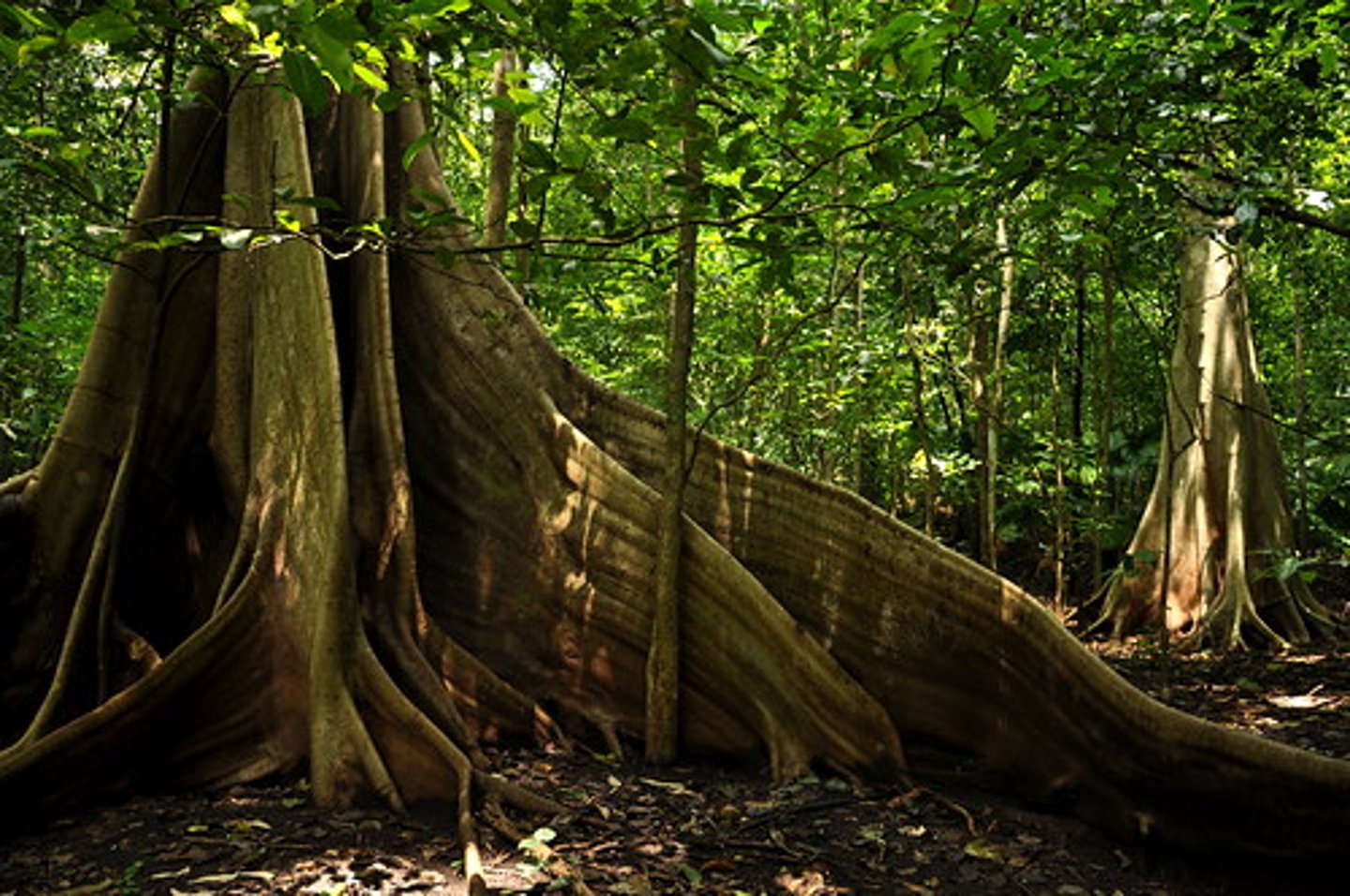
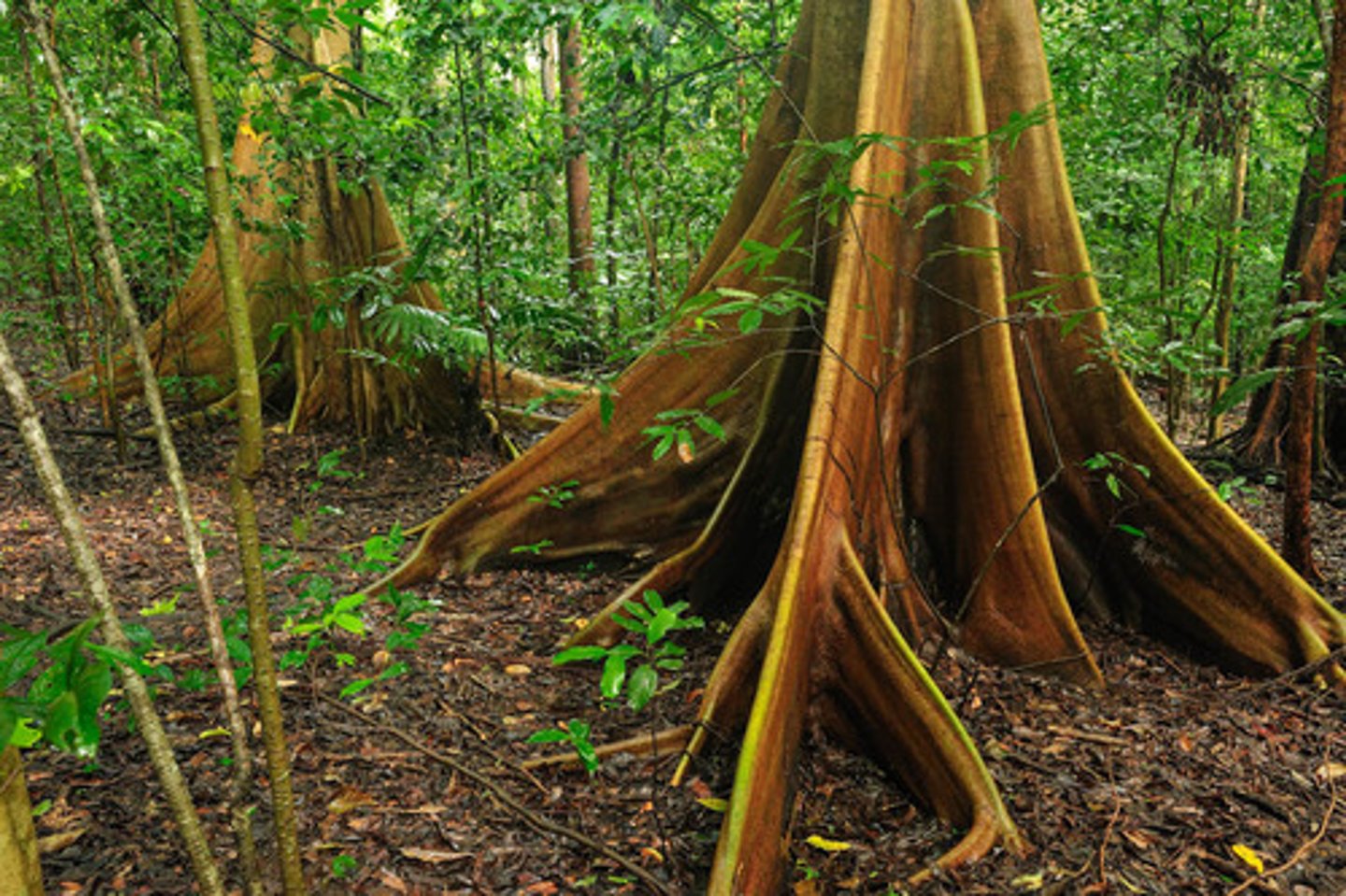
buttress roots
large, above ground roots that provide stability in tropical trees and access to fertility in leaf litter.

