Lecture 8 | DNA Damage
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Causative agent
Something that causes DNA damage
a single agent may cause more than one type of damage
Lesion
Generic term for DNA damage
mutations result when DNA damage is not properly repaired
Adduct
A type of lesion, and add-on to the DNA
Mutation
Change in DNA sequence
not all mutations are carcinogenic, but a considerable amount can lead to cancer
Spontaneous DNA damage
Happens in the body in the absence of an external agent and can lead to mutations if not repaired
can even be an initiating event in cancer
Sources:
Natural instability of DNA
Deamination
Depurination
Oxidized bases
ss DNA breaks
Oxidative damage
DNA polymerase errors
Induced DNA Damage
Alkylation
Oxidative damage → ionizing radiation
Bulky adducts, including UV dimers
When does spontaneous DNA damage occur
Happened in the body in the absence of an external agent
If not repaired, can lead to mutations
Can be an initiating event in cancer
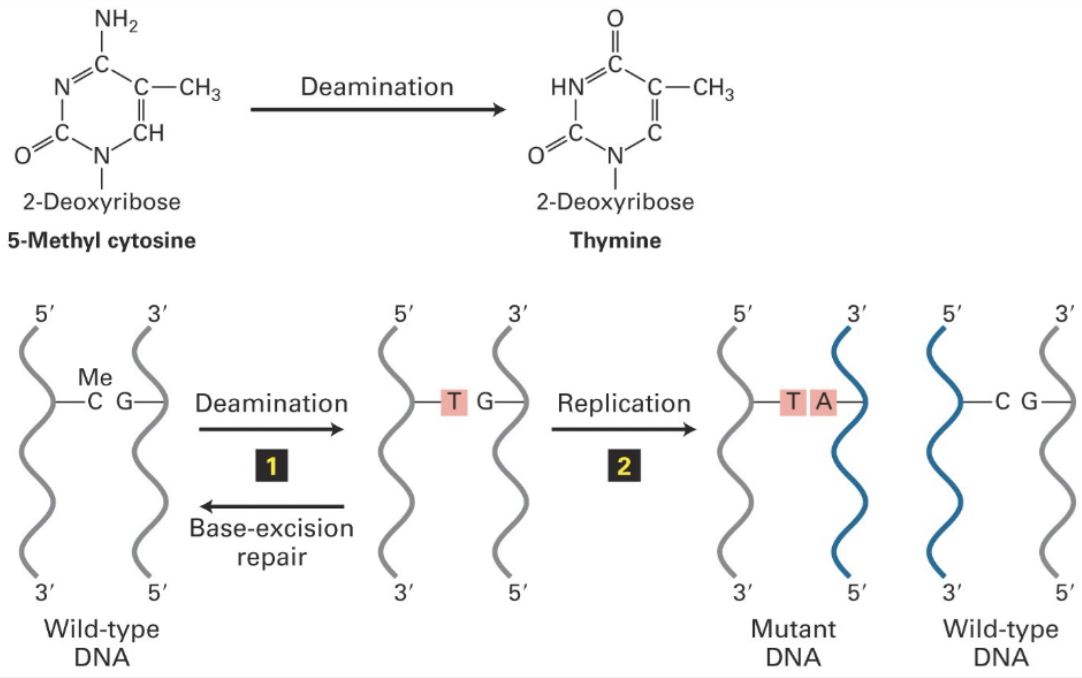
Deamination
Spontaneous DNA damage
Lose of NH2 is most common
C → U
DNA replication reads U as T, resulting in C to T point mutations → transition mutation
So… converts 5meC → T
5meC are regulatory marks in CpG islands and hotspots for mutagenesis and cancer
1/3 of all inherited human diseases are at 5meC in Cp6 islands
Depurination
Spontaneous DNA damage
Hydrolysis of glycosylic bond (5000/cell/day)
Result in abasic site → single base substitution (point mutation)
Oxidative damage
Spontaneous and Induced DNA damage
Oxidized bases and single strand breaks
caused by free radicals O2 -
Result: oxidized bases → abasic sites
Most common: 8-oxo-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG) & Thymine glycol
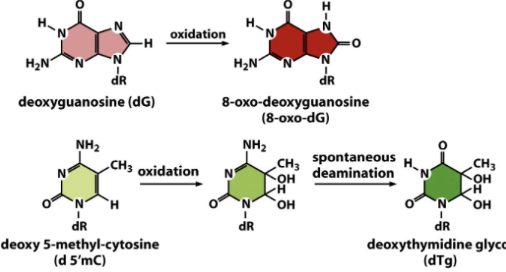
problems: 8-oxo-dG mispairs with deoxyadenosine
Where do are radicals come from for oxidative damage?
Both spontaneous and induced
Spontaneous causes: metabolism, inflammation
Induced: Smoking, radiation
Polymerase errors
Spontaneous DNA damage
Overall DNA replication error rate is 10^-10 mutations/bp/cell generation
results: mismatches (point mutations), misalignment (insertions, deletion)
However, error rate is low in part because of our proof reading mechanism intrinsic to DNA polymerase
Main errors: mainly result from slippage and misalignments and are highest in regions of repetitive sequence
Alkylation
Induced source #1
Caused: Nitrosamines and other methylation
Results: point mutations
Methyldiazonium ion acts as an alkylating agent
Mechanism of radiation-induced cancers
IR penetrates a tissue and gives up energy through a series of random collisions with molecules in its path
produces e- and free radicals (OH) that damage DNA by breaking chemical bonds
radiation can damage DNA directly via free electrons
Type of DNA damage induced by radiation
Double stand breaks
Modified bases leading to basic sites due to chemical instability
Single strand breaks (easily repaired) and complex lesions (not easily repaired)
Law of Radiosensitivity
Radiosensitivity of a tissue is directly proportional to its mitotic activity and inversely proportional to the differentiation of the cell

Missense mutation
CHange in aa
Nonsense mutations
introduces a stop codon