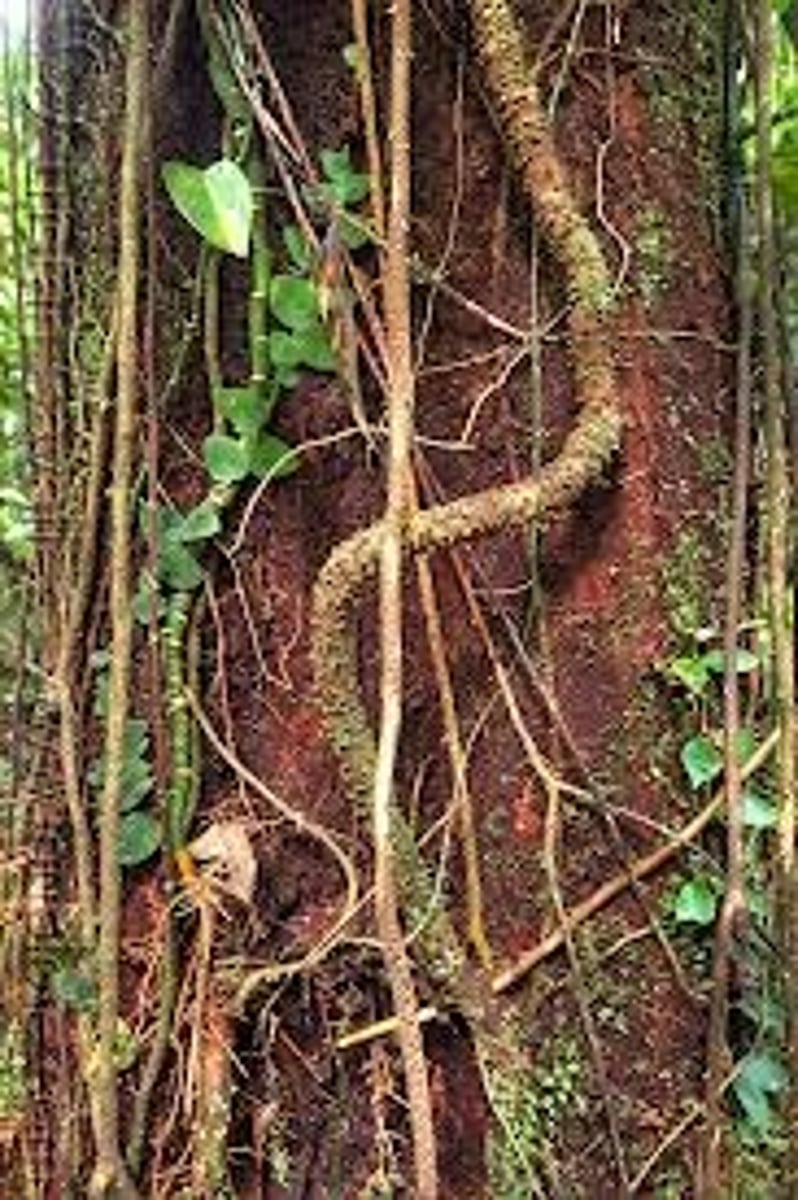
Lianas
Climbing woody vines that drape rainforest trees.

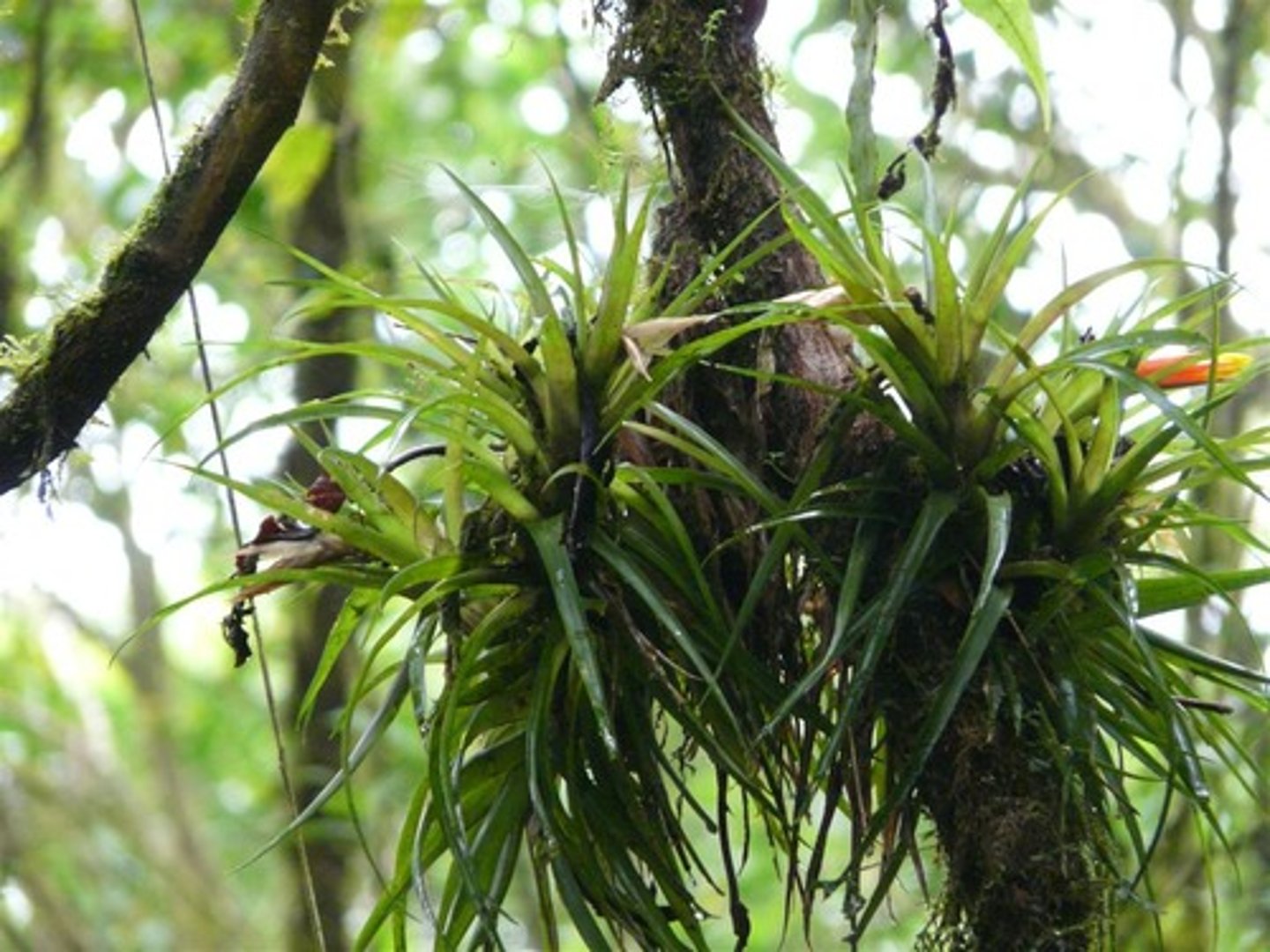
Epiphytes
Plants that grow on other plants

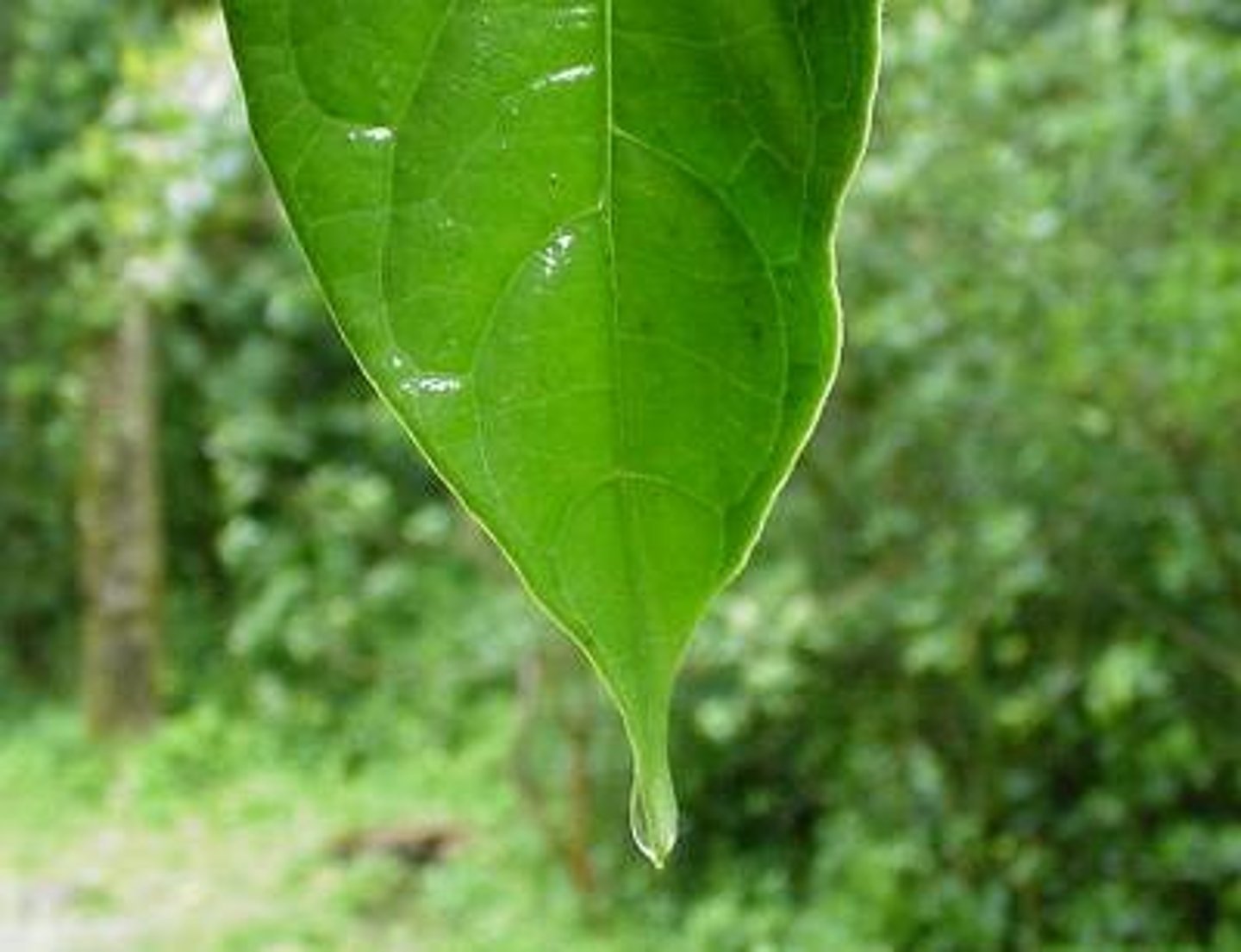
Drip tip leaves
Leaves that allow water to drip down onto the ground to avoid it being damaged by high amounts of rainfall.

Emergent trees
Tallest trees that grow higher than the rainforest canopy
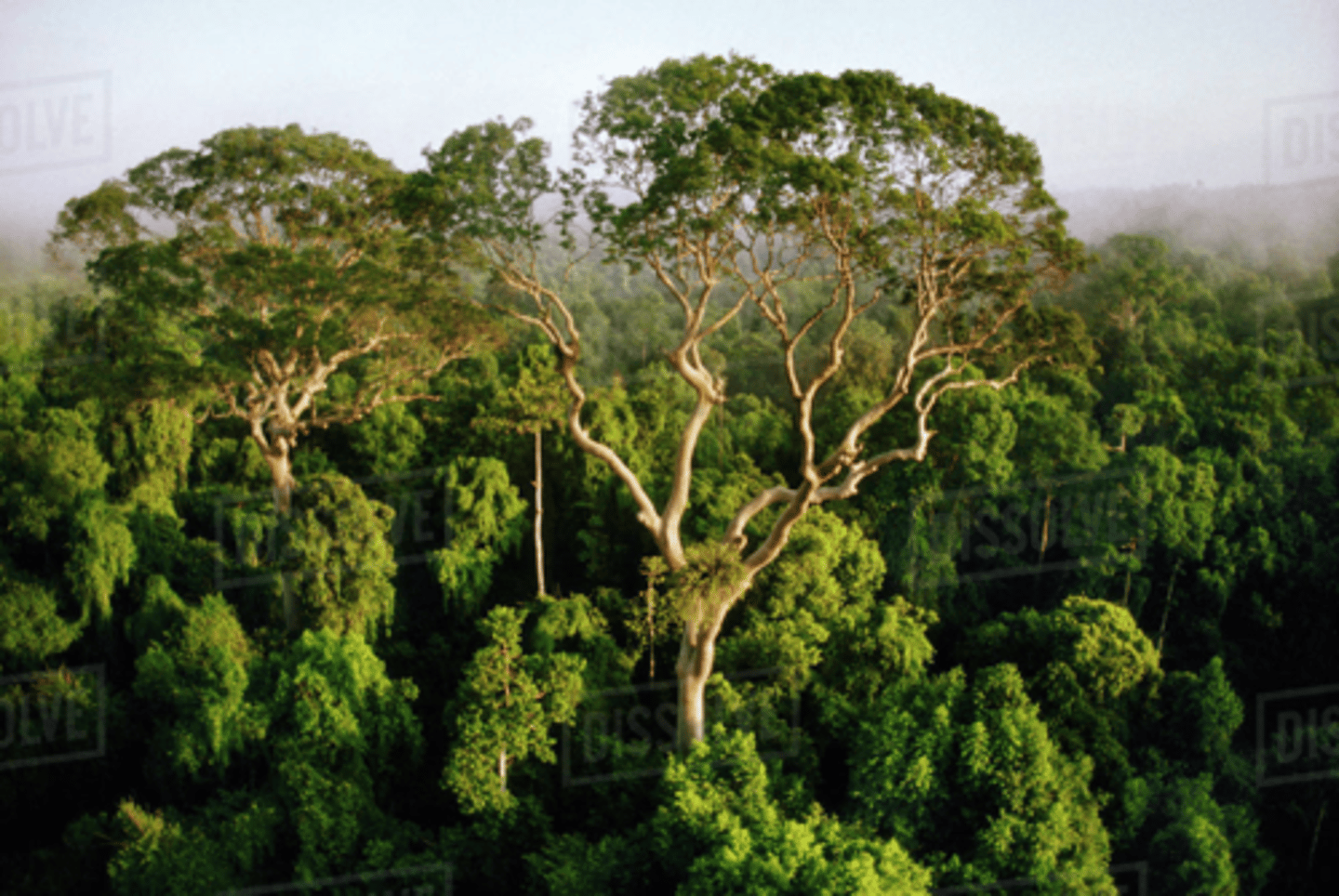

Rainforest canopy
uppermost layer of forest where the branches meet
(because the light is blocked, only small plants can grow on the floor)
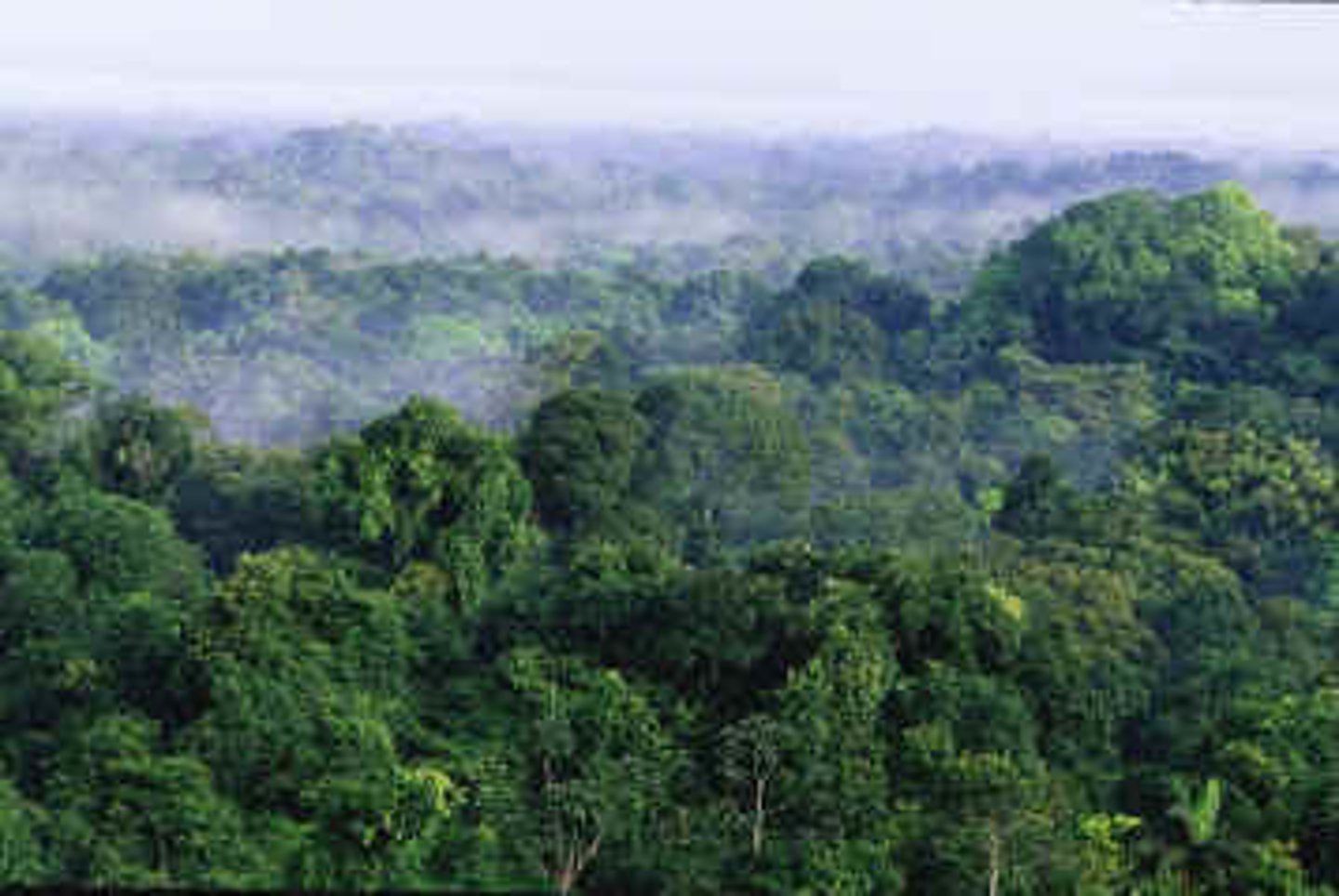

understory layer
Located under the canopy layer and consists of leafy plants with large leaves to gather sunlight.
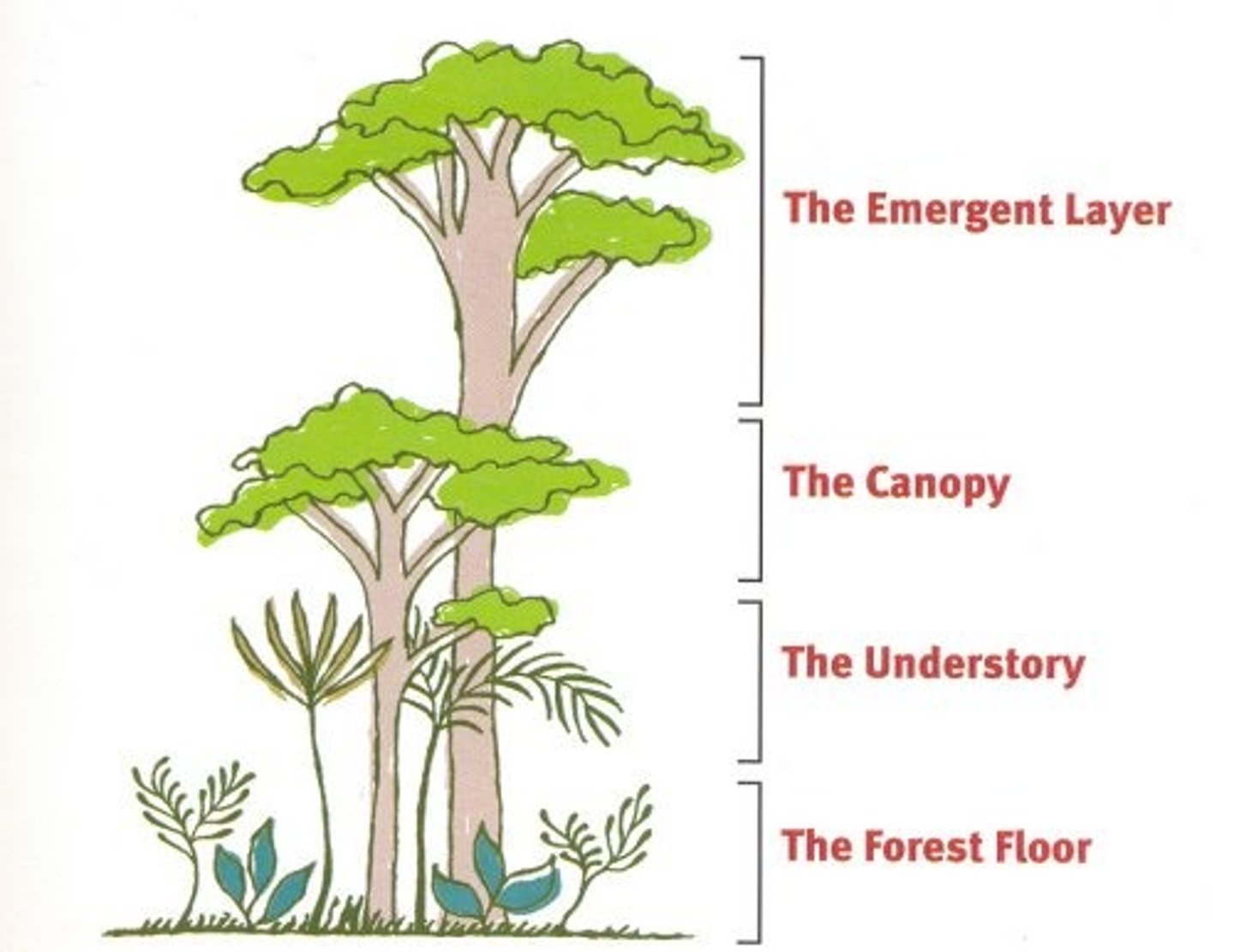
Forest floor
the bottom layer, or ground, of a forest, very dark in tropical rainforests.

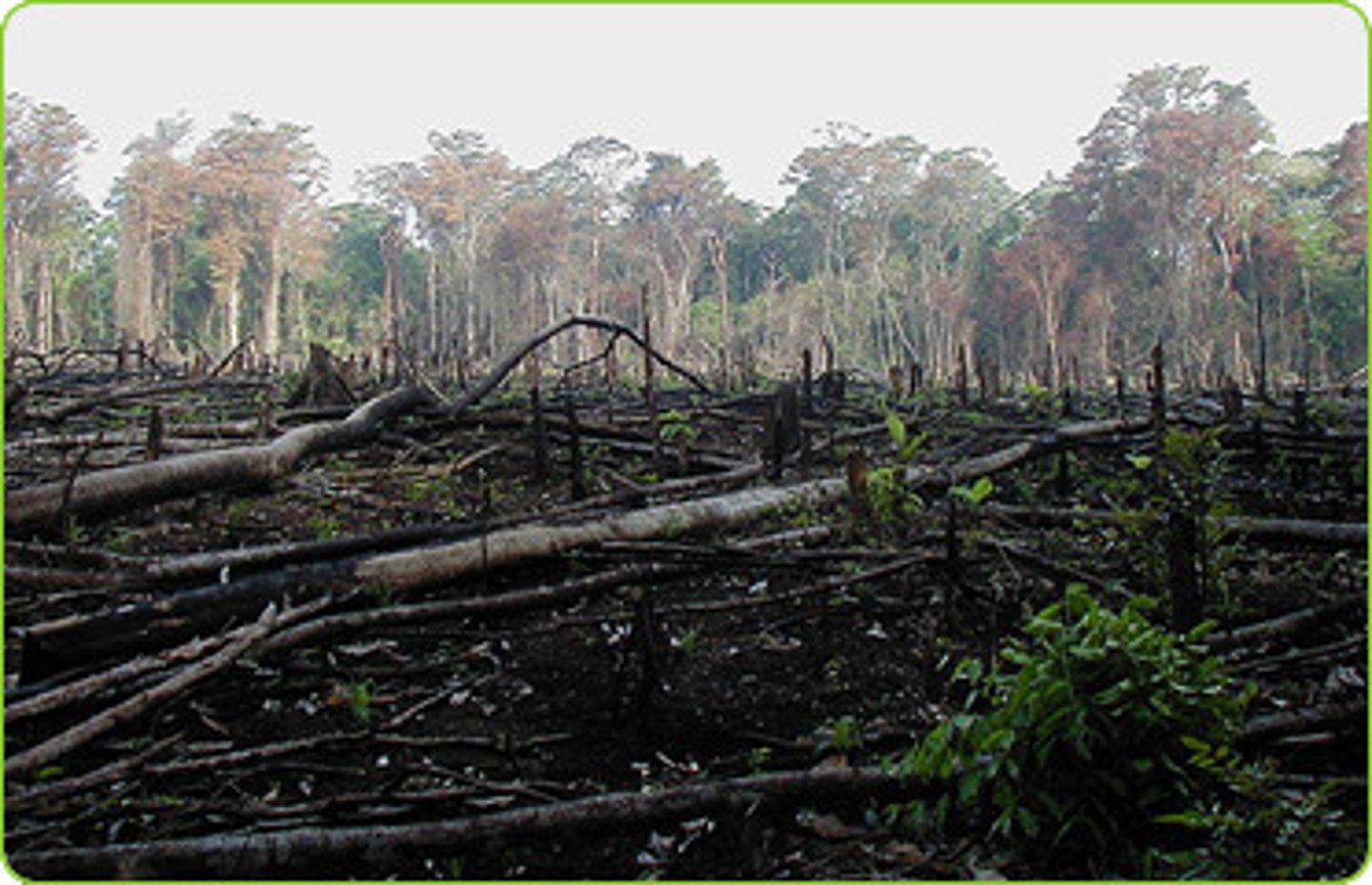
Deforestation
The removal of trees faster than forests can replace themselves.

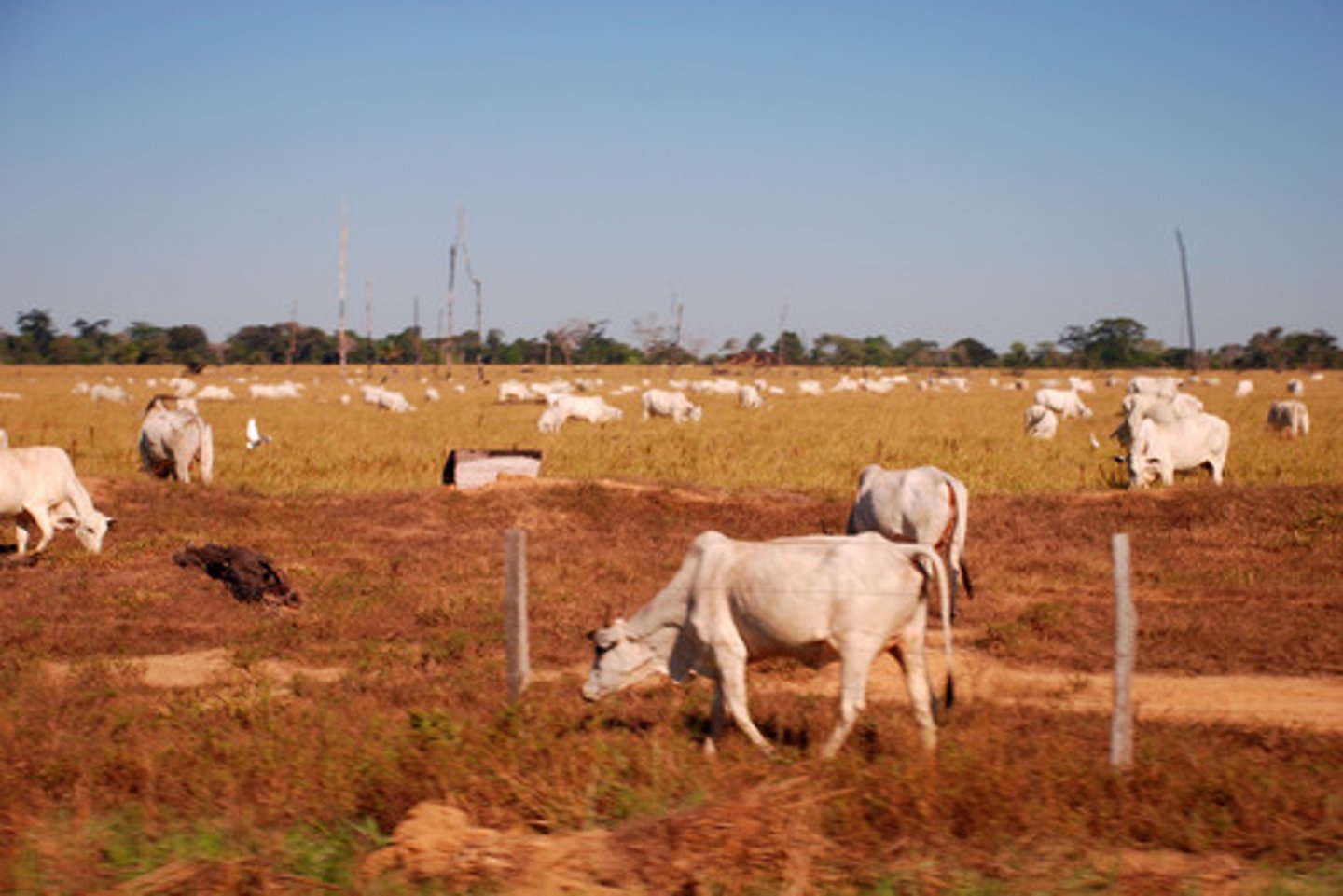
Cattle ranching
Raising herds of cattle on an extensive farm, often on deforested land.

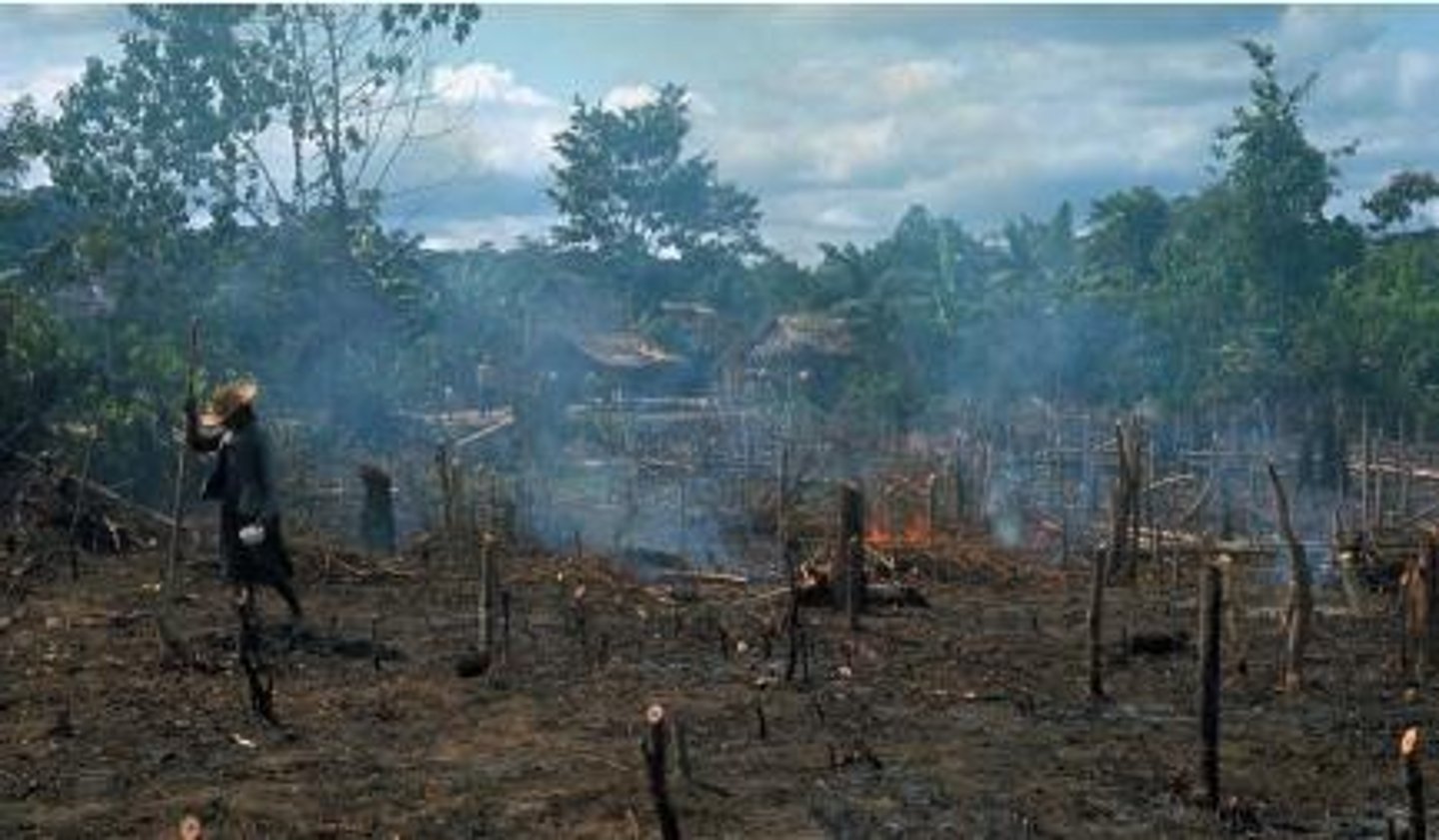
Slash and burn farming
A sustainable type of agriculture in which forests are cut and burned to clear land for planting.

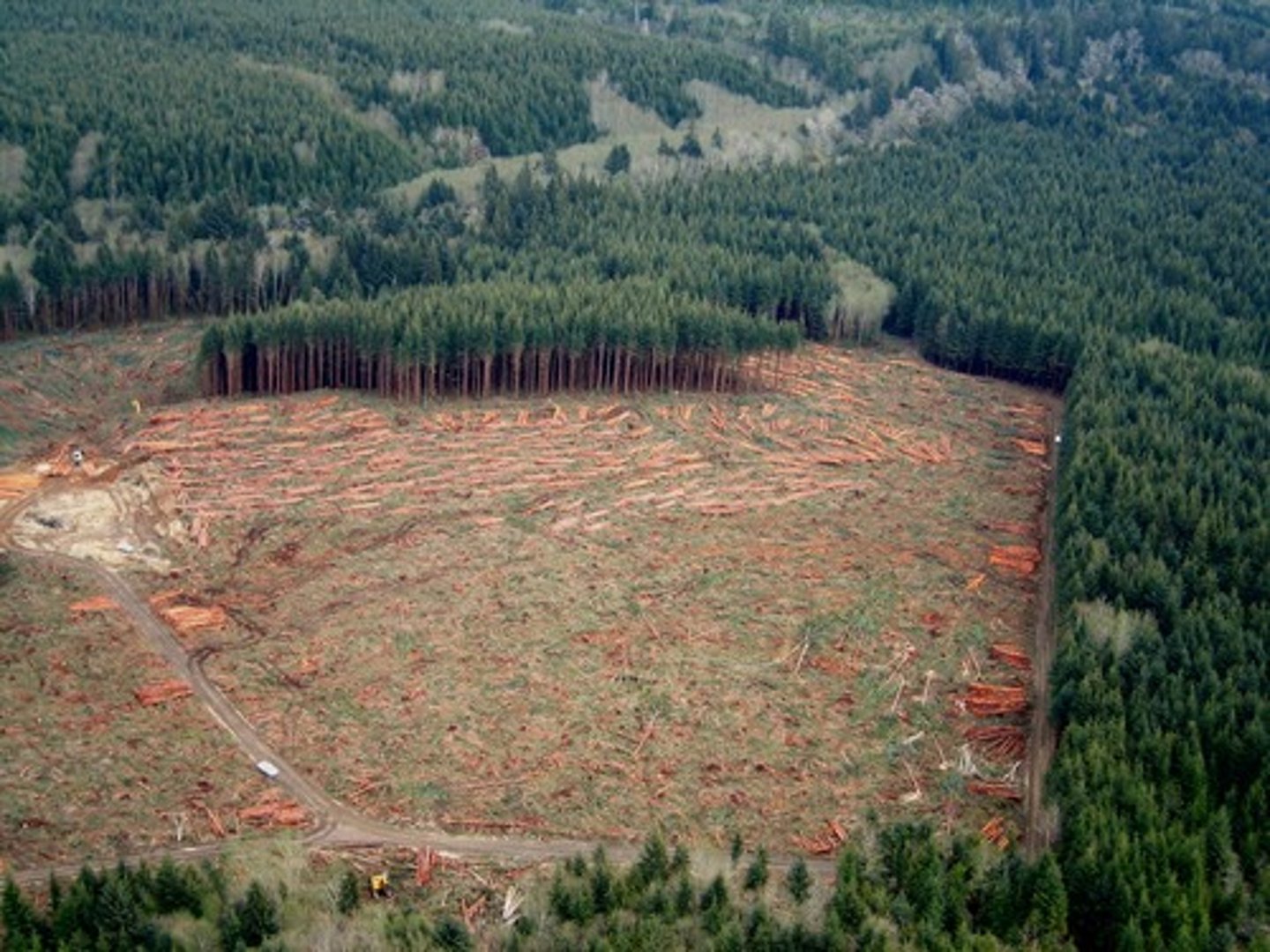
Clear felling
Absolute clearance of all trees from an area

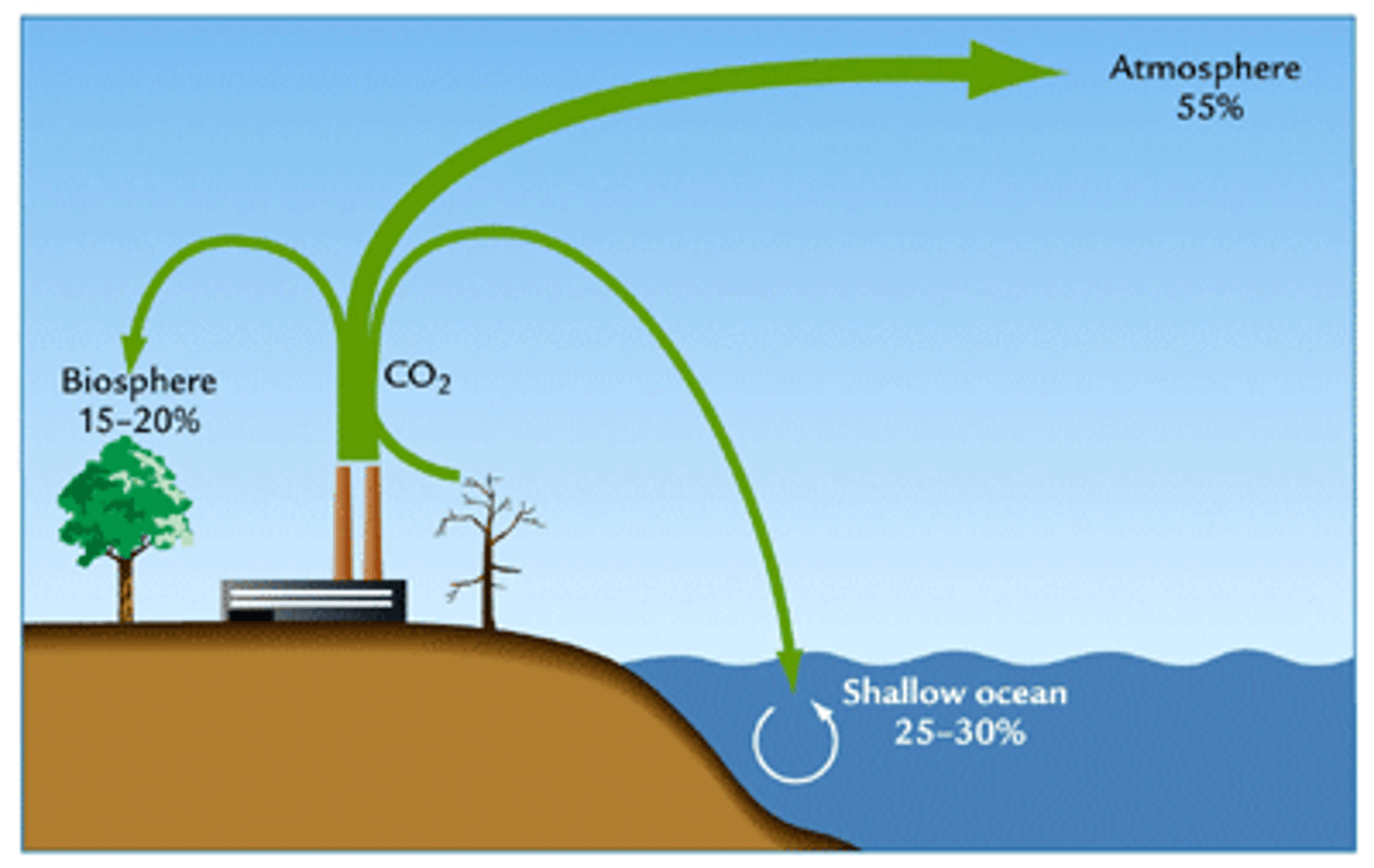
Carbon sink
A forest, ocean, or other natural environment viewed in terms of its ability to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
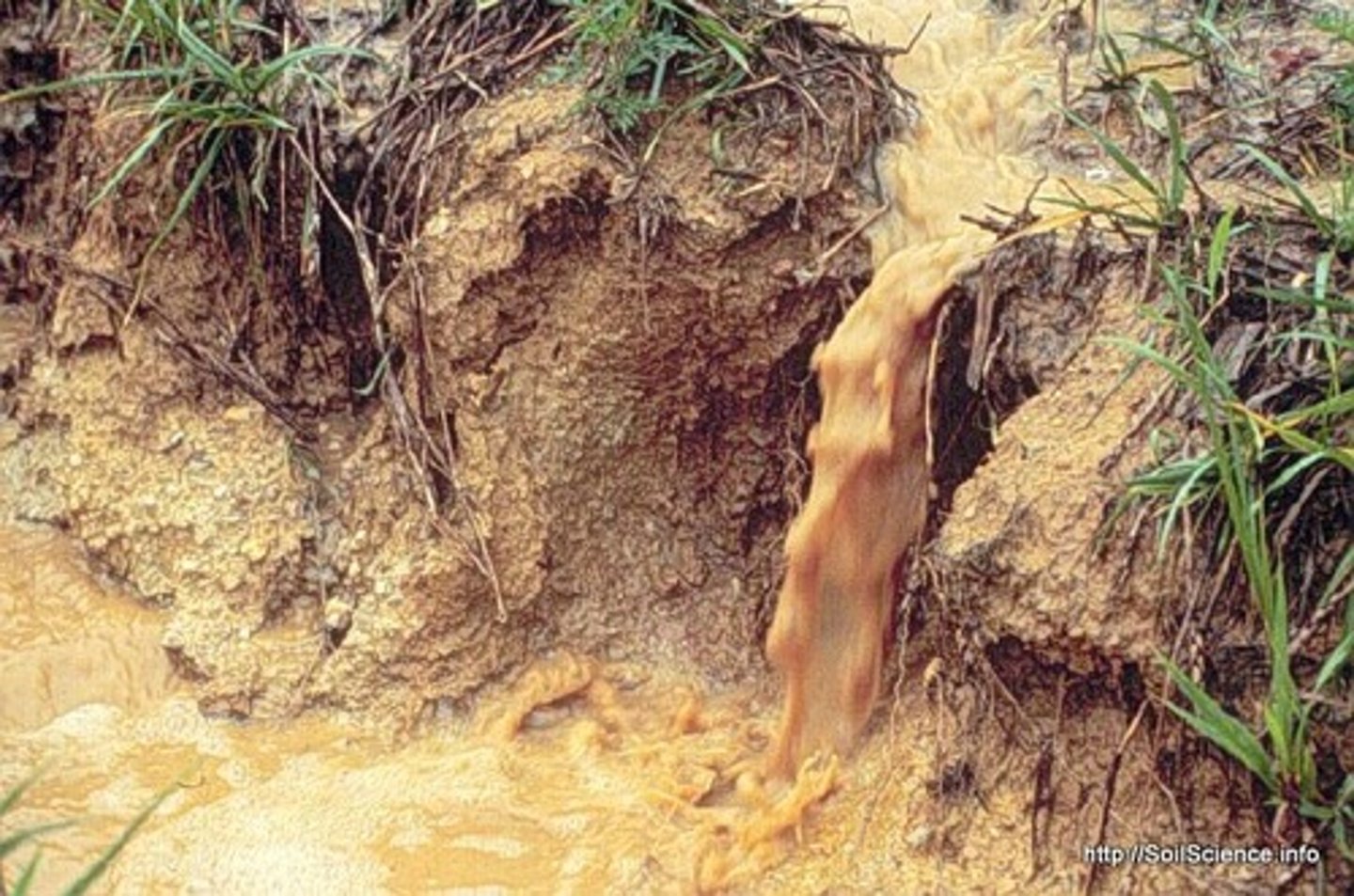
Soil erosion
Wearing away of surface soil by water and wind, more common when there are fewer trees to bind the soil with their roots and intercept the rain.

Conservation/preservation
Allows the use of resources in a responsible manner by setting aside areas and protecting them legally from human activities.

Ecotourism
A form of tourism, based on the enjoyment of scenic areas or natural wonders, that aims to provide an experience of nature or culture in an environmentally sustainable way.

Selective logging
The cutting out of trees which are mature, desirable or inferior, to avoid damage to the whole forest. Can be done by helicopter.

Afforestation/replanting
Planting trees to restore damaged forest areas.

FSC (Forest Stewardship Council)
An independent, non-profit organization established to promote the responsible management of the world's forests. It labels products that come from responsibly managed forest and from verified recycled sources.

sloth adaptations
Found in the trees. Nocturnal, it is cooler so they save energy
Slow metabolism, they don't have to eat as much
Hooked claws and long arms, helps them grip trees
Move very slowly, algae grows on them which camouflages them from predators.

Parrot adaptations
Large beak for breaking apart seeds, able to fly to reach food in the canopy.
